Bedsores are a common occurrence in bedridden patients. They appear in places where the body is in constant contact with a hard surface (mattress, bed). Most often, in bedridden patients, bedsores affect the buttocks, sacrum, area between the shoulder blades, and the back of the head. Bedsores must be treated immediately after they appear, and it is better to prevent their occurrence, since they progress very quickly.
To treat bedsores, special plasters are used that have a backing and an adhesive surface. The substrate can be impregnated with antiseptic and medicinal agents that disinfect the wound and promote its healing. The sticky part of the patch painlessly peels off from the body, since it does not come into contact with the wound. Patches against bedsores for bedridden patients have good effectiveness in the development of necrotic process of 1st and 2nd degree. When adipose and bone tissue is affected (stages 3 and 4 pressure ulcers), the help of medical professionals will be required.
The Yusupov Hospital provides assistance to bedridden patients with bedsores of any stage. Early consultation with a doctor will help prevent the progression of bedsores. In severe cases, the Yusupov Hospital will provide the patient with the necessary treatment that promotes quality wound healing.
Plasters for securing bandages
Not all specialized dressings have an adhesive layer along the edge. To completely cover a large wound with a bandage, you can use roll-on patches made of non-woven material.
Trade names:
- Omnifix
Omnifix patch. Photo: medicaland.ru
- Plastofix
Plastofix patch. Photo: avatars.mds.yandex.net
- LEIKO bandage
LEIKO bandage. Photo: www.ukazka.ru
- Curafix H
Curafix H dressing. Photo: www.netran.ru
Wound healing and factors influencing this process
The wound healing process can be disrupted by many factors.
Healing is the process of repairing damaged tissue and restoring its integrity. During the healing process, certain processes occur. We will not dwell on them in more detail, but will only indicate those factors that may disrupt the healing process:
- Age. As a rule, this applies more to older people. The child's body has great regenerative capabilities. This is due to the high level of anabolic (construction) processes in the body.
- Attachment of infection.
- Decreased immunity.
- Poor circulation in the wound area.
- Chronic diseases (diseases of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems, diabetes, tumors and others).
Healing complications
- Attachment of infection . Most often, a nonspecific purulent infection develops. The threat is tetanus, rabies, diphtheria. Therefore, injuries that have been bitten and contaminated with soil or old metal objects should be immediately examined by a surgeon with a number of preventive measures taken (administration of anti-tetanus serum, rabies vaccine).
- Bleeding.
- Divergence of defect edges.
- In some cases, healing may be complicated by a hypertrophic scar or keloid . They are an abnormal scar that can spread beyond the defect area and also contribute to the development of complications.
Ointment mesh dressings
Mesh dressings are mesh of varying thickness, coated with ointments with different effects. Such dressings do not absorb exudate (liquid that is released from tissues), but can perfectly maintain a moist environment. This prevents the wound from drying out and protects it from sticking. The dressings can be used either alone or in combination with other dressings, such as simple gauze bandages.
In this case, you can put a mesh bandage on the bottom of the wound, and use gauze or other dressings to absorb the discharge from above.
Most often, ointment mesh dressings are used to treat superficial smooth wounds and grade 2 bedsores.
- Coloplast Physiotulle® Ag
Coloplast Physiotulle® Ag. Photo: www.mystoma.ru
- Branolind N dressing
Branolind N/Branolind N. Photo: www.eapteka.ru
- Ointment dressing "Voskopran" with dioxidine
Voskopran with dioxidine. Photo: mednabor.ru
- Parapran dressing with chlorhexidine
Parapran with chlorhexidine. Photo: www.netran.ru
- JELONET
JELONET/JELONET. Photo: invimed.ru
- Bactigras dressing
Bactigras dressing. Photo: www.aramed.ru
- Voskopran Povidone-Iodine dressing
Voskopran Povidone-Iodine dressing. Photo: www.netran.ru
- Atrauman Ag (Atrauman Ag)
Atrauman Ag. Photo: rekate-medical.ru
- Lomatuell H
Lomatuell H. Photo: rekate-medical.ru
What wounds require ties and why?
The tape screed method has proven itself well in plastic and cosmetic surgery, for bringing together the edges of small superficial wounds and cuts. The downside of the device is that it is intended to restore only the skin. If veins, tendons, muscles are injured, or the injury is located in the abdominal wall, on the chest, sutures are required. Useless for large cutting depths. Used to fix fresh scars after recent operations. The adhesive material is highly durable and adheres securely to the body.
Unlike stitching, gluing with adhesive does not leave scars and causes less pain and discomfort. The doctor can inspect the damaged area at any time and provide emergency care in case of complications. Used by plastic surgeons after removal of sutures.
You can close the wound without stitches for cuts on the face and other parts of the body where it is important to maintain aesthetic appeal. The reduction of edges is carried out by specialists in a medical institution.
For the procedure, special epidermal patches are used, which are tightly attached to the skin and can be easily removed after healing.
Hydrocolloid dressings
Trade names:
- granuflex;
- DuoDerm;
- Suprasorb H;
- Hydrocoll;
- Hydrocoll Sacral;
- Tegaderm Hydrocolloid;
- Comfeel Plus.
The coating base of hydrocolloid dressings consists of microgranules of sodium salt, pectin and gelatin. Such headbands began to be used in the early 80s and they are still one of the most popular.
The dressing can absorb a small amount of discharge from the wound, retains a moist environment well and converts excess moisture into a gel.
Hartmann bandages. Photo: www.mystoma.ru
Turning into a gel, the hydrocolloid acquires a characteristic, not very pleasant odor and a yellow color, which can be mistaken for pus. Therefore, this dressing should not be used on infected, inflamed wounds or wounds with a large amount of discharge. It simply cannot cope with such a volume of liquid and bacteria and will quickly melt. But for superficial, shallow wounds with a small amount of discharge, hydrocolloid dressings are perfect.
Bandage. Photo: cdn.diacheck.ru
Some bandages are made in a special shape to make it easier to stick to certain places where bedsores form (sacrum, elbows, knees, etc.).
Specially shaped bandage. Photo: prozabota.ru
Main types of chronic wounds
- Diabetic foot syndrome (DFS) is a set of anatomical and functional changes that develop against the background of diabetes mellitus, increasing the risk of injury and infection of the soft tissues of the foot. According to the World Health Organization, the risk of developing DDS in diabetics with 5-10 years of experience is about 15%. For diabetics with more than 15 years of experience, it increases to 90%.
- Prevention: protecting feet from injury, comprehensive foot and nail care, wearing shoes for diabetics.
- Trophic ulcers are complications of venous insufficiency caused by changes due to thrombophlebitis or deep vein varicose veins. Poor circulation and blood supply to the legs leads to venous congestion, and this leads to the formation of poorly healing ulcers on the ankles or legs.
- Symptoms are swelling, impaired skin pigmentation (redness or pallor), eczema, a feeling that the legs are bursting from pressure (more often in the evening).
- Prevention: timely treatment of the underlying disease, wearing elastic tights, treating the skin with antiseptic and healing agents.
Sponge dressings
Sponge dressings are made of polyurethane foam material with large pores. They can quickly absorb large amounts of discharge and retain it, which reduces irritation of the tissue around the wound. Sponge dressings come with an adhesive edge (adhesive) - they themselves stick to the body and do not require additional fixation with adhesive tape. And not adhesive - they must be additionally secured with a plaster or fixing bandage.
Used for non-infected wounds. In the presence of inflammation and infection, bandages or ointments with an antibiotic, antiseptic or silver-based are added to them. These dressings are covered with a vapor-permeable layer on top, which allows the wound to “breathe” but protects it from external influences.
Many dressings additionally have a wound coating with silicone or hydrogel. This is necessary so that they do not stick to the wound and retain moisture better.
- Coloplast Non-adhesive sponge dressings with Biatain®Ag silver
- Coloplast Adhesive Biatain® sponge heel dressings
Beataine bandage. Photo: medkalopriemniki.ru
- Self-adhesive sponge dressing with hydrogel coating HydroTac Comfort
HydroTac Comfort bandage. Photo: www.careproducts.ru
- Adhesive dressing Suprasorb P Silicone
- Mepilex Ag sponge bandage with silver antibacterial
Mepilex Ag sponge bandage with silver is antibacterial. Photo: www.netran.ru/
- Permafoam comfort sponge self-adhesive dressing
Permafoam comfort. Photo: images.ru.prom.st
- Neofix FibroSorb Ag (Neofix FibroSorb Ag)
Neofix FibroSorb Ag (Neofix FibroSorb Ag). Photo: rekate-medical.ru
- Askina Transorbent (sterile sponge dressing with hydrogel layer)
Askina Transorbent. Photo: rekate-medical.ru
Other
In the medical products category you can find Silkofix Strips adhesive plasters. Designed for tightening the edges of wounds on the surface of the skin, small surgical and cosmetic incisions, and tears. Can be used alone or in combination with threads. Reliable when used on raised areas, limbs, joints.
They have enhanced adhesion, do not cause allergic reactions, are elastic, and sterile.
Recently, scientists announced another unique tightening device called microMend. It works on the principle of medical equipment. Applied to a cut or injury like an adhesive sticker, it heals the wound. Tightly holds the edges of damaged skin, eliminates pain, protects against infection.
Alginate dressings
These dressings are made from seaweed and are similar in structure to glass wool. The dressings contain calcium or sodium alginate, which turns into a gel upon contact with liquid.
Alginates are natural polysaccharides. The main source of alginates in nature is seaweed of the genus Laminaria, where they are contained in the form of alginic acid salts, mainly sodium alginate.
These dressings are suitable for use in deep wounds and pockets. They perfectly absorb large amounts of liquid and bacteria. In the form of a gel, they do an excellent job of soaking necrosis, fibrin and crusts of dead tissue. That is why such dressings are used to treat bedsores and chronic wounds of 3-4 degrees.
Diaper rash and bedsores: how to treat at different stages In what places do bedsores form, and in which diaper rash, how to treat them depending on the stage Olga OsetrovaTatyana Parfenova
Symptomatic treatment
Nowadays such bandages are made with reinforcement. This is necessary so that the alginate particles do not disintegrate and remain in the wound. If using a non-reinforced dressing, the wound can be irrigated to remove alginate particles. Alginate is not absorbed and is quickly washed off with saline solution.
The alginate dressing must be secured on top with another dressing. It can be a film bandage, hydrogel or sponge. The alginate dressing can also be covered with napkins and secured with a self-adhesive bandage.
If you are using an alginate dressing on a very wet wound, it can be used dry. If the wound is dry and covered with necrosis, then the alginate is pre-moistened with saline solution. This is necessary to restore a moist environment to the wound.
- Algisite M
Algisite M. Photo: www.aramed.ru
- Alginate dressing Suprasorb A
Alginate dressing Suprasorb A. Photo: www.bonanzamarket.co.uk
- Medisorb A
Medisorb A. Photo: www.eapteka.ru
- Algitek S silver bandage
Algitek S silver bandage. Photo: mtkimpex.ru
Features of using tightening plasters for wounds, sutures, cuts
A tightening plaster for wounds, which is used to treat sutures, injuries, and deep cuts, has the following distinctive features:
- does not cause skin irritation during prolonged wear;
- the edges of the medical device have better fixing ability;
- during prolonged use, the bactericidal strip does not deform or slip;
- the local action of the biochemical components included in the tightening patch is ensured;
- a minimal amount of antibacterial and anti-inflammatory substances with which the gauze base of the patch is impregnated penetrates into the bloodstream;
- when removing the bactericidal strip there is no discomfort, pain or sticking of tissue to open areas of the wound;
- patches with a tightening effect not only protect the wound from the effects of environmental factors, but also have a compression effect, squeezing the edges of the wound surface for faster healing.
The main feature of the use of tightening plasters for wounds, sutures, and cuts is the high efficiency, availability and safety of these products. Germicidal strips are an indispensable part of first aid kits during outdoor activities, long trips, hiking, and performing high-risk work.
Hydroactive dressings (solution activated dressings)
The coating of these dressings consists of sodium salt fibers and carboxymethylcellulose, which upon contact with wound secretions turn into a transparent gel. It creates a moist environment on the surface of the wound and does not stick to the wound.
Aquacel Extra
Aquacel Extra. Photo: cdnx.jumpseller.com
HydroClean plus - dressings with active Ringer's solution
The bandage inside contains a gel that has absorbed Ringer's solution. Ringer's solution is a saline solution that draws out drainage and pus from a wound. It absorbs the exudate, and Ringer's solution washes the wound. Works great on dry wounds with necrosis. Cleans wounds containing pus and dead tissue.
HydroClean plus. Photo: prom.ua
Instructions for using tightening patches
The procedure for fixing the tightening plasters depends on the type of wound surface and the nature of the injury. Particular care is required when applying strips to areas of the body that have been subjected to surgery using suture material.
Rules for using a tightening plaster for cuts and abrasions
The application of fixing strips after skin damage due to a cut with sharp objects occurs in compliance with the following rules:
- Wash your hands thoroughly using warm water, laundry or toilet soap.
- Pull back the edges of the wound and make sure that no dirt or other foreign particles get into the exposed tissue.
- Remove the patch from the individual packaging.
- Tear off the protective backing of the strip, which releases the adhesive part of the medical device.
- Do not touch with your fingers the part of the patch that should be fixed on the damaged part of the body.
- Apply a tightening patch to the wound so that the surface of the medical device, which is impregnated with medicinal plant extracts, anti-inflammatory, healing and antiseptic agents, is adjacent to the damaged tissue, and the adhesive base is fixed to the dry and healthy parts of the epithelium.
If a compression plaster was applied during first aid, you should consult a surgeon or traumatologist. The fixing strips are changed every 8 hours.
Instructions for using a tightening plaster on contaminated wounds
Damage to the skin, with dirt and other foreign particles getting into the wound, is covered with a fixing plaster in compliance with the following instructions:
- Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and warm water.
- Rinse the open wound with hydrogen peroxide to remove any contamination.
- Print out the tightening patch, preparing it for installation.
- Apply the impregnated part of the medical device to the wound surface, and attach the adhesive segment to clean and dry skin.
After sanitary treatment of damaged tissues, a person should be observed by a traumatologist or surgeon. Precautionary measures are aimed at preventing bacterial inflammation of the wound.
Applying a compression plaster to postoperative wounds
Fixation of bactericidal strips on the surface of a postoperative wound is carried out in compliance with all of the above rules. Antiseptic treatment of the area of the body on which suture material is applied is performed only by medical professionals.
After printing the patch, it is fixed on the wound surface. A part of the medical device, impregnated with drugs, is applied to the segment of the connection of the dissected tissues. The adhesive part of the strip is attached to dry and healthy skin, but as far as possible from the seams. To do this, use a large plaster.
Hydrogel dressings
Transparent hydrogel dressings provide long-lasting wound hydration due to their high water content, about 60%. These dressings are used to moisturize smooth, dry, uninfected wounds with little discharge.
Bandage on the wound. Image: www.mystoma.ru
The hydrogel is also produced in the form of a tube or syringe, from which it is convenient to squeeze it into deep wounds and pockets. It fills the wound, supplies it with fluid, prevents it from drying out and rejects dead tissue. This gel can be easily washed off with saline solution when dressing. It can remain in the wound for up to 4 days. The gel is used only in those wounds where there is necrosis and fibrin - black and yellow dry crusts and films. It is not used on ordinary clean wounds, as it greatly softens the tissue, and in the case of a clean wound this is not necessary.
- Hydrogel dressing with lidocaine Gelepran
Gelepran. Photo: lan-med.ru
- Phleboton - hydrogel bandage
Phleboton. Photo: rekate-medical.ru
- Hydrosorb Comfort is a self-adhesive hydrogel dressing.
Hydrosorb Comfort/Hydrosorb Comfort. Photo: fortemed.ru
- Hartmann Gidrotak Transparent hydrogel dressing
Hartmann Hydrotak Transparent. Photo: apteka-sale.ru
- Aquabint
Aquabint Oval. Photo: apteka.ru
- Matopat Medisorb G hydrogel dressing
Matopat Medisorb G hydrogel dressing. Photo: www.eapteka.ru
- Hydrosorb Gel
Hydrosorb Gel. Photo: orto-nova.ru
- Gel Suprasorb G
Gel Suprasorb G. Photo: www.netran.ru
- Purilon gel
Purilon gel. Photo: medmag24.ru
- Neofix FibroGel Ag
Neofix FibroGel Ag. Photo: rekate-medical.ru
- Hydrogel Intrasite Gel Applipak
Hydrogel Intrasite Gel Applipak. Photo: www.netran.ru
Anti-bedsore patch for bedridden patients: when is it needed?
Bedsores are very common in elderly patients, severe cancer patients, patients with a broken leg or hip, intensive care patients, and paralyzed people. For the prevention and treatment of bedsores in bedridden patients, plasters, bandages and other dressings have been specially developed to reduce pain in the affected area, disinfect the wound and absorb purulent discharge. The advantage of bedsore patches for bedridden patients is their ease of use. The patch is easy to attach to a wound, including in a hard-to-reach place (the area between the shoulder blades, the tailbone), where it is difficult to bandage. It is easily removable and can be changed quickly and easily. The bedsore patch does not compress adjacent tissues and does not cause discomfort to the patient.
Treatment of pressure ulcers with a patch should begin at the first signs of wound development. If areas of redness appear on the patient’s body, the skin does not turn white when pressed, it is necessary to urgently treat this surface. Bedsores can progress almost at lightning speed and very quickly affect all layers of the skin, penetrating to the bone tissue.
Pressure sore patches are highly effective for grades 1 and 2, when patients experience redness or small ulcerative wounds. With the development of grade 3 and 4 pressure ulcers with the formation of a deep wound with purulent discharge and necrosis of bone tissue, plasters are an additional means to the main surgical treatment.
Absorbent dressings
Absorbent dressings are often used on wounds that are very wet and have a lot of drainage. Such dressings help to cope with the unpleasant odor of infected wounds and wounds with tumor decay. They contain superabsorbents and silver.
- CARBONET (Carbonet) - absorbent deodorizing non-adhesive dressing with activated carbon
CARBONET (Carbonet). Absorbent deodorizing non-adhesive dressing with activated carbon. Photo: rekate-medical.ru
- Absorbent bandage Mesorb
Absorbent bandage Mesorb. Photo: ukrmedshop.ua
- Zetuvit E steril dressing
Zetuvit E steril dressing. Photo: www.deznet.ru
- Askina Calgitrol Ag
The combined dressing consists of a sponge layer, alginate and silver. Absorbs exudate well, reduces odor, and maintains a moist environment. Used on infected wounds, necrosis.
Askina Kalgitrol Ag. Photo: www.bbraun.ru
Bedsores on the head: prevention and treatment Samara hospice doctors tell how to prevent bedsores on the head of a seriously ill person and what to do if they appear Olga OsetrovaTatyana Parfenova
Symptomatic treatment
Please remember that using modern dressings to treat bedsores does not solve the problem. Bedsores can be successfully treated only when we remove the cause of their occurrence - long-term exposure to body tissue, when a person lies in one position for more than two hours. Without constant changing of posture and correct positioning, no bandage will help cure bedsores.
How can you pull
Surgeons have at their disposal a large number of methods for suturing and tightening wounds. The choice of the optimal option depends on the area of the cut or laceration and its location on the body. All types of sutures, unlike plasters, are divided into continuous, interrupted, Z or U-shaped. In relation to the surface they are located horizontally or vertically. Based on the application technique, a distinction is made between manual and mechanical.
Common types of skin sutures for tightening wound edges:
- nodal. It differs in that the needle enters and exits at the same distance from the edges, 1–3 mm. The location of the stitches from each other is 1–2 cm. Smaller gaps will impair microcirculation inside the skin, which threatens necrosis;
- continuous. Performed with one long thread. The needle is inserted on one side and removed from the other. The first knot is made at the beginning of the first puncture, the last one is necessary for information and fastening. Removes in one motion.
There are a large number of subspecies, differing in the form of application of knots and stitches.
Thanks to modern developments, surgeons and patients now have a non-invasive, seamless technique for closing superficial skin lesions using adhesive strips - adhesive plasters.
An adhesive bandage on a wound can be made in one of the following ways:
- longitudinal. Fastening on both sides, the free edges of the strips are sewn together with threads. Ready-made devices are available for sale. A zipper remains in the center, allowing for washing and inspection;
- transverse. Used on fixed parts of the body, limbs. The edges are brought together, a sterile napkin or cloth is applied to the skin, and fixed with long thin pieces of plaster. Location: across the wound. After fastening, a bandage is recommended.
It is permissible to apply a screed to moving parts of the body; it is necessary to use special medical strips and not ordinary bactericidal strips from a pharmacy.
When using on hairy parts of the body, pre-shave is recommended. If this is not possible, for example, a cut to the head, then the area of the strip increases by 3–4 times.
Epidermal types of adhesive plasters from the category of professional wound care products are used to connect surgical incisions and small lacerations. They are characterized by high strength, flexibility, and adhesion to the skin. After application, they reliably adhere to the surface and do not come off due to temperature changes, friction with clothing, or movement. They have a flesh color that matches the skin tone, which makes them invisible to others.
What types of postoperative sterile patches are there?
Surgery requires the subsequent application of a sterile medical post-operative plaster. It can replace a sterile dressing, providing the same functions - protecting a fresh wound from infection and subsequent problems. If the incision is small, it is possible to fix the edges of the wound. Manufacturers offer products with different impregnations, the effect of which is selected taking into account the need.
- Antibacterial patch for wound healing with silver. Accelerates skin regeneration. The absorbent base allows for repeated dressings much less frequently. There are products for children and adults, standard and waterproof.
- A postoperative non-woven bandage is made of elastic materials and is designed specifically for moving areas of the body. The microporous surface provides air exchange, which eliminates irritation and diaper rash. During dressing, the adhesive composition is easily separated from the skin, and no traces remain.
- Product for resolving sutures after surgery. Indications for use: epithelization of wounds and protection against re-infection. The material absorbs wound secretions well and protects the surface from mechanical and other impacts. Due to the transparent base, you can observe the process without peeling off the film each time.
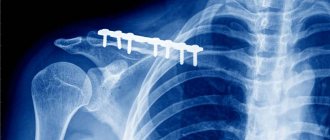
Subcutaneous suture
A subcutaneous suture using a continuous thread is often used by surgeons after surgery performed under sterile conditions. This is a quick way to close large wounds. In special situations, three other types of sutures can be used. Slit wounds are closed with either an upholstery suture or a vertical mattress suture. Tubular structures, such as the intestine, are closed with a "purse string" circular suture that can be pulled tight. Of the absorbable suture materials, the most commonly used is plain or chrome-plated catgut, produced from lamb or pig intestines. Silk, nylon, various polymers and wire are used as non-absorbable materials.