- Indications for the procedure
- Contraindications to the procedure
- Stages of cryodestruction of skin tumors
- Expected result: will there be scars and how many sessions are needed?
- Rehabilitation: skin care after cryodestruction
- Which is better: cryodestruction or laser removal
- Cost of cryodestruction of tumors
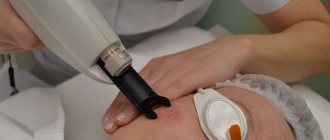
Cryodestruction is a minimally invasive technique for removing tumors using ultra-low temperatures. It is painless, safe and has a quick recovery period.
The essence of the cryodestruction method is to freeze tissues that have undergone pathological changes with liquid nitrogen. When exposed to cold, water in tissues turns into ice crystals, which damage cell membranes. Irreversible destruction (destruction) of cells occurs.
The procedure is used in cosmetology, gynecology, dermatology and aesthetic medicine to remove benign and malignant formations on the skin, mucous membranes and internal organs.
In cosmetology, cryodestruction is used to remove common and plantar (flat) warts, papillomas, moles, calluses with a core, keratosis, and condylomas.
Stages of cryodestruction of skin tumors
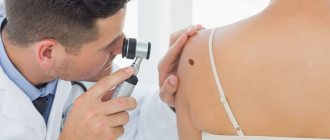
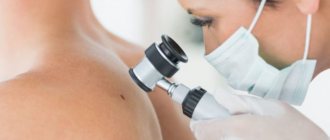
- Inspection. Cryodestruction is not carried out until the type of tumor is accurately determined. Usually, an inspection is enough for this. If the doctor remains in doubt, the tissue sample is sent for histological examination, and the procedure is postponed.
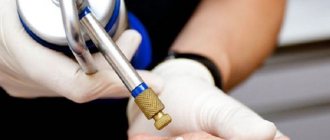
- Treatment of formation with liquid nitrogen. The doctor freezes the tumor with liquid nitrogen at a temperature of -195.8 °C. To do this, either cryodestruction equipment is used with automatic supply of cooled nitrogen through a nozzle, or a miniature applicator, which the cosmetologist lowers into a thermos with liquid nitrogen.
- Deadening of the growth. The treated area begins to turn pale. The patient feels a tingling sensation. The doctor checks the quality of the treatment to make sure that nitrogen has affected 100% of the neoplasm tissue.
The procedure takes about 15 minutes. The price depends on the size of the education.
Removal of neoplasms with liquid nitrogen
Removing tumors with liquid nitrogen is a time-tested, effective treatment method. Many patients often perceive tumors as cosmetic problems on the skin, rather than as a disease, and turn to a doctor late for help. Benign epithelial skin tumors differ in size, color, number, location, but they are more often of a viral nature or associated with self-medication. So, many patients bandage skin tumors with female or horse hair, trim them with nail scissors, etc. This does not solve the problem, but creates an environment for a secondary infection to occur. Injured tumors grow faster, disturb the owner, become wet, bleed, become crusty, and are painful. It is much easier to see a doctor without self-medication
Expected result: will there be scars and how many sessions are needed?
After cryodestruction, the growth dies and is gradually replaced by healthy skin. At first, the removal site resembles a burn, and then becomes covered with a crust. If you don’t peel off the scab and let it fall off on its own, there will be no scar left.
Deep tumors are not removed at once, so as not to damage healthy tissue around it by too intense freezing. In this case, 2-3 sessions are prescribed with an interval of 3-4 weeks.
How long does it take for skin to heal after cryodestruction?
After cryodestruction, the treatment area turns red and swells within 2-3 hours - this means the blood supply is restored. A blister appears at the site of formation, which gradually dries out and becomes covered with a crust. The scab then peels off as new, healthy skin forms underneath. This process takes 3-4 weeks. The shade and structure of young skin will differ from the rest of the skin for some time. After 4-5 months this difference will no longer be noticeable.
Advantages and disadvantages of liquid nitrogen removal:
Important: Benefits:
- No anesthesia required (no need to give an injection)
- The method can be used repeatedly on the same tumor
- No bleeding after removal
- Rarely leaves scars
- Good results for small pedunculated formations (papillomas)
Flaws:
- You cannot take a biopsy (microscopic analysis) of a remote lesion
- The need for repeated use of liquid nitrogen, especially for large tumors and located in areas with a thick layer of epidermis (on the palms and soles).
Rehabilitation: skin care after cryodestruction
- Do not allow the treated area to come into contact with clothing to avoid damaging the protective film.
- Do not cover with adhesive tape so as not to disturb air exchange. It is acceptable to cover with a gauze bandage.
- Do not puncture the blister. If its integrity is compromised, an infection may enter the wound, and a scar will form in its place after healing.
- Do not peel off the crust so that a scar does not appear.
- You can take a shower, but you cannot rub or steam the treatment area.
- Use healing ointments as prescribed by a doctor. They will speed up the healing of the skin after cryodestruction and prevent complications.
Causes of warts
Prerequisites for the formation of warts:
- neglect of personal hygiene rules (using someone else's shoes, washcloths, towels, manicure and pedicure instruments);
- increased skin moisture, especially hyperhidrosis of the feet and hands;
- immunodeficiency states of the body (HIV infection, cancer, treatment with cytostatics, viral hepatitis B and C);
- chronic stress;
- chronic dermatoses requiring treatment with external hormonal agents (atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, eczema and other itchy dermatoses);
- metabolic disorders in the body and hormonal dysfunctions.
Warts also often appear on thin baby skin.
Which is better: cryodestruction or laser removal
The difference between cryodestruction and laser removal of tumors lies in the technique of the procedure and the duration of the postoperative period.
- During laser removal, the growth is evaporated, and during cryodestruction, its tissue is frozen.
- Larger formations in skin folds and mucous membranes are removed with laser, and small ones in open areas of the body are removed with liquid nitrogen.
- Laser removal is more accurate, therefore it damages less tissue, but leaves an open wound. Cryodestruction covers a larger area, but is considered less painful and does not require anesthesia.
Only a doctor can choose the appropriate removal method. You can find out whether cryodestruction is suitable for your case or whether you should choose another method at an appointment at Dr. Kurenkov’s clinic. We are waiting for you in Moscow at Rublevskoye Shosse, 48/1.
Indications and contraindications for cryodestruction
As a rule, patients decide to remove skin tumors wanting to get rid of cosmetic defects. First of all, it is recommended to remove moles and warts located in “unsuccessful” areas where they are regularly injured.
There are practically no contraindications to cryotherapy: it is recommended even for children, if necessary. But there are cases when it does not give the desired effect, for example, if the diameter of the tumor exceeds 4 mm.
It is better to refrain from cryodestruction during infectious and inflammatory processes until they are cured.
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Cost of cryodestruction of tumors
| Cryomassage and cryodestruction of benign neoplasms |
| Service code | Service name | Number of services | Price |
| A24.01.004.001 | Cryodestruction of skin: removal of papillomas, keratomas, warts, condylomas (up to 0.5 cm 1 element) Code: A24.01.004.001 | 1 | 500 ₽ |
| A24.01.004.002 | Cryodestruction of the skin: removal of papillomas, keratomas, warts, condylomas (0.5 - 1.0 cm. 1 element) Code: A24.01.004.002 | 1 | 1 000 ₽ |
| A24.01.004.003 | Cryodestruction of the skin: removal of papillomas, keratomas, warts, condylomas (more than 1.0 cm, 1 element) Code: A24.01.004.003 | 1 | 1 500 ₽ |
| A24.01.005 | Skin cryomassage (1 zone, 1 procedure) Code: A24.01.005 | 1 | 800 ₽ |
Removal of benign tumors with liquid nitrogen
Fibroepithelial polyps
Fibroepithelial polyp (papillomas) are benign neoplasms on the skin in the form of wart-like growths, rising above the level of the skin, with a wide base or on a stalk, grayish or brown in color, with a diameter of 0.3 - 1.5 cm or more, round or irregular in shape. Most often they are located on the neck (along the lateral surface) and in large folds. The surface of papillomas is villous or covered with easily detachable horny masses.
Fibroepithelial polyps occur in 50% of the world's population, and in women during pregnancy they increase in number and size. In pregnant women, these tumors often appear on the nipples, which is dangerous for breastfeeding for the unborn child.
Seborrheic keratosis
Seborrheic keratosis (syn.: seborrheic wart, senile wart, basal cell papilloma) is the most common benign skin tumor. Usually develops in middle and old age from the epidermis. Its pathogenesis is unclear, but it is believed that this lesion develops from cells of the basal layer of the epidermis or keratinocytes of the most superficial part of the hair follicle and is not associated with human papillomavirus. In accordance with modern ideas, there is no connection with solar radiation. It occurs predominantly in elderly and senile people, but is often observed in young people, equally often in men and women.
The tumor develops very slowly, sometimes over several decades. Initially, a limited spot of yellowish or brown color appears, which gradually increases, sometimes reaching 4-6 cm or more in diameter. The surface of the stain is gradually covered with greasy crusts, which are easily removed. Over time, the crusts become denser, but often retain a greasy surface, riddled with cracks. The thickness of the crusts can reach 1-2 cm. The tumor becomes yellow-brown, dark brown or black. Localization can be very diverse. Lesions can be single or multiple. In rare cases, keratoses can become malignant.
Removing warts with liquid nitrogen
Warts are small, usually painless growths on the skin caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV).
More than 100 types of HPV are known. HPV affects the top layer of skin and usually enters the body through damaged skin. The virus causes the top layer of skin to grow rapidly, forming warts.
Most warts, but not all, are usually harmless and will disappear on their own within a few months or years. Warts can grow on any part of the body. They are most common among children and young adults - so liquid nitrogen removal is especially effective for hard-to-reach wart habitats.
Sometimes warts can be disfiguring, especially if they grow on the face or hands and cause psychological discomfort to their owner, and some of them also cause itching and pain.
Warts can appear at any age. Infection occurs through the shoes of an infected patient (plantar warts), in swimming pools, baths, gyms with exercise equipment, and in hairdressing salons through manicure accessories (periungual warts).
Vulgar warts
Warts vulgaris are the most common type of wart in humans. Other names are simple or common warts.
Remember: the cause of the appearance of vulgar warts is the already known Human Papilloma Virus (type 2).
Infection occurs in childhood. The virus gets onto injured skin (abrasions and scratches are common in children) and penetrates the skin. While in the body, it gradually multiplies in the basal layer of the skin and after a few months ordinary warts appear.
The clinical manifestations of the disease are simple. Rounded elevations ranging in size from 3 to 10 mm, no more, appear on the skin of the fingers and on the back of the hands and feet. A characteristic feature of this disease is the multiple nature of the rashes. That is, next to one simple wart on the hand, a second, daughter wart may soon appear, then another one nearby, etc.
Another sign characteristic of vulgar warts in most cases is the so-called kissing warts. This is their location when two simple warts appear on two adjacent fingers, opposite each other, touching each other when the fingers are closed.
Flat warts
Among all neoplasms caused by the human papillomavirus, flat warts are considered the most harmless. But this is only at first glance, sometimes leaving the problem without proper attention, a person gives the green light to further development, contributing to the spread of flat warts over a much larger area of the body. Flat, or juvenile, warts usually grow on the face, arms, or legs. They are small 1-5 mm, have flat tops in irregular nodules, and can be pink, light brown or light yellow in color. They occur mainly in children and adolescents. During the treatment of warts, the feet can and should be washed, because treatment with liquid nitrogen is not traumatic, does not open tissue, and does not release the virus. It is advisable to use liquid soap with tea tree oil. After warts on the feet are rejected, it is necessary to disinfect shoes, get rid of slippers, socks, and stockings to avoid reinfection.
Genital warts or genital warts
Transmitted sexually in 60% of cases through contact with an infected partner. This is the most common HPV infection (HPV types 6, 11, 16, 18, 42, 44, 54). Externally, genital warts are moist, soft, cauliflower-shaped nodules. They often ulcerate, turning into foul-smelling sores. Favorite localization is the genitals (mucous membranes and skin folds). Removal of warts with nitrogen is a painless removal without anesthesia followed by healing without scars.
During the treatment of benign epithelial tumors of the skin and mucous membranes, after a blood test for HPV, the use of immunomodulators and antiviral drugs is indicated both on the skin and mucous membranes, and, if necessary, orally.
What complications can there be during the procedure?
- Immediate complications: pain, fainting, headache, swelling (especially periorbital), blistering.
- Delayed: infection, bleeding, slow healing.
- Long-term but temporary: hyperpigmentation, milia.
- Constantly: hypopigmentation, ectropion, atrophy, alopecia.
The procedure is usually safe if done carefully, although there are sometimes exceptions. For example, cryotherapy treatments near the eyes may cause the eyelid to swell for a day or two, although the swelling will soon subside.
How is cryodestruction performed?
A freezing agent called cryogen (usually liquid nitrogen) is used to directly apply extreme cold to unwanted skin growths. Cryogen is applied to the target area where it destroys skin tissue and also stimulates a local immune system response. Over time, the unwanted tissue will crust over and then fall off, leaving behind healthy tissue to heal and repair itself. Along with the cosmetic benefits (clearer skin), young patients and their parents can rest easy knowing that unwanted tissue growth no longer poses a potential health threat.
Although liquid nitrogen is the most commonly used cryogen, there are other substances that can be used depending on individual circumstances. Cryogen is applied with a thin stream from a medical spray bottle. A cotton swab can also be used as an applicator. Treated skin will naturally tingle a little and then usually blister. The pain experienced is surprisingly tolerable if the procedure is performed by an experienced dermatologist.
After a few days, a scab will form, which will dry out and fall off over the next week or two. In severe cases, repeat cryotherapy is used to ensure complete removal of the lesion with little chance of recurrence. Cryotherapy is an inexpensive, reliable and safe procedure, but should only be performed after an accurate dermatological diagnosis, as the procedure is not suitable, for example, for the treatment of aggressive melanoma.
How is the treatment carried out?
Cold treatment is not a new method in gynecology, but is widely used due to its simplicity and effectiveness. The procedure is carried out using a cryoprobe (also known as a cryodestructor), through which a coolant is sprayed - nitrous oxide, liquefied or carbon dioxide liquid gas.
Cold and volatile liquid upon contact with the body instantly freezes tissues - the liquid in the cells and intercellular space crystallizes, blood circulation stops. The nutrition of the tissues stops - they collapse and die. A couple of minutes - and the freezing depth reaches several millimeters. But still, nitrogen cannot cope with large areas.
Contraindications
- Decompensated diabetes mellitus;
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- Diseases associated with blood clotting disorders;
- Uncompensated connective tissue diseases;
- History of anaphylactic shock (the decision is made individually);
- History of cancer;
- Vascular diseases which are based on the processes of their spasm (narrowing);
- Severe pigmentation of the skin;
- Some types of anemia (eg, cold hemolytic anemia);
- History of cold urticaria;
- Tendency to form keloid scars.
Who should not undergo cryodestruction?
Despite the fact that cryodestruction is a minimally invasive operation, the effect is targeted and no scars remain after healing, the procedure has a number of contraindications.
Conditions in which cryodestruction is not performed:
- pregnancy;
- menstruation;
- inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs;
- cicatricial deformation of the cervix;
- advanced endometriosis;
- fibroids requiring surgical removal;
- malignant neoplasms on the cervix;
- the boundaries of the affected areas are poorly defined or the erosion is large.
Not all cervical erosion requires treatment. If several doctors agree and strongly recommend undergoing surgical treatment, do not put off solving the problem indefinitely, risking facing dysplasia or more serious problems. It is faster and easier to get rid of any disease when it is at an early stage!
Find out the prices and sign up for cryodestruction of the cervix in one click!
What diseases can be treated with cryodestruction?
Dermatological _
Riosurgery allows you to treat a wide range of benign and precancerous skin conditions, such as:
- Angiomas
- Warts, including plantar warts
- Seborrheic and actinic keratosis
- Birthmarks
- Age and sun spots
- Dermatofibromas
- Molluscum contagiosum
- Condylomas
- Hemangiomas
- Acne
- Keloids
In most cases, a single application of cryodestruction is sufficient. Keloids require three times of treatment in two months, and dermatofibromas and ingrown toenails require two times of treatment in two months.
The main advantages of cryosurgery:
- Low cost of treatment
- No pain thanks to a combination of precision, freezing temperature and freezing power.
- Fast and effective treatment in intensive practice conditions
- No preparation time required
- Anesthesia is optional
- Excellent cosmetic results
- No need to remove sutures
- Minimal wound care
- Safe procedure
- Low risk of infection
- No bleeding
- No restrictions on physical activity
Dermatologists
- Ayvazyan Linda Volodyevna
Experience: 5 yearsDermatovenerologist, mycologist, trichologist
Rating: 0/5 — 0 votes
Make an appointment
- Osipova Daria Sergeevna
Experience: 14 years
Deputy chief physician for medical work. Dermatovenerologist
Rating: 0/5 — 0 votes
Make an appointment
The cryodestruction method is widely used in dermatology to remove various skin tumors. This is a modern, effective way to correct cosmetic defects and treat diseases. Cryodestruction can remove warts, moles, basal cell carcinomas, papillomas, condylomas, scars, old calluses and other undesirable phenomena from the skin. There are practically no traces left.
At the Kutuzovsky Children's Center, cryodestruction treatment is performed by experienced dermatologists. The procedure is performed on an outpatient basis in our clinic in Moscow. Prices for cryodestruction are indicated on the website.