The most common dermatological diseases include lichen - an infectious lesion of skin areas caused by the action of microscopic fungi or viruses. The danger of lichen is that it is easily transmitted by contact from person to person or from sick animal to person and has several varieties that require a special approach to treatment.
What kind of lichen occurs, what type of therapy is more effective in each specific case, how to avoid complications - this will be discussed further.
Pathogens and carriers of lichen
The content of the article
Dermatologists distinguish several types of lichen, caused by different pathogens.
Most often, the appearance of lichen on human skin is initiated by fungi:
- zooanthropophilic - transmitted to humans from an infected animal, including from pets;
- anthropophilic - live only on human skin;
- geophilic - live in the soil and come into contact with human skin upon contact with the ground.
In addition to fungi, viruses are often the causative agent of lichen. Their cunning lies in the fact that they can live asymptomatically in the human body for a number of years and become more active when the immune system is weakened. This is exactly how, for example, those familiar to many with herpes or shingles behave.
Measures to prevent the disease
Since there can be many causes of lichen infection, it is impossible to completely exclude the possibility of the disease. However, compliance with preventive measures will reduce the risks. Prevention of lichen includes:
- timely treatment of acute respiratory diseases;
- compliance with hygiene procedures;
- taking a vitamin complex;
- increasing the level of immunity;
- use of shampoos with antifungal gels;
- hardening of the body;
- providing quality oral care, treatment of caries, gums and throat diseases;
- proper nutrition;
- avoiding contact with people infected with the fungus;
- vaccination of pets and periodic examinations at a veterinary clinic;
- giving up bad habits (smoking, alcoholism);
- preventing hypothermia of the body.
When diagnosing a chronic form of lichen, it is recommended to periodically visit a dermatologist’s office in order to identify possible foci of the disease.
Types of lichen
In order to cure lichen, it is not enough to make a general diagnosis. It is equally important to promptly determine the type of lichen, since each is characterized by its own symptoms and requires its own treatment.
Dermatologists distinguish the following types of lichen:
- shearer;
- encircling;
- pityriasis;
- pink;
- red flat;
- tubular;
- solar;
- scaly.
Only a competent dermatologist can draw a line between them and correctly prescribe a set of therapeutic measures. Therefore, under no circumstances should you self-medicate. The surest way is to go to the clinic at the first sign of deprivation.
Now about what changes in the skin should alert a person.
What consequences can lichen cause?
The most common and harmless type of lichen is pink. The course of the disease passes without complications.
Shingles can cause the following complications:
- inflammatory process in the membrane of the spinal cord and brain;
- partial or complete loss of vision;
- dysfunction of the musculoskeletal system;
- viruses that infect the respiratory organs and liver;
- postherpetic neuralgia.
Ringworm and versicolor often provoke the appearance of a secondary infection, which complicates the treatment process. In most cases, antibiotics are necessary. In addition, trichophytosis often leaves bald patches at the site of the fungal infection, which can remain forever.
A flat red fungus contributes to the manifestation of bacterial infections and the development of an inflammatory process in the patient’s oral cavity.
More often than others, the following categories of patients suffer from various types of lichen:
- pregnant and lactating women;
- people who do not care about their health and do not observe personal hygiene rules;
- children;
- pet owners;
- people with a low level of protective properties of the body.
Ringworm
The source of trichophytosis - this is the second name for ringworm - can be any of the fungi that primarily affects the hairy parts of the body (head and beard), neck, shoulders, face. The symptoms of this type of lichen are usually as follows: first, swollen pink or red spots with clearly defined edges appear, then the edges of the spots become covered with bursting blisters and an itchy crust, and finally, the center of the spot begins to peel off, and the hair in the affected area breaks off and thins.
Ringworm is diagnosed using a Wood's lamp. If the disease is confirmed, the patient - children often suffer from ringworm - is protected from contact with others and is prescribed complex therapy, including taking special tablets (for example, Terbinafine) and the use of antifungal ointments. In particularly difficult cases, it is possible to take hormone-containing agents that help stop the inflammatory process on the skin.
Symptoms
Each type of fungus manifests itself differently on the skin.
The girdling appearance is characterized by the following features:
- a feeling of numbness in the affected area;
- lymph nodes increase in size;
- painful sensations in muscles and joints;
- swelling of the affected area of the skin;
- formation of small bubbles;
- burning and soreness of the skin.
The name of the species of lichen is directly related to its appearance. The disease seems to surround the body. As a rule, the lesion is located on the head, in the chest or abdomen in the direction from the chest to the spine.
Shingles begins its manifestation with the formation of small blisters with liquid on the skin. After a few days, the color of the bubbles becomes more cloudy and they “dry out.” A dry crust forms at the site of the lesion, which gradually peels off. After it disappears, the area of the skin becomes covered with pigment. There is a high risk of bubbles reappearing. The period during which the patient can infect other people is 2 weeks.
Pityriasis manifests itself as follows:
- a bright pink spot with a diameter of about 5 cm appears at the site of the lesion;
- within 2 weeks the skin peels off.
Most often, this fungus is located in the abdomen, back and upper torso. Small lesions may merge into one large area as they spread.
Symptoms of pityriasis versicolor are severe itching, peeling and burning sensation, and the formation of light pink spots on the skin. Without treatment, the duration of this type of disease can be several years. Pityriasis usually occurs in the area of the shoulders, neck and back, much less often on the lower extremities, head and genital area.
Lichen planus is a dark burgundy-colored swelling or bump on the skin. This place is very itchy. The patient's legs, torso and genitals are mainly affected. Also, the fungus can cover the nail plates, feet, palms and mouth. In this case, the fungus appears as whitish spots. The nail subsequently splits.
Trichophytosis affects large areas of the skin. Mainly found on the scalp. It is characterized by unpleasant itching and pink spots that do not have clear boundaries. The spots may become covered with small cloudy blisters or a flaky crust. The infection period can last from 5 to 7 days.
Herpes zoster
It is caused by a virus that remains “dormant” in the human body for the time being. It appears in the form of fluid-filled blisters, usually located in the intercostal part of the body. Associated symptoms of herpes zoster: pain (caused by damage to the intercostal nerve endings) and itching of the skin in the affected area; sometimes fever with chills, headaches.
Treatment of herpes zoster is complex. Since the blisters of shingles burst, they are initially treated with brilliant green. And to lubricate the crust that forms in their place, use dermatol ointment. In parallel, the doctor may prescribe antipyretic, painkillers and antiviral drugs, quartz and laser therapy.
Complications and consequences in adults, children, pregnant women
Ringworm in an advanced form, or if the patient ignores treatment, is dangerous for the development of many complications:
| In adults | In children | In pregnant women |
| Attachment of a secondary infection in the presence of open wounds from scratching the rash. | ||
| Transition of the disease into a chronic form with regular exacerbations. | ||
| Formation of scars and welts at the site of the rash. | ||
| Hair loss. In case of damage to the scalp of the epidermis. | ||
| Weakening of the immune system. | ||
| Damage to nerve endings. | ||
| Disruption of the activity of internal organs and systems when infection penetrates the circulatory system. | ||
| Deterioration of vision and hearing in the presence of rashes in the eyes and ears. | ||
| Deterioration of the skin condition. | When hair falls out, bald spots may not be covered with new “vegetation.” | Impaired fetal development when infection enters the circulatory system. |
| Spontaneous urination (if the bladder or nerve endings are damaged). | Risk of miscarriage or premature birth. | |
| Developmental delay due to infection of brain cells. | ||
In pregnant women and children, the body is in a weakened state, so it is more susceptible to infection with lichen and the development of complications. Additionally, this category is characterized by restrictions in the choice of medications due to side effects.
Pityriasis versicolor
It is also called multi-colored, because the small pink - and sometimes greenish - rash that appears on the back, stomach, shoulders, and chest changes color and turns brown as the disease develops. Moreover, on tanned skin (in summer) these spots appear discolored, but on white skin (in winter), on the contrary, they look quite dark.
Diagnosis of pityriasis versicolor can be carried out by a specialist who has resorted to microscopic examination of the dermis, Balzer iodine test, and Wood's lamp. He will also prescribe a special drug treatment (with the help of Orungal, Mycozolon, etc.) that can kill the fungus that causes the disease.
With proper therapy, pityriasis versicolor can be eliminated quite quickly (although without treatment, the disease drags on for many years). Additionally, the patient is recommended to adjust their lifestyle (a concomitant cause of this type of lichen may be increased humidity or air temperature), and carry out a complete treatment of clothing and linen.
Complex of drugs
To eliminate lichen, complex treatment is required with medications taken externally and orally. And also with diet and physical therapy. The type of therapy depends on the causative agent of the lichen.
Overview of prescribed funds:
| Release form | Category | Name of medicines |
| Pills | Antihistamines |
|
| Painkillers |
| |
| Immuno-strengthening |
| |
| Vitamin complexes |
| |
| Antibiotics |
| |
| Antiviral |
| |
| Antifungal |
| |
| Ointments | Painkillers and anti-inflammatory |
|
| Hormonal |
| |
| Antibacterial |
| |
| Antifungal |
| |
| Antihistamines and antipruritics |
|
Independent choice of medications or their replacement is unacceptable.
Lichen rosea (or Zhibera)
A little-studied type of disease that usually develops against the background of a weakened immune system in the autumn or spring season. The risk group in this case consists of girls who have a hormonal imbalance in their body.
The manifestation of lichen is the appearance of round or oval pink and light brown spots on the chest, shoulders, back, sides, and skin folds. Dermatological changes, accompanied by itching and flaking of the skin, may go away on their own within a few weeks, however, when the first signs of the disease appear, it is recommended to consult a doctor to rule out the presence of syphilis similar in symptoms.
Causes of pityriasis
Despite the fact that Gibert's disease is very common, the mechanism of the disease is not fully understood. The following factors are believed to play an initial role:
- Exposure to viruses (type 7 herpesvirus, etc.), bacteria and other infectious agents. This is confirmed by tests that prove the presence of pathogens in the body. Very often, skin disease appears against the background of influenza, acute respiratory infections and other infections.
- Attachment of allergic reactions.
- Bites from bedbugs, lice and other blood-sucking insects.
- Reduced immune defense.
- Frequent hypothermia and stress.
- Violation of gastrointestinal functions and metabolism.
- Introduction of vaccines.
Lichen ruber planus
Flat multi-colored (from pale pink to purple) nodules of lichen red often appear on the mucous membranes, nails (they crumble), and delicate skin of the chest and abdomen. Their appearance is accompanied by severe itching, which, as a result of scratching, leads to the rapid growth of foci of skin damage.
Dermatologists find it difficult to determine the cause of the appearance of lichen red, but note that it is quite common in patients with diabetes, as well as those suffering from diseases of the stomach, liver, and biliary tract. Moreover, women over 40 years of age are primarily at risk.
What is pityriasis rosea and why is it called pink dandruff?
The content of the article
Pink dandruff (Pityriasis rosea - PR) is an acute inflammatory disease of unknown etiology, characterized by the appearance of skin rashes mainly on the torso and limbs. It is an erythematous, scaly disease. The disease occurs seasonally. The etiology is most likely viral. The most likely factor is herpes virus type 7 (HHV7).
Most cases (75%) involve people aged 10 to 35 years, although there have been reports of cases diagnosed in a 3-month-old infant and in an 83-year-old man. The disease occurs throughout the world without any particular racial predilection.
Pityriasis rosea is a disease for which patients visit a dermatologist with a frequency of up to 2% of all visits per year. Occurs mainly in spring and autumn; in summer the level of symptoms decreases significantly.
The disease affects more women than men in a 2:1 ratio. The duration of the disease is 6 to 8 weeks, but is highly variable.
Tinea tubularis
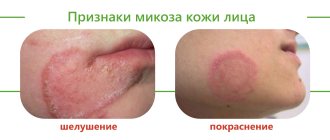
Malasezzia is the name of the fungus that causes tubular lichen. This fungus can live in the human sebaceous glands for a long time without revealing itself in any way. Under certain conditions: for example, a decrease in immunity or an imbalance in the acid balance of the skin, severe hypothermia or excessive sweating, endocrine disorders or the development of certain chronic diseases - it begins to multiply intensively.
As a result, small flaky spots appear on the skin, which gradually grow and merge into one large spot. And although the victim practically does not feel itching or pain, he should not postpone a visit to the doctor.
After diagnosing the disease (methods used - scraping test, iodine test, use of a Wood's lamp, etc.), the dermatologist prescribes local or complex antifungal drugs.
Sources
- Anderson KR: Treatment with dapsone in pityriasis versicolor vesicularis rosea, 1971;
- Andrews GK: Skin Diseases 1954;
- AranjoT. et al.: Human Herpesviruses 6 and 7, 2002;
- Bernhardt R.: Skin diseases: 1922;
- Bjornberg A, Hellgren L: Pityriasis rosea. Statistical, clinical and laboratory research, 1962;
- Buckley K: Rash resembling pityriasis rosea in a patient receiving omeprazole, 1996;
- Gutowski W.: Attempt to treat Gibert's pink dandruff with bismuth and penicillin, 1950;
- Kempf W. et al.: Pityriasis rosea is not associated with human herpes virus, 1999;
- Parson JM et al: Update on pityriasis rosea, 1986;
- Sharma PK, Yadav TP: Erythromycin for pityriasis rosea, 2000;
- Wass I.: Treatment of pityriasis rosea with nonspecific substances, 1948.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
Ringworm solar
Under the influence of sunlight, excessive sweating, abuse of solariums and antibacterial agents, uneven, flaky dark spots may appear on the skin. Their occurrence is provoked by a fungus that multiplies on the dermis as a result of a violation of its acidity. Gradually, the spots grow to significant sizes, which causes aesthetic discomfort to a person: they clearly stand out against the tan. And although solar lichen is rarely accompanied by itching and pain, it requires mandatory therapy.
As a rule, solar lichen is diagnosed quickly: it is often enough to conduct an iodine test or use a Wood's lamp. At the initial stage of the disease, local antimicrobial drugs help well; in cases where the disease is advanced, the doctor prescribes complex therapy.
Treatment of pityriasis
When a patient is diagnosed with Gibert's disease, the dermatologist develops an individual treatment regimen to avoid dangerous complications. There is an opinion that pityriasis rosea will go away on its own in a few weeks. As a result, complications arise, and the patient comes to the dermatologist with an advanced form of the disease.
Drug treatment includes the following medications:
- antihistamines that relieve the patient from itching, swelling and redness on the body
- corticosteroid, desensitizing and antipruritic ointments. Medicinal compositions containing betamethasone, hydrocortisone, etc. are applied to the affected skin and lightly rubbed in. The medications eliminate rashes, get rid of peeling, and effectively restore the skin.
- drying agents containing zinc to accelerate skin healing
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics are indicated in cases where a bacterial infection is associated with pityriasis rosea. It is unacceptable to start taking antibacterial drugs on your own, since they are selected individually, taking into account laboratory tests.
- antifungal medications: drugs containing clotrimazole and other active substances are prescribed topically in the form of gels and ointments
- antiviral drugs containing acyclovir and other active components. Dermatological tests have confirmed that if antiviral drugs are prescribed in combination with antibiotics from the first days, the patient quickly recovers.
- neutral water-shaken preparations Dermatologists prescribe pharmacy talkers containing zinc oxide, menthol and anesthesin to patients with pityriasis rosea. These products relieve itching and pain in damaged areas and speed up recovery.
- iodine is an aggressive, but extremely effective remedy. Injured skin is treated with iodine in the morning and evening. Initially, the skin begins to peel off more actively, but then there are no extra scales left on it. Not all experts recommend that their patients cauterize damaged areas with iodine, since this drug can be harmful if used incorrectly.
Recommendations for patients
During the treatment period, the patient is recommended to adhere to the following recommendations:
- Follow a hypoallergenic diet: avoid nuts, citrus fruits, chocolates, honey, etc. Products containing artificial colors should be excluded from the menu. It is worth limiting the consumption of fried foods, carbonated drinks, fast food, strong alcohol and coffee.
- Limit water treatments within reasonable limits and give preference to the shower.
- Refuse to use aggressive hygiene and cosmetic products for the body. Gels and other detergents should not dry out the skin.
- Give preference to underwear made from natural fabrics.
- Moderate sunbathing - ultraviolet light helps the skin recover faster.
- Follow the recommendations of a dermatologist, apply to the skin only products recommended by a specialist.
- Folk remedies can be used only after consultation with your doctor.
Ringworm scaly
The causes and treatment of this lichen, better known as psoriasis, are not fully understood. However, it is noted that it appears more often in people suffering from diseases of the endocrine and nervous systems and prone to alcoholism.
Psoriasis is a chronic disease, often occurring latently, i.e. is hidden. First, small reddish spots appear on the skin - most often the bends of the legs and arms, lower back and buttocks, causing severe itching due to dryness. Gradually, the spots grow and turn into a lesion that affects a large area of the skin. The peculiarity of psoriasis is that when the plaque is removed, the lichen begins to bleed.
It is necessary to treat scaly lichen under the supervision of a doctor, who will select the necessary topical medications (when applying them, you must strictly follow the instructions), and, if necessary, prescribe antibiotics.
Features of treatment for children and pregnant women
The types of lichen in humans differ in chronic and acute forms. If the skin is affected by lichen during pregnancy or childhood, treatment is carried out with extreme caution.
Nuances of therapy:
- select medications strictly according to age parameters and approved for pregnant and lactating women;
- aggressive medications (antifungal tablets, antibiotics and hormonal) should be used only in extreme cases and in severe cases of the disease;
- If side effects are detected, the course of treatment is immediately interrupted. The product is replaced by a specialist;
- give preference to drugs for external use.
During pregnancy, it is important to have time to eliminate pathologies before birth. Otherwise, the infection may affect the unprotected skin of the newborn. Before using medications in children, consultation with a pediatrician is required to exclude contraindications.
Are all types of lichen contagious?
Many people believe that absolutely all types of lichen are dangerous to others. Meanwhile, this is not entirely true. So, with pink, ringworm or shingles, the patient will really need to be isolated. But, for example, pityriasis or scaly ones are not dangerous for others.
And this is another reason why any change in the skin should be the reason for going to a specialist - only he will be able to correctly determine the type of lichen, assess the degree of its danger, give recommendations for treatment, and finally select a set of medications and therapeutic measures aimed at including general strengthening of the body.
Diagnosis of pityriasis
If you find suspicious spots on the skin, you should promptly contact a dermatologist. During a visual examination, the doctor assesses the nature of the rashes, their shape, size, location on the body and is able to make the correct diagnosis. After dermatoscopy, the following studies are additionally carried out: biochemical tests of blood and urine, RMP (microprecipitation reactions with antigens), skin scrapings from injured areas.
A more complex diagnosis is carried out if the skin disease lasts more than six weeks. In these cases, discharge from the affected lesions is sent for bacterial culture. A biopsy and subsequent histological studies will help make the correct diagnosis. In order to distinguish Zhiber's disease from other types of lichen, toxicerma, psoriasis, complicated syphilis and other pathologies, fluorescent diagnostics are carried out, scrapings are checked for the presence of pathogenic fungi, RPR tests are done for syphilis, etc.
Forecast
If you follow all the recommendations prescribed by your dermatologist, the prognosis is favorable . To confirm the success of treatment, skin particles are scraped from the lesions and examined for the presence of fungal flora.
This procedure is carried out the next day after completion of the treatment cycle, after 7 days and for the last time - after 60 days, to confirm the absence of an infectious agent. Upon receipt of the first negative result for flora, the dose of the drug is adjusted (as a rule, the number of doses is reduced by 2 times).
Routes of infection
How can you get lichen?
The source of the infectious agent is hair, skin flakes or particles of nails of an infected person, which come into contact with healthy skin through household items (towels, bed linen, clothing, comb) or through direct contact.
Predisposing factors for active proliferation of fungi are:
- decreased immunity due to recent infectious, general somatic diseases, stress;
- increased body temperature;
- increased environmental humidity;
- skin injuries, which are the entrance gates of infection;
- endocrine diseases.