Premature puberty in girls
To successfully stop early puberty in girls, it is necessary to clearly understand the reasons that led to it, and in order to find out the cause, it is necessary to understand the processes that occur in the child’s body at different stages of its development.
Parts of the brain such as the pituitary gland and hypothalamus are responsible for the production of most hormones that influence puberty. It is in the hypothalamus that gonadotropin-releasing hormone is produced, which in turn affects the processes occurring in the pituitary gland, and it begins to secrete large amounts of LH and FSH. Luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hormones trigger the production of female sex hormones estrogen in the ovaries. Thus, the body begins to change and prepare for puberty.
If factors appear that begin to influence the hypothalamus, pituitary gland or ovaries, then the secretion of hormones may begin earlier, triggering the process of puberty. The reason for this may be damage or disease of the nervous system, the presence of tumors in the brain, and more.
Classification
The main forms of premature sexual development in girls are:
central (gonadotropin-dependent);
· peripheral (gonadotropin-independent);
· partial.
The central or true form is caused by large production of gonadotropic hormones in the pituitary gland. They stimulate the sex glands, and the maturation process starts. The reason for their early action is usually brain tumors, damage to the nervous system or gene mutations. Very often it is not possible to identify the exact cause of the gonadotropin-dependent form.
The peripheral form occurs due to malfunction of the adrenal glands or the formation of tumors in the adrenal glands and gonads. The causes of dysfunction of the adrenal glands can be gene mutations and advanced hypothyroidism (lack of thyroid hormones).
The gonads, which are the glands of the reproductive system, have a great influence on human sexual functions; they are capable of producing sex hormones and gametes (sex cells).
The partial form of early maturation in girls is expressed in the premature maturation of one organ or link. For example, premature development of the mammary glands without other signs of puberty. In this case, the problem most likely lies in excess production of FSH due to disruption of communication between the pituitary gland, hypothalamus and gonads. Also, only the growth of pubic hair in a girl can be observed; this condition is associated with the early maturation of certain areas of the adrenal cortex responsible for the production of the hormone DHEA-S.
Diagnostics
Self-diagnosis is an external examination. The boy should stand directly in front of the person examining him. Outwardly, it can be seen that the breasts can increase by about ten to fifteen centimeters. The breasts may swell and gain significant weight.
One or both glands are affected. The nipple can also be enlarged to a diameter of approximately three to four centimeters.
The breasts may be tender to the touch, and your teen may feel heaviness, burning, and throbbing from the inside. A lump may also be felt in the chest. The glands may become more sensitive.
Sometimes colostrum is released from one nipple. It is a white liquid similar to milk.
At the advanced stage there are:
- Severe pain on palpation.
- Bloody discharge from the nipple or its shape.
- The axillary lymph nodes are significantly enlarged and cause discomfort.
- Changes in the condition of the skin on the chest (appearance of rashes, ulcers).
Call your doctor if your teen has swollen breasts. During a medical examination, the doctor discovers that the breast size does not correspond to the boy’s age.
The doctor is also required to conduct an examination, including palpation of the breasts and testicles. To find out about the genetic characteristics of the body, you must undergo an interview.
Hormone therapy is prescribed or a decision is made about surgery.
Treatment, with the exception of surgery, consists of observing the rules of personal hygiene. This is necessary to prevent infection from entering the body.
Therapy consists of:
- Uses hormones to balance their levels in the body. Relies on a complex of vitamins and sedatives.
- Schedule a date for physical therapy.
- Use of folk remedies.
- Diet (if the problem is obesity).
- Surgical intervention is the removal of the glands and fat layer, followed by rehabilitation and drawing up a list of recommendations from the surgeon. It is performed if a breast tumor is suspected.
In the absence of pathologies, the operation is performed for cosmetic purposes if treatment with hormonal drugs is ineffective.
Every person is endowed with a so-called biological clock. Its job is to regulate the growth, development and functioning of a person. The body is at different stages of life.
Signs of early puberty
Puberty is characterized not only by physical changes in a girl, but also by changes in her emotional and psychological health, so parents should pay attention to the general well-being and behavior of their child so as not to miss changes.
The main physical signs of the onset of puberty in a girl are:
· the mammary glands increase in volume, nipple enlargement, their deformation, etc. may be observed;
· with puberty, girls begin to grow pubic and armpit hair;
· the formation of a female figure type occurs (the hips are rounded, the waist appears);
· the arrival of the first menstruation (during this period it does not have to be monthly);
· appearance of the smell of sweat;
· Acne may appear on the face and other parts of the body.
An important symptom may be a sudden growth spurt in a child. This is due to the fact that during puberty the amount of hormones in the body increases significantly, which give impetus to growth hormone, which promotes bone growth.
Treatment and prognosis
Treatment of young children is always a very big responsibility, therefore, before prescribing treatment, all kinds of diagnostic procedures and consultations with specialists in various fields are carried out. The main thing is to correctly determine the cause of isolated thelarche, so that treatment is aimed not at relieving symptoms, but directly at the cause that caused them.
The most common reason is problems with hormonal imbalance, in which case either hormonal drugs or their substitutes, antihormonal drugs, are prescribed. Usually, non-hormonal herbal preparations are enough to help the patient. Under no circumstances should you prescribe or discontinue medications on your own; this should be done by a doctor based on medical indications and expediency.
Hormonal medications may be prescribed to a child if non-hormonal therapy does not help and the disease progresses.
The prognosis if you consult a doctor in a timely manner and follow clinical recommendations is favorable, all symptoms may go away, and the child’s development will proceed as expected, but you will have to constantly monitor your health and visit a doctor. If the problem is neglected, then at such a young age it can lead to various disorders of organs and tissues:
- degeneration of breast tissue, formation of cysts, etc.;
- isolated thelarche can develop into general precocious maturation, which will disrupt the child's development process and lead to unforeseen consequences for the entire organism.
Diagnosis of PPR in girls
There are several basic procedures for identifying PPR in girls under 8 years of age; they are prescribed by a pediatrician or pediatric endocrinologist after examining the child and collecting an anamnesis. During the examination, the doctor assesses the degree of puberty and bone growth, and measures the patient’s overall height.
The main studies to confirm or refute the diagnosis are:
X-ray to determine bone age;
Ultrasound examination of the pelvis and some glands;
· in certain cases, an MRI of the brain may be indicated (performed to evaluate the functioning of some of its parts, which produce the main hormones that affect maturation);
· blood test for the concentration of gonadotropic hormones.
Specialized tests are listed above, but in addition to them, blood tests for sex hormones (testosterone, LH, FSH, prolactin, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate, 17-hydroxyprogesterone) and thyroid hormones, as well as general and biochemical analysis can be prescribed.
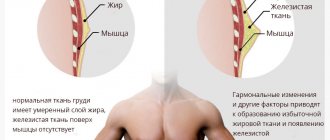
Treatment of gynecomastia in adolescents
Physiological gynecomastia in adolescents does not require treatment.
But the doctor evaluates the degree of mammary gland enlargement, the causes of possible pathology and concomitant diseases. If the increase in volume is significant, then surgical treatment of gynecomastia is carried out at an early age, so that psychological trauma and personality deformation do not occur due to appearance. Treatment of gynecomastia is mandatory if:
- fibrosis of breast tissue occurs over time;
- symptoms persist for more than 3 years;
- Gynecomastia is symptomatic and is a manifestation of other diseases.
If the doctor focuses on the clinical forms of persistent gynecomastia, then he can use conservative therapy. For the normopubescent variant of gynecomastia in a teenager, thiamine bromide (Vitamin B1) is prescribed. It blocks aromatase and reduces the intensity of the conversion of androgens to estrogens. In some cases, antiestrogenic drugs are indicated:
- clomiphene citrate;
- tamoxifen;
- toremifene.
In patients with hypopubertal type of gynecomastia, anabolic steroids are prescribed in combination with halidor to enhance testosterone synthesis. It suppresses the production of serotonin and enhances the effect of androgens. For the hyperpubertal type of gynecomastia, vitamin B6 is required, which enhances the activity of dopamine receptors. Bromocriptine is prescribed under the control of blood prolactin levels. For gynecomastia associated with hypogonadism, hormone replacement therapy with testosterone preparations is prescribed. In some cases, human chorionic gonadotropin is used. If hypogonadism is associated with Klinefelter syndrome, a teenager from 13-14 years of age is prescribed a long-acting form of testosterone to stimulate the development of secondary sexual characteristics. In this case, the manifestations of gynecomastia are significantly reduced, and surgery can be avoided. If symptomatic gynecomastia is diagnosed late, a significant amount of fibrous tissue appears in the mammary gland, so regression becomes impossible. The only treatment option is surgery. To get rid of gynecomastia, a subcutaneous mastectomy is performed. The areola and nipple are preserved. The operation has a good cosmetic effect. With a mixed type of gynecomastia, mastectomy is sometimes supplemented with liposuction. Recovery after surgery is short. The patient is given a bandage that must be worn for 2 weeks. The incision is made under the areola, so after healing, the scars are invisible.
Treatment of PPR in a girl
Treatment is prescribed depending on the cause and type of premature puberty. Usually, if early puberty in girls does not deviate by more than a year, then no special treatment is required, only constant monitoring and diagnosis of the condition is prescribed.
For example, treatment of the central type of premature maturation is decided in each case individually. On the one hand, it is necessary to allow the bone tissue to develop independently, and on the other hand, it is necessary to take into account the child’s condition, his psycho-emotional health and the appropriateness of the treatment itself. When making a decision, an experienced doctor will rely on the age and degree of puberty at which the girl is, how quickly the maturation process is moving and, most importantly, the emotional state of the child and his readiness for puberty.
If a decision is made to carry out treatment, then it consists of taking special drugs that will block the production of rapidly secreted hormones or drugs that will balance the balance in the hormonal system.
Extremely rarely, the cause of PPR may be a tumor in one of the parts of the brain, which affects the secretion of hormones in them. In this case, it is better to perform an operation and remove the formation.
Which doctor should I contact?
If PPR is suspected in girls, it is better to immediately consult a specialist rather than adopt a wait-and-see approach. Early detection of a problem promises its complete and speedy elimination than advanced cases.
I, Romanov Georgy Nikitich, are an endocrinologist. My experience is over 20 years and my knowledge is extensive. I studied not only in Belarus and Russia, but also in European countries such as Great Britain and Germany. I know classical and modern methods of treating many diseases.
You can make an appointment with me at a medical office in Gomel or sign up for a paid online consultation in one of the messengers: . As part of an online consultation, I can assess the existing symptoms and recommend the necessary studies, adjust treatment, or evaluate diagnostic results and prescribe therapy.
Breast asymmetry
Breast asymmetry: causes, types and methods of correction
Our bodies are not symmetrical.
For some, the tip of the nose “looks to the side”; for others, the entire back of the nose is curved. Many men are characterized by uneven muscle development; in particular, the muscles of the back or chest on the left or right may be developed a little more than on the opposite side, and even intense strength training cannot correct this. Considering the imperfection of our bodies, slight breast asymmetry should not cause concern or psychological complexes. This is a common, normal phenomenon that does not require surgical correction. A slight lag or advance of one mammary gland in development has practically no effect on the aesthetics of the body, just as it does not affect the sexuality, charm, charm and attractiveness of a woman.
Only severe breast asymmetry of the second or third degree can be considered a real problem. You will learn from the proposed material how an aesthetic defect can manifest itself, what causes it, and what can be done.
Causes of breast asymmetry
All the causes of the aesthetic problem under consideration can be divided into three groups. Let us focus on the fact that the problem of bust disproportion is of an aesthetic nature. It does not threaten a woman’s health, but the exception is cases when a violation of proportionality is caused by the development of a pathological process.
The first group of reasons is associated with a hereditary factor. Genetic characteristics determine the rate of development of the mammary glands. It often happens that the development of one mammary gland is faster than the development of the other. It is impossible to explain the phenomenon, but it is reliably known that some degree of breast asymmetry is typical for 80% of women. If you find that your breasts are not symmetrical, know that you are far from alone.
The second option is post-lactation asymmetry of the mammary glands, the causes of which should be sought in the characteristics of breastfeeding. It often happens that a baby or toddler, for completely unknown reasons, prefers the left or right breast. Perhaps everything is explained by the better development of the milk ducts, thanks to which it is easier to suck milk from one breast than from the other, but for obvious reasons no scientific work has been carried out on this issue.
If a woman more often places her baby on the left or right breast, after breastfeeding is completed, the development of breast asymmetry cannot be ruled out. It can manifest itself in different ways. In some women, differences in the size of the mammary glands appear; in other women, the glands and/or nipple-areolar complexes are stretched and located at different levels.
The third group of causes of mammary gland asymmetry is pathological formations. It is not at all necessary that the cause of the problem is a malignant tumor. It is much more likely to encounter fibrocystic mastopathy, that is, a benign neoplasm. The development of a tumor process may be indicated by the appearance or increase in the severity of breast asymmetry after the age of 30-35 years without a clear connection with the lactation period.
If breast asymmetry appears after the age of 30, you must undergo a mammogram and consult a mammologist.
The development of fibrocystic mastopathy may be indirectly indicated by a difference in the size of the mammary glands, an unexplained enlargement of one breast, as well as a feeling of discomfort, pain, and the presence of compaction in the tissues. If such symptoms appear, a woman should consult a specialist. After diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe treatment, which can be either medicinal or surgical.
Types, types and degrees of breast asymmetry
Further sections of this publication are devoted to those variants of breast asymmetry that are in no way related to the tumor process and can be the subject of aesthetic correction.
Asymmetry of the mammary glands, which develops in adolescence or after completion of lactation, can be hypertrophic or hypotrophic. In the first case, the decisive role in the appearance of the defect is played by the excessive development of one breast. In the second option, one mammary gland is characterized by normal development, and the second - insufficient.
Depending on the severity of hypertrophy or hypotrophy, three degrees of breast asymmetry are distinguished:
- Mild: the glands differ slightly.
- Moderate breast asymmetry: the difference in volume reaches a third of the size.
- Heavy: the left or right breast is twice the size of the other.
If there is slight disproportion, there is no need to do anything, since it does not affect the aesthetics of the body. As mentioned earlier, minimal breast asymmetry is typical for 80% of women, and it is very likely that this figure is even underestimated. However, if a woman considers a slight imbalance to be a problem, she can resort to the help of a plastic surgeon. The operation is performed in the absence of contraindications.
Moderate and severe breast asymmetry can be considered as a direct indication for surgical correction. Surgical tactics depend on many factors. The age of the patient, the presence or absence of ptosis, the initial size and shape of the mammary glands, the position of the nipple-areolar complex and other factors, including constitutional features (physique), height, weight, width of the chest, are important.
Up to this point, we have talked mainly about the variant of disproportion in which the size of one breast is larger. There are other types of symmetry breaking. With the same size, one gland may be located slightly lower than the other. The height of the bust projection, the location of the nipple, and the shape of the mammary glands may differ. All these defects are considered indications for surgery and influence the surgical strategy.
Correction of breast asymmetry
Is it possible to correct an aesthetic defect with the help of gymnastics or strength exercises? Unfortunately this is not possible. There is no muscle tissue in the parenchyma of the mammary glands, and therefore physical stress does not affect it. The only way to restore harmonious proportions is plastic surgery.
Correction of breast asymmetry is carried out using various methods of plastic surgery. Depending on the initial data, the doctor may recommend the patient installation of implants, lipofilling, reduction mammoplasty, or mastopexy. Below we will talk about each of the listed operations in more detail.
Augmentation mammoplasty with implants
The installation of silicone endoprostheses is indicated for women with insufficient development of one or both mammary glands. To restore harmonious proportions, implants differing in size and shape are installed in the right and left breasts. If indicated, unilateral breast augmentation can be performed. Choosing the right implants in such a situation is not easy, so it is better to entrust the planning and execution of the operation to an experienced and highly qualified plastic surgeon.
Augmentation mammoplasty with implants is also indicated for patients with different gland shapes and the same volume. In this case, endoprostheses of different profiles and heights, but of the same size, are installed. During the operation, it is possible to restore the harmony of the bust, increasing its volume by one, one and a half or two sizes.
Lipofilling
Bust augmentation by transplanting your own fat cells is an ideal way to correct minor and moderate disharmony. Parts of the body with excessive or sufficient development of fatty tissue become a donor of fat cells for surgery. Usually this is the gluteal area or thighs. The fat is extracted using modern methods and purified in the laboratory. Then the transplant material is enriched with growth factors, after which it is injected into the mammary gland tissue.
Lipofilling is carried out without incisions; cells are transplanted by injection. There are no scars after the operation, which is one of the advantages of the method. The second advantage is that autolipotransplantation allows for targeted, “jewelry” correction, which is impossible during the installation of implants. In some cases, two or three procedures may be needed to completely restore the harmony of the mammary glands, but the result is definitely worth it.
Reduction mammoplasty
Reduction, also known as reduction mammoplasty, is indicated for women with hyperplasia of one or both mammary glands. This is a complex operation that is accompanied by significant trauma to tissues and milk ducts. For this reason, breast reduction is not recommended for young women who want to have a baby and breastfeed it.
But if the reason for contacting a surgeon is post-lactation deformation, reduction mammoplasty can be the optimal method of correction. Very often, hyperplasia of glandular tissue is accompanied by ptosis of the bust; in this case, a breast lift is performed simultaneously with the reduction.
Mastopexy
This operation is indicated for patients whose cause of disharmony is involutional (age-related) or post-lactation prolapse of the mammary glands. In this situation, the glands may differ in size, shape, height, location of the nipple and areola, or all of the above.
Mastopexy is another traumatic operation that is not indicated for women planning to have a child. The operation is performed through a vertical, circular or anchor surgical approach. The choice of surgical procedure is determined by the degree of breast ptosis.
Together with a lift, both reduction and augmentation mammoplasty can be performed. Breast reduction is indicated for women with signs of bust hypertrophy, while breast augmentation or lipofilling is indicated for patients with age-related or post-lactation hypoplasia.
Recovery after surgery
Various operations are used to correct breast imbalances, but rehabilitation after any operation follows general rules:
- Intense training, dancing, yoga, and household physical activity are prohibited for three months. You can't lift weights.
- Diets are strictly prohibited. Nutrition should be complete.
- You cannot go to the solarium or sunbathe for 3 months.
- For two to three months, any thermal procedures (sauna, hot baths, etc.) are contraindicated.
- Intimacy is contraindicated for three weeks.
- Sleep and relax - only on your back!
A separate rule applies to compression bras. Perhaps this is the central requirement of the recovery period. For the first four weeks it must be worn constantly, even at night. From the second month, compression garments can be removed at night. You can completely abandon it after 3-4 months. In the future, throughout the year, you need to wear underwear with good support, wide straps and a belt that fits perfectly.
Note.
After breast lipofilling, you do not need to wear compression garments! Since there are no incisions during the operation, healing is fast, the recovery period is reduced to three to four weeks.
Other requirements of the rehabilitation period include cessation of smoking and alcohol, rationalization of the work and rest regime, and exclusion of active leisure activities that can lead to accidental mechanical damage to the mammary glands.
At the Galaktika aesthetic medicine clinic (Moscow), breast asymmetry correction is carried out by experienced, highly qualified specialists. You can sign up for a free initial consultation by calling the numbers listed on the website of the medical institution.