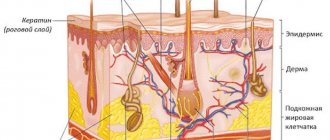
In some diseases, the metabolism changes in such a way that diffuse hyperpigmentation develops, that is, the skin darkens over large areas of the body and on the face. To exclude regular tanning, examine the inner surface of the forearms. The skin on these parts of the body is usually lighter in color. In addition, you need to ask the patient if he visits a solarium.
Why the skin on the face and body darkens and what disorders this may be associated with will be discussed in this article.
Causes
There are the following groups of reasons why the skin on the face and body darkens:
- Increased production of melanocyte-stimulating hormone.
- Other internal diseases accompanied by metabolic disorders.
- Taking certain medications.
- Malignant tumors of internal organs.
Nine “provocateurs” of lentigo
With the advent of old age, the specialist notes, lentigo appears in everyone, even if everything was fine in youth. But there are situations when senile pigmentation may appear earlier than expected. The list of provoking factors includes:
1. Tanning . “I don’t burn,” we say in our youth, brushing aside recommendations to use creams with an SPF filter. In the summer we don’t even go into the shade during lunch hours, and in the winter we run to the solarium as if we were going to work, sometimes to the point of notorious fanaticism. “The production of melanin is a protective process - as the skin darkens, it becomes less susceptible to sunlight. By exposing ourselves to ultraviolet tests in our youth, we deliberately deplete the ability of the skin layers to properly produce melanin,” says Alsou Shaimardyanova.
Article on the topic
Stain remover won't help. What you need to know about facial pigmentation
2. Improper care. During the summer, it is not recommended to carry out deep cleansing and thermal procedures. Under the influence of high solar activity, the epidermis cannot recover normally, says the cosmetologist, the same failure occurs: excessive production of melanin as a way to increase the protective functions of the epidermis and the formation of age spots on the face.
3. Inflammatory manifestations. Acne and severe rashes may be accompanied by pigmentation. To achieve results, drugs and procedures for removing spots must be combined with acne treatment measures.
4. Disturbances in the production of hormones. “Chloasma - dark brown spots with jagged edges - appear during sudden hormonal changes (age-related, during pregnancy). The most important thing is to focus your energy on restoring your hormonal levels. Then chloasma goes away on its own,” notes Alsou Shaimardyanova.
5. Stress and senile disorders. “Nerve” spots are difficult to classify by color and size. The key point is metabolic disorders due to chronic fatigue. For severe skin manifestations, consultation with a neurologist and psychotherapist is recommended.
6. Taking medications. Antibiotics, hormonal drugs and even a course of vitamins lead to pigmentation. Tell your doctor about this so that your medication regimen can be adjusted in a timely manner.
“Wash off” stains. How to get rid of pigmentation on the skin Read more
7. Poor nutrition. Pigmented formations signal the body about a lack of copper and vitamins C and PP.
8. Allergy to low-quality cosmetics. They go away when changing cosmetics or after light whitening procedures.
9. Heredity. Before deciding how to get rid of age spots on your face, it’s worth remembering how your relatives dealt with this problem. “Freckles, moles—all of these, like the production of melanin, are hereditary “gifts.” And you don’t always need to devote all your efforts to removing them if there is no threat to health,” notes the cosmetologist.
Question answer
Which crops contain anthocyanins? Infographics
Hypersecretion of melanocyte-stimulating hormone
The skin darkens when the level of melanin, a coloring pigment contained in special cells called melanocytes, increases. The production and release of this substance into the skin is activated under the influence of one of the pituitary hormones - melanocyte-stimulating.
Active synthesis of this hormone occurs in Addison's disease, one of the main causes of skin hyperpigmentation.
Addison's disease is a chronic adrenal insufficiency that occurs due to tuberculosis, infection, amyloidosis and other damage to these important organs. The adrenal glands stop synthesizing hormones, to which the body responds with increased secretion of a substance that stimulates their hormonal activity - adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), thus trying to restore their activity. The physiology of this process is such that, simultaneously with the increased production of ACTH, the release of melanocyte-stimulating hormone, which causes darkening of the skin, also increases.
In Addison's disease, the skin is bronze, golden brown, or dark gray in color, often looking like a deep tan. Pigmentation is especially noticeable in open areas - the face, hands, as well as in places where clothing rubs, for example, on the neck. The skin also darkens in the genital area, nipple areolas, and postoperative scars. Dark spots also appear on the oral mucosa.
If you suspect Addison's disease, you should consult an endocrinologist.
Internal diseases with metabolic disorders
Some diseases and physiological conditions cause darkening of the skin, for example:
Hemochromatosis is a hereditary disease in which the absorption of iron from food in the intestines increases. Iron-containing pigments are deposited in all organs and tissues, disrupting their functions.
Skin pigmentation in this disease is smoky, gray, bronze in color, most pronounced on the face and hands, as well as in the genital area, in the armpits, and the area of postoperative scars. With this disease, the liver and heart are affected, endocrine disorders develop, including diabetes mellitus. If you suspect hemochromatosis, you should consult a gastroenterologist.
Liver cirrhosis is characterized by a violation of the neutralization of bile, the absorption of bile pigments into the blood and their deposition in tissues. In patients with liver cirrhosis, parenchymal jaundice develops, accompanied by dark brown pigmentation of the skin. Liver cirrhosis is also characterized by itchy skin and pain in the right hypochondrium. This disease is treated by a gastroenterologist.
Porphyrias are a group of hereditary diseases associated with impaired hemoglobin formation. Intermediate products of its metabolism - porphyrins - accumulate in the skin, where they oxidize under the influence of sunlight. As a result, the skin turns brown. It is easily damaged, becoming covered with ulcers and scars.
Sun exposure is contraindicated for patients with porphyria. A hematologist can help with this disease.
How does an alcoholic's face change when he abuses alcohol?
How does the face of an alcoholic differ from the face of a healthy person? What are the main signs of alcohol abuse and how does alcohol affect your appearance? But there are also several stages of alcoholism. And in each of them the face of an alcoholic is radically different. For example, a simple beer drinker often has a red face. Those who prefer vodka in fairly large quantities experience swelling. How is alcohol related to appearance?
Visual signs of alcoholism
So, the face of an alcoholic is almost always red. This is explained by an accelerated heartbeat (pulse). This reaction is caused by ethanol, or more precisely, its derivative, acetaldehyde. The body perceives this substance as a toxin that needs to be gotten rid of as soon as possible, which causes accelerated blood circulation. The brain simply “gives the command” to quickly cleanse all the blood, driving it through the liver. But if you abuse alcoholic beverages, it causes swelling of the face. The first areas to suffer are the neck, eyes, forehead, and chin. This is also explained by the fact that the liver does not cope with its task of removing large amounts of toxins - alcohol derivatives - from the body. In addition, this process requires a huge amount of water. This is what causes swelling. Accordingly, after giving up alcohol, everything returns to normal. The swelling itself occurs due to an imbalance in the water-salt balance in the blood. It is also common for alcoholics to develop a yellowish tint to their skin color. This is a consequence of gradual liver failure. Some of its cells are simply destroyed, which significantly slows down the process of removing toxins from the blood. They are what give the skin its color. Another important sign of alcoholism is a slightly protruding forehead. This is explained by muscle tension and nervous disorder. Alcohol by its nature can destroy neurons. With radical damage to the central nervous system, all this is accompanied by numerous disruptions in the functioning of the muscular system, as well as the musculoskeletal system. In some alcoholics, this is accompanied by facial asymmetry, when one part of the face “sinks” slightly relative to the other. Plus, the lips of such a person also lose their normal shape. All of the above “signs” of alcoholism refer to those cases when the patient has been abusing alcoholic beverages for a long time. But there is also a category of people who are also dependent on alcohol, but drink small amounts of alcohol, preferring beer, wine or low-alcohol carbonated drinks. How does this appear to them externally?
Primary signs of alcoholism
The most common signs of the initial stage of alcoholism are the appearance of acne, rashes and other skin spots. This is explained by intoxication and the presence in the upper layers of the epithelium of too many substances that must be excreted along with sweat. It is no secret that a huge proportion of toxic components leave the body during the process of sweating. However, their maximum number is limited. If there are more toxins than the skin can remove through sweat in the next few days, then those same spots will appear.
Essentially they are:
- inflamed hair follicles;
— epithelial cells affected by infection (its immunity decreases by 4-6 times);
- vascular networks.
At the same time, the skin itself looks flabby, flaky, saggy and inelastic. Over time, all these “symptoms” on the face will be more noticeable, as the amount of alcohol derivatives in the blood gradually increases. Alcohol is not eliminated from the body within a few hours after taking it. A full ethanol processing cycle requires 24-30 days! And all this time the alcohol is inside, poisoning every organ. It especially affects the central nervous system, as well as the liver. A yellowish tint to the skin can appear even with minor alcohol consumption. Why is this happening? Due to improper flow of bile. The latter is a consequence of an unhealthy diet and the presence of other problems in the gastrointestinal tract. As practice shows, jaundice occurs in 40% of those who drink alcohol at least sometimes. However, it is not always accompanied by a visually noticeable yellowing of the facial skin. It should also be mentioned that the signs of alcoholism are more noticeable among the fair sex. This is due to the fact that their skin is thinner. Accordingly, acne, inflammation and swelling become visible much faster with frequent alcohol consumption. But the changes in the body are absolutely identical in both men and women.
Functional disorders from alcoholism
It would be useful to remember about the so-called functional disorders that appear on the face. They can be divided into the category of temporary or local paralysis. That is, some muscles simply begin to work incorrectly. They are in a tense state for a long time, which causes swelling, redness and, by the way, is accompanied by quite severe pain. In this case, either one muscle or a whole series of them can be affected. Most often, this sign appears on the forehead, in the back of the head. Functional disorders also include sagging lips. This is also a sign of paralysis. It can manifest itself both along the entire length of the lip fold, and on only one side. Naturally, along with this, the chewing function is also impaired. Alcoholics are also often found to have a defect such as muscle tremors. On the face these are most often the cheekbones. It looks as if the patient is constantly chewing chewing gum, although in fact there is nothing in his mouth. Moreover, he may not even notice such an action.
Hyperpigmentation due to medications
If the cause of darkening of the skin is unclear, the doctor should ask the patient if he is taking any of the following medications:
- oral contraceptives;
- chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine;
- preparations of silver, gold;
- amiodarone;
- busulfan and bleomycin;
- aminazine
Combined oral contraceptives can cause liver dysfunction with the development of parenchymal jaundice. Chloroquine and its derivatives are used to treat malaria, photodermatoses, as well as connective tissue diseases - systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis. These products may cause the skin to turn bluish-gray.
Darkening of the skin due to malignant tumors
Skin color may change due to malignant tumors of internal organs, including lymphomas. This phenomenon is called acanthosis nigricans maligna ( malignant acanthosis nigricans ) and is accompanied by dark symmetrical spots and stripes in the neck, armpits, external genitalia, and inguinal folds.
Acanthosis nigricans also occurs in benign diseases of the nervous and endocrine systems in young people.
For any change in skin color of unknown origin, you should consult a dermatologist. After the initial diagnosis, this doctor can refer the patient to an appropriate specialist. Darkening of the skin cannot be ignored, because this sign is a symptom of many serious diseases.
Why does human skin color change?
The diversity of human appearance and form has intrigued biologists and beauticians for centuries, but nearly 100 years after William Bateson coined the term "genetics" in 1906, the genes underlying this diversity remain an unsolved mystery. One of the most obvious phenotypes that distinguish our species is differences in skin pigmentation. They are among the most mysterious.
There is a huge range of human skin colors, these may be related to climate, continents or cultures, but we know very little about the underlying genetic architecture. Is the number of common skin color genes closer to 5, 50, or 500?
Do gains or losses of function for a small set of genes lead to phenotypes at opposite ends of the pigment spectrum? Did natural selection influence similar pigmentation phenotypes independently of each other and along similar pathways? And should we finally care about the genetics of a person's pigmentation if it's just skin?
Why should we take care of our skin?
From a clinical point of view, insufficient protection from sunlight has a serious impact on human health. In Australia, the cumulative lifetime incidence of skin cancer approaches 50%, but the oxymoronic "smart tanning" industry continues to grow and there are conflicting opinions about the extent to which different types of melanin influence susceptibility to ultraviolet (UV) radiation.
At the other end of the spectrum, inadequate exposure to sunlight leads to vitamin D deficiency and rickets. It was cured thanks to advances in nutrition made in the early 19th century. In both cases, understanding the genetic architecture of human skin color will likely provide greater insight into the underlying biological mechanisms, internal organs, and blood vessels. And it may also be that mutational hotspots in the TP53 gene helped educate the public about the risks of tobacco.
From a basic science perspective, changes in human skin color provide an unprecedented opportunity for cell biologists, geneticists, and anthropologists to learn more about the biogenesis and movement of subcellular organelles. To better characterize the relationship between genotypic and phenotypic diversity, to further explore human origins and understand how recent human evolution may have been shaped by natural selection.
How does skin color change?
Historically, the measurement of human skin color has been based on subjective categories, such as "medium brown, rarely burns, tans very easily." More recently, quantitative methods based on reflectance spectrophotometry have been applied, which allow for redness caused by inflammation and increased hemoglobin. To be distinguished: from darkening caused by increased melanin content
As a factor - Melanin
Melanin itself is an organic polymer built from oxidative derivatives of tyrosine and comes in two types: a cysteine-rich red-yellow form known as pheomelanin and a less soluble black-brown form known as eumelanin. Distinguishing between pigment types in biological samples requires chemical extraction, but is worth it as we know little about common changes in human pigmentation, including switching pigment types.
Characteristic light skin type
The characteristic phenotype of fair skin, freckles, and wheaten-red hair is associated with high amounts of pheomelanin and low amounts of eumelanin and is caused by loss of function alleles in one gene, melanocortin 1 receptor (MC1R). However, MC1R variation has a significant effect on pigmentation only in populations where red hair and fair skin are common, and its main effects—stimulating eumelanin synthesis at the expense of pheomelanin synthesis or vice versa—contribute little to changes in skin reflectance between or between major ethnic groups.
Changing pigment for different skin types
More important than the ratio of melanin types is the total amount of melanin produced. In addition, the histological characteristics of different skin colors provide some clues as to the cellular mechanisms that likely lead to pigment changes. For the same area of the body, people with light and dark skin have the same number of melanocytes (there is a significant difference between different areas of the body), but pigment-containing organelles called melanosomes are larger, more numerous and more pigmented in dark compared to light skin. skin, which corresponds to individuals whose recent ancestors were from Africa, Asia or Europe.
In this view, oxidative enzymes such as tyrosinase (TYR), which catalyzes the formation of dopaquinone from tyrosine, or melanosomal membrane components such as pink-eyed dilution protein or membrane-associated transport protein (MATP) influence substrate availability . and TYR activity are logical candidates that genetic variations may contribute to the diversity of human skin color.
Equally important is what happens inside melanocytes and what happens outside. Each pigment cell actively transfers its melanosomes to approximately 40 basal keratinocytes; Ultimately, skin reflectance is determined by the number and distribution of pigment granules in keratinocytes rather than melanocytes.
In general, melanosomes in African skin are larger and more widely dispersed than in Asian or European skin. Notably, keratinocytes from dark skin cultured with melanocytes from light skin induce a melanosome distribution pattern characteristic of dark skin and vice versa. Thus, at least one component of skin color change is a gene or genes whose expression and action influence the environment of the pigment cells rather than the pigment cell itself.
The genetics of skin color
For any quantitative trait, with many contributing factors, the most important questions are: overall heritability, the number of genes that may be involved, and the best strategies for identifying those genes. For skin color, heritability in the broad sense (defined as the combined influence of genetic and nongenetic factors) is very high, provided that the most important nongenetic factor, exposure to sunlight, can be controlled.
Statements about the number of human skin color genes refer to several studies; one of the most complete is Harrison and Owen (1964). In this study, skin reflectance measurements were obtained from 70 residents of Liverpool whose parents, grandparents or both were of European ("with a large Irish component") or West African ("mainly from the coastal areas of Ghana and Nigeria") origin and who were roughly classified into "hybrid" and "reverse" groups on this basis.
An attempt to separate and analyze the variance of backcross groups resulted in minimal estimates of three to four “effective factors,” in this case independently separating genes. Aside from the keyword-minimal (Harrison and Owen's data could also be explained by 30–40 genes), one of the most interesting findings was that skin reflectance appeared to be largely additive. In other words, the average skin reflectance of the "F1 hybrid" or "inverse hybrid" groups is intermediate between their respective parent groups.
An alternative approach to considering the number of potential human pigmentation genes is based on mouse coat color genetics, one of the original models for identifying and studying gene action and interaction, for which nearly 100 different genes have been identified.
Leaving aside mouse mutations that cause white patches or predominant effects outside the pigment system, there remain no more than 15 or 20 mutations, many of which have been identified and characterized and most of which have human homologues in which null mutations cause albinism.
This brings us to the question of candidate genes for skin color, since, as with any quantitative trait, a reasonable place to start is with rare mutations known to cause extreme phenotypes, in this case Mendelian forms of albinism. The basic assumption is that if a rare null allele causes complete loss of pigment, then a set of polymorphic, i.e., more frequent alleles, with subtle effects on gene expression, will contribute to the spectrum of skin colors. The TYR, P and MATP genes discussed earlier are well known causes of albinism, the main effect of restricted pigment cells; Among them, the P gene is highly polymorphic, but the phenotypic consequences of P and gene polymorphisms are not yet known.
Regardless of the phenotype, the gene responsible for selecting for different skin colors should exhibit a population signature with a large number of alleles and rates of sequence substitution that are greater for nonsynonymous (which change an amino acid in a protein) than synonymous (which do not change any amino acid) changes. Data were collected only for MC1R, in which the most notable finding is the lack of allelic diversity in African samples, which is remarkable given that polymorphism for most genes is higher in Africa than in other geographic regions. Thus, while MC1R sequence variation does not significantly contribute to human skin color variation worldwide, functional MC1R is likely important for dark skin.
Selecting skin color
The primacy for describing the relationship between latitude and skin color in modern humans is usually attributed to the Italian geographer Renato Basutti, whose widely reproduced "skin color maps" illustrate the correlation of dark skin with equatorial proximity. Later research by physical anthropologists confirmed and expanded these observations; a recent review and analysis of data from more than 100 populations found that skin reflectance at the equator is lowest, then gradually increases, about 8% at 10° latitude in the northern hemisphere and about 4% at 10° latitude in the southern hemisphere. This pattern is inversely correlated with ultraviolet radiation levels, which are higher in the southern than in the northern hemisphere. An important caveat is that we do not know how UV exposure patterns have changed over time; More importantly, we don't know when skin color likely changed, with multiple migrations out of Africa and extensive genetic exchange over the last 500,000 years
Despite this, most anthropologists agree that differences in ultraviolet radiation caused the choice of dark skin in humans at the equator and light skin in humans at higher latitudes. This remains controversial. The most popular theory states that the protection provided by dark skin from ultraviolet radiation becomes a disadvantage in more polar latitudes due to vitamin D deficiency (Murray, 1934). UVB (short-wave UV) converts 7-dehydrocholesterol into an essential precursor of cholecaliferol (vitamin D 3)); When dietary supplementation is not otherwise provided, vitamin D deficiency causes rickets, a characteristic growth pathology and bone deformities.
An often-cited anecdote in support of the vitamin D hypothesis is that Arctic populations whose skin is relatively dark given their latitude, such as the Inuit and Sami, Chukchi and Eskimos, ate diets rich in vitamin D. The sensitivity of modern humans to vitamin D deficiency is evident from -due to the widespread prevalence of rickets in industrial Europe in the 19th century, but whether dark-skinned people migrating to the polar latitudes tens or hundreds of thousands of years ago encountered such problems remains in question! In any case, the risk of vitamin D deficiency can only be explained by choosing light skin. The most reliable protection against sunburn and skin cancer is due to the physical barrier created by epidermal melanin.
Solving the mystery of pigmentation
Recent developments in several areas present an exciting opportunity to better understand the diversity of human pigmentation. Improved spectrophotometric tools, advances in epidemiology and statistics, multiple genome sequences, and efficient methods for analyzing sequence variations give us the opportunity to replace misunderstandings and myths about skin color with a scientific approach.
The same approaches that have been used to study traits such as hypertension and obesity—genetic and association studies—can be applied in a much more powerful way to study human pigmentation, since the sources of environmental variation can be controlled and we have deeper knowledge of the basic sciences: biochemistry and cell biology.
This approach is particularly attractive given the dismal success rate in molecular identification of complex genetic diseases. In fact, knowledge of the genetic architecture of skin color may be useful in designing studies of other quantitative traits.
Current debates in the human genetics community include strategies for selecting populations and candidate genes to study the characteristics of polymorphisms that should be considered as potential disease mutations and the extent to which common diseases are caused by common (and presumably ancient) alleles. Although the specific answers will be different for each phenotype, there may be common themes and some answers are better than nothing.
Harrison and Owen concluded their study of human skin color in 1964, stating: "The shortcomings of the data in this study are highly appreciated by the authors, but since there is no opportunity at present to improve the data, it seems warranted to analyze it as far as possible." Almost 40 years later, possibilities are opening up and the mystery of human skin color may be solved.
Which doctor should I contact?
If there is widespread or limited discoloration of the skin, you should consult a dermatologist. After ruling out skin diseases, the patient is usually referred to a general practitioner, where he undergoes an examination of the internal organs. After clarifying the diagnosis, a consultation with a specialized specialist is scheduled: endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, hepatologist, hematologist, oncologist.
Any change in skin tone, if it did not occur under the influence of sunlight, is a serious signal about a disruption in the functioning of internal organs.
So, for example, if the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted, the shade of the face may change from healthy to gray; it may turn blue if there is impaired blood circulation, diseases of the cardiovascular system or respiratory failure; in addition, a purple tint indicates congenital heart disease, and a yellow hue indicates liver diseases.
Gray facial skin - a disease or a consequence of bad habits
A sharp and noticeable change in complexion from natural and healthy to gray is most often a sign of a malfunction of the digestive system . At best, your face may turn gray due to banal constipation or poor nutrition, at worst, due to gastritis or the development of a stomach ulcer. It is hardly possible to independently diagnose the disease on the basis of dyschrony alone, so in this situation it is better to go to an appointment with a gastroenterologist.
In addition, gray facial skin does not always portend illness. Often, against the background of smoking, sedentary work and constant stress, people's blood circulation is impaired and blood vessels narrow, which is also manifested by a deterioration in complexion.
Dull complexion
The health and appearance of the skin depend mainly on its level of moisture and the state of local blood circulation, and a dull complexion is a consequence of an unhealthy lifestyle. The condition of facial skin is negatively affected by lack of sleep, fasting or strict diets, physical inactivity, bad habits, and excessive tanning.
As a result of chronic lack of sleep, the skin does not have time to rest and recover normally overnight, resulting in pallor, deteriorating complexion, and the process of premature cell aging. Dietary restrictions lead to the skin not receiving enough essential nutrients, microelements and vitamins, which are the “building material” for new cells. Staying in one position for a long time (for example, sitting at a computer) leads to overstrain and spasm of the muscles of the cervical-collar region, resulting in impaired blood circulation in the neck and head. All this is immediately reflected in the appearance of the skin - the complexion becomes dull and lifeless.
Excessive use of tanning (prolonged sunbathing or frequent visits to the solarium) contributes to the violation of the hydro reserve, loss of elasticity and photoaging of the skin, causing the appearance of hyperpigmentation. Therefore, skin damaged by excess ultraviolet radiation looks dehydrated, dull and tired. The complexion changes due to improper skin care or lack thereof. Lack of fresh air, as well as poor environmental conditions, can also cause a dull complexion. It is not without reason that this cosmetic problem is considered relevant for residents of large cities suffocated by smog.
In winter, the condition of the skin is negatively affected by low outdoor temperatures, frosty winds, dry air in apartments and offices, lack of sunlight and vitamin deficiency. Therefore, by the beginning of spring, many women notice that the skin has lost its freshness and the complexion has become dull. Unhealthy complexion can be caused by the accumulation of dead cells and dust covering the skin - oily skin is most susceptible to contamination. In addition, with age, the regeneration of the epidermis slows down, keratinized cells exfoliate more slowly, which also leads to dullness of the epidermal layer.
The expression “smoker's face” has long come into everyday use. Premature wrinkles, grayish tint and dry skin, sunken cheeks, deep nasolabial folds - these are typical touches to the portrait of a person who cannot part with a cigarette. Toxic substances contained in tobacco smoke cause spasm of skin capillaries. In addition, when smoking, the amount of carbon monoxide in the blood sharply increases. This means that the skin of the face is poorly supplied with blood and enriched with nutrients and oxygen. Therefore, smoking inevitably leads to changes in the structure of the skin - increased dryness, sagging, uneven and dull complexion, and premature aging.
In some cases, a dull complexion may reflect poor overall health. Thus, dry and gray skin, brittle nails and hair loss are often signs of hypothyroidism. Changes in the condition and color of the skin are caused by gastrointestinal diseases (cholecystitis, pancreatitis, constipation, dysbacteriosis), osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, long-term use of medications, menopause, etc.
Earthy tint and sharp darkening of the skin - pancreatic disease or oncology
Changes of this kind indicate more serious illnesses. Often, of course, an earthy tint appears due to diseases of the pancreas, adrenal glands, or against the background of long-term use of antibiotics, but if such options are excluded, then the best recommendation in this case would be to turn to modern medicine. Diagnosis of the disease by the skin and on the basis of examinations will allow you to correctly and accurately determine the cause of the change in complexion, as well as timely diagnose the disease that provoked it.
How to improve your skin tone?
There are standard recommendations that will help remove unhealthy complexion:
- you need to undergo a medical examination to determine possible diseases that could provoke this problem;
- carry out treatment that should be prescribed by a doctor;
- lead the right lifestyle, it should be active;
- Get enough sleep. This should be at least 6 hours per day;
- eat the right food - more fresh foods, less pickled, fried, fatty flour, drink clean water and plenty of it;
- exercise;
- walk in the fresh air, ventilate the room;
- do not use a lot of contraceptives, antibiotics;
- avoid stressful situations;
- try quitting smoking and drinking less.
These are the main activities that will help improve your skin tone and help your skin heal.
Vasculitis is a disease of blood vessels in the skin.
This disease involves damage to the blood vessels and tissues of the damaged organ. If the skin vessels are affected, the main symptoms of the disease will be redness, rash and itching. Vasculitis can also affect the circulatory system of the brain, which causes a stroke, the heart, which increases the risk of heart attack, etc., quite often small hemorrhages under the skin are a sign of vasculitis of other organs.
The main symptoms of this disease include: general weakness, fever, loss of appetite, weight loss, rash and itching, joint pain.
A similar syndrome can also occur with systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis and other diseases characterized by damage to connective tissue.
Cuperosis is a vascular skin disease
Couperosis appears in the form of a small red vascular network or so-called on the cheeks, chin and nose when the blood vessels dilate against the background of increased blood circulation. At the same time, the connective tissue squeezes the vessels from the outside, which makes them more visible on the face. This disease occurs among older people, as well as among those with thin and sensitive skin.
Couperosis can be treated either in a cosmetology salon or using traditional methods. Although the first method allows you to get rid of the signs of rosacea in the shortest possible time. But in case of lack of funds or opportunities - facial massage. This way you can normalize blood circulation and tone the blood vessels and muscles of the face. In addition, supplement your diet with foods or dietary supplements rich in vitamins C, P, K, antioxidants, Omega 3 and 6 fatty acids - they strengthen the walls of blood vessels and help normalize blood circulation.
Origins of the problem
What is the reason for the appearance of such a defect? This is the question asked by everyone who has noticed it on their skin. After all, it hints at a person’s age better than other signs. “The appearance of age spots, scientifically called lentigo, will not harm your health. The question is solely about aesthetics and moral dissatisfaction, finding ways to get rid of age spots on the face,” says Alsou Shaimardyanova.
There are several reasons for the appearance of such a defect, the specialist emphasizes. Among them:
- disruptions in the functioning of the body and metabolism;
- Lifestyle;
- heredity.
“Lentigines are not tumor formations that require action. The reason is hormonal changes after 40 years, affecting the synthesis of melanin - the coloring substance of the skin, hair, and iris. Melanin begins to accumulate unevenly, and in some places there is a lot of it. This is how age spots appear,” says the cosmetologist.
Goodbye swelling, wrinkles and pigmentation. Rules for skin care after 40 Read more
Yellow skin – liver disease
Most often, yellowing of the face and body is accompanied by a change in the shade of the eye sclera, mucous membranes, especially under the tongue, feet and palms. At the same time, the color of the urine changes - it acquires a rich dark shade.
Such changes most often occur against the background of increased levels of carotene or bilirubin. In the first case, the skin can become yellow if you follow a diet consisting of oranges or carrots for a long time. If these did not occur, then most likely the matter is an increase in the content of bilirubin - a bile pigment that appears as a result of the breakdown of hemoglobin. The latter is responsible for saturating the blood with oxygen and transporting nutrients not only to skin cells, but throughout the body. When there is a decrease in hemoglobin and an increase in bilirubin, changes occur not only in the layers of the dermis, but also in the liver. Then there is a risk of jaundice. In addition, yellowness may indicate diseases such as hepatitis, cirrhosis of the liver, the formation of cysts, as well as disorders of the gallbladder and biliary tract.
The disease acanthosis nigricans was described in the 9th century and is considered quite rare. The development of acanthosis is accompanied by the appearance of areas of hyperkeratosis in the area of natural skin folds. In these areas, increased pigmentation and skin papillomatosis are found. Large folds of skin are usually affected - the armpits, groin and neck. Timely detection of acanthosis in the early stages can indicate serious processes. Why acanthosis is dangerous and how to recognize it, read on estet-portal. com.
List of things that spoil the skin
Many factors can have a negative impact on the condition of the dermis - from poor nutrition to even the slightest stress. Because of them, the skin loses its elasticity, becomes dull and gray, begins to wrinkle and fade. But this problem is not limited to aging skin. In young people, the epidermis suffers from acne, acne, inflammation and infections. Each negative factor contributes to the deterioration of his condition and early aging.
Stress
The nervous system influences all processes in the body. But its problems are most reflected in the condition of the skin. If you experience irritability, anger, apathy, depression every day, the dermis loses its natural shade and elasticity. Not only the skin suffers, hair and nails are also negatively affected by a nervous breakdown.
It is better to prevent stress, but this is not always possible. In this case, it is necessary to consult a neurologist or psychotherapist who will prescribe sessions to develop stress resistance and sedatives. These may not necessarily be complex antidepressants and tranquilizers with a large list of adverse reactions that also affect the condition of the skin. Modern sedatives of the latest generation contain amino acids. These are peptide drugs that are safe and beneficial for the whole body, and especially for the nervous system.
Nutrition
There is a lot of talk about proper nutrition now. The condition of our skin depends on what we eat. But this does not mean that you need to go on a strict diet right now. On the contrary, nutritionists around the world recommend not to adhere to too many restrictions, but to eat wisely.
Your daily diet should include foods rich in fiber, vitamins and minerals:
- legumes;
- foods containing large amounts of fiber;
- vegetables and fruits;
- fermented milk products;
- fish and lean meat;
- nuts;
- cereals
It is wise not just to count calories, but to know how much protein, fat and carbohydrates the body requires at a certain moment. The easiest way is to keep your usual diet, but avoid the following foods:
- Dishes high in sugar. Excessive amounts of fast carbohydrates have a bad effect on the skin, especially in the presence of acne, comedones, and acne. It is better to replace sweets, pastries and cakes, sweet soda with dried fruits, fruits, berries, natural juices, fresh juices and smoothies.
- Bakery. Such dishes contain a dangerous combination of simple carbohydrates and fats, which is bad for the skin and contributes to excess weight gain.
- Fast food. Snacking on hamburgers, hot dogs, shawarma and other fast food products causes serious harm.
- Fatty, smoked, salty, spicy dishes. All these products are not healthy, and salt also retains water in the body, which leads to swelling.
There is a theory of AGE products that activate the glycation reaction, that is, they form debris that clogs the cell and interferes with its normal functioning. When the components of AGE dishes accumulate in the tissues, the collagen fibers seem to stick together, the skin loses its elasticity, becomes dry and pigmented.
Physical activity and drinking regime
An inactive lifestyle and sedentary work lead to stagnation in the body. Blood circulation and lymph flow are disrupted, swelling appears, and extra pounds quickly accumulate. This is puffiness of the skin, bags and bruises under the eyes, cellulite and other problems.
Daily physical activity is necessary, but training must be done at a reasonable pace and with calculated effort. Each muscle group has its own set of exercises, even face-building for the face and neck.
As for the drinking regime, you need to drink as much water as your body requires. But at the same time, monitor the condition of the skin - if it is dry, it means there is not enough moisture, you need to drink more water.
Dream
The condition of the skin, nervous and immune systems depends on this factor. It has been proven that when circadian rhythms are disrupted, the body is more susceptible to infections, viruses and inflammation. Full sleep for 7 - 8 hours, without awakenings and nightmares, is possible if you follow the rules:
- walk for 30 – 60 minutes 2 hours before rest;
- ventilation of the room;
- giving up gadgets an hour before bedtime - no TV series, news or correspondence;
- last meal at least 2 hours before bedtime.
The mattress should be comfortable and the bed linen fresh. If a pillowcase and sheet are used for a long time, particles of dirt and dust accumulate on them, which are absorbed into the dermis, which leads to inflammation and fading.
Other negative factors
Alcohol and smoking are very bad for the skin. Previously they were called bad habits, now these problems are classified as diseases, they even have an ICD code. It is necessary to give up smoking completely, since nicotine and tar have almost a greater negative effect on the condition of the skin, hair and teeth.
As for alcohol, a glass of good wine from time to time can even be beneficial - to lift your mood or enhance the taste of the dish with which alcohol is served. The main thing is not to abuse it.
Another negative factor is ultraviolet radiation. Exposure to UV rays leads to photoaging of the skin, that is, it begins to fade much earlier. Therefore, you need to go outside with protection - by applying cream with an SPF profile to exposed areas of the body. In winter, an indicator of 30 is sufficient, in summer – at least 50. Sunbathers can afford this before 11 am and after 17 pm. But even at this time it is necessary to use sunscreen.
Diseases of internal organs necessarily affect the condition of the skin, especially chronic pathologies. Gastrointestinal diseases lead to the formation of acne, yellowness, and loss of elasticity. Intestinal dysfunction is one of the main causes of acne, acne and other diseases. Problems with blood vessels are stars, mesh, rosacea on the face and other parts of the body.
What symptoms indicate acanthosis? Forms of acanthosis nigricans
Acanthosis has several forms of progression depending on the cause, which determines the intensity of the development of the process. Dermatologists have identified 3 main forms of acanthosis nigricans:
- Juvenile or benign, which is associated with endocrine and genetic pathologies.
- Malignant or paraneoplastic, which develops with malignant tumors of internal organs.
- Pseudoacanthosis, which develops with obesity and metabolic disorders. This form disappears without a trace when weight is normalized and has the best prognosis.
Clinical manifestations of acanthosis have 3 main symptoms:
- Increased pigmentation - the appearance of black or dark brown spots on the skin.
- Papillomatosis is the presence of fibromas or papillomas on the skin, which are popularly called warts.
- Hyperkeratosis, which provokes roughening and exfoliation of the skin.
Localization of acanthosis on the skin. What symptoms accompany the progression of acanthosis?
The above-described skin changes are most often found on the skin of the inguinal-femoral fold, intergluteal region, elbow bends, on the fold between the back of the head and neck, on the skin of the armpits, in the popliteal region, on the skin under the mammary glands. It is possible that a triad of symptoms may appear on other parts of the body (face, side of the neck and navel area).
In the early stages of acanthosis development, the patient's skin gradually darkens. Many people try to wash their skin thoroughly, thinking that it is dirty. As the disease progresses, the skin begins to darken even more, becomes rough, dry, and thickens. The natural pattern of the skin becomes more pronounced and deep.
At later stages, growths in the form of fibromas and small papillomas appear on the affected areas of the skin. The growths are papillary in shape and arranged in dense rows, giving the skin a warty appearance. These lesions may also be hyperpigmented. All symptoms of acanthosis on the skin are accompanied by mild itching and tingling. There is no hair on the affected areas of the skin.
What are the aspects of diagnosis and treatment of acanthosis nigricans?
If darkening of the skin is detected in certain areas of the skin, which does not go away, but only progresses, you should consult a dermatologist. The specialist will conduct a differential diagnosis with Addison's disease, ichthyosis, and Darier's disease. The final diagnosis of acanthosis nigricans is established based on histological examination of the biopsy specimen. If a malignant form is suspected, consultation with an oncologist is required.
Treatment includes therapy for the underlying disease that led to acanthosis and symptomatic therapy. Prescribe general tonic drugs, vitamin complexes, anti-inflammatory ointments, baths with potassium permanganate, zinc preparations, aromatic retinoids. In severe cases - cytostatics and hormonal drugs, neurotropic drugs, antibacterial therapy. All this must be accompanied by a diet.
In case of massive growths of papillomas, they are surgically removed using cryodestruction or electrocoagulation.
Thus, simple darkening of the skin may hide the course of the oncological process, which is not yet manifested by general symptoms, but only by acanthosis. Therefore, contacting a doctor if you suspect acanthosis can improve the prognosis of the course of pathological processes.