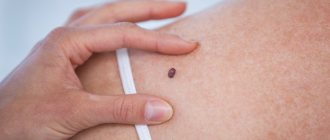
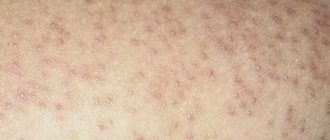
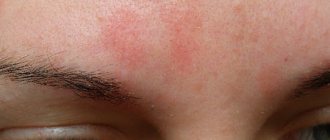
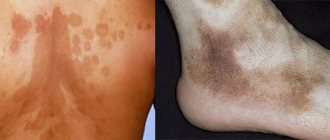
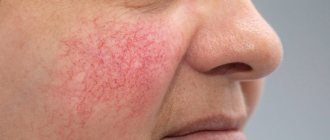
Red moles are benign vascular tumors ranging from a few millimeters to several centimeters in diameter. They are often found in newborn children, but can occur in adolescents and adults. They can be multiple or single: they can be located separately from each other or form clusters of several neoplasms. The following types of angiomas are distinguished by form:
- stellate (point formations from which small blood vessels extend in different directions);
- nodular (seals that protrude slightly above the surface of the skin);
- flat (vascular spots localized in the upper layers of the skin);
- serpiginous (rashes in the form of small burgundy nodules).
Let's take a closer look at why red moles appear on the body when they need to be removed.
Causes of red moles
The exact reason why red moles appear on the body is unknown; it may be a predisposition due to a genetic factor. But there are other reasons:
- pregnancy;
- exposure to chemicals;
- some diseases, including infectious ones;
- unsuitable climate (too hot or cold)
- mechanical damage to the skin, such as a bite or cuts, in which pieces of skin are not completely torn off.
Their manifestations are also possible at a more mature age, this is due to a gradual decrease in immunity. Neoplasms occur in 75% of the population over the age of 60 years.
It is impossible to somehow influence the appearance or non-appearance of red moles on the body, since they are inherent in us at the genetic level; if one of the parents had a lot of them, it means that the children will have a similar situation, and even identical maps of the location of nevi are possible.
Prevention of angiomas
After establishing the true cause of the appearance of red moles, it is important to avoid provoking factors. As a preventative measure, experts recommend:
- drink at least 1.5 liters of water per day;
- eat more fresh fruits and vegetables rich in fiber;
- add olive oil to your diet;
- try to spend less time under the scorching sun;
- sunbathe only in the morning or evening (using sunscreen);
- stick to a balanced diet.
Locations
An increase in the growth of moles is observed in people aged 0 to 20 years, and then from 45 years and older. The rest of the time they appear, but not as actively as in the first and last phases of life. Typically, red moles appear on the upper body, arms, legs and shoulders. Their favorite places are also the head, feet, and hands. They can be located throughout the body, and it is impossible to predict their subsequent locations. Their red color comes from the accumulation of small blood vessels at the base, which supply them with blood.
Types of acquired red moles on the body
- Simple (capillary). Proliferation of newly formed capillaries, small venous and arterial vessels. Looks like a red spot.
- Cavernous. A spongy cavity with blood - a red or bluish nodule. Often forms under the skin.
- Branched (racellose). A plexus of tortuous dilated capillary trunks. They pulsate, noise and trembling are detected. It is rare and occurs on the extremities or face. If injured, life-threatening bleeding may occur.
How to identify hemangioma? Press on top of it and it should fade or disappear.
Types and classification
Moles have two main types:
- Pigmented. These include flat, often brown, nevi.
- Vascular, which are formed from changes in the structure of blood vessels.
They are also:
- Congenital - divided by size: small, medium and large.
- Acquired, divided into three types depending on the location of melanocytes in the layers of the epidermis.
- Hanging ones, they are also called papillomas.
There are invisible nevi that appear changing color over time. Also wandering, which change their location, appearing in one place or another. It is advisable to keep track of the location of your moles.
Peculiarities
- Red, dark pink or burgundy color distinguishes nevi from other types of similar formations.
- They usually have a rough or smooth surface and protrude slightly above the surface of the skin.
- When you touch them, a temporary change in their color occurs: they lighten slightly, but then the permanent color is restored.
- If you try to remove red moles yourself, you may experience some bleeding.
Are red moles dangerous?
Signs to pay attention to if small red moles appear:
- Color. If it is uneven and begins to change, this is a reason to visit a doctor.
- Inflammation around the formation, that is, redness in the form of a halo around the mole.
- An increase in the size of the mole or its thickening.
- The appearance of cracks and ulcers on the body of the mole.
- Hair loss if it grew from a mole.
- The appearance of itching, burning or tingling in the place where the mole is located.
- A change in the edges of the nevus also indicates that it is time to visit a specialist.
An accurate diagnosis can be made by a dermatologist or oncologist, and you can and should turn to them for help. Nevi are not dangerous as long as they are in a stable condition, in which case you can wait to see a doctor.
WHEN YOU NEED TO PAY ATTENTION TO THEM
Specialists from LIC clinics recommend investigating the nature of the origin of red moles, not the subject of oncology, and only after that getting rid of them. After studying the results of the study, the doctor will select the optimal method for removing angiomas.
After red moles have been removed, it is recommended to refrain from visiting saunas, solariums and sunbathing.
Despite the fact that angiomas are usually not dangerous and do not cause harm or discomfort, in most cases, exposure to external factors can cause them to degenerate into malignant formations. This occurs due to damage or exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
In addition, if you accidentally scratch or catch a mole, bleeding may begin.
You need to be more attentive to those skin areas where there is a possibility of rubbing them with clothing - this is the neck, shoulders, stomach, chest. Convex moles are the most vulnerable, so they should be removed if possible.
Red moles located on the lips, mouth, ears and eyes are also dangerous.
If the angioma begins to itch, this is a signal that you should immediately seek advice from a specialist or an oncology clinic. Itching may indicate the growth of the tumor and its degeneration into malignant.
When red moles start to itch, you need to figure out what exactly is the reason; without qualified specialists it won’t be possible, since these are the consequences of hormonal disorders or a malfunction of the body’s systems.
NOTE! After studying laboratory tests, specialists at LIC clinics will determine what causes the appearance of alarming signs and how to act to get rid of them. Just remember that you should never scratch angiomas.
Red moles in children
For most people, the bulk of moles appear in the first 20 years of life, then the formation of moles (nevi) subsides. They also tend to sometimes disappear on their own, and this happens due to the fact that the blood vessels supplying the mole dry out or become clogged. One in 100 newborns are already born with small red moles on their body, and they are considered more prone to change and develop into melanoma. This red neoplasm that rises slightly above the surface of the skin is called a Spitz nevus.
Children can also be born with large blue spots on their backs; they are called Mongolian spots and are most often found in children with Asian roots. Any moles are often injured, especially in childhood. This can cause complications, so it is advisable to sometimes see a doctor, and also try to protect children from such injuries.
Capillary hemangiomas, red birthmarks, otherwise called cavernous hemangiomas or cavernous hemangiomas - cavernomas, etc. “Salmon-colored spots” (“stork bites”) are just some of the varieties of red birthmarks. Learn further about the causes of their appearance and get acquainted with the appropriate treatment.
Skin conditions: red birthmarks
Congenital birthmarks are colored spots on the skin that are either present at birth or develop shortly after birth. Birthmarks can be characterized by many different colors in appearance, including brown, tan brown, black, light blue, pink, white, red or purple. Some birthmarks are just discolorations on the surface of the skin; others are structurally raised above the surface of the skin or extend into tissues beneath the skin.
What are the causes of birthmarks?
The causes of most birthmarks are unknown. Most birthmarks are not inherited.
There are many folk stories and myths about the causes of birthmarks, but none of these stories could explain the true causes of birthmarks.
Do birthmarks need to be treated?
Most birthmarks do not require any treatment. They often go away on their own as the child gets older.
However, some birthmarks may need treatment due to their specific location. For example, a raised birthmark near a child's eye can affect his or her ability to see.
In rare cases, birthmarks are associated with other conditions, such as growths on the liver, lungs, stomach, or intestines.
Types of birthmarks
There are two main categories of birthmarks - red birthmarks and pigmented birthmarks.
Red birthmarks are colored vascular (related to blood vessels) marks on the skin that develop before or shortly after birth. Pigmented birthmarks are marks on the skin that are present at birth. The color of the marks can range from brown or black to bluish or blue-gray. Read on to learn more about pigmented birthmarks.
Red birthmarks
Hemangioma (red birthmark) is the most common type of vascular birthmark. This spot is usually painless and harmless, and its cause is unknown. The color of a birthmark is conditional and occurs due to the extensive development of blood vessels in the area.
Types of hemangiomas include:
- Strawberry hemangiomas (also called strawberry mark, nevus vascularis, capillary hemangioma, hemangioma simplex) can appear anywhere on the body, but they are most common on the face, scalp, back, or chest . They are made up of small, tightly packed blood vessels. They may not be present at birth and may not develop until several weeks later. Strawberry hemangiomas usually grow quickly, remain a fixed size, and then “freeze” or fall off.
In most cases, strawberry hemangiomas disappear by the time the child is 9 years old. Some slight discoloration or wrinkling of the skin may, however, persist and remain in the area where the hemangioma was.
- Cavernous hemangiomas (also called angioma cavernosum or cavernoma) are similar to strawberry hemangiomas, but are located more deeply. They may appear and appear as a red and blue spongy mass of tissue filled with blood.
Some of these lesions may go away on their own, usually as the child approaches school age.
- Capillary hemangiomas are flat, purple to red birthmarks formed from dilated blood capillaries. These birthmarks are most often found on the face and can vary in size. Capillary hemangiomas are often permanent (if left untreated).
- "Salmon spots" (also called stork bites) appear in 30-50% of newborn babies.
These marks are small blood vessels (capillaries) that are visible through the skin. They are most common on the forehead, eyelids, upper lip, between the eyebrows and on the back of the neck. Often these marks disappear as the baby grows.
What are the symptoms of red birthmarks?
Symptoms of red birthmarks include:
- Skin marks that develop before or shortly after birth
- Red rashes or lesions on the skin
- Markings on the skin that resemble blood vessels
- Possible bleeding
How are red birthmarks diagnosed?
In most cases, a medical professional can diagnose a red birthmark based on the appearance of the skin alone.
Deeper birthmarks can be confirmed by tests such as MRI, ultrasound, CT scans or sections, or a biopsy.
What is the possible treatment for red birthmarks?
Many capillary birthmarks, such as salmon spots and strawberry hemangiomas, are temporary and do not require any special treatment.
For persistent skin blemishes, you can use special concealing cosmetics such as Covermark. Oral cortisone may shrink the size of a hemangioma if it is growing rapidly, obstructing the field of view, or if it is pressing on vital structures.
Capillary hemangiomas on the face at a young age can be treated with a yellow pulsed laser using dyes to improve results.
Other treatments for red birthmarks may include:
- Cold treatment - cryotherapy (freezing)
- Laser surgery
- Surgical removal
In some cases, birthmarks are not treated until the child reaches school age. However, birthmarks are treated earlier if they jeopardize vital functions, such as vision or breathing, or are of aesthetic “interest” in masking a skin defect.
Can red birthmarks be prevented?
There is currently no known way to prevent red birthmarks.
Website illustrations: © 2010 Thinkstock.
Do red moles need to be removed?
Not only is it possible, but it is also necessary. If the hemangioma increases in size, changes shape or color, this is, of course, a direct indication to see an oncologist as soon as possible for further examination, and removal if necessary. Of course, not using artisanal or folk methods, but with the help of modern specialists. If the mole behaves quite calmly and does not change shape or color, then most likely there is no need to be afraid and you can postpone removing the moles.
PRECAUTIONARY MEASURES
People with red moles should not have special restrictions. These formations do not require special care or specific treatment.
But some recommendations from experts should still be followed. As mentioned above, the only thing that can be dangerous is mechanical impact, hence the possibility of damage.
Specialists at LIC clinics recommend removing angiomas in places where there is a risk of injury. Also, avoid excessive sunbathing near water, as water increases exposure to ultraviolet rays. But if it so happens that you cannot avoid them at all, then you should use protective creams with a filter of at least SPF 30.
Diagnostics
In medicine, there is a general method for diagnosing skin tumors. These include an initial examination and recording of all patient complaints (history). If a malignant tumor is suspected, an MRI or radiography is prescribed. All data obtained is analyzed and conclusions are drawn, on the basis of which a preliminary diagnosis is made. The main and final point in making a diagnosis is the histological method (biopsy). It is a microscopic sampling of tissue from the body of a mole, and is done to identify the pathology of cells in the neoplasm.
Why do benign formations appear on the skin?
Cosmetologists and dermatologists do not know the exact mechanism of their formation. Most often the cause is:
- injuries;
- viruses;
- systemic diseases of the body, for example xanthomas, occur due to an excess of fat in the blood;
- long-term skin diseases;
- exposure to aggressive substances;
- excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation;
- x-rays;
- heredity (for example, seborrheic dermatosis).
Most skin lesions are benign
Methods for removing red moles
If the mole does not bother you in any way and is not located in high-risk areas, that is, on the arms, feet, or head and back, then it is quite possible not to remove it.
If the hemangioma bothers you, then it can only be removed by specialists, a dermatologist or oncologist. You should not take the risk of removing a nevus from a cosmetologist and exposing the incorrectly removed hemangioma to the risk of growth or the risk of infection.
There are several common procedures for removing them.
- Electrocautery. The nevus is burned with an electric current delivered using a small instrument. The grounding block will be placed somewhere so that the rest of the body is not exposed to electricity.
- Cryosurgery. The mole is frozen using liquid nitrogen. It is destroyed by extreme cold. Liquid nitrogen is sprayed for 10 seconds, the problem is solved in one session. This method is quick and relatively simple. The wound also does not require special care.
- Laser surgery. This procedure uses a concentrated yellow laser beam that emits enough heat to destroy the nevus from the inside. This method is quick and is used on an outpatient basis, meaning it does not require subsequent hospitalization. Depending on how many moles will be removed, one to three procedures may be required. There may be small scars that will disappear within 10 days.
- Surgical method. This is the process of removing a nevus from the upper part of the skin by cutting the lesion and then applying sutures. It is not a frequently used method, and after such an intervention there are scars.
In any case, if you have concerns and questions about why red moles appear, you need to see a doctor, if only to reassure yourself with good tests. Because unexplained questions create stress, which in turn contributes to a decrease in immunity. Be healthy.
Features and advantages of laser technology
Many people prefer to remove moles using a laser. This technique has a number of advantages, including:
- high performance. It is possible to completely get rid of angioma in one procedure;
- comfort. Laser removal is carried out using modern anesthetic substances, so the patient does not experience any discomfort;
- availability. The prices for the technique are low;
- short duration. It takes no more than 20 minutes. The exact time depends on the size and number of moles;
- lack of long-term rehabilitation;
- safety (no bleeding or risk of infection).
Contraindications to the technique are minimal. It cannot be performed in the presence of infectious diseases, diseases of the cardiovascular system, lesions of the central nervous system, which are characterized by increased excitability. The doctor will tell you more about the possibility of using this technology after the examination.
Prevention of skin tumors
Unfortunately, medicine has not yet learned to prevent the appearance of various formations on the skin. But dermatologists give their patients the following preventive recommendations:
- do not delay contacting a doctor if a tumor appears on the skin;
- remove formations only after a specialist and diagnostics confirm their benign nature;
- avoid excessive exposure to the open sun;
- use sunscreen, especially if you are prone to moles and hyperpigmentation;
- do not come into contact with chemically active and carcinogenic substances;
- do not eat foods that contribute to the development of cancer (smoked meats, sausages, animal fats, meat products with food stabilizers).
Do you have a lot of moles? Forget about tanning in the open sun
Do benign formations hide the danger?
Benign neoplasms are unpredictable structures that can manifest themselves at any time or not at all. The process of their transformation into malignant ones has not been fully studied. There is no clear answer to the question of what exactly activates this process. It is believed that mechanical trauma, excess ultraviolet radiation, metabolic disorders and other factors contribute to degeneration. One way or another, if you have a benign skin lesion, you should not experiment and rely on chance. Moreover, today removal does not cause difficulties.