Lipoma and skin atheroma are two common types of benign neoplasms. They require exceptionally attentive treatment, since in some cases (though, fortunately, not often) they can degenerate into malignant tumors. The appearance of atheroma may not cause suspicion - at first it usually does not cause much inconvenience. However, even if the tumor is not painful, you should still see a doctor. Often a lump (lipoma) on the neck or scalp gradually increases in size, in this case you need to visit a doctor urgently - the new growth will need to be examined to determine whether there is a risk of developing cancer.
Lipoma and atheroma are often similar in appearance, and patients often do not distinguish them from each other, defining them under the general name “wen.” Let's try to figure out what the difference is between a lipoma and an atheroma, and also what to do if you have one of these formations.
Lipoma
This is a benign formation consisting of adipose tissue. In essence, it is a local accumulation of adipose tissue under the skin. Lipoma is a benign tumor, although in rare cases, liposarcoma, a malignant formation, can develop under its mask.
Lipomas manifest themselves in the form of soft-elastic subcutaneous formations, mobile, painless, and can slowly increase in size. The skin over lipomas is not changed and easily moves over them. Small lipomas are not visible at all; they can only be detected by palpation. Larger lipomas stand out as “bumps” of round or oval shape. The size of lipomas is very variable - from 1-2 cm to 20 cm or more. Lipomas never become inflamed or suppurate.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made by a dermatologist, surgeon or general practitioner. Most often, a general examination is sufficient for diagnosis, since the appearance of the formation has characteristic features.
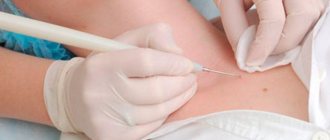
In rare cases, for differential diagnosis with other benign formations - fibroma, lipoma, hygroma - ultrasound is recommended. This reveals a dense capsule and liquid contents of the cyst.
Since the risk of atheroma degenerating into a malignant tumor is extremely low, a biopsy is usually not recommended. After its removal, a histological examination of the capsule can be performed. The result takes 10-14 days to prepare.
Atheroma
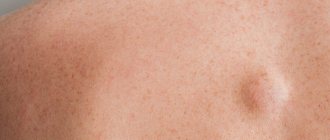
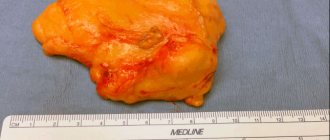
The origin of atheroma is fundamentally different from lipomas. Atheroma develops from the sebaceous glands of the skin. For various reasons, the gland duct becomes clogged, secretion accumulates in the gland, which gradually begins to increase in size. Atheroma is defined as a small (from 0.5 to 2 - 3 cm) formation, which always rises somewhat above the skin and is always fused to it (i.e. the skin above the atheroma does not move), and can grow slowly. Atheroma always has a capsule and contains atheromatous masses resembling crushed lard.
Because The atheroma is connected to the external environment by a duct; there is always a threat that it will become infected through the duct and suppuration will occur. In this situation, moderate pain appears in the area of the previously “quiet” atheroma, the formation quickly (over several days) increases in size, redness appears around it, and body temperature may rise. Suppuration of atheroma requires urgent surgery.
Classification
In practical dermatology, two classifications are used: according to the type of structure of capsule cells (histological) and according to the type of formation. Practitioners mainly use the second one. There are:
- Congenital (or primary) atheromas, the formation of which is caused by congenital changes in the ducts. The size of such formations is up to 0.5 cm, they are multiple and are detected soon after the birth of the child.
- Acquired (or secondary) atheromas develop in initially unchanged gland ducts in people with skin damage or impaired sebum production. The size of cysts can reach several centimeters. As a rule, they are single.
Symptoms
Identifying the problem in both cases is usually not difficult.
Signs of lipoma:
- mobile and painless, sizes can range from a few millimeters to 10-15 cm;
- to the touch - doughy or dense;
- not fused to the skin - the skin easily moves over the formation;
- never becomes inflamed – i.e. There is no redness or swelling of the skin above the lipoma.
Most often, lipomas are located on the limbs, head and torso; they are almost never on the face.
What should I do?
If signs of inflammation appear, you should not hesitate - you must urgently go to the surgeon. But what you definitely can’t do is squeeze out or pick at the formation, trying to make a hole in it. If a breakthrough occurs and the pus is outside, the wound needs to be treated and wait until it heals. After this, the capsule and contents can be removed. The cyst should not be heated or steamed at any stage - this can cause infection.
At an emergency consultation with a surgeon, it may be recommended to relieve inflammation with levomekol or ichthyol ointment. The product is applied to a clean bandage and applied to the cyst, and then secured with a bandage. The compress is applied three times a day until the process subsides.
Symptoms of atheroma
The formation is in the form of a tubercle, painless, mobile, fused to the skin, you can often see the opening of the excretory duct of the gland. Most often, the “bump” is located on areas of the body where there is hair: on the face, scalp, in the genital area, on the legs, on the back, and is found on the face. If a suppurating atheroma appears, the formation increases in size over several days, the skin on the affected area may turn red and become painful, and the temperature may also rise.
Is it possible to open atheroma and treat it at home?
Traditional methods of treatment against atheroma are ineffective. Local exposure using herbal decoctions and alcohol infusions is not effective; it will not help empty the cyst and eliminate the capsule, which becomes a source of re-development of the formation.
You cannot open the atheroma yourself at home. It is impossible to provide a sufficient level of asepsis and sterile surgical instruments outside the conditions of a medical institution. Treatment under such conditions can lead to infection and the development of complications. Atheroma will result in the formation of an abscess or phlegmon. It is especially dangerous if you open an atheroma on the face or head.
Treatment
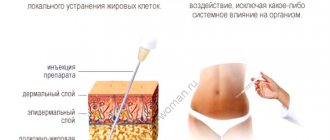
Now that we have figured out the difference between a lipoma and an atheroma, let’s move on to the next question: is it necessary to remove the lipoma or remove the atheroma? Let's start with the fact that conservative treatment of lipoma, as well as treatment of atheroma, is absolutely futile. Moreover, aggressive influence on these formations using various “folk” remedies can cause suppuration of atheroma, as well as malignancy (malignancy) of lipoma.
Tactical approaches to the treatment of lipoma are as follows: if the lipoma is small (2-3 cm), does not grow and does not cause any inconvenience (does not rub against clothes, is not a cosmetic defect, etc.), then it does not need to be removed. In case of growth (especially rapid growth), it is better to go for surgery. If the lipoma grows, then sooner or later you will still have to remove it, but it is better to do this while it is small in order to avoid large incisions and traumatic intervention. Any removed lipoma should be sent for histological (under a microscope) examination.
As for atheroma, it is recommended to remove it in any case, because practice shows that sooner or later they fester, and during surgery against the background of inflammation it is not always possible to completely remove the atheroma capsule, which is fraught with relapse (reappearance of the formation). In addition, when suppuration occurs, the wound is almost never sutured; it heals by secondary intention, which often leads to the formation of a rough scar. If, after removing the atheroma, it turns out that the formation does not have a capsule and does not contain atheromatous masses, it should be sent for histological examination to exclude dermatosarcoma, which is sometimes similar in appearance to atheroma.
Sources of development
Common causes of atheroma formation are presented:
- hereditary predisposition;
- metabolic disorders at the cellular level;
- deviations in hormonal balance - changes in the content of estrogen, testosterone during gestation, menopause, during puberty or against the background of using hormonal drugs over a long period of time;
- stress – psycho-emotional instability leads to active production of sebum;
- increased sweating and violations of personal hygiene rules, the use of decorative cosmetics that cause allergies or other reactions;
- abuse of cosmetic procedures or the use of techniques that aggressively affect the condition of the epidermis;
- pinpoint damage to the sebaceous gland during the removal of acne and pimples;
- violations of the microbial composition of the skin;
- inflammatory processes in the dermis, including acne or rosacea;
- unfavorable influence of the external environment or working conditions.
These sources increase the risk of atheroma formation. The pathological process occurs only with prolonged effects on the dermis and sebaceous glands.
To sum up all of the above, we can say
- Lipoma and atheroma are benign formations of different natures - lipoma simply consists of altered adipose tissue, and atheroma is made of a sebaceous gland with a capsule filled with secretion - sebaceous atheromatous masses.
- Conservative, incl. Treatment of lipoma with folk remedies, as well as treatment of atheroma, is absolutely ineffective and often harmful.
- A small (2-3 cm) lipoma can not be operated on, but observed. In case of growth, as well as any discomfort, surgery to remove the lipoma is indicated.
- Removal of atheroma is always desirable, because they tend to increase in size and fester.
- If you find a subcutaneous formation in yourself, you need to consult a doctor, because... under the guise of a lipoma or atheroma, other formations can develop - dermatosarcomas, liposarcomas, hygromas, lymphadenitis, etc.
Dr. Elshansky I.V. has been involved in the diagnosis and surgical treatment of benign formations of the skin and subcutaneous tissue for many years.
Prevention
There are no effective methods of prevention. If there is increased secretion of the sebaceous glands, atheromas may appear in places near removed bumps or in new locations. As a preventative measure, you can eat less fatty and high-carbohydrate foods so as not to stimulate the glandular apparatus. Use antiperspirants as little as possible; your skin is oily. Use the right skincare products for your skin type to ensure that your pores are free of sebum.
Is it necessary to remove atheroma if it is harmless?
- All atheromas are continuously growing
. And in some cases - extremely quickly. If the atheroma is not removed on time (that is, as early as possible), it becomes larger and larger, sometimes reaching gigantic proportions! Medicine knows of atheromas the size of a child’s head.
- As the atheroma grows, it becomes visible to the naked eye. And if atheroma on the body can be hidden for a long time under clothing, ugly bumps on the face and head arouse the morbid curiosity of others.
- The contents of atheroma often leak out, ruin clothes and have an extremely unpleasant odor that cannot be masked.
- Atheroma is a chronic inflammatory lesion that has negative health consequences. Do you often get colds, get tired, want to sleep, and find it difficult to stand 8 hours at work? All these symptoms are her work.
- The larger the atheroma reaches, the wider the incision is required to remove it. The more difficult it is to hide the scar and skin sagging.
- The contents of atheroma are sebum. This is a delicious delicacy for bacteria. Accumulating sebum, atheroma grows and gradually turns into a time bomb. Infection in the atheroma guarantees the development of purulent inflammation
.
Removing pus from the atheroma will require a large incision, which will leave behind a scar. But greater operational access to atheroma is not the only consequence of suppuration. Such an area rarely heals beautifully, and a painful keloid scar often forms in place of the inflamed atheroma.
The Platinental Clinic offers all the most modern methods for removing atheromas:
- without pain,
- without seams,
- replenishment of tissue volume after removal of atheroma,
- numerous techniques for forming invisible scars.
You can make an appointment with a surgeon online or by phone.
How atheroma is removed at the Platinental clinic
Platinental doctors have all the latest methods for removing atheroma in their arsenal. Depending on the indications, we use the following methods:
- surgical excision with a scalpel. In our work, we use tools made in Europe and the USA: their graphite nanospraying prevents the formation of scars;
- removal of atheroma using the radio wave method;
- laser removal of atheromas.
Expert opinion
“It is worth noting that not a single scheme of these three
cannot be considered worse or better than another.
The main task of the surgeon is to use one method or another to ensure a neat incision and completely remove the atheroma from under the skin without damaging it. The technique is chosen individually each time.
Specialized plastic surgery centers such as Platinental offer not only painless removal with a variety of methods to choose from.
Modern techniques allow me to do without stitches at all in 90% of cases.
«.
Maxim Vasiliev, plastic surgeon.
Photos "before" - "after"
Removal of a large lipoma. There is no need to wait and grow a lipoma to a large size; a small lipoma is easier to remove and the operation is less traumatic. Performed by surgeon: Gladysheva Vladislava.
Surgical removal of back atheroma. “Before” and on the 8th day after surgery: the suture is removed. Surgeon - Vasiliev Maxim.
Preventive actions
Prevention of atheroma will prevent its reappearance. It is necessary to eliminate the root causes that may lead to its development. It is important to observe the rules of personal hygiene and regularly care for your skin (taking into account its type). It is forbidden to squeeze out pimples and other formations on the skin yourself. It is necessary to monitor hormonal levels, controlling metabolism.
Diet plays an important role in prevention. It is necessary to maintain a balanced diet, since a lack of vitamins and microelements, as well as an excess of fried, spicy and fatty foods, lead to malfunction of the sebaceous glands. If atheromatosis is diagnosed, all unwanted foods and alcohol-containing drinks should be excluded from the daily diet.
Why should atheromas be removed by a doctor?
It is believed that atheroma can be squeezed out on its own, just like a comedone. In fact, this will not solve the problem, even if the atheroma is small.
Firstly, after self-removal, a large and extremely noticeable depression remains on the skin. Secondly, your efforts were in vain: in a few weeks a new one will “grow” in the same place - or rather, the old atheroma will be filled with sebum.
This is because atheromas have a specific structure - they are always surrounded by two capsules. The first is the atheroma’s own capsule, in which its contents are packed, like a bag. The second capsule is external. It separates the atheroma from the tissues surrounding it.
If the atheroma capsule is not removed or at least a tiny fragment of its shell remains under the skin, this 100% guarantees the appearance of a new atheroma in the same place in the future. Hence the myth about its incurability.
In fact, you can get rid of atheroma. It is important to choose the right specialist.
“Before” and on the 12th day after removal of myofibrolipoma of the forehead area. Tips&tricks on the forehead for faster resolution of swelling. Surgeon Vladislav Gladysheva.
Symptoms of atheroma.
Since the disease itself is not inflammatory in nature, it also has no general manifestations. Non-festering atheroma is locally manifested only visually - as a skin tubercle, while the color and skin pattern remains unchanged.
Rice. 4. Atheroma occurs due to blockage of the sebaceous gland duct in the skin.
Description of the disease
Atheroma is one of the relatively harmless tumors due to the fact that it does not transform into a malignant neoplasm.
However, there is a risk of significant increase in size, so medical attention is required in all cases. Teenage children are more likely to experience this problem. Boys and girls get sick about the same. The main reason why parents first turn to a surgeon is the presence of a visually noticeable tumor.
The atheroma itself is a small capsule filled with pasty contents. It is sebum, which, due to blockage of one or more glands, did not come out, but remained in the subcutaneous tissue.