The presence of postoperative scars is considered the main disadvantage of plastic surgery.
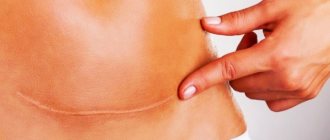
A postoperative scar can have different shapes and lengths. This depends on the breast lift method chosen. So after an anchor breast lift, the scar is much larger than after a vertical or areola lift.
| Typically, a rough scar is a wide scar protruding from the surface of the skin that differs in color from the surrounding skin. In some cases, the scar may be painful to palpation. |
Scars reach their greatest severity by 2-3 months after surgery. During this period, they are most dense, have a scarlet color and protrude above the surface of the skin. If the healing process of scars is not disturbed, then in the future they become less noticeable, lighten, and are compared with the level of the skin, resembling a white thread. It should be remembered that the post-operative scar will still remain noticeable, but since it runs along the bikini line, it can be easily hidden under clothing.
What determines the appearance of scars?
The appearance of scars after any surgery depends on several factors. Among them, the most important are:
- type of suture: the materials and methods that surgeons use to fix the edges of the postoperative incision largely determine the quality of its healing, the thickness and height of the scar;
- location of the incision: if the skin is incised in places of natural folds of the skin or along the border of the areola, the healed scar will be almost invisible;
- quality of postoperative wound care: careful adherence to the surgeon’s recommendations in the postoperative period reduces the risk of inflammation, suture dehiscence and other complications that may affect the appearance of the scar;
- individual characteristics of the body: if a woman has a tendency to form keloid scars, the seams after a breast lift may become convex and contrasting compared to the skin.
Causes of scar formation
There are people whose bodies are not prone to forming scars, and there are those for whom a simple cut is a big problem. This feature can be inherited or indicate a lack of vitamins and health problems.
In the case of mammoplasty, scars are also formed due to skin tension, which is formed as a result of the insertion of implants. After the operation, the incision is sutured, however, during mammoplasty, self-absorbing threads are not used, but with ordinary surgical ones. Therefore, after 10 days they are removed, which is quite painful.
To summarize, the reasons for the appearance of scars after mammoplasty can be as follows:
- Genetics. If you have a family history of keloid scars, chances are you will develop them too. But it is difficult to predict the outcome before surgery.
- Professionalism and experience of the surgeon. The breast tissue is dissected layer by layer and then carefully stitched together. If stitches are applied carelessly, the skin becomes rougher.
- Threads for seams. Self-absorbing threads provoke aseptic inflammation and scarring. Therefore, the doctor uses materials that require further removal, but do not give such side effects.
- Incorrect electrocoagulation. To prevent bleeding, the capillaries are “sealed”, but this can only be done on the inner layers of the dermis.
What types of seams are there?
Modern surgery has at its disposal various materials for fastening the edges of a postoperative wound to each other. The most common and reliable option is classic surgical sutures. They are made using a special needle and special thin but strong threads made of lavsan, vicryl, catgut and other materials. The tissues are sutured in layers, and a cosmetic suture is used for the skin. Thanks to a special technique, after the wound heals, a thin, barely noticeable line is formed, which is not noticeable at all. It is this technique that is used at the GALAXY Beauty Institute.
There are also fixation methods using surgical glue and metal staples, but they have not found use in plastic surgery because they do not provide sufficient reliability or aesthetics.
Indications for scar surgery
The main indication for surgical correction and excision of scars is mature, unaesthetic skin formations. Reconstructive surgery is necessary if:
- the scar is fully formed;
- objectively worsens appearance;
- brings social and psychological discomfort;
- the scar gradually grows, enlarges, and becomes more noticeable - this is a feature of keloid formations.
Surgical excision of scars is the only effective method when it is necessary to remove rough, repulsive, formed defects as a result of serious injuries and burns. After surgical removal, virtually no traces of damage remain.
Where are the stitches located after breast surgery?
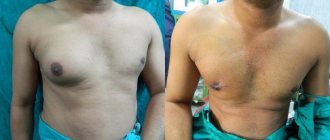
To perform a high-quality breast lift, the surgeon needs good access to the tissue. The larger the volume of the operation, the more incisions are required to be made. Depending on the initial bust size and the chosen lifting technique, doctors use:
- periareolar incision: passes at the border of the skin and areola, used for a small amount of intervention;
- vertical: in addition to the circular incision, the doctor cuts the tissue vertically down from the areola to the inframammary fold;
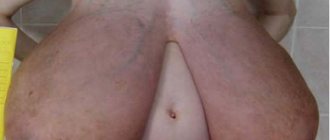
- anchor: periareolar and vertical incisions are complemented by a horizontal one, which runs in the fold under the mammary gland.
Anchor incisions provide the surgeon with the highest quality access to tissue, which is why this technique is used when there is a significant volume of the mammary gland.
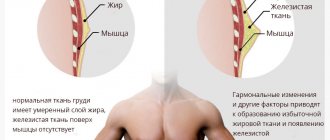
What is fibroadenoma?
Fibroadenoma is a benign tumor that develops against the background of inadequate production of sex hormones, so it is predominantly found in young women. The peak incidence occurs at the time of entry into menopause - approximately 45 years. The end of menstruation leads to involution of the glandular tissue, and benign processes are becoming less common, and cancer is developing much more often.
All hyperplastic processes in the organs of the female reproductive system are controlled by the ratio of estrogen and progesterone, therefore, when a woman has a hormonal imbalance, mastopathy, endometrial hyperplasia, uterine fibroids and benign breast tumors often coexist in one set or another.
To the touch, fibroadenoma has clear boundaries, an even and smooth surface, and dense. It never fuses with the skin, being located inside the gland tissue, it is easily displaced and painless. The size of the tumor node is variable; as a rule, in a small breast it is possible to feel a centimeter-long nodule.
Options for breast fibroadenoma:
- inside the duct - intracanacular, which began to grow in the wall, gradually narrows the duct, involving nearby glandular lobules;
- near the duct - the pericanacular grows around, “twisting” the layers like the rings of a tree trunk, while the lumen of the duct does not change;
- mixed - the vast majority, almost eight out of ten fibroadenomas.
Different tumor variants do not differ in symptoms or course, and therefore have no practical significance in practical medicine.
A benign tumor does not threaten to degenerate into cancer, but breast cancer can develop, masquerading as a fibroadenoma. Early cancer and a small benign nodule are difficult to distinguish even on a mammogram, so all neoplasms in the mammary glands must be subjected to a fine-needle biopsy and removed if there is doubt about the benignity of the microscopic picture.
How is the recovery period after a breast lift?
Immediately after applying the last sutures, the mammary gland is securely fixed using compression garments. It is important not to take it off day or night for 4 weeks, and then wear it only during the day for a while longer. The exact timing is determined by the surgeon, who monitors the healing and restoration of tissue.
In the first days after breast surgery, the sutures are covered with a sterile bandage to prevent contamination and infection of the postoperative wound. While the woman is in the hospital, dressing and treatment are performed by the clinic staff. After discharge, the woman must continue care on her own. The dressings are changed at least once a day (more often if they are dirty or wet), and the scars are treated with an antiseptic: fucorcin, brilliant green or other drugs.
Until the wounds heal, a woman should not take a shower or bath, visit a pool or swim in open water. For six months you must refrain from intense sports and other types of physical activity. It is important to understand that any trauma to the postoperative suture can cause a wider and more noticeable scar to appear.
When does a stitch not heal after a mastectomy?
The speedy healing of wounds depends on the progress of the operation, the location of the tumor and the degree of its development, the professionalism of the surgeon and compliance with his instructions.
What to do to make the scar heal:
- Wear compression garments and change bandages regularly.
- Use only medications prescribed by a specialist.
- Avoid overheating, hypothermia, swimming, sunbathing, overload.
- Treat wounds with antiseptic agents and sterile materials.
Types of postoperative scars
Each organism is individual. The condition of the skin and subcutaneous tissue, the speed of tissue regeneration processes - all this determines the appearance of the postoperative scar. He can be:
- normotrophic: the former incision line has a lighter tone compared to the rest of the skin, does not rise above its surface;
- hypertrophic: the scar is pink and slightly raised above the surface of the skin; this is a normal condition of the tissues, if only a few months have passed after the operation, with proper care the scar evens out and fades within six months to a year;
- keloid: a voluminous, rough scar with a bright color, the condition occurs when regeneration processes are disrupted and excessive tissue formation; requires long-term treatment using hormones, cosmetic procedures and even the help of surgeons.
When can restoration be considered complete?
If the rehabilitation goes well, then after 6 months the traces of the operation are almost invisible. A plastic surgeon may allow beach holidays, visits to baths and saunas. But it is better to postpone tanning after mammoplasty for 1 year, since there is a risk that the scars will darken. During this time, your breasts require special care. It is necessary to remember about regular examination by a mammologist once every six months. Practice shows that complications after mammoplasty, if they appear, occur within the first 6 months. At the end of this period, we can say that the operation was indeed successful and the recovery is complete.
How to speed up the resorption of scars after breast surgery
Is it possible to speed up tissue healing and scar resolution? On the Internet you can find a lot of advice on this matter, both adequate and not so adequate. The main thing is to understand that not all recommendations are effective and safe, and before using this or that product you should definitely consult with a surgeon.
General recommendations that can somewhat speed up tissue restoration include the simplest tips: a balanced diet with a sufficient amount of vitamins, adequate water regime, wearing properly selected underwear that does not injure or chafe the skin, etc. If prescribed by a doctor, you can use Contractubex ointment, which promotes the resorption of scar tissue. It is important to remember that all creams, including moisturizers, can only be used after the wound has completely healed.
If you want your breasts to be beautiful and natural-looking, without scarring to remind you of the surgery, choose your surgeon wisely. At the GALAXY Beauty Institute you will find experienced doctors, high-quality consumables, comprehensive care in the early postoperative period and regular monitoring during rehabilitation. A beautiful bust is real!
Correction of sutures after mammoplasty by cosmetology
If prevention does not protect against scars after mammoplasty, many patients turn to a cosmetologist for help.
The following procedures will help solve the problem:
- peeling with fruit acids;
- cryotherapy;
- microdermabrasion;
- laser resurfacing;
- steroid injections into the scar.
Each of these methods involves additional trauma to the skin . Thus, an injection into the damaged area will leave a hole from a syringe needle, cryotherapy involves cauterization with nitrogen, which causes necrosis of scar cells, and peeling simply cuts off the upper layer of the epidermis - a painful procedure that requires a rehabilitation period. The operating principles of laser resurfacing and microdermabrasion are similar to the work of peeling: in microdermabrasion, the crystal particles that remove the epidermal layer are simply smaller, and in laser resurfacing, their role is played by a laser beam.