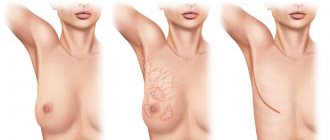
It's one thing when the blush on your cheeks appears and quickly disappears, as, for example, after a winter walk. And it’s quite another thing if it spreads across the face, does not go away for a long time and is also complicated by various rashes on the skin. We learned more about such a disease as rosacea at the X National Congress “Plastic Surgery, Aesthetic Medicine and Cosmetology”.
At the congress, many issues of dermatology were raised, including diagnosis, mechanisms of development and treatment of rosacea (rosacea). In this article we present excerpts from the report of dermatologist, cosmetologist, doctor of medical sciences Elena Arabian, which will help to better understand what rosacea is, what factors can provoke the appearance of this disease and how it is treated today.
Features of the drug
The AestheFill hydrogel composition is based on polylactic acid. PLA is an active polylactide that has long been used in medicine due to its hypoallergenicity, absence of protein and artificial, non-degradable polymers. Natural biodegradation of the substance leads to its decomposition into glycogen and lactic acid, which are removed from the body with water and carbon dioxide.
After injection, the filler breaks down into many AestheFill microspheres in the skin layers. Porous polylactic acid beads fill vacant areas without over-correction. Then, over the course of 2 years, skin cells continuously synthesize their own collagen and hyaluronic acid. A filler based on PLA creates a strong collagen base, and the prolonged action of the drug allows repeated injections only after several years.
The introduction of Estefil filler allows the cosmetologist to solve several problems simultaneously:
- replenish volume in problem areas;
- activate the internal reserves of the skin - collagen synthesis, formation of new tissues;
- maintain the effect of the procedure for a long time.
Plus 3 – permanent result
The appearance of wrinkles and aging is a natural and irreversible process. But why can't we age gracefully? Why passively watch as your face develops new, unwanted lines and wrinkles?
Thanks to the currently available technologies offered by aesthetic medicine, everyone can enjoy a youthful and natural appearance for many years, eliminating the symptoms of not only skin aging, but also tissue volume loss. The effect of treatment with L-polylactic acid lasts up to two years.
L-polylactic acid is especially suitable for people who value natural treatment results. Yes, the skin recovers slowly, but precisely because of this effect, when the patient goes to work after the procedure, no one will understand that she “did something to her face.” It won't look artificial. And after some time, the result of rejuvenation will be clearly visible.
Benefits of AestheFill
The drug AestheFill based on PLA differs from other fillers in a number of positive qualities:
- Absolute safety for the body. The natural process of breakdown of active compounds does not cause allergies or rejection processes - reactions characteristic of the introduction of foreign bodies.
- Fixed action in the problem area. PMC is not able to migrate in tissues. Its particles remain in the injection zone and fix the specified volume.
- The introduction of polylactic acid does not cause capillary clogging due to the correct shape of the microspheres.
- A cosmetologist can independently prepare a suspension of any concentration for injection into different layers of the dermis - superficial or deep.
- For a long time, the skin does not need additional complex invasive cosmetic procedures.
- One bottle of the drug is enough to treat the face, neck, and décolleté. PLA can be injected into the skin of the hands for rejuvenation.
- Painless administration of the product.
- The possibility of combining the drug with other cosmetological technologies (for example, with laser rejuvenation).
- No side effects.
Preparation for the procedure
During a face-to-face consultation, a cosmetologist should examine the patient and ask her about the presence of chronic diseases and contraindications. No special preparation measures are required for the procedure.
Before introducing biogel, standard tests are usually prescribed:
- blood for biochemistry;
- coagulogram;
- allergy tests;
- general urine analysis.
Before installing liquid mesothreads, it is necessary to donate blood for the presence of HIV, hepatitis B and C, and for the level of tumor markers. For a month before the procedure, you should not take antibacterial drugs, perform hormonal therapy, or use any other drugs that affect blood clotting.
The introduction of biogel does not require the patient to follow a specific diet. It is recommended to give up alcohol and smoking only a week before the procedure.
This is due to the fact that nicotine negatively affects the state of the respiratory system, and alcohol creates an increased load on the heart, blood vessels and causes intoxication of the body.
Before the procedure, you should also not overuse natural and artificial tanning. This may result in less pronounced results from the effects of biogel.
Before introducing mesothreads, you should not do other cosmetic manipulations that lead to disruption of the integrity of the skin. The cosmetologist may suggest that you undergo additional diagnostic tests if necessary.
Indications for use of AestheFill
Contour plastic surgery with polylactic acid is indicated in the following cases:
- sagging skin of the face, neck, décolleté, hands, caused by degeneration of adipose tissue in the subcutaneous tissue;
- correction of areas with lost volume, sagging, reduced density;
- sunken areas of the temples, cheeks, pronounced nasolabial, premaxillary folds;
- scars of various origins on the skin - post-surgical, atrophic;
- change in facial contour (asymmetry, lost volume);
- changing the shape of the chin, enlarging the cheekbones and lips.
What is the procedure for administering AestheFill?
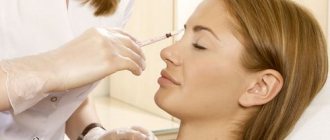
First of all, a cosmetologist examines the patient’s skin and identifies areas that require correction. Then the scheme according to which the specialist will perform the injections is determined. The skin of the face, neck, décolleté or hands is cleansed with a delicate cosmetic product and treated with an anesthetic.
While the anesthetic begins to act, the cosmetologist prepares a suspension of PLA granules in the required concentration. For injections, a special syringe with a microscopic needle is used. These features help minimize pain during the procedure. The finished composition can be introduced into the modeling zones - the places that have undergone the greatest changes (cheekbones, chin, lips, temples, forehead, cheeks). If the specialist decides to perform vector lifting, the drug is administered over the entire face.
To target wrinkles, AestheFill is injected directly into the base of the wrinkles. This method of injections allows the PMC filler to fill voids in the skin and bend wrinkled creases. To add volume to the lips or cheekbones, the cosmetic product is evenly distributed over the entire surface. In this case, quite a lot of injections are performed in small doses. As a rule, the correction procedure using Estefil gel takes from 30 to 60 minutes.
Stages of the procedure
The procedure for installing liquid mesothreads is carried out using local anesthesia. Since the manipulations are low-traumatic and fairly painless, this is enough to ensure the patient’s comfort.
It is very important to choose the right anesthetic. Since fibrotic changes in tissues are usually accompanied by an inflammatory process, the development of pathogenic microflora in the dermis is possible.
The occurrence of edema and hematomas is also possible. Therefore, an incorrectly selected drug for local anesthesia and an incorrect dosage can increase the negative consequences of the procedure and adverse reactions.
It is important to objectively assess the condition of the patient’s skin and select the exact amount of biogel intended for administration. It is possible to adjust the dose of anesthetic during the rejuvenation procedure itself.
Installation of liquid mesothreads is permitted only in a cosmetology salon or clinic. The patient is placed on a chair reclining. The procedure takes no more than 1.5–2 hours. The composition of the biogel is selected individually.
For example, thick biogel with a high zinc content is not suitable for thin skin. The drug is injected to a certain depth in order to involve all layers of the dermis.
Stages of the lifting procedure with liquid mesothreads:
- Cleansing the skin of makeup and impurities with special products.
- Disinfection and degreasing of skin.
- Determining puncture points and marking with a special marker.
- Introduction of anesthetic.
- Introducing liquid mesothreads into targeted points using a medical cannula.
The procedure is quite painless, injection marks disappear within two days.
Typically, biogel is injected into the following areas:
- nasolabial folds;
- area around the eyes;
- cheekbones;
- forehead;
- chin;
- cheeks.
No more than 3 ml of biogel is administered per procedure. Typically, 0.1–0.2 ml of mesococktail is distributed into each puncture. At least two weeks should pass between rejuvenation sessions.
Recommendations for using PMC filler
The AestheFill injection procedure is intended to correct areas of skin that have lost tone, are dehydrated and flabby. After all manipulations, a light massage is required, which will help distribute the drug in problem areas and uniformly fill the voids inside the dermal layers.
After the injection of AestheFill filler, the client is recommended to comply with certain requirements:
- do not use caring and decorative cosmetics for 24 hours;
- do not touch the injection sites so as not to injure the skin or cause infectious complications;
- refrain from visiting the sauna, bathhouse, solarium, swimming pool;
- for 2-3 days, refrain from intense sports and other physical activity;
- eliminate alcohol consumption
The duration of the recovery period is determined for each client individually. The duration depends on the characteristics of the skin and the nature of the defects being corrected. In the event that the changes in the skin are severe, it is advisable to repeat injections of the PMC filler after 2-3 months for the purpose of correction.
The result of correction with polylactic acid gel
After the procedure, the visible effect occurs almost immediately. Over time, visual signs of rejuvenation become more pronounced. Thanks to the effect of PLA microgranules, anti-aging changes occur in all layers of the skin at the cellular level.
As a result, the client notes:
- lasting effect of real rejuvenation at any age;
- compensation for lost volume in the area of the temples, cheeks, cheekbones;
- reconstruction of dense facial contours, chin area, clear cheekbone line;
- smoothing out facial wrinkles in areas around the eyes and mouth covered with thin, delicate skin;
- visible changes in the density and color of the skin of the face, neck, décolleté, and hands;
- elimination of facial wrinkles, age spots, post-acne marks;
- narrowing of pores, smoothness, elasticity, healthy complexion.
Possible side effects
The composition of liquid mesothreads includes components such as hyaluronic acid, lactic acid and zinc. All of them have been used in cosmetology for a long time and are absolutely safe. The likelihood of adverse reactions occurring is minimal. However, some patients may experience:
- skin redness;
- swelling;
- discomfort in the area of gel injection;
- pain at the puncture sites.
These symptoms are normal in the first few days after the procedure. If they do not go away a week after the biogel was introduced, you should consult a doctor for medical help.
Possible complications
No side effects were found following the administration of PMC. The appearance of negative phenomena after the correction procedure is possible only due to the individual characteristics of the skin. In some cases, hematomas, tissue swelling, and skin itching are the result of an error by an unqualified cosmetologist. It is important to entrust your face to a specialist with sufficient experience in the field of minimally invasive cosmetology.
In any case, all negative signs disappear on their own 2-5 days after the procedure for introducing the cosmetic product.
Contraindications
The introduction of biogel is absolutely harmless to health. However, even this procedure has a number of contraindications:
- age under 18 years;
- pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- the presence of chronic diseases in the acute phase;
- herpes in the acute stage;
- diabetes;
- asthma;
- tuberculosis;
- low blood clotting;
- bacterial or viral infections;
- inflammation of the skin at the sites of biogel injection;
- cancer;
- dermatological diseases.
There are no strict age restrictions for the liquid mesothread procedure. However, a competent specialist will not recommend it to you if other methods can be used. The introduction of biogel will be ineffective if the wrinkles are senile, severe, and the skin is weakened.
We recommend
Laser aesthetic cosmetology: the perfect technique for an ideal appearance More details
The result of the procedure depends not only on the drug, but also on the qualifications of the cosmetologist. The doctor must determine whether there is a need to introduce liquid mesothreads and whether they will help eliminate cosmetic flaws. The final effect of the injections can be observed 2 weeks after the manipulations.
Reviews of the drug AestheFill
Professional cosmetologists speak positively about Estefil. The drug has a pronounced rejuvenating effect even on fairly old patients. In almost 95% of cases of use, a visible effect appears in the first hours after administration. The maximum result is determined after 1-2 months in the form of restoration of natural density and skin turgor. Natural firmness and elasticity returns to the face.
All regeneration processes in the deep layers of the skin occur naturally, due to the activation of the synthesis of its own collagen and hyaluronic acid. Compared to other drugs, PMC is injected subcutaneously into problem areas quite quickly. The recovery period takes place in a matter of days. After 1-2 days, post-injection swelling resolves, and after 3-5, hematomas and bruises completely disappear.
The Center for Aesthetic Medicine "Novoklinik" offers to take advantage of a special offer - correction of skin changes using AestheFill gel for only 47,500 rubles instead of 80,000.
Patients who have already used the services of Novoklinik specialists note the rapid restoration of the skin of the face, neck, décolleté and hands. With the help of PMK fillers, they restore their former beauty and attractiveness. One of the significant advantages of the product is its affordable price, which is combined with a long-lasting positive cosmetic effect.
Cosmetic procedures are contraindicated during pregnancy and lactation.
Acid-containing preparations in gynecological practice
The article substantiates the use of acid-containing drugs for bacterial vaginosis (BV). The characteristics of the drugs on the market, which include lactic, citric and ascorbic acids, are given, and issues of their effectiveness and safety are discussed.
Using the example of the drug Lactagel (Orion, Finland), it was shown that lactic acid and glycogen promote the growth and restoration of lactobacilli, which means that acid-containing drugs can be recommended as a means of preventing vaginal dysbiosis during treatment with antibacterial and antifungal agents.
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is a chronic disease characterized by increased vaginal acidity. At a pH value > 4.5, the most favorable conditions are created for the growth of strict anaerobes; the environment is acidic
We have found that acid instillations without additional therapy lead to only a short-term effect, especially in women with a long-term disease. In this case, there is no radical restoration of the pH of the vaginal microecosystem. This can be explained as follows. It is known that lactic acid is formed from carbohydrates by a direct reaction with the participation of the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase. An exogenous increase in the concentration of lactic acid in vaginal fluid (VF) leads to activation of the reverse lactate dehydrogenase reaction, which results in the formation of pyruvic acid (PVA), which, in turn, is used by anaerobes associated with BV in the pyruvate dehydrogenase reaction. Thus, the use of lactate for medicinal purposes from a biochemical point of view should have a temporary and ambiguous effect. Therefore, it is necessary to search for new options for correcting vaginal pH.
According to O.L. Molchanova
(2000) [1], the normal presence of acidophilic microflora in the vagina is determined by a favorable acidic environment, and not by lactic acid formed by lactobacilli. Since the concentration of lactic acid in the liquid is low, the buffer capacity does not depend significantly on it. Nevertheless, the role of lactobacilli and other representatives of lactoflora is significant, since they fill the microecological niche, not only being a biological barrier to pathogenic and opportunistic flora, but also indirectly participating in the function of protection against bacteria and viruses through the generation of reactive oxygen species.
In addition to instillations, various acid-containing products, mainly gels, are currently most often used. Thus, W. Andersch et al.
(1986) [2] proposed local application of a gel containing lactic acid (pH = 3.5) at a dosage of 5 ml for 7 days for the treatment of BV.
This method has comparable effectiveness to taking metronidazole 500 mg 2 times a day for a week. Subsequently, E. Holst and A. Brandberg
(1990) [3] used intravaginal administration of a gel with lactic acid (pH = 3.8) and nutritional components for lactobacilli in a dose of 5 ml before bedtime for 7 days in pregnant women (n = 10). All patients began treatment early, which was completed approximately two months before delivery. Control studies were carried out on the 1st and 5th weeks after the end of treatment. The authors concluded that local treatment, which restores normal vaginal acidity but has no systemic effect, is preferable to oral antimicrobial therapy, especially during pregnancy.
In women prone to relapses of BV, the prophylactic use of acid-containing products plays an important role in maintaining normal vaginal microflora. Thus, in a double-blind placebo-controlled study by V. Andersch et al. (1990) [4] showed that periodic (3 days a month for six months) use of lactic acid gel (Lactal) was effective in reducing the severity of symptoms of bacterial vaginosis (BV) and restoring normal vaginal microflora. The authors confirmed that this treatment does not cause side effects and is an alternative to repeated courses of antibiotic therapy in patients with recurrent BV.
This drug, a gel containing lactic acid and glycogen, was recently registered in our country under the trade name Lactagel (Orion, Finland). The components of the drug promote the growth and restoration of one’s own lactobacilli, so Lactagel can be used not only to quickly eliminate the unpleasant symptoms of BV, but also as a means of preventing vaginal dysbiosis during treatment with antibacterial and antifungal agents. It should be taken into account: the simultaneous use of Lactagel with topical drugs is inappropriate. In addition, it must be remembered that when treating fungal infections accompanied by severe inflammation, in the first days of lactic acid therapy, patients may experience discomfort, which may provoke refusal of preventive treatment for bacterial vaginosis. To avoid such undesirable situations, lactic acid should be prescribed on the 2-3rd day of therapy for the underlying disease. In general, the success of prescribed therapy often depends on patient adherence to treatment. In the case of Lactagel, refusal of treatment is least likely, since the drug does not actually cause unpleasant side effects.
The second component of Lactagel, glycogen, although auxiliary, nevertheless affects one of the causes of disturbances in biocenosis. Menstrual irregularities are accompanied by a decrease in estrogen concentration, which, in turn, leads to a deficiency of glycogen, which is a nutrient substrate for the proliferation of lactobacilli. The introduction of lactic acid in combination with glycogen in women with hormonal imbalances probably contributes to a more rapid restoration of their own lactobacillary flora.
M. Milani et al.
(2003) [5] in a randomized, blinded, controlled trial involving 64 women with BV showed greater effectiveness of a single oral dose of tinidazole 2 g followed by maintenance therapy in the form of intravaginal administration of a buffered acid gel compared with the standard seven-day regimen of intravaginal therapy with clindamycin.
M. Mucci and C. Benvenuti
(2006) from Switzerland and Italy proposed the use of lactic acid with maltodextrin in gel form - Intilac plus (Rottapharm) - for the treatment of BV for 1 week. It was demonstrated that complete recovery or improvement was observed in 88% of women with acute BV or dysmicrobiosis against the background of therapeutic safety and clinical and microbiological effectiveness of the drug.
Also in 2006, M. Brandt et al.
[6] reported on the original drug they developed, Vagisan (Vagisan, Wolff, Germany), which is a suppository with lactic acid. True, in contrast to our methodology (we recommend using lactic acid at the initial stage of treatment), German researchers used Vagisan intravaginally after a course of metronidazole therapy, first daily for 7 days, and then twice a week for another 13 weeks. Good results were obtained in preventing relapses of BV: the relapse rate in the lactic acid group was 7.4% versus 12.7% in the control group. However, these differences were statistically insignificant, since the groups were heterogeneous - 8 and 77 people, respectively. Apparently, the prophylactic use of lactic acid after treatment for BV is very promising, but requires additional research.
As an alternative to lactic acid instillations, we proposed the use of vaginal tampons and gels containing a citrate buffer system, and tested them as therapeutic and hygienic products. Research results have shown that the use of these drugs at the first stage of treatment for BV leads to the rapid restoration of pH and normal microflora in the vagina. The effect of tampons or gels is associated with a longer (4–8 hours) maintenance of the physiological pH level (3.8–4.2) in the vagina than with instillations. As a result, favorable conditions are created for the functioning of proteolytic enzymes. In turn, this has a positive effect on the functional activity of the vaginal epithelium (regulatory, protective, synthetic), since the processes of disintegration of cell layers are interrupted as a result of proteolysis of collagen molecules and proteins that form mucus. Functionally active epithelium restores the acid-base balance, metabolites that determine the increase in pH and have a cytotoxic effect are removed. This creates unfavorable conditions for the life of BV-associated microflora.
The use of citric acid and its salts as the main component of the buffer system is advisable, since in this case chelation of divalent ions Mg2+ and Ca2+ occurs, which are the most important coenzymes of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex of anaerobes associated with BV. The pyruvate dehydrogenase reaction in BV is one of the most important pathogenetic components of the disease. As a result of the reaction, pyruvic acid is utilized by anaerobes to form acetyl-CoA. The latter is used by the anaerobic microflora associated with BV for the synthesis of fatty acids with a short carbon chain. When the concentration of PVC decreases under the influence of the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase, the reverse reaction of formation of PVC from lactic acid is activated. Thus, with BV, the pool of these two important metabolites at the vaginal level is depleted.
The use of citric acid as a chelator leads to an increase in the pool of lactate and PVA in the fluid due to inhibition of the pyruvate dehydrogenase reaction. There is a limitation of contact between anaerobic microflora and PVC, which leads to disruption of the energy supply and metabolism of anaerobes. PVC, while limiting its utilization by microorganisms, is used by the vaginal epithelium in the reactions of gluconeogenesis and glycogen resynthesis, the main substrate for the formation of lactic acid. Restoring the concentration of glycogen in the surface layers of the vaginal epithelium is one of the most important mechanisms for restoring normocenosis, since the acidophilic flora of the vagina uses it in the processes of homoenzyme fermentation and, accordingly, in the energy supply of the processes of reproduction of microbial biomass. The lactate formed during this process turns into pyruvate, and subsequently the cycle of glucose use is closed in the epithelial cells.
In recent years, there has been increasing interest in drugs that increase the acidity of vaginal fluid. Recently, a new drug VITAgyn C (Farma-Derma srl, Italy), the main component of which is ascorbic acid, was registered in Italy. This drug is used to treat the vagina in order to restore the lactobacillary flora. As reported in foreign sources, VITAgyn C helps in the treatment and prevention of BV, mycotic vaginitis and recurrent urinary tract infections. Restoring the vaginal pH to an acidic range of 3.8–4.4 prevents the growth of microorganisms associated with BV. An acidic environment creates unfavorable conditions for E. coli colonization and thus prevents the development of recurrent urinary tract infections. The acidic reaction of the vagina neutralizes the virulence factors of Trichomonas vaginalis and prevents the invasion of Candida fungi into the vaginal epithelium.
Vitamin C supports cellular regeneration and collagen formation by stimulating protein RNA synthesis. In addition, ascorbic acid stimulates cellular immunity, activating chemotaxis and phagocytosis of neutrophils and macrophages (phagocytes), and potentiates intermediate cellular immunity. Maltodextrin creates a metabolic substrate (exogenous glucose) for lactobacilli. Therapy for BV with VITAgyn C is carried out by administering 1 ovule every other day for 20 days. To prevent BV, vulvovaginal mycoses (VVM) and recurrent urinary infections, use 1 ovule 2 times a week for 12 weeks or longer.
A similar drug - Femiprim - is produced in Belgium, contains 250 mg of ascorbic acid and is prescribed for the same indications for 1 vaginal ovule 1 time per day for 6 days. The drug Vaginorm-C (Vagi-C) produced in Luxembourg is registered in Russia. The active substance of Vaginorm-S vaginal tablets is the retard form of L-ascorbic acid (250 mg). The effectiveness and safety of vaginal vitamin C tablets in the treatment of BV was studied by E. Petersen and P. Magnani (2004) [7] in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. The effectiveness of therapy was assessed by its effect on the four main clinical symptoms of BV. The results showed a statistically significant difference between the treatment group and the placebo group. At the end of therapy in the vitamin C group, bacterial vaginosis was verified in only 14% of patients, while in the placebo group – in 35.7%. Key cells and bacteria disappeared in 79% and 53% and in 77% and 54% of patients in the vitamin C and placebo groups, respectively.
Vaginal pH decreased significantly in both groups, but the number of patients with pH ≥ 4.7 1 week after stopping treatment was significantly lower in the vitamin C group (16.3%) than in the placebo group (38.6%). Adverse events during therapy were observed in 4 patients: two in the placebo group (itching, cystitis) and two in the vitamin C group (candidiasis). The effectiveness of therapy with Vaginorm-S was 86%, placebo – 8%. The incidence of side effects was comparable in both groups: in 8.8% of women in the placebo group and in 10.6% of women using Vaginorm-S.
We have repeatedly highlighted the role of modulating the acidity of the gastrointestinal tract in the treatment of BV with the use of ascorbic acid [8, 9]. The main effect of Vaginorm-S, according to researchers, is a direct decrease in the pH of the vaginal environment. As a result of acidification of the environment, there is a pronounced suppression of the growth of anaerobic bacteria and at the same time the restoration of the normal lactobacillary microflora of the vagina, for which an acidic environment is optimal. The advantage of Vaginorm-S is that the tablet dissolves gradually. This ensures a prolonged effect of the drug throughout the day and prevents irritation of the vaginal epithelium.
Vaginorm-S can be successfully used for a long time, which is very important during pregnancy, as well as in patients with constantly unstable vaginal flora, that is, prone to recurrent BV. In such cases, it is impossible to constantly use antibiotics or other drugs that have a large number of contraindications and complications. Vaginorm-S can be recommended as a well-tolerated, effective treatment that has no contraindications to long-term therapy. It may become the drug of choice, especially for prophylactic treatment in order to prevent another relapse of BV.
If the effectiveness of treatment for BV is assessed by the eradication of pathogenic flora, then the duration of maintaining the positive effect of treatment depends on the restoration of the lactobacilli flora of the vagina, as well as its quality (the ability to produce peroxidase and bactericidal substances). It has been proven that women with unstable and functionally defective lactobacilli are more likely to experience relapses of BV. Sometimes, after treatment, microorganisms are found that are similar to lactobacilli, but do not have the protective properties characteristic of lactobacilli. In these cases, repeated courses of therapy are carried out. At the same time, selecting a drug causes certain difficulties, since not all existing drugs are well tolerated by patients. The use of Vaginorm-S makes it possible to achieve high adherence of patients to treatment, since when using the drug, lactobacilli grow, capable of producing peroxidase and bactericidal substances, which significantly reduces the frequency of relapses of BV. In addition, the drug was well tolerated, and the incidence of side effects was comparable to placebo.
It should be borne in mind that Vaginorm-S is not indicated for the treatment of candidiasis, since ascorbic acid, unlike lactic acid, is not an antiseptic. It is known that fungi are able to reproduce at any pH level. Treatment of BV by any method (including using Vaginorm-S) can lead to the manifestation of candidiasis. It is no secret that women with BV often experience colonization with Candida albicans, which is often asymptomatic, which is associated with the release of a large number of anaerobic factors by the unwanted bacterial flora during BV, which inhibit the growth of the fungus. After treatment, the number of anaerobic factors decreases, which leads to the activation of candidiasis.
Unfortunately, there are no evidence-based randomized controlled studies of the effectiveness of ascorbic acid in IVM. This is why we are faced with conflicting opinions: some authors believe that ascorbic acid preparations can be used in the treatment and prevention of candidiasis, others argue that they cannot. Where is the truth?
The choice of therapy in each specific case depends on the severity and duration of BV, the patient’s adherence to treatment, as well as on medical history, primarily the presence of relevant risk factors. We emphasize: disturbed vaginal flora, especially BV, is a risk factor for the development of various infectious complications both during pregnancy and during childbirth, the postpartum period or during surgical interventions. That is why the fact of disturbed vaginal flora in this contingent of patients should be treated with maximum caution and, if detected, treated. In addition to the oxidation effect, vitamin C supposedly has a complex positive effect on the cervix, vaginal mucosa and, in particular, on the membranes of the fertilized egg. However, this hypothesis requires proof and, accordingly, additional research.
G. Miniello
(2007) [10] proposed using a combination of vitamin C and silver citrate in the form of a vaginal cream to prevent relapses of BV after standard treatment. Silver ions have an antibacterial and antifungal effect: by binding to bacterial and fungal proteins, they have a destructive effect on the cell membrane of a microbial or fungal cell, and can also penetrate into the cells of microorganisms, disrupting DNA synthesis or leading to its denaturation. Denaturation of RNA by silver contributes to disruption of the synthesis of certain proteins of pathogenic bacteria. G. Miniello hopes that his proposed modification for the prevention of BV will be quite effective. Evidence-based research is required to confirm this assumption.
In Italy, women are offered solutions of phytoextracts containing lactic acid as intimate hygiene products. For example, NormoVagin P (Pharma, Italy) contains extracts of chamomile, calendula, witch hazel, echinacea, mallow, essential melaleuca oil, lactic acid, polysorbate 20, benzyl alcohol and a number of other ingredients. This product is recommended for intravaginal hygienic use for the intimate toilet, as well as for the prevention of various infections, and in some cases, to maintain normal vaginal microecology after treatment of infections. Thus, the acidic environment of the vagina is important from a pathogenetic point of view and an absolutely necessary factor for maintaining local homeostasis of the vaginal biotope. That is why the use of acid-containing drugs as part of complex therapy for bacterial vaginosis is an effective, safe and inexpensive method of treating the disease, which is confirmed by the results of numerous studies.