From this article you will learn:
- keloid scar and hypertrophic scar - what is the difference,
- laser resurfacing of scars: before and after photos, video,
- what is the best ointment for scars?
A keloid scar is the result of excessive growth of scar tissue. It looks like a hard, smooth, tough, nodular growth, often in various shades of red. Many people mistakenly refer to it as “colloidal scar,” which is a grammatically incorrect name.
Keloid scars (keloids) can begin to form immediately after injury or several months later. They can be significantly larger than the original wound itself. Unlike other types of scars, this type of scars/scars never lighten or become invisible over time.
Keloid scar: photo
They occur on any part of the body where there has been damage to the skin, but the following parts of the body are most susceptible to the formation of keloids: chest, shoulders, neck, knees, ankles, earlobes.
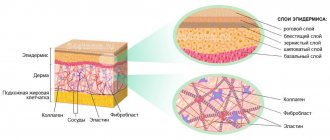
What is a keloid scar and what does it look like?
A keloid scar is a growth of connective tissue in an injured area of the skin. This is a rough, raised red scar that enlarges over time, itches, itches and significantly exceeds the size of the original wound.
External symptoms of the formation of a keloid scar at the site of burns, wounds or surgical sutures appear 2-3 weeks after tissue damage. They may appear as follows:
- the presence of compactions in the healed area;
- discomfort at the scar site, itching, burning or increased sensitivity of the skin;
- the appearance of hard, smooth granules at the site of a healed wound;
- the scar changes color to bright red, blue, purple or, conversely, turns pale;
- the damaged area and discomfort extend beyond the boundaries of the scar.
In the early stages, a bright color of the scar is most often observed, this is due to the fact that collagen fibers actively grow and put pressure on the capillaries and small blood vessels nearby.
Swelling and bruising after blepharoplasty
After almost any operation, swelling and bruising occur in the area of surgical trauma due to the intersection of blood and lymphatic vessels. All patients are concerned about the question of when the swelling and bruising will go away after blepharoplasty, how long they last and how to remove them. As can be seen from the rehabilitation calendar, during the first 3 days the swelling increases and then begins to gradually subside. By 2-3 weeks, most patients already have a presentable appearance. The swelling completely subsides by 6 months. A number of remedies can help remove dark circles under the eyes and swelling:
Lyoton
Gel for external use.
Direct anticoagulant for external use, which has a local antithrombotic, antiexudative, moderate anti-inflammatory effect, accelerates the processes of resorption of hematomas and blood clots and reduces tissue swelling.
traumeel
Ointment for external use. A multicomponent homeopathic medicine, the effect of which is determined by the components included in its composition.
troxevasin
Troxevasin® is a flavonoid (rutin derivative). Has P-vitamin activity; has venotonic, venoprotective, decongestant, anti-inflammatory, anticoagulant and antioxidant effects. Reduces the permeability and fragility of capillaries, increases their tone.
Common places for scarring
Keloid scars form in the décolleté area, on the back, neck, face and earlobes . These areas contain a large number of testosterone receptors, which plays a significant role in the development of keloid. Most often, the formation of such scars is associated with some kind of cosmetic surgery.
For example, after blepharoplasty , a scar forms across the entire length of the upper eyelid and looks like a thin red stripe. If a keloid occurs, it can not only spoil the appearance, but also prevent the eye from closing.
After rhinoplasty - surgical intervention in the nose area - a scar forms near the nostrils, nasal septum, and also in the area of the upper lip.
Another popular operation is mole removal . In this case, a keloid forms if the wound becomes infected after the procedure, or an unhealed crust at the site of the mole is removed ahead of time.
In the décolleté area, keloid scars can appear after mammoplasty, and on the earlobes and other puncture sites - after piercing.
Rehabilitation calendar after blepharoplasty by day
immediately after surgery
At the end of the operation, strips are glued to the eyelid area, and the patient is transferred to a ward, where ice is applied to the periorbital area to reduce swelling.
photo immediately after upper blepharoplasty surgery
As a rule, there is no pain after blepharoplasty. After 1-2 hours the patient is discharged for outpatient observation by a surgeon
first day
On the first day after surgery, the patient is bandaged. On days 1-2-3, swelling begins to increase. It is necessary to make cold lotions with antiseptics.
second day
On the 2nd day in the morning, you can take a single diuretic tablet (only as prescribed by your doctor) to reduce swelling. ъ
the third day
Swelling on day 3 is usually maximum. You are allowed to shower and wash your hair.
fourth day
On the 4th day, the swelling begins to gradually decrease, and the tension in the eyelids goes away.
5 day
During this period, the strips and stitches from the eyelids are removed.
6th day
After the stitches are removed, the strips are stuck on for a few more days.
7th day
By this time, the bruises are almost completely gone, the swelling is significantly reduced.
After a week, the most noticeable swelling in patients goes away, and you can already go to work, although it is optimal to stay at home for up to 2 weeks.
9th day
At this time the strips are completely removed
The swelling is significantly reduced. The suture line is reddish. You can start using cosmetics.
2 weeks
Even at this time, the redness begins to gradually decrease, the swelling continues to decrease.
in three weeks
There is no longer any visible swelling and bruising, patients come to the clinic for routine dressing changes, and they can slowly resume light sports activities.
a month later
You can return to full physical activity.
2, 3, 6 and 12 months
Scheduled control inspections are carried out. They assess the condition of the scars.
Causes of keloid scars
Some people have a genetic predisposition to the formation of keloids, especially blacks. But most often, a scar is formed due to insufficient sterile care of a wound or burn, as well as under the following circumstances:
- with “lacerated” wounds;
- with wound suppuration;
- with strong tension of the skin in the area of injury;
- in case of hormonal imbalance;
- in case of traumatization of an already forming young scar;
- reduced immunity.
The appearance of a scar can be avoided by following the doctor's recommendations, as well as by establishing a healthy diet and rest regime.
Zolotov Sergey Alexandrovich
- Candidate of Medical Sciences, surgeon, specialist in laser surgery.
- From 2003 to 2009 completed training at the State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education "Russian National Research Medical University" named after. N.I.Pirogov Ministry of Health of Russia.
- From 2009 to 2011, he completed his residency at the Moscow State Budgetary Healthcare Institution, Research Institute of Emergency Pediatric Surgery and Traumatology, specializing in Pediatric Surgery.
- In 2011, he completed training under the program of additional professional education of doctors in laser medicine at the State Scientific Center for Laser Medicine of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency of Russia. From 2011 to 2014, he studied full-time graduate school at the Moscow State Budgetary Healthcare Institution Research Institute of Emergency Pediatric Surgery and Traumatology.
He has extensive experience in removing various benign formations of the skin and subcutaneous tissue using laser surgical methods.
More than 5 years of experience in surgery.
Stages of development of a keloid scar
An annoying defect is formed in 4 stages:
- Epithelialization . An epithelial layer forms on the injured area; after 7–9 days it thickens and turns pale. After 2–3 weeks, the damaged area turns red and swells.
- Swelling . In 3–4 weeks, the damaged epidermis thickens. Injured skin takes on a red tint.
- Seal . The injury becomes much denser. A bulge is noticeable on the skin.
- Softening . The scar fades and softens. Pain may occur.
The sooner treatment begins, the sooner and easier it is to get rid of a keloid scar. However, any external medicinal and cosmetic products should be used only after the wound has completely healed.
Care after blepharoplasty of the upper and lower eyelids
After blepharoplasty, patients are prescribed various medications (for example, antibiotics) and undergo physiotherapeutic treatment (lymphatic drainage massage, microcurrents, electrophoresis and ultrasound) for quick recovery.
The speed of rehabilitation after blepharoplasty depends on proper care of the surgical area. It includes a set of measures affecting the skin of the eyelids, suture lines and eyes. It’s worth looking at this in more detail:
seam care
Immediately after the operation, a special patch is glued to the suture area - strips, which act as a protective bandage. They are removed after 5-7 days. For a week, it is necessary to treat the suture line with antiseptics, for example, an alcohol solution of chlorhexedine and apply cool lotions with furatsilin 5-6 times a day for 15 minutes, 3-4 days, then less often, 3-4 times a day (you can use cool bags of brewed tea, medicinal herbs - chamomile, St. John's wort).
eye care
The eyes are not injured in any way during the operation, so they do not require special care. However, wearing lenses is avoided to avoid causing irritation. Very often after blepharoplasty, symptoms in the eye area such as irritation, itching, dryness and redness may be observed.
If the above symptoms occur, you must use special eye drops. They will help you quickly and painlessly get rid of unpleasant manifestations. The most common drugs include:
- Artificial tear;
- Tobrex;;
- Systane.
upper and lower eyelid care
pursues the following goals:
- protects seams from contamination
- accelerates the resolution of edema
- stimulates the wound process and rapid healing
In addition to the recommendations of the plastic surgeon, in the postoperative period, you can perform a special set of exercises for the eyes, which is necessary to improve blood supply to the surgical area, to accelerate the resolution of swelling and reduce the inflammatory process.
Self-massage also helps in restoring the periorbital area. The essence of the massage is that point circular pressure is applied with the fingers in the eyelid area.
Prevention
It is impossible to predict the behavior of a scar after an injury , but you can reduce the risk of keloid scars. Silicone gels and patches can help with this; they help prevent the growth of scar tissue. These methods are effective provided that the scar is fresh (no more than six months). Silicone products help maintain the correct water balance in scarred skin and create additional pressure, due to which the blood vessels in the scar are reduced.
It is recommended to start preventing scar formation after 3-4 weeks, when the crusts have completely come off from the wound. The healing area must be kept clean, washed with soap and under no circumstances remove the stratum corneum from the wound - this will cause infection, and this is a sure way to the formation of a keloid scar!
How to remove keloids surgically
Surgical removal of keloid scars is not often used. Because this is a serious trauma to the scar and most often a relapse occurs later. Excision is performed mainly for rough scars and when it is necessary to remove the width of the scar. This can be done in two ways:
- using a classic scalpel;
- laser removal using a laser scalpel.
The scalpel laser in the treatment of keloid scars is more traumatic. Therefore, it is not recommended in the treatment of this pathology.
The essence of the method is not only to remove the scar, but also to create favorable conditions for wound healing using other methods of prevention and treatment of pathological scars, both before and after surgical treatment.
Possible treatments for keloid scars
Despite the abundance of advice on the Internet, folk remedies cannot get rid of keloid scars; they can only be used in combination with medications, physiotherapy or cosmetology.
The most popular ways to get rid of keloid scars are drug treatment, that is, the use of gels, ointments, creams and injections in combination with physiotherapy, for example, ultraphonophoresis or electrophoresis and the injection of corticosteroid hormones under the skin. Mesotherapy is also effective - injections into the scar tissue of vitamin complexes and medicinal substances that absorb excess collagen and excess hyaluronic acid.
If conservative methods do not give the expected result, then surgery is resorted to.
Drug treatment
Pharmacy and cosmetic products come in different directions:
- contain interferon;
- corticosteroids;
- enzymes or enzyme-containing preparations.
Interferon-containing products inhibit collagen production. In other words, the scar stops growing in size, however, it remains at the stage to which it has grown now. A similar method of treating keloid scars is used after surgery in the form of injections of alpha and beta interferon.
Injections are given every centimeter along the entire length of the scar; the course lasts 4 months.
Corticosteroids can be administered either on their own or in combination with other substances and any therapy. They are injected not into the keloid scar itself, but into the nearest place next to it. This protects from further thickening of the scar, and, despite the course of treatment - 5 weeks, relapses are observed in 20-30% of patients.
To prevent re-formation of the scar, therapy is supplemented with laser or surgical removal of the scar. These methods are very painful and do not exclude relapse (re-formation of a scar). Laser resurfacing requires a long recovery period.
Enzyme-containing preparations break down excess collagen and excess hyaluronic acid - the main components of scar tissue. Due to this, the relief and color of the skin are restored. The scar becomes elastic and its active growth is prevented.
Pressotherapy
The method is more close to prevention than to treatment, but some experts note a positive effect.
Various silicone dressings, bandages and plates are applied to the problem area. It is believed that a scar that is constantly compressed decreases in size. Pressotherapy means include:
- cotton underwear and special bandages (recommended to be worn for six months, made to individual measurements);
- silicone and gel pressure plates;
- gel-based liquids - collodion with polysilicone or silicone.
All this can be found in any orthopedic salon or pharmacy, but this method alone will not be able to completely remove the keloid scar. The pressotherapy method is effective only in complex therapy in combination with other methods of scar correction.
Microcurrent physiotherapy
During the procedure, the body is exposed to a weak current, which stimulates metabolic processes in the tissues of the epidermis, the keloid decreases in size and smoothes out.
Stages of therapy:
- treating the scar with an antiseptic;
- applying a drug that destroys the scar;
- connecting the device, applying electric current to the scar;
- remove remaining medication with a tissue.
The procedure is not difficult to perform, however, there are contraindications to it:
- acute viral diseases;
- poor blood clotting;
- pathologies with the heart;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- neurological abnormalities.
This procedure is considered ineffective compared to other types of physiotherapy. Moreover, it is not cheap.
Radiation exposure
Involves controlled x-rays that destroy fibroblasts within scar tissue. The intensity of the rays is assigned based on the severity of the problem: after all, 90% of the total flow will be absorbed by the epidermis, and only 10% will reach the deeper layers of the skin.
However, therapy is carried out only in combination with other treatment, otherwise the risk of relapse increases by 50%.
Contraindications for use:
- scars on the face, neck and chest;
- oncology;
- kidney diseases;
- impaired blood circulation.
The usual radiation dose is 15–20 Gy. The procedure is repeated once every 2 months, but no more than 6 times.
However, radiation exposure is considered one of the most effective methods in the fight against scars, regardless of the cause of their appearance.
Keloid removal with laser
There are several types of laser resurfacing: argon , carbon and dermabrasion . The purpose of the procedure is to evaporate fluid from the scar's connective tissue, causing it to dry out and shrink in size. Dead cells are removed surgically, and the laser procedure itself is performed under local anesthesia.
Advantages of laser removal:
- during the first session, up to 70% of the scar disappears, which indicates a quick visible result;
- The duration of therapy is from 20 minutes to one and a half hours, depending on the complexity of the problem.
The procedure is quite painful and requires a long period of rehabilitation.
To avoid relapse, doctors advise combining laser with other types of treatment for keloid scars: the use of anti-scar gels will be an excellent assistant on the path to healthy skin.
Cryotechnique
Effect of liquid nitrogen on keloid. It burns out scar tissue cells, in their place healthy skin is formed. The contact time of the scar with nitrogen is 10–30 seconds; in case of an overdose, pigmentation is possible, and there is also a high risk of developing an atrophic scar. You need to be extremely careful with this correction method!
A visible effect is achieved in 1–3 sessions, but for better results cryotherapy is combined with hormonal injections with glucocorticosteroids.
However, for large scars, it is better to combine nitrogen cauterization with surgery. The main disadvantage of the method is pain.
Cosmetology
Cosmetic procedures will help make the scar less noticeable. They will not be able to completely get rid of the scar, but in combination therapy these methods are very effective:
- dermabrasion;
- peeling;
- mesotherapy.
Peeling. With the help of peelings, you can polish the scar, even out the skin texture and eliminate pigmentation. As a result, the skin becomes smoother and the scar more elastic.
Deep dermabrasion - exfoliation of the stratum corneum of the epidermis. The procedure is sensitive and involves the use of hardware technology. The cosmetologist decides how deep and long the session should be.
Mesotherapy - injections of heparin, an immunomodulator or a vitamin complex into the problem area. Has an anti-inflammatory and softening effect.
For small scars, dermabrasion or mesotherapy is recommended, while large and old keloids are removed in combination with drug therapy.
Surgery
Prescribed as a last resort when other therapies are not effective enough. Excision of the keloid is carried out a couple of years after its formation and in several stages:
- a small incision with a scalpel on the scar under local anesthesia;
- the edges of the scar are sewn together with cosmetic stitches for better healing of the incision;
- after resorption of the sutures - hormonal injections and enzyme therapy.
After surgery, prevention against relapse is indicated, because a fresh scar is more amenable to correction. During the rehabilitation period, radiation therapy, injections with immunomodulators and hormones, as well as external agents in the form of gels and ointments are often prescribed.
Price list for medical services of the laser surgery department
Consultation
| Name | Cost in rub. |
| Initial consultation | 2 000 |
Research
| Name | Cost in rub. |
| Cytological examination | 500 |
| Histological examination | 2 800 |
Anesthesia
| Name | Cost in rub. |
| Application anesthesia | 500 |
| Infiltration anesthesia | 500 |
| Conduction anesthesia | 1 500 |
Bandages
| Name | Cost in rub. |
| Adhesive bandage | 300 |
| Aseptic dressing | 500 |
| Bandage with medicines | 1 000 |
Removal of formations using laser radiation
| Anatomical zone | Cost in rub. for 1mm in maximum diameter |
| Scalp | 500 |
| Hands, forearms, feet, legs | 500 |
| Neck, chest, abdomen, back, armpits, shoulders, hips, crotch | 600 |
| Forehead, temporal region, ears, postauricular region | 600 |
| Eyebrows, nose, nasolabial triangle, chin, cheeks, cheekbones, red border of lips | 700 |
| Lower upper eyelids | 850 |
| Ciliary edge of the eyelids | 1 000 |
| External genitalia - single elements* *per 1 mm. 600 rub. | 1 000 |
Removal of papillomas with a diameter of up to 2.0 mm
| Name | Cost in rub. for a unit |
| Neck, chest, abdomen, back, armpits, shoulders, hips, crotch | 300 |
| Lower upper eyelids | 500 |
| Ciliary edge of the eyelids | 1 000 |
Scar treatment
| Name | Cost in rub. |
| Drug injection into the scar | 1 200 |
| Laser dermabrasion (resurfacing) per cm² | 1 200 |
Removal of vascular formations using laser radiation*
| Name | Cost in rub. |
| Photodestruction of the vessels of the wings of the nose | from 5 000 |
| Photodestruction of cheek vessels | from 10 000 |
*exact cost depends on capillary density, repeated stage of vessel destruction minus 30%
Treatment of ingrown toenails using laser radiation
| Name | Cost in rub. |
| Marginal resection of the nail plate | 6 000 |
| Removal of hypergranulations | 1 900 |
| Nail plate removal | 3 500 |
| Complex plastic surgery for ingrown toenails | 8 500 |
Removal of lipoma, atheroma
| Name | Cost in rub. |
| Lipoma removal | 18 000 |
| Removal of atheroma up to 5 mm | 6 000 |
| Removal of atheroma from 5 to 10 mm | 12 000 |
| Removal of atheroma more than 10 mm | 18 000 |
Symptoms
What should you pay attention to if you suspect a colloid scar?
- Smooth and constant growth;
- Change in skin color;
- Pain with pressure;
- Termination of excretory processes and hair renewal;
- Localization in areas characteristic of keloids.
Diagnostics
Photo: stoprodinkam.ru
Diagnosis of a keloid scar consists of examining and taking a piece of tissue for histological examination. An examination using laboratory and instrumental methods is indicated, as well as a preliminary detailed collection of the disease history.
Additional Methods
Common factors predisposing to the development of keloid include hyperandrogenemia. Therefore, all patients undergo blood sampling to determine the content of male sex hormones.
Also required methods are:
- study of thyroid hormones (stimulate the activity of fibroblasts in keloid tissue),
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland,
- studying the condition of the pituitary gland using MRI or x-ray of the skull with examination of the sella turcica,
- determination of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and corticosteroids (cortisone) - their lack also affects the nature of the pathological connective tissue.
To establish a diagnosis, the external manifestations of the scar itself are assessed based on the growth pattern.
Diagnostic criteria for keloid
Keloids are characterized by the following clinical features.
They are formed at the site of extensive skin damage as a result of a burn (thermal, chemical, electric current), after skin incisions, including after any surgery or injury (especially in the presence of a tension factor). Keloid-dangerous areas include the sternum and upper shoulder girdle, as well as the neck, ears and face.
The main external sign is a red-blue ridge protruding above the surface of the skin, its density reminiscent of a cartilaginous structure. It grows for a long time and constantly (several years). The growth of pathological tissue extends beyond the original damage. Does not grow into subcutaneous fat.
In the area of the keloid, itching, burning and pain with pressure and simple touch are often noted.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with hypertrophic scars, which are also pathological.
Biopsy sampling is required in controversial cases to exclude other processes. An objective method would be to study the morphology of cells with a conclusion made by a histologist.
A correctly established diagnosis will allow you to choose the right treatment tactics to reduce the percentage of relapses in the future and improve long-term consequences.