Causes Symptoms Diagnostics Treatment Advantages of treatment at MGK Prices
Xanthelasmas of the eyelids look like small single or multiple flat yellowish plaques located at the inner corner of the upper (usually) or lower eyelid. Xanthelasmas are benign formations that are not prone to malignancy; their appearance is associated with general disorders of lipid metabolism.
General information
Xanthelasma (xanthoma) of the skin of the eyelids is a benign formation in the form of a flat, slightly raised yellowish plaque on the skin.
The predominant localization of the pathological formation is the inner corner of the upper eyelid. Formations can be either multiple or single, symmetrical, varying in consistency and shape - soft/hard, even flat or nodular. Eyelid xanthelasmas are a type of xanthomas that appear on the eyelids when they are absent elsewhere on the body. Histologically, eyelid skin xanthoma consists of xanthoma cells (histiocytes), which contain intracellular fat deposits, that is, they contain vacuoles that are filled with partially esterified cholesterol . They are located predominantly in the upper reticular layer of the dermis/perivascular region, less often in the area of the appendages. These formations are not prone to malignant degeneration and do not pose a threat to life.
Xanthelasma of the eyelids (a type of xanthoma) is the most common manifestation of xanthomatosis. It occurs more often in females (1.1%) and much less frequently in males (0.3%) aged 15-75 years with a peak at the age of 30-50 years. Xanthomatosis is a disease characterized by multiple deposits of lipid substances, mainly in the skin (elbows, buttocks, thighs), less often in tendons, bones, dura mater), caused by hyperlipidemia .
Common xanthoma
- Xanthoma-like lesions are caused by a rare form of histiocytosis.
- Lipid metabolism is normal.
- The skin lesions usually consist of hundreds of small yellowish-brown or reddish-brown bumps that are usually evenly distributed on both sides of the face and torso. They can be especially hard on the armpits and groin.
- Small bumps may join together to form sheets of thickened skin.
- In 30% of affected people, the mucous membranes of the mouth, respiratory tract or eyes (mucous membranes) are affected. Warty plaques in the mouth are called verruciform xanthoma.
- 40% of affected people develop diabetes insipidus, a condition that results in an inability to control water loss (leading to constant thirst and excessive urine production). This occurs due to the overgrowth of histiocytes on the lining of the brain (meninges).
- May affect internal organs (eg liver, lungs, kidneys, etc.)
- Self-limiting and eventually improves on its own, but may persist for many years.
Causes
The development of xanthelasmas is based on a disruption of the process of lipid metabolism with the gradual development of a state of hyperlipidemia, in which the content of lipoproteins of various fractions in the blood significantly increases. They are associated both with genetically determined (primary) disorders - primary hyperlipidemia types 2 and 4, and with fat metabolism disorders, which are based on various types of disorders/diseases - increased blood cholesterol ; hypothyroidism , diabetes mellitus , pancreatitis , cirrhosis , lipoid nephrosis , severe hepatitis .
In some cases, the cause of xanthelasma is age-related changes in the body, taking certain medications ( estrogens , corticosteroids , anabolic steroids , cyclosporine , antihypertensives , retinoids ), as well as abuse of cholesterol/fat-rich foods and alcohol-containing drinks.
Primary forms of xanthomatosis occur predominantly in persons under 40 years of age, including children, while secondary forms occur mainly in older/elderly people. However, xanthomas and xanthelasmas can also appear against the background of a normal lipid profile due to an inflammatory process on the skin, allergic contact dermatitis and erythroderma .
Surgical excision
This method is used in cases where it is necessary to remove xanthomas - large fused formations. The surface of the plaque and the area around it are carefully treated with an antiseptic, then separated using scissors or tweezers. The edges of the wound are treated with ferric chloride, then with potassium permanganate or brilliant green. The main disadvantage of this method is the high probability of relapse.
Surgical excision may be prescribed if the patient has contraindications to other techniques.
In general, this method is rarely used these days, trying to carry out treatment before the plaques grow to large sizes.
Symptoms
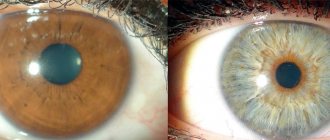
Xanthelasma is a light orange/yellow plaque that slightly protrudes above the unchanged surface of the skin, with a predominant localization on the upper eyelid (at the border of the fixed/moving part), sometimes at the inner corner of the eye. On palpation, the formation has a soft consistency and is painless. They can be single/multiple, located on one or both eyelids. In some cases, xanthelasmas merge to form a solid yellow stripe with an uneven contour or lumpy elements.
Characterized by slow, steady development, a tendency toward slow fusion of neighboring elements and the absence of spontaneous healing. There are no subjective sensations on the part of the patient. The formation can grow to the size of a large bean, but does not transform into a malignant neoplasm. In cases where xanthelasmas are symptoms of xanthomatosis, they can also be located on the lower eyelid and other parts of the body: on the face, elbow/knee joints, neck, buttocks, etc.
The resulting xanthelasmas do not regress on their own and persist throughout life. In some cases, their number continues to gradually increase. Below is a photo of xanthelasma.
Electrocoagulation
Destruction of xanthelosis plaques using high-frequency electric current. An electrode is placed on them, current is applied, and the tumor is cauterized. Tumor cells are destroyed. At the site of each plaque, a red crust remains, which must be cared for with ointments. The eyelids finally heal in about 10 days. Electrocoagulation is performed under local anesthesia on an outpatient basis. The patient can go home on the same day. The method is used for small tumors, since removal of large xanthelasmas that have merged into xanthomas with electric shock can be quite traumatic.
Tests and diagnostics
The diagnosis is made by examining the patient based on the location/characteristic appearance, color and consistency of the mass. During examination, diascopy is used - pressing on the neoplasm with a glass slide, which allows you to bleed the formation and clearly determine their yellow color and the contours of the formation. If necessary, a lipid profile study is prescribed: determination of lipoprotein/cholesterol and triglyceride fractions in the blood serum. Differential diagnosis must be carried out with dermal cysts, wen, elastic pseudoxanthoma, syringoma and other skin tumors.
Eruptive xanthoma
- Lesions usually appear as seedlings of small red-yellow papules
- They most often occur on the buttocks, shoulders, arms and legs, but can occur throughout the body
- Rarely the face and inside of the mouth are affected
- Lesions may be tender and usually itchy
- Lesions may resolve spontaneously within a few weeks
- Associated with hypertriglyceridemia (increased levels of triglycerides in the blood) often in patients with diabetes mellitus (diabetes mellitus)
Diet
Diet for vascular atherosclerosis
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 2 months
- Dates: no data
- Cost of products: 1700-1800 rubles. in Week
In the diet it is necessary to exclude/significantly limit:
- Saturated fats (all animal fats, butter, and coconut and palm oils).
- Foods rich in cholesterol (egg yolks, liver, kidneys, butter, high-fat fats, ghee, fish roe, shrimp).
- Simple carbohydrates (various sweets, confectionery, sweet carbonated drinks, ice cream, condensed milk).
Olive oil, legumes and plenty of vegetables (Mediterranean diet) should form the basis of a cholesterol-lowering diet. A diet low in animal fats, simple carbohydrates and high in fiber can normalize slightly elevated lipid levels. To do this, you need mainly dishes from vegetables in any form, fish, legumes and grains. If you are obese or overweight, it is important to reduce your intake of high-calorie foods and at the same time increase physical activity.
Prevention
There are no exact recommendations for prevention of xanthelasma.
Need to know! Experts can only give general recommendations that will help patients get out of the risk group and avoid the appearance of such formations with age:
- monitor your weight and introduce more healthy foods into your diet;
- add foods containing fiber , and also eat up to three hundred grams of vegetables and fruits daily;
- Replace animal fats with vegetable fats , but consume them in reasonable quantities;
- drink at least 1.5 liters of water per day ;
- exercise regularly ;
- try to give up smoking and alcohol ;
- control metabolism , if necessary, visit a nutritionist and endocrinologist.
Consequences and complications
Xanthelasmas are not dangerous because they are a benign formation and there is no possibility of their degeneration into a malignant tumor. They also do not affect vision. Removal of formations is carried out for aesthetic reasons. In isolated cases, especially with injury, inflammation (suppuration) may develop. If we consider the consequences after surgical treatment, we can note frequent relapses of the disease. To avoid such consequences, the patient must strictly follow a diet (vegetable-protein diet) and take medications prescribed by the doctor. Also, a scar (hypertrophic or keloid) may form at the site of surgical removal of the formation. Most often this is noted with a predisposition to the development of keloid scars.
Prices for treatment for xanthelasma
The cost of surgical treatment of xanthelasma starts from 2000 rubles. (in the presence of a single formation up to 5 mm). The final cost of removal will depend on the number and size of formations, as well as the volume of therapeutic and diagnostic procedures performed.
You can find out the cost of a particular procedure by calling (499) 322-36-36 or online using the appropriate form on the website; you can also read the “Prices” section.
Go to the "Prices" section
Make an appointment
List of sources
- Surkichin S.I., Gryazeva N.V. Xanthelasma of the eyelids: management tactics / Medical alphabet 2022 No. 7 /, volume No. 1, pp. 63-64.
- Trukhan D.I., Viktorova I.A., Bagisheva N.V. Skin changes in somatic diseases // International Journal of Applied and Fundamental Research. 2016. No. 8. pp. 736–740.
- Cronenberg G. M. et al. Obesity and lipid metabolism disorders / Translation from English, ed. I. I. Dedova, G. F. Melnichenko. M.: Read Elsiver LLC, 2010. 264 p.
- Vizir V.A., Berezin A.E. Modern approaches to the treatment of hyperlipidemia / Zaporozhye Medical Journal. - 2011. - volume 13, no. 1, pp. 108-117.
- Machekhin V.A. Clinical and histological analysis of tumors of the eye and its protective and auxiliary apparatus // PRACTICAL MEDICINE. - 2012. - T. 2, No. 59. - P. 255-259.
Cryodestruction
This is a method of removing skin lesions - xanthelasmas, warts, papillomas - by freezing with liquid nitrogen. The procedure gives a good cosmetic effect. The fatty plaque is frozen at an ultra-low temperature of 190 degrees, after which its structure is destroyed and cell growth stops. During the rehabilitation period, you must strictly follow the care recommendations: protect your eyes from the bright sun, do not visit the solarium, and do not use facial cosmetics.
Our specialists
- Kiani Ali
Candidate of Medical Sciences, laser medicine specialist, dermatocosmetologist.
Sign up
- Stepanova Inna Igorevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, maxillofacial surgeon, specialist in laser medicine.
Sign up
- Fedotova Marina Andreevna
Surgeon, dermatocosmetologist, laser medicine specialist
Sign up
- Popovkin Pavel Sergeevich
Surgeon, oncologist, laser medicine specialist.
Sign up