Stomatitis
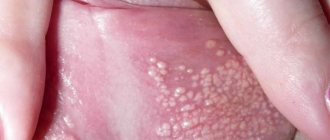
Stomatitis is an inflammation of the oral mucosa, which can occur in mild and severe forms. The development of pathology is possible at any age. Risk factors for the appearance of white pimples on the inside of the lip include insufficient hygiene, smoking, and lack of iron in the diet. In this case, genetics and gender do not matter.
Causes of Fordyce granules
This is a light rash that can form on the lips, cheeks, genitals and groin area, on the chest, oral mucosa, and other places. At the moment they are not considered a pathology, but sometimes cause discomfort. Another name for granules is seborrheic cysts. They are not transmitted by contact and are more of an aesthetic defect.
Most often, their occurrence occurs during puberty, when hormonal changes occur in the body. It is believed that the formation of these white pimples on the lips may be due to the close location of the sebaceous glands to the surface of the skin.
There are the following reasons for the appearance of white pimples on the lip:
- smoking;
- abnormal location of the sebaceous glands;
- improper care;
- hormonal disorders;
- narrowing of the excretory canals of the sebaceous glands.
This rash may resolve on its own.
What to do if pimples appear on your lips?
If you have pimples on your lips, you shouldn’t immediately run to the pharmacy for saving ointment. Despite popular misconception, the term “acne” does not refer to any specific disease. The rash can be a manifestation of many dermatoses. Only a specialist, having studied her character and collected anamnesis, will be able to prescribe adequate treatment.
With acne, inflammation around the lips is usually rare, but if the rash around the lips turns out to be acne, the doctor may prescribe topical antibiotics18. These include Clindovit® gel. Its main active ingredient is clindamycin phosphate, which upon contact with the skin is hydrolyzed to form clindamycin6. The drug is active against propionibacteria and helps reduce the level of free fatty acids6. To reduce the risk of developing antibiotic resistance, it is recommended to combine the use of Clindovit® with azelaic acid preparations (Azelik® gel) or benzoyl peroxide28.
Why do white dots appear on the lips?
Most often, small white formations, felt like lumps on palpation, appear in women after the lip augmentation procedure. And the reasons for this may be:
- incorrect injection of filler - the depth of injection is not maintained;
- violation of lip care rules after the procedure;
- allergic reaction to anesthetic drugs;
- reduced general immunity.
But there are other reasons why white dots appear on the lips:
- Fordyce granules. They can occur in both men and women; doctors assess them as microcystic formations localized in the sebaceous glands. They are formed against the background of excessive production of sebaceous secretions, which leads to blockage of the glands. They also appear due to hormonal imbalance, physiological characteristics of the body, and narrowing of the sebaceous ducts.
- Dysbacteriosis. Accompanied by diarrhea or constipation, which reduces overall immunity and promotes the accumulation of toxic substances. This is due to an imbalance of healthy and pathogenic microflora in the intestines.
- Avitaminosis. Small white dots also form when there is a lack of minerals and vitamins in the body. It can be triggered by an unbalanced diet, a strict diet, pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Zhiroviki. Whitish spots (lipomas) appear under the skin; they are defined as soft, mobile in consistency, and belong to the category of benign neoplasms. They can form due to hormonal imbalance, problems with the functionality of the gastrointestinal tract, and the use of low-quality cosmetics.
- Herpes. It usually occurs on the upper lip, appears as a bubble, is accompanied by itching and swelling, and sometimes causes mild pain. This is an infectious disease that occurs when the immune system is weakened.
White dots on a child’s lips can form:
- with candidal stomatitis – the fungus of the genus Candida is activated and begins to actively multiply;
- due to herpes virus - transmitted from mother to baby during the birth canal and during breastfeeding;
- with allergic stomatitis - the body’s reaction to internal irritants (food, milk formula, purees), usually localized on the inside of the lip.
When such formations appear, consultation with specialists is necessary.
Diagnostics
To undergo a diagnostic examination, you must first visit a therapist . He will give referrals to doctors of narrow specialization: dermatologist, endocrinologist . Women will also need to be examined by a gynecologist to confirm or deny the causes of the rash.
If the number of granules is small - 2-5 pieces, then a specialist in most cases makes a diagnosis immediately after a visual examination. There is no need to take tests or undergo hardware diagnostics (except for controversial issues or doubts).
When the rashes are profuse, in addition to discomfort, there is also itching, then a detailed examination, tests and specific procedures are mandatory for making a diagnosis and starting treatment. Additional examination is carried out in order to exclude the possibility of medical error. It is easy to attribute the granules to manifestations of eczema, rashes of an allergic nature, neurodermatitis, or molluscum contagiosum.
The main method of examination is taking a skin sample from the damaged area (biopsy) . Additional tests (general blood and biochemical) may be required if the doctor suspects the development of lichen ruber. Also, tests are prescribed by specialized specialists (for hormones, examination of the thyroid gland) when there are suspicions or additional symptoms characteristic of the disease.
Important! Despite the abundance of rashes, the quantity or color of the granules does not pose a health hazard. The main disadvantage is the visual unaesthetic. The transformation of neoplasms into malignant types of tumors (cancer) has not been detected over all the years of observation and examination.
Relevance
Every year the popularity of such a branch of medicine as injection cosmetology is steadily increasing.
According to ASAPS (The American Society for Aesthetic Plastic Surgery), between 2014 and 2022 alone, the number of procedures using hyaluronic acid (HA) fillers increased by more than 58% [1]. The widespread use of such interventions makes it important for doctors to know not only about the benefits of a particular filler, but also about possible complications, side effects and methods for their correction. It is important to increase patient awareness of the potential risks associated with such injections. In modern literature, various reports of side effects after injection contouring are increasingly being published, most of which include hematomas, asymmetries, skin ischemia and necrosis, infections and allergic reactions [2].
Currently, various types of injectable fillers are used in cosmetological practice, which can be classified according to their origin (the most popular of them are HA in various modifications, calcium hydroxyapatite, poly-L-lactic acid, collagen) and the time of persistence in tissues (temporary, semi-permanent and constant) [3, 4].
Despite statements by manufacturers and various authors that HA fillers are as safe as possible in terms of immunogenicity or that the occurrence of such complications is extremely rare, side effects of this kind are still periodically observed. Systematic reviews have shown that all known HA-based fillers on the market are capable of causing early and late side effects. Their true prevalence is unknown but appears to be significant. The nature of most late side effects is inflammatory and immune-mediated. The most common occurrences are edema, granulomas, carcinophobic disorders and cellulite. Autoimmune reactions and immediate hypersensitivity are more rare [5].
In recent years, there has been great interest in studies of cases of delayed and persistent inflammatory reactions that occur after the administration of various excipients. According to some authors, infectious diseases [6], trauma [7], and vaccination [8] can be trigger factors.
Currently, the role of biofilm formation at the injection sites of fillers is being actively studied, because More and more researchers suggest that many cases of delayed complications arise due to its formation, and not due to the development of allergic reactions or other inflammatory response [9, 10].
Biofilms are a collection of microorganisms whose cells form three-dimensional structures by adhering to each other or to various surfaces. These microorganisms are capable of forming a matrix of extracellular polymeric substances (carbohydrates) around their colonies, which complicates the bioavailability of antibiotics and forms local resistance to them. There are five stages of biofilm formation: initial attachment, irreversible attachment, maturation I, maturation II, and dispersal. It is in the dispersion phase that the biofilm most actively forms its protective barrier.
After their formation, biofilms remain dormant (low-grade infection), but their activation with the occurrence of inflammatory reactions can be caused by trauma, hematogenous infection or iatrogenic manipulations [11].
Identification of biofilms is difficult. Cultures from biofilm-infected tissue are usually negative. Some authors consider fluorescence hybridization using peptide nucleic acid to be the most accurate in situ method [12].
Although HA-based fillers belong to the class of non-permanent fillers, a number of them are able to persist in tissues for 6 to 36 months [13], which provides bacteria with enough time to organize into biofilms.
As a clear illustration of the delayed immunoinflammatory response to the injection of HA filler, we present the following clinical case.
Clinical example
Patient N., 45 years old. She contacted the Department of Dermatology and Cosmetology of the JSC Institute of Plastic Surgery and Cosmetology with complaints of periodic swelling of the middle third of the face and pain in the area of the nasolacrimal groove and cheeks, pronounced pigmentation in the periorbital area after the injection of HA filler (Fig. 1).
From the anamnesis (according to the patient): about 1.5 years ago, 1 ml of HA filler was injected into the area of both nasolacrimal grooves and nasolabial folds. After the procedure, satisfactory correction was noted. 6 months after the injection of fillers, the patient suffered from severe infectious mononucleosis (she was hospitalized with meningitis). During hospitalization, she first noted the sudden appearance and intensification of swelling, pain, redness and hardness in the area of the nasolacrimal grooves and cheeks. The swelling increased during the day (Fig. 2).
In connection with this, an emergency consultation with a maxillofacial surgeon was carried out and a diagnosis of T78.3 (angioedema) was made. After drips with prednisone (three times), the patient noted an improvement. The swelling has decreased significantly.
After being discharged from the hospital a month later, the patient again noted swelling, pain, redness and hardness in the area of the nasolacrimal grooves and cheeks. She also began to notice the appearance and increase of diffuse symmetrical pigmentation in the periorbital area. The patient independently prescribed a course of antibiotic therapy, which she completed without effect. She also independently administered a single intramuscular injection of prednisolone (90 mg). After which she noted a significant decrease in symptoms.
Having associated her condition with filler injections, the patient turned to a doctor who had previously injected filler for its enzymatic resorption. After which, within six months, the negative symptoms resolved and were no longer observed.
Six months ago, the patient again turned to a cosmetologist to correct problem areas (nasolacrimal groove, cheeks, nasolabial folds).
The same filler used earlier was reinjected. After which, within 3 days, swelling, pain, and redness reappeared in the treated areas. When contacting a cosmetologist, intramuscular injection of dexamethasone and enzymatic resorption of the filler with hyaluronidase (one-time) were performed. A month later, the patient again noted the occurrence of periodic facial swelling in the area of filler injection, which was relieved by intramuscular administration of dexamethasone.
Objectively: at the time of examination there is no swelling of the face; painful lumps in the area of the nasolacrimal grooves (mainly on the right), the medial part of the cheeks and nasolabial folds are palpated. There is pronounced pigmentation of the periorbital and buccal area.
According to ultrasound examination, in the projection of the nasolacrimal grooves and nasolabial folds, residual inclusions of the drug are determined, which according to the ultrasound picture are characteristic of HA-based fillers. There is a local area of infiltrative changes (without a pronounced increase in blood flow) in the subcutaneous fatty tissue of the nasolacrimal groove on the right.
Diagnosis: L08.9 – Local infection of the skin and subcutaneous tissue, unspecified.
Treatment: amoxicillin + clavulanic acid 875 mg/125 mg once a day for 12 days; dexamethasone orally 1 mg/day for 20 days with a gradual reduction in dosage.
In the first 5 days of treatment, while taking the main medications, daily physiotherapy was carried out, consisting of the following sequence of procedures: ultrasound with dexamethasone, then pharmacophoresis with Longidase. Over the next 7 days, against the background of continued antibiotic therapy, enzymatic resorption of filler residues was carried out with hyaluronidase at a dilution of 3000 IU per 4 ml, using the technique of multiple injections and wide infiltration not only with the treatment of key areas, but also with the capture of surrounding intact areas (twice with an interval of 3 days) .
At the end of the course of treatment, a control ultrasound was performed, which revealed no signs of inflammation or residual filler fragments.
During therapy, a complete reduction of all the above-described clinical symptoms was noted. By the end of the course of therapy, there was a pronounced lightening of the pigmentation foci (Fig. 3).
Discussion
Potentially, any biomaterial injected and in contact with blood can sooner or later cause a wide range of side effects, both local and systemic. To date, there is not enough research and clinical experience regarding the treatment of these conditions. Management of both acute and systemic reactions is often difficult and requires an integrated approach using anti-inflammatory and sometimes immunosuppressive therapy. This problem requires further observations, development of diagnostic criteria and sound therapeutic protocols.
Conclusion
This clinical case is of potential interest for cosmetologists, dermatologists, plastic surgeons, and physiotherapists as an example of diagnosis, prevention and treatment of such pathological conditions.
Can I cope on my own or should I consult a doctor?
You can get rid of the problem yourself if a person has knowledge in the field of cosmetology and dermatology. It is best not to try to get rid of the problem yourself , since symptoms may indicate the presence of specific problems in the body that require professional solutions and constant medical supervision.
You should not delay your consultation if there is obvious discomfort when talking or eating. The appearance of discharge or blood from the granules, increasing itching or pain also indicates the need for a medical examination.
Ulcers caused by oral diseases
White sores in the mouth can appear due to diseases of the oral cavity. The most common cause is stomatitis. It comes in several types:
- aphthous;
- herpetic;
- bacterial;
- fungal.
| White ulcers in adults and children occur with aphthous and herpetic stomatitis. This disease can appear due to stress, untreated caries, lack of vitamin C, or overexertion. It is better not to self-medicate, but to immediately consult a doctor. Recommendations, in addition to medications, may include treatment of caries, a balanced diet, stress reduction, etc. |
| There are two separate forms of stomatitis - Bednar's aphthae and Setton's aphthae. The former develop only in a child due to injury to the mucous membrane or poor oral hygiene. Such rashes are also called erosions. Setton's aphthae is a more complex and painful phenomenon. It begins with the appearance of compactions, which then develop into painful ulcers. They most often form on the inside of the cheeks, in the corners of the lips and on the sides of the tongue. |
| Another cause of white sores is gingivitis. In smokers, such rashes are much more common due to the effects of nicotine on the mucous membranes. Those who have poor oral hygiene, reduced immunity and hormonal imbalances are also at risk of encountering gingivitis. If left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis: when the tissue that supports the tooth is affected. And this is a direct path to tooth loss. |
How to remove white dots on lips - treatment depends on the cause
What the white dots mean must be determined by the doctor - and only after that can treatment begin. Three methods are usually used: medication, surgery and folk remedies.
Drug treatment of whiteheads
Under no circumstances should you cut off, open with a needle or burn such formations on your lips yourself - this is fraught with the formation of wounds, ulcers and infection. The doctor will be able to select effective medications, taking into account the diagnosis:
- for Fordyce syndrome - Suprastin tablets, Fenistil gel, D-Panthenol cream;
- for herpes - Acyclovir ointment, Panavir gel;
- for dysbacteriosis - jojoba oil (to lubricate the lips), orally - "Acipol" or "Bifidumbacterin" (to restore intestinal microflora).
All medications are selected by the doctor, who also indicates the duration of therapy, and it can take several weeks.
Surgery
If conservative treatment does not give positive dynamics, then doctors can change the tactics of their work. How are white spots on the lips treated surgically? For this purpose the following are used:
- cryotherapy – removal of the problem area with liquid nitrogen; the procedure can be complicated by the formation of scars on the skin;
- electrocoagulation - “drying” white spots using high frequency current;
- laser therapy - the use of a laser beam that excises spots;
- Radio wave therapy is the most painless and non-traumatic method; after it there are no marks left on the skin.
The most difficult procedure is the one that uses liquid nitrogen. It is not only painful, but also requires multiple sessions. As a result, dense scars may form, which in the future will require the intervention of plastic surgeons.
Even if white spots on the lips do not bother you, you should seek help from a doctor and find out the true reason for their formation. The skin reacts to the slightest changes in the body; perhaps they are the first symptom of serious problems with the functionality of internal organs and systems.
Ulcers caused by trauma
The main reason for the appearance of ulcers when the mucous membrane is injured is infection in the wound. Most often, white rashes occur due to the habit of biting nails or the tip of a pencil or pen.
Fans of seeds and hard toothbrushes may also be at risk. Many people believe that hard bristles remove plaque better. Actually this is not true. If you carefully brush your teeth with such a brush, you can damage the enamel, gums and cause inflammation.
Other causes of mucosal injury:
- uncomfortable dentures;
- braces or other orthodontic structures;
- habit of unconsciously biting your cheek or tongue;
- exposure to mucous membranes with drugs or acids.
How to treat?
It is enough to remove the irritating factor and wait 1 - 2 weeks. Usually the ulcers go away on their own. If this does not happen, it is recommended to consult a doctor.