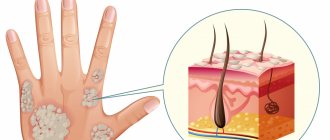
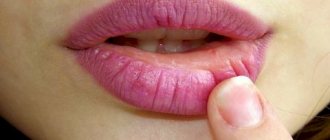
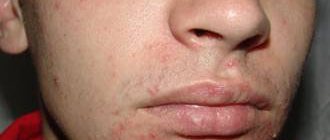
What is itchy skin like?
Itching of the skin can be of various types:
- Physiological and pathological itching. In the first case, the skin may itch due to some mechanical or chemical irritants, as well as insect bites. Pathological itching is a sign of a skin disease or other pathological condition, for example, neurological disorders or hormonal imbalance;
- Localized and generalized itching. Itching can be localized in a specific place, for example, under the hair on the head, in the genital area or anus, etc. As a rule, the symptom is paroxysmal in nature, often combined with other pathological manifestations of a particular disease. We are talking about generalized itching when literally the whole body itches. Often the symptom is associated with an allergic reaction or dry skin caused by dysfunction of the sebaceous glands;
- Constant and paroxysmal itching. With constant itching, the symptom persists throughout the day, its intensity may increase at a specific time of day, often in the evening. Paroxysmal itching appears independently or under the influence of certain irritating factors.
Peeling skin
Measles
Scarlet fever
Fungus
Syphilis
Allergy
23073 December 14
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Peeling of the skin: causes, diagnosis, what diseases it occurs with, methods of treatment.
Definition
Peeling of the skin occurs as a result of the death of cells (keratinocytes) of the stratum corneum of the epidermis. Normally, the process of rejection of keratinized epithelium occurs constantly, but the scales and their number are small enough to be visible to the naked eye. When the processes of keratinization and death of keratinocytes are disrupted, the number of scales increases significantly; they can fall off the skin in tiny particles or merge to form large plates.
Types of peeling skin
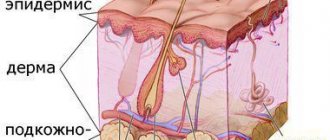
The skin consists of several layers, the structure and role of each of them provides it with a barrier function.
Disruption of physiological processes in the skin leads to increased keratinization processes and the appearance of an excessive number of dead cells.
The color of the flaky scales can vary from gray-white to dark gray. With hyperfunction of the sebaceous glands, the scales stick together into large and fatty-looking plates. With hypofunction, the scales resemble tiny dust.
The location of peeling may depend on the disease that caused it. Increased peeling is usually observed on the scalp, in the folds of skin behind the ears, between the fingers, and on the flexor and extension surfaces of the limbs.
Possible causes of peeling skin
Peeling skin can occur in any skin type, but dry skin is most susceptible to it. Loss of skin moisture can be caused by improper selection of cosmetics (especially a passion for peeling, as well as alcohol-containing cleansing lotions and tonics), prolonged exposure to the wind, sun, dry indoor air, constitutional characteristics and age-related changes (lack of female sex hormones).
Peeling of the skin occurs due to a deficiency of vitamins (vitamin A and group B) and microelements (for example, iron).
What diseases cause skin peeling?
Atopic dermatitis
. This disease is one of the common allergic pathologies caused by immune disorders. It manifests itself as itching and rashes on the skin in the form of pink plaques or blisters with their subsequent pigmentation and peeling. In young children, an erythematosquamous form of dermatitis with redness of the skin and peeling is observed; in children 2–13 years of age, thickening of the skin with folds and scaly plaques predominates; in adolescents and adults, dryness and peeling of the skin mainly on the face and upper torso.
Psoriasis
. Psoriasis is one of the autoimmune diseases. Hereditary predisposition, immune, endocrine disorders, environmental factors and the state of the human nervous system play a significant role in its development. The disease can be provoked by stress, infectious diseases, injuries, and medications. As a rule, psoriasis begins with the appearance of pink itchy plaques on the skin, which, merging, form spots of various shapes, covered with silvery-white scales.
Plaques are localized mainly on the scalp, the extensor surface of the elbow and knee joints, and on the lower back.
When the rash is scraped, small scales give the plaque the appearance of a greasy stain, and after removing the scales, the surface of the plaque may bleed. With exudative psoriasis, the scales, under the influence of the oozing contents of the plaques, form crusts and are difficult to tear off. It is possible to localize the rashes only in areas with oilier skin (on the scalp, in the nasolabial and behind-the-ear folds, in the chest area and between the shoulder blades). In such patients, the peeling border goes down below the hairline to the skin of the forehead. With an exacerbation of the disease, psoriatic erythroderma can develop, when the process spreads to almost the entire skin, leading to swelling, redness and peeling of the skin.
Severe psoriasis is accompanied by damage to the joints, including their deformation and limited mobility.
Seborrheic dermatitis
. The disease is characterized by excess or insufficient function of the sebaceous glands. With increased sebum secretion, the stratum corneum of the skin thickens, and it becomes oily and flaky. With insufficient production of sebaceous secretion, small scales or large dry plates are formed, which are easily separated from the skin. Seborrhea affects areas with a large number of sebaceous glands (scalp, forehead, nasolabial triangle, ear area). With seborrhea of the scalp, the hair thins and falls out.
Children's infectious diseases (measles, scarlet fever)
. The rashes that appear with measles gradually become pigmented, acquiring a brown color. Their surface is covered with small scales. With scarlet fever, the skin begins to peel off after the rash disappears, small scales may cover the face, and patches of skin on the palms and soles may come off in patches.
Demodicosis
.
The disease is caused by mites of the genus Demodex
, which can also be present in small quantities on healthy skin. They are found in hair follicles and sebaceous gland ducts on the face and scalp, as well as eyebrows and eyelashes. As the colony of mites grows, pinkish spots form on the skin around the hair follicles, covered with small or large scales. Papules (nodules) and pustules sometimes form, similar to acne. In advanced cases, the skin thickens and loses elasticity. Peeling, itching, oily skin and hair loss are characteristic symptoms of the disease.
Pityriasis versicolor (lichen versicolor)
. This type of keratomycosis is caused by yeast-like fungi of the genus Pityrosporum, affecting the stratum corneum of the epidermis.
Pityriasis versicolor is not contagious, but a genetic predisposition to pityriasis versicolor has been identified in persons who are consanguineously related.
Most often, the lesion is noted at the age of puberty, since intensive proliferation of fungi correlates with hyperfunction of the sebaceous glands. Fungi form colonies in the form of yellowish-brown dots around the sebaceous glands. Merging, the colonies form pink-yellow spots, which gradually become brown-yellow. The surface of the spots is covered with pityriasis scales; they are easily scraped off, revealing lighter areas of the skin.
Pink lichen of Zhiber
. To date, the cause of the disease has not been established, but the prevailing opinion is that the lesion is viral in nature (presumably, these are herpes viruses). The disease begins with a prodromal period, which is characterized by muscle weakness, fever, and swollen lymph nodes. Then pink plaques up to 5 cm in diameter with raised edges appear on the skin, which lighten after a week. Over the course of several months, the plaques gradually disappear, becoming pigmented and peeling off. The disease develops mainly in adolescents and young adults.
Syphilis
. Syphilitic rash (papular syphilide), which is accompanied by peeling of the skin, is more common with secondary syphilis. Yellowish or bluish-red rounded papules, slightly protruding above the surface of the skin, have a dense consistency and a smooth shiny surface. Peeling of papules leads to the formation of a rim around them.
Ichthyosis
. This name combines a group of diseases, the characteristic feature of which is diffuse keratinization of the skin of the “fish scale” type. All variants of the disease (vulgar, X-linked, lamellar ichthyosis, congenital bullous ichthyosiform erythroderma) are hereditary in nature. Areas of hyperkeratosis and peeling can be localized in various parts of the body. Thus, with vulgar ichthyosis, peeling is more pronounced on the extensor surfaces of the extremities, but is also present on the skin of the thighs, forearms and buttocks, and deep folds can be seen on the palms and soles. In X-linked ichthyosis, the skin of the palms and face is not affected by hyperkeratosis. The color of the scales varies from light to dark brown. With lamellar ichthyosis, peeling affects all parts of the body.
Which doctors should I contact if my skin is peeling?
If foci of peeling appear in children, you should first contact a doctor who can refer the child to a dermatologist. Adult patients should immediately visit a dermatologist and, if necessary, an allergist-immunologist.
Diagnostics and examinations for peeling skin
To diagnose a disease characterized by peeling skin, it is necessary to do a number of laboratory tests:
- clinical blood test;
When to see a doctor
You should consult a dermatovenerologist if skin itching and peeling do not go away for a long time (more than two weeks), contribute to sleep disturbances and decreased performance during the day, spread throughout the body, and are combined with other pathological symptoms. These symptoms in combination with an inflammatory or infectious process require urgent contact with a specialist.
Itchy skin, as well as flaking of the skin, can indicate a serious illness, the absence of treatment of which will lead to serious complications. Experienced doctors at the SANMEDEXPERT clinic will conduct a comprehensive diagnosis and prescribe adequate therapy for the identified pathology in order to eliminate unpleasant symptoms and their cause.
What not to do for flaky skin?
As mentioned, there are a huge number of reasons why the skin of the face becomes dry. Often women and girls either do not take enough care of their facial skin, or do it excessively and incorrectly.
There are certain rules that must be followed for those who have dry, flaky skin. The following is not allowed:
- Forget about hydration. It is necessary to use day and night creams for moisturizing;
- Peel off loose flakes when peeling. This can cause severe irritation, and there is also a possibility that an infection will enter the epidermis;
- Use scrubs, as they further injure areas of damaged skin. You can use peeling, but not more than once every 2-3 weeks;
- Wash with hot water. It should be at room temperature;
- Eliminate or consume in insufficient quantities foods containing vitamins B, A, E, C. In order to look healthy, the skin must receive the full range of essential vitamins;
- Dry the skin with masks and hygiene products. Masks should be nutritious and natural, for example, cucumber or aloe. Hygienic products must be selected for individual skin type;
- Use powder, as it dries out the skin greatly. You can opt for a BB cream, which evens out the complexion and does not dry out the dermis.
What diseases cause itching and flaking of the skin?
There are quite a few diseases accompanied by itching and peeling of the skin of varying degrees of intensity and prevalence:
- allergies to food, medications;
- contact dermatitis;
- seborrhea;
- psoriasis;
- eczema;
- fungal skin diseases;
- disruption of the sebaceous glands;
- infectious diseases;
- diabetes;
- hormonal disorders;
- thyroid diseases;
- blood diseases;
- parasitic diseases (scabies, demodicosis, etc.).
Seborrheic dermatitis. Causes
The main causes of this disease are:
1) genetic predisposition;
2) metabolic processes;
3) influence of the external environment.
In 1874, the French microbiologist L. Malassez first hypothesized that the causative agent of seborrheic dermatitis is the yeast-like lipophilic fungi Pityrosporum, which later received its name in honor of this scientist. Fungi of this species are concentrated in the middle and superficial parts of the stratum corneum, inside and between the horny scales, as well as in the hair follicles.
Until now, both names of the causative agents of the disease can be found in the literature: Pityrosporum and Malassezia. Currently, the role of the pathogen Pityrosporum in the pathogenesis of seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp and dandruff has been confirmed by numerous clinical and laboratory studies.
These yeast-like lipophilic fungi are a permanent component of the healthy skin microflora in more than 90% of the population. Fungi concentrate around the sebaceous glands and use their secretions for growth and development. Pityrosporumovale (P. ovale) or according to another classification Malassezia furfur is more often found on the scalp, and Pityrosporumorbiculare on the skin of the trunk.
Medicinal pharmacy inexpensive ointments
Doctors consider the following to be the most effective and inexpensive ointments:
1. Ointment containing hydrocortisone 5%. This substance has anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effects. The product can only be applied to flaky skin in a targeted manner.
When using ointments for peeling skin on the face, the main thing is not to exceed the recommended dosage, so as not to get irritation and an allergic reaction.
The course of treatment procedures lasts no more than 14 days. Cannot be used during pregnancy. Price category from 25 rub. in 5 years
Be careful! With prolonged use of ointment for peeling skin on the face with hydrocortisone, addiction can occur and also negatively affect the health of internal organs.
2. Aquaphor ointment - eliminates dry skin and flaking.
It is based on the substance petrolatum, which is obtained from a mixture of mineral oils and solid paraffins. The ointment is distributed in an even layer onto areas of skin with peeling. Therapy lasts about 14 days. Price from 350 rub. for 50 years;
3. Dexpanthenol ointment - regenerates cells well, has an anti-inflammatory effect, accelerates cellular metabolism.
The ointment contains the main component - vitamin B, which penetrates deeply into the layers of the epidermis and restores subcutaneous blood flow.
Apply a thin layer to clean and dry areas of the facial epidermis in the area of peeling. If the peeling is very strong, then the procedure should be carried out up to several times a day. Cost from 120 rub. for 30 years
Interesting fact! Long-term use of the drug does not cause harm to health and can be used during pregnancy and lactation.
4. “Bepanten” - an ointment for peeling skin on the face, containing provitamin B. It actively regenerates the cellular structure of the skin, moisturizes and strengthens skin fibers. Fights inflammation well. The ointment should be applied no more than 2 times a day in a light layer to the affected skin.
Continue therapy until positive results appear. You can also use ointment to prevent peeling. The price of the ointment is from 360 rubles. for 30 years;
5. Panthenol ointment. Active substance – dexpanthenol 5%. Restores the strength of skin fibers, accelerates cellular metabolism, heals skin tissue. It moisturizes the skin well and prevents it from losing moisture.
Can be used up to 4 times a day, spreading over flaky areas of the face.
Does not harm nursing mothers or pregnant women. The price of the product is from 115 rubles. for 25 years; 6. Zinc ointment is an effective remedy for getting rid of flaking on the skin of the face.
Removes the feeling of tightness, dryness, heals wounds. The main component is 10% zinc oxide, as well as substances such as paraffin and petroleum jelly.
Can be used for peeling on the face during pregnancy and lactation. The price of the product is from 30 rubles. for 25 years
Read the site’s popular article: Effective ways to boost an adult’s immunity at home.
Do you need to moisturize oily skin and how to do it?
You cannot do without products that replenish the moisture deficiency in cells, because water is lost during cleansing. If you skip the “feeding” stage, you will feel dryness, tightness, and discomfort. To avoid discomfort, apply special creams and light lotions every day. You can buy a special gel - it is absorbed much faster. You should not use oil-based cosmetics - they are ideal only for dry and dehydrated skin.
In this article, I told you about ways to combat one of the most common problems - lack of moisture. It can be solved simply - just proper care, a balanced diet and restoration of a normal drinking regime are enough. If you want the discomfort to go away, use liposomal cosmetics containing natural ingredients. They are hypoallergenic, easy to apply, quickly help restore protective properties, promote regeneration and restore a healthy glow. Now you know how and what is the best way to moisturize your facial skin at home - light creams, gels, tonics and masks from a special series.
| Problem | Solution | Means |
| Dryness | Hyaluronic acid saturates cells with life-giving moisture. | Quick view 75 mlMoisturizing cream with peach seed oil920 ₽ Add to cart Checkout |
| Peeling | Aloe and ginseng extracts soothe and remove flaking. | Quick view 50 ml |
Clinical researches
The effectiveness, safety and tolerability of La-Cri products have been clinically proven. The products are recommended by the Union of Pediatricians of Russia. During clinical studies, specialists were able to record excellent results. It has been empirically proven that La Cree emulsion moisturizes and nourishes the skin, relieves itching and irritation.
Sources:
- Chapman M. Shane, Habiff Thomas P., Zug Catherine A., Dinoulos James G. H., Campbell James L., Dermatology. Handbook of differential diagnosis, MEDpress-inform, 2014.
- Sukolin Gennady Ivanovich, Illustrated clinical dermatology. Brief alphabetical reference book, Lux Print publishing house, 2010.
- Sukolin Gennady Ivanovich, Clinical dermatology. A short guide to the diagnosis and treatment of dermatoses, Notabene, 2017.
Why moisturize your facial skin and how to do it correctly
The need for moisture saturation is due to constant exposure to the external environment. In summer it is the sun's rays, in winter it is cold wind and frost. Not only the face, but also the hands suffer, but they can be protected by hiding them under clothes, and the face is always open to the winds, direct sunlight, and dust flying into it.
That is why proper care aimed at intensive hydration is vital. For this, it is best to use proven products - based on natural ingredients that do not cause allergies.
We must not forget about the basic rules for saturating the epidermis with moisture:
- The products you use should be selected according to the needs of your skin type.
- Every day it is necessary to cleanse the face - light foams, tonics and emulsions are ideal for this.
- Apply a special cream morning and evening - I recommend using products based on natural extracts with the addition of hyaluronic acid and vitamins.
- Once or twice a week, masks based on essential oils are useful, restoring the protective functions of cells, promoting intensive nutrition and regeneration.
- How and with what can you moisturize your facial skin from the inside? Drink at least 1.5 liters of water per day. This will help you replenish fluid reserves in the body and eliminate the unpleasant feeling of tightness and dryness.
Don't forget about proper seasonal care:
- From the sun - use products with SPF that minimize the negative effects of ultraviolet radiation.
- For frost protection, creams that form a protective film and intensely nourish throughout the day are ideal.
How to moisturize facial skin with folk remedies
You can use the following recipes
- Cucumber mask
For it we need the pulp of one cucumber, mixed with heavy cream and rose essential oil. The resulting composition is applied to a previously cleansed face for 10-15 minutes, then thoroughly washed off with warm water.
- Herbal cocktail
Made from chamomile and mint (2 tbsp each). Herbs are poured with boiling milk. The resulting cocktail should cool. Afterwards it is filtered and applied with a cotton pad for 30 minutes, then washed off.
- Vitamin E cream
For it we need a tablespoon of tocopherol mixed with jojoba or patchouli oil. You will also need beeswax, previously ground on a grater. All ingredients are heated in a water bath until thickened. After this, add aloe juice (1 tbsp) and rose oil (4-5 drops) to the mixture. The components are thoroughly mixed. This home remedy should be stored in the refrigerator in a glass jar.
Here's what you can do to moisturize your skin instead of professional cream. However, such recipes can not help in all cases. They often lead to allergic reactions and cause deterioration of the epidermis. This occurs due to improper storage, the use of active ingredients in the wrong dosage, and failure to comply with the conditions for preparing masks, lotions, cocktails, and tonics. I advise you not to take risks and try professional products developed by leading cosmetologists and dermatologists - they also contain natural extracts and oils, but in this case the risk of allergies is minimal, and the benefits are obvious.
Cosmetic ointments and creams for peeling skin on the face
1. La-Cri cream contains natural plant extracts: violet, walnut, avocado, string.
Also contains panthenol and bisabolol. The components of the ointment remove dryness and fight flaking. The skin becomes hydrated and less sensitive to external influences.
Apply the ointment in a thin layer in the morning and evening for 20 minutes. before going to bed. During cold weather, when the skin is more susceptible to peeling, you need to apply the product 40 minutes in advance. before leaving home.
Price range from 150 rub. for 30 years up to 360 rub. per 100 g of product.
2. “Losterin” ointment has an exfoliating and anti-inflammatory effect. Helps restore damaged skin and relieves itching.
As a result of using the ointment, the skin of the face becomes moisturized and the feeling of dryness disappears.
The composition contains almond and castor oil, d-panthenol, salicylic acid. To eliminate peeling, the ointment is distributed in a small layer onto problem skin areas 2 to 3 times a day.
Ointment for peeling skin on the face "Losterin" does not contain fragrances, dyes, hormones, and is also non-addictive. Price approximately 530 rub.
for 75 ml. 3. Lipobase cream does an excellent job of flaking skin and also relieves itching.
In the cold season, it will be a salvation from chapped facial skin. Restores the epidermis of the skin, softens and moisturizes it.
The composition of the product is enriched with many natural oils, such as avocado, olive, jojoba, shea butter, and bogaro.
These components make the cream not only an SOS product, but also care for the skin of the face. Vitamins A and E make the skin elastic and smooth.
The cream must be applied with light massage movements on the face 2 times a day on dry affected areas. Allow the product to absorb well.
The duration of use has no time restrictions. The cost ranges from 260 rubles. for 75 ml.
Be careful! Pregnant women should use Lipobase ointment for peeling skin on the face with caution. You must first do a test on the inner bend of the elbow to determine the tolerance of the components of the product.