What is an umbilical cord remnant and when does it fall off?
While the baby was in the womb, he received nutrients and oxygen through the umbilical cord. When the baby is born, the umbilical cord is clamped and cut. It is not painful because there are no nerve endings in the umbilical cord.
The clip (or "clothespin") usually remains for one to two days. It can be removed as soon as the remaining umbilical cord dries and stops bleeding.
After the clamp is removed, there will be a remnant of the umbilical cord on the baby's belly, which will gradually dry out, harden and turn from yellow to brown-black.
The remaining umbilical cord usually falls off on its own within a few weeks of the baby's birth. If this does not happen within three weeks of birth, contact your pediatrician.
In some cases, there is a reason why the umbilical cord remnant does not fall off, such as an infection or an immune system disorder. A doctor can determine the exact cause.
When the residue falls off, a wound forms. It may become slightly wet due to the fluids released. Keep your newborn's belly button dry and clean and it will heal completely in no time. If the umbilical cord has not healed within two weeks after the remainder of the belly button falls off, contact your pediatrician.
Adjustment methods
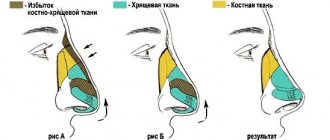
Typically, an unsightly belly button is treated by a plastic surgeon. Of course, surgical correction of the defect is not necessary, but is carried out only at the request of the patient. However, in some situations, doctors strongly recommend surgery as soon as possible. Such special cases include a rupture of the skin, the presence of a hernia, severe protrusion of the scar, inflammation of the skin, or unsuccessful liposuction. Surgery performed on the site of a natural scar is called umbilicoplasty.
How to care for the remaining umbilical cord and umbilical wound
The main thing is to keep the navel area dry and clean. Clean the belly button when changing a diaper or bathing your baby.
Here are some tips worth heeding:
- Keep the remaining umbilical cord dry and clean. Now experts recommend the “dry method” - the remainder of the umbilical cord is in contact with air, it should not be wetted or ointments should be used. You may have heard of a treatment option where the remainder of the umbilical cord is wiped with alcohol, but with the modern approach, the best way is to wait until the remainder falls off naturally. If you have questions, consult your pediatrician.
- Avoid irritation. Try to make sure that the diaper does not come into contact with the remaining umbilical cord. You can fold the diaper waistband or use a disposable diaper with a navel cutout, such as Pampers Premium Care.
- Watch for signs of infection. Transparent discharge, drops of blood and crusts during the healing process of the navel are not a cause for concern. But if you notice any signs of inflammation or your child has a fever, contact your doctor.
- Don't try to tear off the rest. The umbilical remnant should fall off on its own. Don't try to tear it off, be patient.
- Watch for signs of bleeding. When the umbilical stump falls off, you may notice a few drops of blood, and this is completely normal. If there is more blood, contact your pediatrician.
- Do not place a coin on your belly button or cover it with a band-aid. You may come across the opposite advice for preventing an umbilical hernia, but you don’t need to follow it - it can harm the child. If you are concerned about the shape of your belly button or suspect that your baby has an umbilical hernia, consult your pediatrician.
Diagnostics
In newborns and young children, the cause of navel deformity is determined by a neonatologist or pediatrician. Adult patients are most often examined by a surgeon. During the survey, the specialist finds out when the shape of the navel changed, what symptoms accompanied it, and how quickly it developed. During the examination, the doctor assesses the general condition of the patient and the appearance of the abdomen, performs palpation and percussion. Based on the results of a physical examination, the patient may be prescribed the following procedures:
- Sonography
. Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity for an umbilical hernia is used to determine the contents of the hernial sac, intestinal patency, and the severity of the adhesive process. In children with omphalitis, it makes it possible to exclude complications. In case of ascites, it allows you to assess the size of parenchymal organs and exclude tumor lesions of the peritoneum. Can be supplemented with Doppler ultrasound to study blood flow in the portal system. - Other visualization techniques
. In patients with umbilical hernias, contrast radiography of the stomach and small intestine is informative; in patients with omphalitis, plain radiography of the abdominal cavity is informative. To clarify the cause of ascites, CT scan of the abdominal cavity, laparocentesis with fluid sampling, and diagnostic laparoscopy are performed. - Lab tests
. Examination for ascites involves performing liver tests, immunoglobulin testing, general urine analysis, and cytological examination of ascitic fluid. Children with omphalitis undergo a microbiological analysis of the discharge to determine the pathogen.
Pregnant patients are advised to undergo routine ultrasound and laboratory tests in a timely manner. If a pathological course of gestation is suspected, an unscheduled examination is recommended.
Correction of the navel shape
Bathing the baby during the healing period of the navel
Until the rest of the umbilical cord falls off and the wound heals, it is better not to bathe the baby, but to wipe him with a damp sponge or cloth two to three times a week. At the same time, you can cleanse the navel area.
To wash your baby this way, you will need:
- bowl of warm water
- cloth napkin or small towel
- baby soap
- cotton ball moistened with water
- towel
- clean diaper
- change of clothes
Place your baby on a soft, flat surface: a mattress on a changing table or a towel spread on the floor. All items on the list should be at your fingertips. Never leave your baby unattended during water procedures if he is on a high surface - for example, on a changing table. Fasten it with a seat belt and additionally hold it with one hand.
Wrap your baby in a towel, exposing only those parts of the body that you are wiping. This will keep him warm and comfortable. Wipe your face first, without using soap to avoid getting it in your eyes. Then add soap to a bowl of water and begin to wipe the rest of the body, paying attention to the folds on the neck, behind the ears, and in the genital area.
When treating your newborn's belly button, follow the tips listed above. The area around the navel can be wiped with a cotton ball soaked in water, but do not wet the remainder of the umbilical cord itself.
As soon as the remainder of the umbilical cord falls off, you can bathe the baby in the children's bathtub or sink.
Treatment
Conservative therapy
Infants with an amniotic navel undergo daily dressings with aerosols that create a protective film on the surface of the wound. Small dermoid and sebaceous cysts should be monitored regularly. In children of a younger age group, umbilical hernias can regress on their own, so patients under 5 years of age are observed, exercise therapy, abdominal massage are prescribed, and an adhesive bandage is applied to the navel.
For ascites, the underlying pathology is treated. To reduce the amount of effusion, a salt-free diet, limiting the amount of fluid, and diuretics are recommended. Correction of water-salt metabolism disorders. Hepatoprotectors are used, ACE inhibitors are used to reduce pressure in the portal vein system. Albumin and plasma infusions are performed.
Surgery
Intervention is necessary for all infants with omphalocele. Most children undergo surgery in the first days of life. The option for eliminating the defect is chosen taking into account the volume of the protrusion. In mild cases, the internal organs are immediately immersed in the abdominal cavity, and the abdominal wall is sutured. For large hernias, the organs are protected with a silicone bag and then gradually moved into the abdominal cavity. In the presence of other severe developmental anomalies, children are managed conservatively until a massive ventral hernia is formed, which is subsequently also sutured.
For patients with sebaceous and dermoid cysts, excision of the cyst is recommended when the formation grows. When cysts become infected or abscesses form in patients with omphalitis, opening and drainage of abscesses are indicated. Uncomplicated umbilical hernias are operated on as planned. Hernioplasty is performed using local tissue or mesh prostheses. If a hernia is strangulated, emergency surgery is required - dissection of the strangulating ring, sometimes bowel resection.
If conservative measures are ineffective, patients with ascites undergo laparocentesis or a peritoneal catheter is installed. Otherwise, the tactics of surgical treatment of ascites depend on the nature of the underlying pathology. Portacaval shunting, reduction of the splenic duct, splenectomy, formation of a lymphovenous anastomosis, and removal of the peritoneum are possible.
Changing diapers while the navel is healing
In our separate article you will learn how to change your baby's diaper. In the first weeks, be especially careful not to touch or wet the remaining umbilical cord when changing your baby's diaper.
If the remaining umbilical cord has not yet fallen off, fold the diaper over your baby's tummy or use diapers with a belly button cutout to prevent friction and urine from getting into the belly button area.
Follow the care instructions described above. We remind you: while changing the diaper, you can also gently wipe the skin around the navel with a cotton ball soaked in water.
What should the belly button be like?
© kamontad123 / Getty Images
According to scientists from the University of Helsinki
, who showed photographs of navels to men and women, small, vertical navels in the shape of the letter T were considered the most beautiful. Such a navel can make its owner more attractive in the eyes of the opposite sex.
Four incredible facts about the human body
In addition, Finnish researcher Aki Sinkkonen
(Aki Sinkkonen), believes that a woman's navel can reveal information about a woman's reproductive potential, including the risk of certain genetic and maternally inherited congenital anomalies.
Possible problems
When it comes to the belly button and umbilical cord, there are two conditions that occur in babies. Contact your pediatrician if you notice any of these signs in your child:
- Fungus of the navel (granuloma).
After the remaining umbilical cord falls off, you may notice a reddish, moist nodule that may become enlarged and leak a little fluid. In some cases it will disappear in about a week, but if not, contact your pediatrician
- Umbilical hernia.
If your baby's belly button sticks out when he cries, it may be an umbilical hernia. An umbilical hernia is a small hole in the abdominal wall through which tissue protrudes when there is pressure, such as when a baby cries. An umbilical hernia usually heals by the age of –18 months.
Why does navel deformity occur?
Congenital defects in newborns
Congenital anomalies accompanied by deformation of the umbilical zone are detected immediately after birth.
In babies with a cutaneous umbilicus, the skin of the abdominal wall extends onto the adjacent portion of the umbilical cord. As a result, a noticeable bulge forms after the umbilical cord falls off. As the child grows, the bulge sometimes retracts and the appearance of the navel returns to normal. But in some patients, a bulging navel persists throughout their lives. Less common is a defect in which the umbilical area is covered not by skin, but by the amniotic membrane, which passes to the anterior abdominal wall from the umbilical cord (amniotic navel). In this case, the falling off of the umbilical cord is accompanied by the formation of a superficial wound. The deformation is temporary - subsequently the wound is gradually covered with unchanged skin, there are no scars.
During healing, epidermal cells may penetrate into the depths of the umbilical wound, which entails the formation of dermoid or sebaceous cysts that deform the navel. Subsequently, such cysts may increase in size, which aggravates the deformity. Another reason for the violation of the shape of the navel is suppuration of the cyst, which results in the formation of a rough scar.
In infants, complete and incomplete umbilical fistulas can also be detected. With complete fistulas, the intestine or the unclosed urinary duct is connected to the external environment through the navel; a wound with a wide opening is visible in the navel area, through which urine or intestinal contents are released. In case of incomplete fistulas, the navel defect is practically not expressed, and there is weeping and irritation of the skin.
Omphalitis
Infection of the umbilical wound leads to the development of inflammation of the skin and surrounding subcutaneous fat. The navel protrudes, the skin turns red and swells. Pus is released from the wound. There is a deterioration in the general condition, hyperthermia, crying, appetite disturbances, and regurgitation. Red stripes may appear on the abdomen, indicating lymphangitis. In weakened children, tissue necrosis is possible. As a result of omphalitis, scars form. The severity of navel deformation depends on the severity and extent of the inflammatory process.
Umbilical hernia
The exit of internal organs through the umbilical ring is more common in children in the first years of life, but can also develop in adults. A severe variant of the pathology diagnosed in fetuses and newborns is an embryonic umbilical hernia (omphalocele), a condition in which organs protrude due to underdevelopment of the abdominal wall. This defect is often combined with other severe developmental anomalies; a favorable outcome is rarely observed.
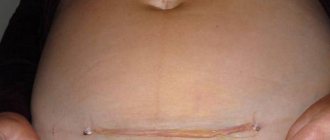
Acquired umbilical hernia in children has a more favorable course. The main symptom is a deformed navel. A protrusion is detected in the umbilical zone, which increases with straining, coughing and crying, and decreases when the child lies on his back. At the initial stage, a small spherical bulge appears in the area of the umbilical ring, which can be easily reduced when pressed.
Then the diameter of the formation gradually increases to 1-5 cm. In adults, the size of the formation can reach 10-15 cm or more. With a prolonged course, the hernia ceases to be reduced due to the formation of adhesions. Formations with wide hernial orifices are asymptomatic. With a narrow hernial orifice, patients are bothered by pain, nausea, and constipation caused by compression of the intestine.
Navel deformity in pregnant women
Pregnancy
Navel protrusion can be detected in the second half of pregnancy. The deformity is a physiological condition, caused by rapid enlargement of the abdomen, and disappears after childbirth. Predisposing factors that cause an early, very noticeable change in the appearance of the navel are the presence of several fetuses, polyhydramnios, and a rapid increase in a woman’s body weight.
Increased intra-abdominal pressure
Due to the increasing load on the abdominal wall from the inside, an increase in intra-abdominal pressure is accompanied by protrusion of the navel of varying degrees of severity. With flatulence, the navel becomes slightly more convex than usual, the deformation is short-term, disappears after the gases pass.
The most serious cause of navel protrusion due to increased internal pressure is ascites. The abdomen increases in volume, hangs downward when standing, and spreads out to the sides when lying down. The degree of deformation of the navel correlates with the amount of fluid in the abdominal cavity - the more fluid, the stronger the bulge. Ascites can be observed with portal vein thrombosis, portal hypertension, and peritoneal carcinomatosis. In chronic renal failure it is combined with anasarca. For rheumatic diseases it is supplemented with hydrothorax and arthralgia.
Other reasons
Other possible causes of navel deformation are scars resulting from surgical operations on the abdominal organs, injuries to the anterior abdominal wall, and local infectious processes. Sometimes the aesthetic characteristics of a given anatomical area deteriorate when tissue sagging after pregnancy or sudden weight loss.
Contraindications
The following disorders may be contraindications for umbilicoplasty:
- Malignant tumors.
- Diabetes.
- Acute and chronic diseases in the acute stage.
- Blood clotting disorder.
- Infectious diseases.
Complications that may occur after navel surgery include:
- Formation of a seroma (an abnormal accumulation of serous fluid) or hematoma.
- Suture infection.
The aesthetic effect after surgery is lasting. People often turn to umbilicoplasty because of an umbilical hernia or after a sudden weight gain. Navel piercing can also cause serious complications - purulent inflammation, scars, which will lead to repeated plastic surgery on the navel.