from 320,000 rub.
Cost of the operation
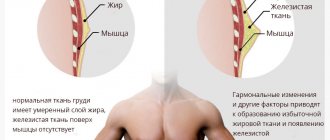
If a woman is not satisfied with the natural volume or shape of the mammary glands, endoprosthetics - breast surgery using implants - will help correct the situation. Augmentation mammoplasty enjoys well-deserved popularity among women of all ages, allowing to eliminate such disadvantages as:
- underdevelopment (lack of volume) of the mammary glands,
- pronounced asymmetry of the mammary glands,
- lack of breast volume due to loss of skin tone (usually after childbirth and breastfeeding),
- absence of mammary glands (usually associated with the removal of tumors due to breast cancer).
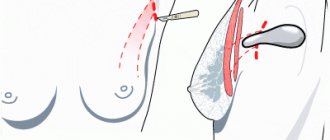
A breast augmentation implant is placed in a “pocket” formed from tissue under the pectoral muscle or directly under the gland. Implant placement can also be done through several types of access. The main (most common) are:
- submammary,
- transareolar,
- transaxillary.
Of course, each access has its own specific features and its own scope of application.
Submammary access
The incision in this case is no more than 5 centimeters long and is located in the natural fold under the breast (submammary fold). Submammary access allows you to perfectly accurately form a symmetrical “pocket” for placing an endoprosthesis. The breast tissue is not affected; there are no restrictions on the use of round or anatomically shaped implants with this type of access. The implant can be freely installed both under the muscle and under the gland.
In total, the main advantages of this access:
- simple, versatile and safe,
- allows the surgeon to gain full control of the position of the endoprosthesis.
The disadvantage of this method is that in patients with an insufficiently pronounced inframammary fold, the postoperative scar may be very noticeable.
Method for forming a submammary fold
The invention relates to medicine, namely to oncology. Before the operation, the future submammary fold is marked with the patient in an upright position. In this case, the markings are made 1.5-2 cm higher than the opposite submammary fold. A liposuction area is marked 2 cm above and below the marking line, liposuction is performed from two approaches along the edges of the submammary fold being formed and fatty tissue is removed from the dermis to dense tissues. Then, in the projection of the submammary fold, dense underlying tissues (fascia, periosteum) are exposed from several accesses no more than 2 cm long and the skin is fixed to the underlying dense tissues with submerged sutures using non-absorbable suture material, and the formation of the submammary fold is completed by layer-by-layer suturing of the accesses. The method allows you to restore the shape of the reconstructed mammary gland more closely to the natural one. 5 ill.
The present invention relates to the field of medicine, namely to oncology, reconstructive surgery, and can be used in a complex of rehabilitation operations for breast reconstruction.
Available sources of information have not identified identical technologies for the formation of a submammary fold. After breast reconstruction, for example, with a TRAM flap on a pedicle (rotational version of the flap), there is no submammary fold, which is destroyed during surgery when forming a channel for passing the flap from the abdomen to the chest wall. The absence of a submammary fold causes dissatisfaction among operated patients, as it reduces the naturalness of the reconstructed breast (1, 2, 3).
Based on the existing level of technology for breast reconstruction, the task was set to ensure the restoration of the shape of the reconstructed breast closer to the natural one.
The problem was solved as follows.
The formation of a submammary fold is carried out as follows: before the operation, the future submammary fold is marked with the patient in an upright position. Then maximum liposuction is performed in the marking area. After this, in the projection of the submammary fold, dense underlying tissues (fascia, periosteum) are exposed from several approaches no more than 2 cm long and the skin is fixed to the underlying dense tissues with submerged sutures using non-absorbable suture material. The formation of the submammary fold is completed by layer-by-layer suturing of the approaches.
We explain the essential distinctive features of the proposed method.
Performing maximum “aggressive” liposuction in the area of the markings allows you to reduce the amount of fatty tissue, similar to what it looks like in the place of the natural submammary fold.
Exposure of dense underlying tissues (fascia, periosteum) in the projection of the submammary fold from several approaches no more than 2 cm long and fixation of the skin to the underlying dense tissues with submerged sutures and non-absorbable suture material ensures the formation of a durable scar, which subsequently creates the naturalness of the formed submammary fold.
Completion of the formation of the submammary fold by layer-by-layer suturing of the approaches is necessary to give the postoperative scars a cosmetic quality.
The essence of the proposed method for forming a submammary fold is as follows.
The formation of an inframammary fold is carried out as follows: before the operation, the future inframammary fold is marked with the patient in an upright position, and the marking is performed 1.5-2 cm higher than the opposite inframammary fold. The liposuction area is marked 2 cm above and below the marking line. Then, on the operating table, maximum “aggressive” liposuction is performed in the marking area with a curved cannula with a diameter of 3-4 mm. Liposuction is performed from two approaches along the edges of the formed submammary fold and fatty tissue is removed from the dermis to dense tissue (Fig. 1, a). After this, in the projection of the submammary fold, from several accesses no more than 2 cm long, dense underlying tissues (fascia, periosteum) are exposed and the skin is fixed to the underlying dense tissues with submerged sutures using non-absorbable suture material (prolene 2-3-/0) (Fig. 1, b ). The formation of the submammary fold is completed by layer-by-layer suturing of the approaches (Vicryl, Monocryl 4/0).
The proposed method is illustrated by drawings, where
in figure 1, a - the stage of liposuction and marked incisions along the formed submammary fold, b - diagram of the application of fixing sutures;
Fig.2 - photographs of patient M. are presented after mastectomy of the left breast;
Fig.3 - the state of the left mammary gland of patient M. before the formation of the submammary fold: a - front view, b - side view on the right, c - side view on the left, d - with arms raised up;
Fig.4 - the condition of patient M. after the formation of a submammary fold: a - front view, b - side view on the right, c - side view on the left, d - with arms folded back;
Fig.5 - the condition of patient M. after the formation of the nipple-areolar complex: a - front view, b - side view on the right, c - side view on the left.
The essence of the proposed method is presented by a clinical example.
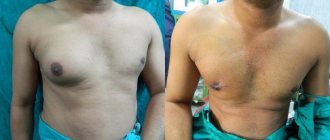
Patient M., born in 1955, was treated at the Irkutsk Regional Oncology Center in 2002 for left breast cancer, stage 2 A, T2N0M0. After the mastectomy according to Maden, 4 courses of adjuvant polychemotherapy according to CAF were carried out (Fig. 2). In 2005, i.e. After 3 years, the patient turned to the Scientific Center for Reconstructive Surgery of the Eastern Scientific Center of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences with a request to restore the lost breast.
On February 15, 2005, she underwent delayed plastic surgery of the left breast with a rotational TRAM flap. The postoperative period passed without complications (Fig. 3a, b, c, d).
The patient did not stop at the stage of acquiring tissue volume on the left half of the chest. She insisted on several corrective surgeries. She was primarily concerned about the absence of the inframammary fold and the nipple-areolar complex.
On September 20, 2005, the formation of a submammary fold was performed using the proposed method.
Before the operation, with the patient in an upright position, the future inframammary fold of the left breast was marked 1.5 cm higher than the position of the inframammary fold of the right breast. Then, 2 cm above and below the existing markings, the liposuction area is outlined. On the operating table, maximum “aggressive” liposuction was performed in the marking area from two approaches along the edges of the formed submammary fold with a curved 3 mm cannula, removing adipose tissue from the dermis to the fascia and periosteum. After this, incisions were made in the projection of the submammary fold from several accesses no more than 2 cm long, the fascia and periosteum were exposed, to which the skin was fixed with submerged sutures using non-absorbable suture material - prolene 2-3-/0. The formation of the submammary fold is completed by layer-by-layer suturing of the access points with vicryl.
The result is stable (Fig. 4a, b, c, d).
Then, on November 8, 2005, mastopexy was performed on the right according to Lejour. Plastic surgery of the nipple-areolar complex on the left according to Little (Fig. 5a, b, c).
The patient is satisfied with the result. He insists on a slight correction of the shape of the right gland.
Thus, the proposed method of forming a submammary fold, in comparison with known technologies, makes it possible to restore the shape of the reconstructed mammary gland closer to the natural one.
Sources of information taken into account
1. Schusterman MA, Kroll SS, Weldon ME Immediate breast reconstruction: why the free TRAM over the conventional TRAM flap? // Plast. Reconstr. Surg. - 1992. - Vol.90, No. 2. — P.255-261.
2. Gherardini G., Arnander S., Gylbert L., Wickman M. Pedicled compared with free transverse rectus abdominis myocutaneous flaps in breast reconstruction // Scand. J. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Hand. Surg. - 1994. - Vol.28, No. 1. — P.69-73.
3. Xu X., Maillard GF Breast reconstruction by abdominis musculocutaneous flap // Chung. Hua. Wai. Co. Tsa. Chih. - 1995. - Vol.33, No. 2. — P.117-118.
A method of forming a submammary fold, characterized in that before the operation, the future submammary fold is marked with the patient in an upright position, while the marking is performed 1.5-2 cm higher than the opposite submammary fold, the liposuction zone is marked 2 cm above and below the marking line , perform liposuction from two approaches along the edges of the formed submammary fold and remove fatty tissue from the dermis to dense tissues, then in the projection of the submammary fold from several accesses no more than 2 cm long, expose dense underlying tissues: fascia, periosteum and fix the skin to the underlying dense tissues with submersible sutures with non-absorbable suture material, the formation of the submammary fold is completed by layer-by-layer suturing of the approaches.
Transareolar access
An incision made in the area of the areola (around the nipple) allows for a completely invisible post-operative scar. It is permissible to install round or teardrop-shaped implants under the gland or under the pectoral muscle. A significant drawback of the method is that during penetration, the breast tissue is dissected, and subsequent damage can provoke lactation disorders (up to the impossibility of breastfeeding). A limitation to the use of this method is the size of the areolas: if the patient has miniature areolas, the surgeon will not be able to make an incision around the nipple long enough to install the prosthesis.
A little theory
Everyone has small nasolabial folds - it's a fact! But it’s one thing when they appear from a smile or laughter - at that moment we are so beautiful that no wrinkles can spoil our beauty! And it’s quite another thing when the insidious nasolabials begin to feel like full-fledged mistresses and confidently restore their order to our faces. Then, instead of beautiful and cheerful us, someone is reflected in the mirror, someone who is always gloomy and tired.
Forbidding yourself to smile is not an option at all. There are too many good moments in life that deserve laughter, and a smile is too beautiful to lose it! What to do? Relax tissues and restore muscle tone!
Transaxillary access (endoscopic technique)
This access is located in a natural fold in the armpit area and allows you to completely hide the fact of the intervention (the incision quickly becomes invisible).
It is also important that the breast tissue is not affected. Transaxillary access allows you to install implants of any shape in any way.
The main disadvantage of the transaxillary approach is the complexity of execution. Despite this, this option remains preferable.
Anton Igorevich Zakharov performs various plastic surgeries in Moscow, and over the years of practice he has acquired vast experience in this field. Endoscopic breast augmentation (enlargement with transaxillary access) is one of the main specializations of Dr. Zakharov
Correction methods
Surgery to eliminate double breast folds requires general anesthesia. Access to the prosthesis is made at the site of the previous incision. The scale of the manipulations performed varies greatly and is determined by the reasons for the defect being corrected:
- Capsulorrhaphy.
If the implant has been displaced, then as part of the re-intervention, the boundaries of the pocket are changed by performing capsulorrhaphy - it expands, and the endoprosthesis is moved into this area. In some cases, additional dissection may be required. This operation is performed both with and without breast implant replacement. - Reendoprosthetics.
To avoid thinning of the implant cover, some surgeons resort to pre-strengthening it with alloderm. If this was not done during the primary breast surgery, one of the possible options is subpectoral endoprosthetics. - Breast lipofilling.
In some cases, the problem is solved by performing lipofilling, when the deficit in adipose tissue volume is compensated by introducing autologous fat grafts. The procedure involves preliminary collection of biomaterial from the inner surface of the thigh, back or abdominal area directly from the patient herself. After this, purification in a centrifuge and subsequent injection of fat cells into the recipient area.
Regardless of the techniques used, repeated mammoplasty is aimed at giving the mammary glands an aesthetic appearance, creating symmetrical submammary folds, eliminating waves and other defects. If necessary, the intervention can be supplemented with one-stage mastopexy.
Why do they go deeper
There are many reasons. These include heredity, malocclusion, features of facial anatomy, and too dry skin. In many cases, our habits and actions lead to the deepening of nasolabial wrinkles: incorrect posture, excessive weight gain or loss, stress and lack of sleep, improper skin care, insufficient ultraviolet protection and others.
For example, with low pressure, tissues can hang sluggishly due to the lack of adequate blood supply and a decrease in turgor (elasticity), and with structural features of the face - a short upper jaw from birth - soft tissues cannot take an anatomically correct position and “fall” down. But even in such cases, with the help of Revitonics you can significantly reduce creases and wrinkles. It is also worth mentioning the nasolabial ridges - defects that form a kind of lymph pocket in which excess fluid accumulates. This change develops due to muscle hypertonicity.