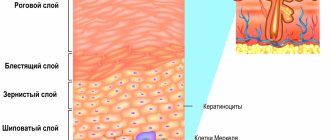
One of the disorders of skin pigmentation is skin hyperpigmentation (increased, excessive formation of pigment), which occurs under the influence of external and internal factors, as well as the individual characteristics of the body. As a rule, a small number of freckles is normal, especially for a certain type of appearance (fair skin, blond or red hair, etc.). But sometimes pigmented areas appear suddenly and have different colors and shapes, which already indicates a problem not only cosmetic, but also medical. And this problem requires a solution.
To treat skin hyperpigmentation on the face and other areas, it is necessary to find out the cause of the pathology and the stage of its development. There are various causes of excess (pathological) pigmentation, which are taken into account when selecting a treatment regimen.
In medicine, they take an integrated approach to the diagnosis and treatment of various skin diseases and pathologies such as hyperpigmentation, which, along with a cosmetic defect, also brings psychological discomfort. The main thing is to remember that removing age spots on your own will not lead to anything good. Your doctor will tell you how to get rid of freckles without causing harm.
How to recognize lentigo?
Treatment of this problem should begin with a correct diagnosis. The main symptom is a thickening of the stratum corneum of the skin, so that lentigo spots in most cases rise slightly above the surface. These spots are located both on the face and on the body.
Other characteristic symptoms:
• bright color of all shades of brown; • round or oval shape, clear boundaries; • visual sensation of swelling; • size from 1 to 3 mm, in rare cases the spot grows up to 2 cm; • severe itching with lentiginosis.
Lentigo therapy at home
You can treat lentigo yourself at home if it is clearly established that the pathology is benign.
All folk recipes are based on the use of natural lightening agents:
- lemon juice;
- hydrogen peroxide;
- ammonia;
- rowan;
- calendula;
- black currant;
- parsley;
- almonds;
- honey
Here are some productive recipes for homemade masks:
- The stems, leaves and roots of parsley are finely chopped to a paste. Then add honey. The resulting composition is applied to problem areas and, after leaving for half an hour, washed off with warm water.
- Place the lemon peel in boiling water and keep it warm for about 30 minutes. Then let the water sit and wipe the stains up to 3 times a day.
- Grind almonds in a coffee grinder and mix them in equal proportions with oatmeal. Add 5-7 g of milk powder and flavor with a small amount of water to form a mass similar to sour cream. Use this thickener to scrub the affected areas for about 5 minutes and wash off any remaining residue. Do this no more than 2 times a week.
- Dilute dry white clay (1 tbsp) with warm water until smooth and add a little lemon juice. Apply the composition to age spots and wash off after 20-25 minutes. This mask is used every day.
The suggested masks should be done in the evening, when you are not planning to go outside. This is due to the fact that after the procedure you cannot expose the skin to UV exposure.
As a treatment for lentigo, it is recommended to use pharmaceutical ointments with a whitening effect:
- zinc;
- sulfuric;
- Clotrimozole;
- salicylic.
Among the creams, the following brands are distinguished: Skinoren-gel, Melanativ, Clearvin. They should be applied to the skin twice a day.
I recommend using a combination of whitening cream (hydroquinone 4%) and tretinoin (vitamin A). But it will take months of treatment to achieve results. The laser is much faster.
Plastic surgeon Sam Naficy
Causes
Lentigo is nothing more than an accumulation of excess melanin - a coloring pigment. These spots can either be inherited or appear unexpectedly in adulthood. Unfortunately, doctors have not yet fully studied this disease.
The following reasons for its appearance have been precisely defined: 1. Old age. Lentigo on the face is very common in people over 70 years of age, sometimes these spots begin to appear after 40. 2. Young age. The so-called juvenile lentigo in children and adolescents is known. Its causes are unclear; with the onset of adulthood, the spots disappear on their own. 3. Skin injuries. Occurs at the site of superficial wounds. 4. Excessive insolation. Excess ultraviolet radiation always has a negative effect on the skin, solar lentigo is proof of this. 5. Lentiginosis, or congenital lentigo, is inherited and manifests itself not only on the face, but also on the body together with other unpleasant pathologies: heart disease, congenital deafness, etc. 6. Malfunctions of the liver and intestines. There are cases where lentigo spots disappeared after surgical operations on the gastrointestinal tract.
Hyperpigmentation: types and symptoms
Abnormal pigment formation on the skin can be congenital or acquired. The localization of pigments can also be different, generalized (widespread) and local: hyperpigmentation appears on the face, back, arms and other parts of the body.
What types of enhanced pigmentation are there and how are they characterized?
- Freckles (small spots of different colors) are a congenital pigmentation: they can be located only in one area (for example, the face) or cover a large area (the back, arms or the whole body).
- Birthmarks (congenital pigmentation) can be of different sizes and shapes and “choose” different locations; they can change or remain unchanged during a person’s life.
Acquired hyperpigmentation includes the following types:
- diffuse melasma, which manifests itself in the form of spots of a brown or bronze hue and is located on open areas of the body, as well as near the nipple areolas, in the perineum or along the white line of the abdomen;
- arsenic melasma, which appears after treatment with arsenic products, spreads throughout the limbs, sometimes throughout the body;
- focal (in the oral cavity) and generalized melasma;
- melasma appears after too long exposure to the sun, in the form of spots of different shapes and colors;
- chloasma refers to pigmentation, which more often appears as a result of hormonal changes in the form of spots with clear boundaries (the main location is the face);
- lentigo is called age-related pigmentation that appears naturally;
- pigmentary toxicerma, limited pigmentation of the forehead and Broca's pigmented perioral dermatosis, etc.
Skin pigmentation should not be ignored, since (as stated above) any pathology can be not only a consequence of some external influence, but also a symptom of some general disease
For any changes in pigment, you should consult a doctor, at least for your own peace of mind, to make sure that everything is fine and there is nothing to worry about. If pigmentation is a signal of disturbances in the functioning of the body, then a timely visit to the doctor is an opportunity to take care of your health in a timely manner.
Treatment of lentigo on the face
The connection between lentigo and certain diseases of internal organs and the risk of developing skin cancer is alarming. Therefore, if freckles and moles rarely pose a danger to our health, then if lentigo occurs on the face, treatment should begin immediately.
First of all, you need to reconsider your lifestyle: avoid direct sunlight, apply creams with a high level of SPF protection to your skin, and do not skimp on skin care in terms of nutrition and hydration. If necessary, a dermatologist will prescribe the use of certain medications.
In addition, it is worth following a diet that excludes possible allergens. You should also check your gastrointestinal tract and put it in order; if you are overweight, you will have to mercilessly say goodbye to it.
Is it possible to cure this disease and how?
It is necessary to treat lentigo when the spot is too large, is constantly exposed to mechanical and solar influence and spoils the appearance with its presence.
Typically treatment comes down to the following steps:
- regular whitening of pigmented areas on the skin with special medications;
- constant application of protective creams against UV radiation to the skin;
- superficial exfoliation of the epidermis using various cosmetic procedures.
Don't worry if the spots disappear and then return after a few days or weeks. The pigment usually consists of several layers, so peeling occurs layer by layer.
Anesthesiologist Laura Rome
As a last resort, they resort to surgical intervention. Then the lentigo is cut out from the skin surface.
During the operation, the specialist captures part of the healthy tissue so that the stain does not appear again in the future. The remaining scar is easily removed plastically.
Arbutin, azelic acid and licorice extract have a good effect as whitening agents.
They contain ascorbic and kojic acid, retinoids and hydroquinone. The latter component is present in modern drugs, but in minute quantities. All other components are absolutely harmless and easily tolerated.
Laser destruction
For those who want to get rid of lentigo without subsequent scars, laser therapy is recommended.
With it, the beam captures and destroys only the neoplasm, and does not affect healthy tissue in the neighborhood. This procedure is painless and is performed without local anesthesia.
If you have persistent solar lentigo/sun spots, the best combination is the Fraxel Dual laser and Yag laser.
Dermatologist Michelle Green
During the session, the patient may feel a slight tingling sensation on the skin.
Immediately after pigmentation has been reduced, redness may appear in the areas treated with the laser. If you are prone to allergies, slight darkening may appear in these places.
Before laser therapy, the patient must undergo a series of examinations to exclude existing contraindications.
Phototherapy
If the diagnosis of malignant pigmentation is excluded in the patient, then a phototherapy method may be offered.
This means exposing problem areas to a light beam. This stimulates the natural synthesis of collagen, thereby increasing the regenerative capabilities of tissues and rejuvenating them at the cellular level.
I have better results with the Q-swithced laser. I have used the Cutera Laser Genesis with great success. For patients who want a more conservative approach, a combination of hydroquinone and retin-A creams is suitable. IPL phototherapy is effective in some patients, but it is still superior for treating melasma.
Plastic surgeon Temp Patterson
Peeling
People with light age spots are recommended to resort to chemical peeling of the skin. The fact is that, in addition to removing darkened areas, adjacent healthy skin is also affected.
The following types of peelings are often used:
- retinoic;
- TCA peel;
- ABR peeling;
- pyruvic;
- azelaic.
This procedure is performed with local anesthesia. This is followed by a short recovery period of 10-12 days. As a result, the skin structure is completely restored and pigmentation disappears without a trace.
However, in addition to the beauty treatment, you should also follow a proper skin care regimen to brighten your skin.
Plastic surgeon Grant Stevens
There are many different types of peelings, but experts often praise these options:
- Peeling Cosmelan. The peeling itself is brown in color and has a thick consistency. Contains azelaic, phytic, kojic, ascorbic acids, as well as arbutin. The product brightens the skin well. First, in the clinic, the patient is applied a mixture of Cosmelan 1, which should remain on the skin for about 8-12 hours. At home, the mask is removed with cleansing cosmetics. 2 days will pass, after which the patient independently applies the Cosmelan 2 mixture every day. This must be done throughout the year.
- Jessner peeling. This name is given to a patented product that contains salicylic, lactic acids and resorcinol. This is a medium peel. The effect is amazing. The product will not only help remove pigmentation, but will also eliminate many other problems (acne, wrinkles, etc.).
Lentigo – treatment with the M22 device
Modern methods of getting rid of lentigo include photothermolysis - treatment with IPL light or laser radiation. The essence of this method is the pulsed effect of light beams on the skin in the affected area, during which excess melanin is destroyed without affecting healthy areas of the skin.
It is generally accepted that laser copes with this problem better. However, modern light devices, for example, the M22 multi-module platform, demonstrate a high rate of removal of various age spots. For each type of hyperpigmentation, including lentigo, a special program is provided, which significantly increases the effectiveness of M22 compared to other photosystems. M22 rays penetrate the skin, destroy excess melanocytes and keratinized cells, cause the synthesis of collagen and elastin fibers and other active substances. These processes promote rejuvenation and rapid regeneration of damaged areas, lightening of spots and smoothing of the relief. After just a few sessions, the spots cease to be noticeable and the skin acquires a healthy color.
There are solar lentigo and age-related (senile).
This type of pigmentation is very persistent, does not depend on the time of year and does not disappear on its own. Solar lentigo occurs in those who spend hours under the scorching sun on the beach and, of course, in tanning bed lovers.
Senile lentigo appears in old age and is often called “senile ripples” or senile keratomas. It is associated with a slowdown in the metabolic process during age-related hormonal changes in the body.
Birthmark (nevus ). This is perhaps the most common type of hyperpigmentation. Perhaps not one person is deprived of this type of pigment formation disorder. They are a collection of melanocytes. Nevi can appear at any age, but are especially active in adulthood.
Melasma (chloasma). Large pigment spots that do not have a clear shape or specific size. Mostly appear on the face of young women. Their favorite location is the face, and the main cause is hormonal changes, mainly such as pregnancy, lactation and oral contraceptives. In some cases, they disappear on their own when hormonal levels normalize.
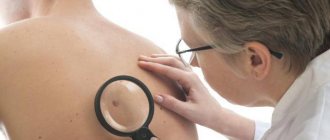
How is skin melanoma diagnosed?
The most effective method for early detection of skin melanoma is periodic self-examination of the skin. There is a kind of “melanoma alphabet” that describes a number of signs of degeneration of a mole, indicated by the first four letters of the Latin alphabet:
- A (asymmetry) - asymmetry: the shape of “good” moles is often symmetrical;
- B (border irregularity) - the edges of the mole are usually smooth and clear. An uneven, scalloped outline is more characteristic of melanoma;
- C (color) - benign nevi are colored more or less evenly. The unequal color of different parts of the neoplasm is more characteristic of a degenerated mole;
- D (diameter) - the diameter of a mole is more than 6 mm: the larger the mole, the greater the likelihood of its degeneration. Malignant degeneration is indicated by various kinds of changes in a pre-existing mole. It was found that pigmented formations on the skin that regularly changed shape and color turned out to be melanoma 4 times more often than those whose appearance remained unchanged. Therefore, to the first four letters of the “alphabet of melanoma,” a fifth was added;
- E (evolving) - the appearance of any external changes in the mole, which most often are: change in color (decrease or sharp increase in pigmentation); violation or complete absence of skin pattern in the area of the nevus, “varnish” surface or peeling; the appearance of an inflammatory areola around the mole (redness in the form of a corolla); change in configuration along the periphery, blurring the contour of the nevus; an increase in the size of the nevus (especially over the age of 30) and its compaction; itching, burning, tingling in the mole area; the appearance of cracks, ulcerations in the mole area, bleeding; loss of existing hairs on the mole; sudden disappearance of a mole (especially after tanning in the sun or in a solarium).
Very valuable additional clarifying information can be obtained by performing a dermoscopic examination of a pigmented skin tumor, which allows for a visual assessment of the tumor at 10-40x magnification.
Risk groups and factors predisposing to the development of skin melanoma.
Individuals at increased risk of developing melanoma include:
- with white skin, red hair, blue, gray or green eyes;
- constantly sunburned;
- those who have suffered sunburn and have been exposed to the sun for a long time, especially under the age of 20;
- having close relatives with melanoma (other skin cancer);
- having more than 100 moles on the body or more than 50 before the age of 20;
- having Dubreuil's melanosis (precancerous skin disease).
There are well-known cases of melanoma being diagnosed after injury to a pigmented nevus of the skin (mole). Melanoma often occurs after accidental or intentional (cutting, burning) injury to a mole. Sometimes 1-2 injuries are enough for melanoma to occur.
Trauma to the nevus can be chronic and occur unnoticed. For example, a well-starched shirt collar can injure moles on the neck, and bras can injure moles on the torso. Moles localized on the soles of the feet, palms, and perineum are chronically injured.
The influence of certain hormones on the development and clinical course of melanoma is assumed. Puberty, pregnancy and menopausal changes are regarded as risk factors for the development of melanoma from pigmented nevi.
Genetic predisposition plays a role (familial cases of melanoma).
Skin melanoma treatment stages 1, 2, 3. Symptoms, signs, metastases, prognosis.
Content:
- General information about melanoma
- What are the different forms of melanoma? Superficial spreading melanoma
- Nodular melanoma
- Malignant lentigo melanoma
- Acral melanoma
- Atypical (dysplastic) nevi
- Primary metastatic melanoma
- Surgical treatment of skin melanoma
Stages of skin melanoma
Establishment of the stage of melanoma is carried out on the basis of data from a morphological study of the remote primary tumor focus, regional lymph nodes (if they are metastatic) and data from instrumental examination.
- stage 0 melanoma in situ (I level of invasion according to Clark) (atypical melanocytic hyperplasia, severe melanocytic dysplasia, non-invasive malignant lesion);
- Stage I melanoma less than 1 mm thick and non-ulcerated melanoma up to 2 mm thick;
- Stage II melanoma with a thickness of more than 2 mm and ulcerated melanoma with a thickness of up to 2 mm.
Primary metastatic melanoma
- Stage III - all melanomas with the presence of metastases in regional lymph nodes;
- Stage IV - all melanomas with the presence of metastases in distant organs and tissues.
What determines the success of treatment
The result of hyperpigmentation treatment depends on how deep the pigment lies.
Based on the depth of the pigment, all types of hyperpigmentation can be divided into two large groups. It is this classification that allows us to understand whether our treatment will be successful or not.
Epidemal hyperpigmentation is pigmentation with clear boundaries, sometimes protruding above the surface of the skin, usually dark brown in color. She is the one who responds well to treatment
Dermal hyperpigmentation is a dull light brown pigmentation, sometimes with a grayish tint, that does not have clear boundaries. This type of pigmentation is practically untreatable.
Mixed hyperpigmentation - pigmentation has areas of dark and light shades at the same time. Treatment in this case has a partial positive effect.
Observation and examination after treatment
After radical surgery, local tumor recurrences are extremely rare. However, given that melanoma metastases can develop many years after removal of the primary tumor, lifelong monitoring by an oncologist is necessary.
Therefore, patients who have completed treatment must undergo an examination, which includes:
- examination of all skin;
- palpation of regional lymph nodes;
- X-ray examination of the chest organs;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- general and biochemical blood test;
- determination of the level of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) in blood serum (for melanoma with metastases).
In some cases, it is necessary to use other examination methods (MRI of the brain, CT of the abdominal and thoracic cavities, osteoscintigraphy, etc.).
During the first two years, control examinations are carried out every 3-6 months. During the third year every 4-12 months, then annually.