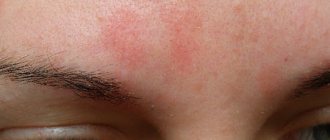
What does lichen look like?
As the disease progresses, rashes appear - most often they take the form of small red or brown-purple lumps (on the skin) - a characteristic sign is the shine of the affected areas.
- On the scalp, lichen planus may take the form of small itchy bumps.
- In the mouth - on the surface of the mucous membrane - it can appear as a reticular change in white color.
- On the nail plate, lichen can form cavities and yellowish grooves, and in extreme cases, lead to atrophy of the nail plate.
Lichen planus is an inflammatory disease. It is worth emphasizing that this is not an infectious disease.
Lichen planus
Lichen planus of the oral mucosa
Lichen planus - medicinal
Lichen planus hypertrophic form
General notes on therapy
- The choice of treatment method depends on the severity and localization of clinical manifestations, the form and duration of the disease, information about the effectiveness of previously administered therapy.
- Treatment is not required for damage to the oral mucosa that is limited to reticular rashes of a typical form, not accompanied by subjective sensations. In other cases, patients require therapy.
- During the period of exacerbation of the disease, patients are recommended to take a gentle regimen with limited physical and psycho-emotional stress. In the food regime, salted, smoked, fried foods should be limited. In patients with damage to the oral mucosa, it is necessary to exclude irritating and rough foods.
treatment goals
- regression of rashes;
- improving the quality of life of patients.
indications for hospitalization
- ineffectiveness of outpatient treatment;
- widespread and severe lesions of the skin and mucous membranes, including hyperkeratotic, bullous, erosive and ulcerative.
External therapy
In the presence of limited rashes, treatment begins with the prescription of topical glucocorticosteroid drugs of medium and high activity (possibly alternating them):
- betamethasone, cream, ointment 2 times a day externally to the lesions for 12 weeks, or
- clobetasol, cream, ointment 2 times a day externally to the lesions for 4-8 weeks, or
- fluocinolone acetonide, cream, gel, ointment 2 times a day externally to the lesions for 4-8 weeks, or
- hydrocortisone-17 butyrate, cream, ointment 2 times a day externally to the lesions for 4-8 weeks, or
- triamcinolone ointment 2 times a day externally to the lesions for 4-8 weeks, or
- mometasone, cream, ointment, lotion 1-2 times a day externally to the lesions for 4-8 weeks, or
- betamethasone + salicylic acid, ointment 2 times a day externally to the affected areas for 4-8 weeks, or
- salicylic acid + flumethasone, ointment 2 times a day externally on the affected areas for 4-8 weeks.
Alternative Treatments
- tacrolimus ointment 2 times a day for 2 weeks
- calcipotriol ointment 2 times a day for 2 weeks
Systemic therapy
1. Systemic glucocorticosteroid drugs:
- prednisolone 20-30 mg per day orally for 1-2 months followed by gradual withdrawal or
- betamethasone 1 ml once every 2-3 weeks intramuscularly or intralesional, for a course of 3-4 injections.
2. In the treatment of patients with lichen planus, antimalarial drugs can be used, which are used as systemic therapy and can be prescribed with glucocorticosteroid drugs:
- Hydroxychloroquine 200 mg orally 2 times a day for 5 days, then a break of 2 days, treatment courses are repeated for 1-2 months or
- chloroquine 250 mg orally 2 times a day for 5 days, then break for 2 days, courses of treatment are repeated for 1-2 months.
3. To relieve itching, one of the antihistamines is prescribed
1st generation, which is used both orally and in injection forms:
- mebhydrolin 100 mg orally 2-3 times a day for 7-10 days or
- clemastine 1 mg orally or intramuscularly 2-3 times a day for 7-10 days.
Also, in order to reduce itching, an antipsychotic with non-blocking activity can be prescribed: hydroxyzine 25-100 mg per day orally for 28 days.
Alternative Treatments
- Metronidazole 500 mg 2 times a day for 10 days
Non-drug treatment
1. For minor infiltration of the lesions, narrow-band medium-wave phototherapy with a wavelength of 311 nm is prescribed 3-4 times a week for 6-12 weeks.
2. For patients with more pronounced infiltration in the lesions, PUVA therapy with oral or external use of a photosensitizer is indicated:
- PUVA therapy using oral photosensitizers: methoxsalen 0.6 mg per kg body weight or
- PUVA therapy with external use of photosensitizers: methoxalen 0.5-1 mg/l for a course of 8 to 23 procedures.
Treatment of lichen planus of the oral mucosa
1. First-line drugs for the treatment of patients with LP of the oral mucosa are topical glucocorticosteroid drugs:
- betamethasone, cream, ointment 2 times a day externally to the lesions for 8 weeks, or
- triamcinolone ointment 3 times a day externally to the lesions for 12 weeks, or
- fluocinolone acetonide, cream, gel, ointment 2 times a day externally to the lesions for 4-12 weeks, or
- clobetasol, cream, ointment 2 times a day externally to the lesions for 4-8 weeks.
2. In case of ineffectiveness of topical corticosteroid drugs, retinoids are prescribed for external use:
- isotretinoin gel 2 times a day externally to the lesions for 8 weeks.
3. Additionally, painkillers and wound healing agents are used:
- aloe vera leaves, liniment 2 times a day externally on the lesions;
- lidocaine + chamomile flower extract, gel: a strip 0.5 cm long is applied to painful or inflamed areas of the oral mucosa and rubbed in with light massaging movements 3 times a day;
- choline salicylate + cetalkonium chloride, dental gel 1 cm for adults and 0.5 cm for children, squeezed onto a clean finger and rubbed with light massaging movements into the affected area of the oral mucosa 2-3 times a day before or after meals and before bed.
4. In the case of severe lichen planus of the oral mucosa, resistant to therapy, systemic glucocorticosteroid drugs are used: prednisolone 0.5-1 mg per kg of body weight for 3 weeks.
For the treatment of children
topical glucocorticosteroid drugs are used.
Tactics in the absence of treatment effect
If the therapy is ineffective, patients may be prescribed acitretin or cyclosporine:
- acitretin 30 mg per day orally for 3-8 weeks or
- isotretinoin 0.5 mg/kg/day for 8 weeks
- cyclosporine 5 mg per kg body weight per day orally for 3-8 weeks.
Due to the possibility of developing undesirable effects during retinoid therapy (changes in the level of transaminases, hepatitis, hypertriglyceridemia, hypercholesterolemia, hyperglycemia, etc.), it is necessary to monitor the level of lipids, blood glucose, and liver function. Due to the teratogenic properties of retinoids, women of reproductive age should use reliable contraception 4 weeks before, during and for 2 years after the end of acitretin therapy. If pregnancy occurs, it should be terminated for medical reasons.
During treatment with cyclosporine, regular monitoring of plasma creatinine concentration is necessary - an increase may indicate a nephrotoxic effect of the drug and requires a dose reduction: by 25% if creatinine increases by more than 30% from the original and by 50% if its level doubles; When dose reduction within 4 weeks does not lead to a decrease in creatinine, cyclosporine is discontinued. It is recommended to monitor blood pressure, blood levels of potassium, uric acid, bilirubin, transaminases, and lipid profile. During the treatment period, immunization with live attenuated vaccines is contraindicated.
Lichen planus - causes
Although the reasons for the appearance of lichen on the skin or mucous membranes remain a mystery, this disease is often associated with autoimmune diseases. The immunological basis of the disease is indicated by the frequent coexistence of lichens with autoimmune diseases, that is, those in which cells of the immune system attack the body for unknown reasons, destroying “healthy” cells.
Lichen planus may appear in people diagnosed with diabetes, vitiligo, alopecia areata, certain liver diseases (including hepatitis and cirrhosis), and ulcerative enteritis (Crohn's disease). Likewise, lichen planus is more common in people who have had a transplant (especially graft-versus-host disease - GVHD) or are taking certain medications, such as penicillamine, methyldopt.
Causes of tinea versicolor
The content of the article
Ringworm affects middle-aged people. Medicine identifies the causes that lead to the appearance of this disease in humans. These include:
- Predisposition to fungal skin diseases.
- Disruptions in the course of physiological processes in the epidermis.
- Endocrine diseases.
- Lack of a good night's sleep.
- Lack of rest.
- Time zone change.
- Excessive hygiene, using antiseptics.
- Improper functioning of the human immune system.
- Frequent bathing in salt water.
- Lack or excess of vitamins.
- Wearing clothes made of synthetic materials.
- Improper functioning of the lymphatic drainage system.
- Long-term use of steroid hormones.
- Nervous system problems.
- Hormone imbalance.
- Lack of hygiene measures in public places.
Lichen planus - symptoms
Symptoms of the disease are well expressed:
- red or purple papules;
- skin lesions are usually shiny;
- formations that tend to stick together and appear in groups;
- whitish lines on the surface of the skin (the so-called Wickham grid);
- itchy skin.
Itchy skin
Symptoms of lichen planus usually appear suddenly - skin lesions during lichen planus are usually limited, the rash does not increase after the first symptoms appear.
Types of lichen planus
There are many varieties of lichen planus, including: lichen planus, pigmented, nodular, pemphigoid, linear, follicular, erosive.
The type of lichen can also be determined by the place of its appearance: lichen planus in the mouth, lichen on the nails, lichen of the perianal area, lichen on the genitals: in men, lichen planus is found on the foreskin and on the head, in women, lichen can be found on the genitals lips - and resemble leukoplakia.
Ringworm in humans
All types of lichen require treatment. Initially, competent diagnosis is required to select adequate therapy. Shingles on the body is of viral herpetic origin. Localization - intercostal area, along the location of the nerves. It may also appear in other places with the main nerve trunks. Most often it occurs on one side of the body in the form of a blistering rash with the formation of a crust later. The incubation period for lichen is on average 14 days, but the range can be from 11 to 21 days. If the form of the disease is ocular, without timely treatment you can lose your vision.
Ringworm in a child is most often diagnosed as ringworm. Trichophytosis and microsporia can affect the skin of the face, head, shoulders, and neck. The nature of occurrence is Microsporum and Trichophyton fungi. In most cases, ringworm on a child’s head develops of the ringworm type. There are ways of infection: through household contact, through contact with a sick person or animals.
Ringworm on the head appears in the form of pink spots with gradual rejection of hair in its growth zone, which causes bald spots to form. Over time, itching may begin, and until active manifestation it is asymptomatic.
Pityriasis rosea (erythematous squamous dermatosis, pityriasis or Gibert's disease) is viral in nature. The disease is provoked by herpetic virus type 6 or 7. Occurs most often in the autumn-spring period. It is typical that pityriasis rosea appears in the groin, as well as on the arms and legs. Plaques up to 20 mm in diameter. The center is yellowish brown or pink. When the mother (largest) spot disappears, cold symptoms are felt. Ringworm on the arm, as in other places, is accompanied by itching.
The pityriasis type of the disease is caused by the fungus Malassezia. The peak of the disease occurs in the summer. This cutaneous lichen is prone to recurrence. It is characterized by pigment spots of yellow, pink, brown, which merge over time. There is no inflammation, but there is characteristic peeling. Localization - throughout the body, except for the limbs and head. A typical picture is lichen on the back. Requires treatment, otherwise the disease may progress to a chronic stage.
The red flat appearance is quite rare. Lichen is localized in the mouth, on the mucous membranes, forearms, ankle and wrist joints. May destroy nail plates. In women, if there is a disease in the oral cavity, there is a high probability of damage to the external genital area. Lichen also appears on the chest. Itching can spread to the entire body. In men, lichen on the penis is concentrated in the area of the head.
The white (sunny) type of the disease is the least aggressive. The course of the disease can last for years. Ringworm is caused by yeast fungi. It often affects people under 30 years of age. Ringworm shows symptoms in the head and chest area. It has nothing to do with the sun, but is clearly visible on tanned skin. Ringworm on the arm can also appear. Psoriasis or the scaly form of the disease has a non-infectious nature of development. Refers to autoimmune pathologies. If left untreated, the risk of developing arthritis increases.