For Kosmetic International magazine
Anna Smirnova,
dermatovenerologist, dermatocosmetologist
International Medical (The Platinental Aesthetic Lounge Moscow)
“Everything is poison, and nothing is without poison; The dose alone makes poison a medicine." Paracelsus, 16th century
The first mentions of ozone therapy date back to the end of the 18th century. The Dutch physicist M. van Marum, while researching electricity, discovered that when sparks appear in an electric machine, the oxidizing properties of the air change and a strange smell arises. In 1840, the German chemist Christian Friedrich Schönbein was able to compare previously conducted scientific research and came to the conclusion that a new gas had been discovered. It was he who named this gas ozone, which translated from Greek means “smell.”
For the first time, ozone as an antiseptic was used in Germany back in 1915 during the First World War, but extensive and systematic research in the field of ozone therapy began only in the mid-70s of the last century, when ozone-resistant polymer materials appeared in everyday medical practice and easy-to-use ozonation units. In subsequent years, information gradually accumulated about the successful use of ozone in the treatment of various diseases. However, for a long time, ozone therapy methods associated with direct contact of gas with the outer surface and various body cavities were mainly used when treating purulent wounds, trophic ulcers, abscesses, etc.
In Russia, little was known about the therapeutic use of ozone. Only in the 60-70s, several works on the use of ozone in the treatment of certain skin diseases appeared in the domestic literature, but since the 80s this method has become increasingly widespread. By 2000, the Russian school of ozone therapy had finally formed its own, different from the European, approach to the use of ozone as a therapeutic agent. The main differences are the widespread use of saline as an ozone carrier and the use of significantly lower concentrations and doses of ozone. The desire of most Russian doctors to use the lowest effective concentrations of ozone reflects the basic principle of medicine - “do no harm.”
What is ozone therapy and what is the mechanism of action of ozone?
Ozone therapy is a non-drug physiotherapeutic method based on the use of ozone for therapeutic and prophylactic purposes . The main active component is an unstable megamolecule formed by three oxygen atoms and having one free bond, which ensures its high activity. Ozone has a very high electron affinity (1.9 eV), which determines its properties as a strong oxidizing agent: only fluorine surpasses it in this regard (S. D. Razumovsky, 1990). Ozone oxidizes all metals except gold and platinum, as well as most other elements. Despite its high oxidation potential, ozone reacts extremely selectively. The reason for this selectivity is the polar structure of the ozone molecule, or more precisely, the positively polarized oxygen atom, which gives the entire molecule an electrophilic character. Therefore, molecules with high electron density are the most preferred reactive elements. Compounds with free C=C double bonds react instantly, phenols and free amines are oxidized in seconds, while, for example, alcohols are oxidized within a few hours.
Ozone is a gas that is toxic if inhaled. It irritates the mucous membrane of the eyes and respiratory tract, and damages the surfactant of the lungs. The sequence of painful manifestations when inhaling ozone was described by the German hygienist K. Flugge. First, drowsiness sets in, then breathing changes - it becomes deep, irregular. At the end there are breaks in breathing. Death occurs, apparently, as a result of respiratory paralysis. Pathological studies showed a characteristic picture of ozone poisoning: the blood does not clot, the lungs are riddled with numerous confluent hemorrhages. As a result, the maximum permissible concentration (MAC) of ozone in the air of a working room has been set at 0.1 mg/m2, which is 10 times the olfactory threshold for humans.
At high concentrations (more than 200 µg/l) ozone is toxic, but in the therapeutic range of concentrations (from 8 to 200 µg/l) for external use (on the skin and wound surface), enteral ( per os et per rectum )
and parenteral administration, ozone does not have a toxic effect on the human body.
Among the reasons for the bactericidal effect of ozone, the most often mentioned is a violation of the integrity of bacterial cell membranes, caused by the oxidation of phospholipids and lipoproteins. Gram-positive (G+) bacteria are more sensitive to ozone than gram-negative (G-), which is apparently due to differences in the structure of their shells. There is also evidence of the interaction of ozone with proteins. The ability of ozone to penetrate inside a microbial cell has been discovered, which leads to its reaction with cytoplasmic substances and the transformation of a closed DNA plasmid into open DNA; thereby reducing bacterial proliferation.
The virucidal effect of ozone is associated with damage to the polypeptide chains of the envelope, which can lead to disruption of the ability of viruses to attach to target cells and the splitting of one strand of RNA into two parts, undermining the foundation of the reproduction reaction. Encapsulated viruses are more sensitive to ozone than non-encapsulated viruses. This is explained by the fact that the capsule contains many lipids that easily interact with ozone.
The targets of ozone exposure in the body are:
- unsaturated fatty acids;
- free amino acids;
- amino acids in peptide bonds;
- nicotinamide coenzyme.
Since during ozone therapy reactive oxygen species enter the body, the question of the effect of ozone on the process of free lipid peroxidation (LPPO) is very important. Numerous studies have shown that therapeutic doses of ozone stimulate the antioxidant system and reduce the intensity of lipid peroxidation. In the process of ozone therapy, the initial activation of free radical oxidation under the influence of ozone therapy naturally occurs, since ozone (the molecule of which is unstable) and oxygen are introduced into the body, but at the same time the antioxidant defense system is quickly launched, which ozone apparently indirectly stimulates.
Thus, medical ozone has the following biological effects:
- bactericidal effect;
- virucidal effect;
- fungicidal effect;
- restoration of microcirculation and peripheral circulation;
- reduction of tissue hypoxia;
- restoration of oxygen transport function of the blood;
- stimulation of antioxidant protection;
- decreased blood clotting;
- detoxification effect;
- anti-inflammatory effect;
- acceleration of metabolism;
- immunomodulatory effect (small doses of ozone stimulate the immune system, large doses suppress it);
- analgesic effect.
Methods of using ozone for medical purposes
Ozone affects the body in two ways: locally or systemically. The choice of method entirely depends on the degree and duration of the disease, on how active the inflammatory processes are in the human body, whether there are pathologies or any contraindications. Ozone concentration is very important for treatment effectiveness. Thus, with the external use of high concentrations (from 80 -200 μg/l) of gaseous ozone and ozonized solutions when treating infected wounds, bedsores, gangrene, etc. its powerful oxidative properties directed against microorganisms are manifested. Ozone kills all types of bacteria, viruses, fungi and protozoa. Moreover, unlike many antiseptics, ozone does not have a destructive or irritating effect on tissue, since the cells of a multicellular organism have an antioxidant defense system. Medium concentrations (40-80 µg/l) - to reduce pain and inflammation, and in small concentrations (8-40 µg/l) ozone promotes rapid healing of uninfected wounds.
In cosmetology, both local and systemic methods of application are used:
Topical ozone application methods include:
- irrigation with ozonated water;
- application of ozonated oils, masks and massage with ozonated oil.
Systemic methods of ozone therapy include the following parenteral methods:
- large autohemotherapy with ozone;
- minor autohemotherapy with ozone;
- subcutaneous ozone injections;
The effect of parenteral administration of medium and low concentrations of ozone in pathologies accompanied by hypoxic disorders is based on the activation of oxygen-dependent processes, which contributes to the inclusion of compensatory mechanisms aimed at eliminating disturbances of homeostasis.
Contraindications, possible complications and side effects
According to MT Jacobs (1986), in relation to the total number of ozone therapy procedures, the level of complications is 0.006%. The number of reliable complications among patients treated with ozone is 7 cases per 1 million - this is a negligible value compared to other types of treatment. Most often, side effects of ozone therapy occur during intravenous procedures, especially with intravenous administration of an ozone-oxygen mixture, which has now been practically abandoned. The causes of side effects are incorrect administration technique and incorrectly chosen dosage. Ozone therapy procedures can be carried out by either a doctor or a nurse, but the first procedure must be carried out in the presence of a doctor. At the slightest deterioration of the patient's condition, the procedure should be stopped.
Contraindications:
- all bleeding disorders, including thrombocytopenia, hemophilia;
- hyperthyroidism;
- tendency to seizures;
- allergic reaction to ozone;
- acute alcohol intoxication;
- menstruation period;
- deficiency of the enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase - G-6-FDG;
- the use of drugs that reduce blood clotting.
Possible complications and side effects
From experience, we can say that there are usually no significant side effects; there may be small hematomas at the injection site, which disappear, like a regular bruise, within a week. Their appearance is associated with individual morphological features of the structure of the intradermal vascular network. Possible: redness and soreness at the injection site (disappear within half an hour after the end of the procedure), slight dizziness, which also disappears within half an hour, as well as a transient decrease in blood pressure, pressing pain in the chest, dyspnea.
But you should always remember about a possible allergic reaction, therefore, at the slightest suspicion of it, you should stop the procedure and look for alternative treatment methods in the future.
Areas of application in cosmetology
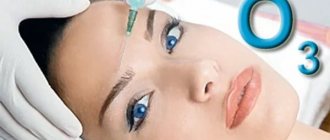
Ozone therapy for the face is aimed at improving the texture of all skin covers (rejuvenates and tightens). For example, injections into the forehead, cheeks, and neck increase blood flow and trigger normal collagen production. The ozone-oxygen mixture helps get rid of double chin, bags under the eyes, successfully and, most importantly, quickly treats acne. In a word, ozone therapy can be used all over the face - depending on the wishes of the client and the recommendations of the cosmetologist.
General requirements for medical ozonation units
The above information about the properties of ozone indicates the need for careful handling. Ozone should not leak in areas where people work. Its content in the air should not exceed the maximum permissible concentration - 0.1 mg/m3.
A medical ozonator installation must include an air-cooled ozonizer and a system that opens, regulates the speed and shuts off the gas flow. Measuring the flow rate is desirable, although not a mandatory requirement, but in any case, a flow indicator is required, which informs the doctor about the normal operation of the gas tract. The concentration of ozone in the gas mixture at the outlet of the ozonator should vary in a wide range from several units to a maximum - not lower than 70-80 mg/l. Moreover, the ozone concentration should be smoothly regulated and measured throughout this range. Only in this case can the installation ensure the use of all known methods of ozone therapy.
In Russia, the production of high-quality ozonation units is now being actively developed, which significantly facilitates the implementation of the technique, since due to low-quality devices, ozone has not been used for medical purposes.
Contraindications
The following factors are contraindications to the procedure:
- cardiovascular pathology in the stage of decompensation;
- disorders of the blood coagulation system;
- endocrine pathology;
- epilepsy.
The time limit for the procedure is menstruation.
The advantages of the procedure are high efficiency, noticeable effect after the first procedures. In addition, ozone therapy is the method of choice when it is impossible to carry out photodynamic therapy or mesotherapy due to the development of allergic reactions.
Result of the procedure: before and after photos
Ozone therapy as a method of cosmetic treatment
The path to the spread and recognition of ozone therapy as a unique technique was very long and difficult. As I already said at the beginning of the twentieth century, the unique antibacterial properties of ozone attracted the attention of doctors. The ozone-oxygen mixture began to be used in the treatment of tuberculosis, anemia, and pneumonia. But with the advent of antibiotics, interest in ozone therapy waned. It seemed that antibacterial drugs made all other methods of fighting infection unnecessary. Only when the euphoria from using new drugs wore off did it become clear that antibiotics have a lot of side effects, and over time, bacteria manage to adapt to them. Then doctors again remembered their old and trusted friend - ozone.
Interest in ozone therapy increased as data accumulated on the biological effects of ozone on the body and reports appeared from various clinics around the world about the successful use of ozone in the treatment of a number of diseases, including aesthetic problems. In Russia, the research and use of ozone was hampered due to the lack of ozone-resistant polymer materials and convenient ozone installations. Side effects were also alarming. Only over time, when the list of contraindications was fully established and the number of complications subsided, ozone therapy quickly took off, gaining more and more supporters, including among cosmetologists.
In our clinic we solve problems such as: acne, pyoderma (due to the bactericidal mechanism, improved microcirculation, immunomodulatory effect, antioxidant effect), focal alopecia (increased mitotic activity of keratinocytes and increased proliferation of epidermal cells in the area of baldness, stimulation of healthy growth hair), obesity and cellulite (ozone is able to oxidize fats and eliminate intoxication of the body), aging problems (ozone does not affect the signs of skin aging, but its root cause - a lack of oxygen in the tissues).
Acne
The following treatment methods are used to treat acne:
- Subcutaneous injection of pustular elements with an oxygen-ozone mixture 3 - 4 times a week, a total of 6 - 8 procedures per course.
- Irrigation of lesions with ozonized distilled water (daily, until pus is completely eliminated from the skin).
For purulent skin lesions and acne, medical ozone, prescribed in the form of subcutaneous injections of lesions or injection of a gas mixture into a boil or acne (infiltrative and pustular elements), can be successfully used as monotherapy. The lipolytic properties of ozone help to influence the accumulated sebum in cystic formations, and improving blood circulation at the injection sites accelerates the resorption of scar changes. In some cases, the procedure of injecting with an oxygen-ozone mixture is performed after their sanitation (opening and emptying of purulent contents). All patients with acne after the first injection procedure experience clinical improvement, expressed in softening of infiltrates, reduction of pain, hyperemia, and swelling. The treatment time for acne was reduced by 2–3 times compared to traditional treatment methods. No complications or adverse reactions were identified. In total, 5–6 procedures are performed per course of treatment with a frequency of 1 time every 5 days.
For widespread acute inflammatory rashes, as well as for long-term, sluggish processes, it is advisable to prescribe intravenous administration of ozonized saline solution (6 to 10 procedures per course of treatment, 1-3 times a week).
It is advisable to carry out repeated courses of subcutaneous injections of acne 1 - 2 times a year, preferably in the autumn-winter period.
Cellulite
The problem of cellulite is one of the most pressing in modern aesthetic medicine. This is a pathology of subcutaneous fatty tissue of a polyetiological nature. Clinically, this pathology manifests itself in the formation of “orange peel”, cellulite “nodules” and “lumps” in areas of the greatest accumulation of subcutaneous fat (under the skin of the thighs, buttocks and abdomen, less often - the legs, shoulders and lumbar region).
The following reasons lead to the development of this pathology:
- Hereditary characteristics of adipose tissue.
- Impaired microcirculation in subcutaneous fat.
- Passive lifestyle.
- Poor nutrition (predominance of animal fats, cholesterol, inorganic salts in the diet).
- Disturbances in the endocrine system.
- Violation of water-salt balance.
According to the latest data, despite the variety of causes that cause cellulite, the main link in the pathogenesis of this disease is a violation of microcirculation. Therefore, subcutaneous injections of an oxygen-ozone mixture, which have recently been actively used to correct cellulite, are an effective, pathogenetically substantiated method of treatment. In addition to its well-known properties as the strongest natural oxidizing agent, which has a powerful bactericidal effect, ozone, when administered subcutaneously, is capable of:
- Improve microcirculation in the skin and subcutaneous fat.
- Promote the transformation of resistant fats into less resistant ones, which makes them easier to burn.
- Activate oxygen-dependent reactions and release oxygen into surrounding tissues.
- Promote the resorption of fibrous membranes surrounding fat cells and forming “cellulite nodules” due to the fibrinolytic properties of ozone.
The following treatment methods are used to treat cellulite:
- Subcutaneous injections of medical ozone combined with intravenous infusion of ozonized solution and massage
No specific features of the regime or special restrictions on the duration of ozone therapy are required. Procedures are carried out 1-2 times a week, a total of 8-10 sessions per course of treatment. After completing the course, the “orange peel” effect disappears, the skin acquires a soft pink tint, becomes smoother and more elastic, and the underlying adipose tissue becomes denser and more compact. The effect remains lasting provided that courses of treatment are carried out 2-3 times a year. A rare complication that was observed is dizziness, which goes away after the procedure within 5-10 minutes.
Aging problems
Skin aging can be stopped and the skin structure restored by neutralizing the pathological processes caused by aging, thus affecting the cause, and not the effect - the appearance of wrinkles. This is precisely the goal of ozone therapy. Ozone has a complex, integral effect on the human body. To treat “aging” skin and wrinkles, local and systemic ozone therapy methods are used: local - subcutaneous administration of an ozone-oxygen mixture and the use of ozonated olive oil in the form of masks and for massage; systemically - intravenous drip infusions of ozonized solutions, major and minor autohemotherapy with ozone. Subcutaneously administered ozone activates the metabolic process, normalizes active membrane transport (K-Na pump), permeability, deformability, viscosity and electrical properties of membranes. In addition, “oxidative stress” is prevented, the activity of the antioxidant defense system is increased and the destructive effects of free radicals are neutralized. The synthesis of proteins, including your own collagen and elastin, is stimulated, and the regenerative capabilities of the germ layer of the skin are increased. The volume of tissue fluid in the deep layers increases and the skin’s natural ability to retain water is restored, and, as a result, “crow’s feet” and deeper wrinkles smooth out and disappear, and a pronounced rejuvenating effect is achieved. The approach to treatment and the choice of techniques are strictly individual. The recommended course of treatment is 4-5 procedures, 1 r/week, a total of 3-4 courses per year.
Alopecia areata
The use of oxygen-ozone therapy in the treatment of alopecia areata has been proposed and pathogenetically substantiated as a method of metabolic action that improves energy in cells and tissues, regulating metabolic processes, in particular aimed at eliminating chronic tissue hypoxia. Oxygen-ozone therapy is carried out to patients in the form of subcutaneous injections of an oxygen-ozone gas mixture directly into alopecia areas on the scalp, with a frequency of 1-2 times a week, 5-7 procedures per course. On average, 2-3 courses of ozone therapy are carried out with a break of 2-3 months.
So, the accumulated experience allows us to conclude that ozone therapy is characterized by ease of use, good tolerance by patients, almost complete absence of side effects and high medical, social and economic efficiency.
Ozone therapy takes its rightful place in the arsenal of modern cosmetology, and once again confirms the postulate, once brilliantly proven with drugs based on botulinum toxin type A - only the dose determines the effect and distinguishes medicine from poison.
You can make an appointment with Anna Nikolaevna Smirnova at the Platinental clinic by phone
Impact zones
Currently ozone therapy is carried out:
- Face, neck and décolleté areas. The entire surface or only problem areas are chipped: wrinkle lines, nasolabial folds, marionettes, crow's feet, forehead, double chin, cheeks, rash areas.
- Bodies. The hips, buttocks, abdomen, waist, sides, chest, legs, knees, forearms, and back are subject to correction.
- The scalp. The method allows you to strengthen your hair and stimulate its growth.
- Joints. Ozone therapy is recommended for arthrosis, arthritis, and osteochondrosis.
The ozone concentration depends on the area of exposure. The highest doses are administered in the treatment of cellulite and inflammation.
Therapeutic properties of the procedure
One of the main properties of oxygen is the ability to react with many elements of the periodic table. It cannot be adjacent to other substances in a cream or mask - the molecules will oxidize before they reach the skin. Therefore, the terms “ozone cosmetics” and “oxygen cosmetics” are just a marketing ploy.
But scientists managed to “tame” ozone and make it work for the benefit of beauty. The effect of this gas on the body for the purpose of healing and rejuvenation is called ozone therapy. Its effect is based on a number of beneficial properties of gas:
- Acceleration of cellular metabolism due to the synthesis of ATP and its subsequent breakdown.
- Destroying pathogenic bacteria.
- Improving blood supply by dilating blood vessels.
- Increasing immunity.
- Relieving pain from injuries or inflammation.
Anti-aging properties are explained by stimulating fibroblast function. These are skin cells that produce structural proteins - collagen and elastin. The elasticity of the skin depends on them. In adulthood, when cellular turnover slows down, fibroblasts produce fewer structural proteins. The skin loses its elasticity. This process cannot be stopped, but it can be significantly slowed down with stimulation.
The skin framework consists of elastin and collagen
More ATP means more energy for cells – more collagen and elastin. This is how we can briefly describe the rejuvenating effect of the procedure.