Anesthesia (anesthetics, general anesthetics) are medications that cause anesthesia - a temporary loss of consciousness and all types of sensitivity, primarily pain. In large doses, anesthetics inhibit reflexes and cause deep muscle relaxation.
Another name for anesthesia is general anesthesia.
It is important not to confuse general anesthesia with local anesthesia. With local anesthesia, the loss of pain sensation is limited to a small area of the body around the injection site of the local anesthetic. In addition, with local anesthesia, the patient is conscious, unlike general anesthesia.
Any anesthesia occurs in four stages:
- The stage of pain relief (analgesia) is the loss of pain sensitivity, but the patient is still conscious.
- Excitation stage – speech and motor excitation; a very short stage, practically absent with modern anesthetics.
- The stage of anesthesia is loss of consciousness, decreased muscle tone, suppressed reflexes. Depending on the depth of general anesthesia, superficial, light, deep and ultra-deep anesthesia are distinguished.
- The stage of recovery from anesthesia is awakening. In case of an overdose of anesthesia, the exit stage is replaced by the agonal stage with respiratory depression and cardiac arrest.
All anesthetic drugs have a rapid effect, causing the patient to black out within a few seconds of the start of administration.
Types of anesthesia in dentistry
Anesthesia in dentistry can be general or local. The first includes intravenous sedation, as well as general anesthesia. That is, the drugs do not act locally in the oral cavity, but throughout the entire body. Actually, this is ordinary general anesthesia, which is used everywhere in medicine - it’s just that certain types are used in dentistry. Local, as it is already becoming clear, includes the familiar “freezing”, which is administered by injection.
Separately, we can also distinguish xenon sedation or xenon therapy - the second name will be even more correct, since such anesthesia is used to prepare for local or general anesthesia. It allows you to reduce the level of anxiety and stress, saturates the body's cells with oxygen, due to which it has a general healing and even rejuvenating effect! It is not an independent type of pain relief, but is used in combination with other approaches.
How will you feel?
Nothing, because sedation relieves all unpleasant sensations. At the same time, it can be superficial - you will be in a state of half-asleep or half-asleep (answering doctors’ questions, periodically falling asleep, but remaining in a relaxed state), or complete, when you will be sleeping throughout the entire time the operation lasts . Here the choice is yours. But in both cases you will not feel anything. The maximum is the “moving” of the instruments in the oral cavity, because you understand that the doctor is doing some kind of work.
Comfortable treatment without pain! We carry out thorough diagnostics, select medications and dosages strictly individually. It's safe here!
Enroll now
Xenon sedation or xenon therapy to prepare for main anesthesia
This is a separate type of anesthesia that can be used in combination with both local and general anesthesia (if necessary). Xenon is an inert gas that quickly begins to act and is just as quickly eliminated from the body. It has a relaxing effect: anxiety decreases, the patient relaxes. Moreover, during the operation he is fully conscious, can communicate with the doctor, and understands everything that is happening around him. The procedure can be interrupted if necessary if there is discomfort. At the same time, local anesthetics are used, since xenon itself does not have a pronounced analgesic effect.
Among the pleasant “bonuses” are saturation of cells with oxygen and restoration of metabolic processes. That is, this is not only a reduction in stress, but also a general improvement in the body’s health.
General anesthesia in dentistry
With general anesthesia, the patient falls asleep for 1-2 hours or more, i.e. for the entire duration of treatment. The drug is administered intravenously, less often by inhalation. If possible, general anesthesia should still be avoided, since its effect on many organs is quite toxic. Even despite the fact that dentistry uses “lighter” drugs than during complex surgical operations. This is a fairly large load on the body, especially on the heart, nervous and cardiovascular systems.
How is treatment performed under intravenous sedation?
The essence of using intravenous sedation is that certain anesthetics are introduced into the body, which put the person into sleep. The drug itself and its dosage are selected based on the patient’s weight, health status, and the duration of the procedure. If necessary, the drug can be reintroduced during surgery.
A catheter is inserted into a vein in the arm through which the medication is administered. The catheter remains in place until the end of the entire treatment, as repeated administration of the drug may be required.
The operation is performed on an empty stomach: you cannot eat or drink for 6 hours before sedation. The procedure is not limited in time. The patient wakes up naturally within 20 minutes after the end of the drug and is under the supervision of specialists for a maximum of 1-2 hours who will monitor their health.
After treatment under sedation, it is strictly not recommended to drive, as concentration decreases. There are no more restrictions.
Intravenous sedation
Intravenous sedation does not have such pronounced negative consequences for the body. Softer and gentler drugs are used here. Sedation puts a person into a half-asleep state - the patient can respond to the doctor’s commands, communicate and understand him. At the same time, the person is completely relaxed and may even fall asleep for several hours. Thus, intravenous sedation is a more gentle and safe type of pain relief.
This is interesting! The word “sedation” itself means “calming.” It can be carried out either by inhalation (nitrous oxide or safer and more effective xenon is used for this), as well as intravenously with the selection of drugs strictly individually.
We treat without pain and discomfort!
Intravenous sedation
Safe and pain-free Treatment in your sleep Quick recovery from RUB 8,000. from 8,000 rub.
Xenon sedation
Relaxation before treatment No stress on the body Recovery in 2-3 minutes from RUB 5,000. from 5,000 rub.
With us you will stop being afraid of dentists! Individual selection of drugs, the most modern equipment and certified doctors who professionally work with all types of anesthesia.
Enroll now
What is sedation?
Sedation is a process of relaxation and anxiety relief. The word itself comes from the Latin “sedatio”, which translates as “calm”. In dentistry, various sedatives are used for these purposes, which are administered by inhalation or intravenously. Thus, it is customary to distinguish several types of such anesthesia:
- inhalation sedation: for this direction we use the inert gas xenon, which does not anesthetize, but relaxes before introducing the main anesthesia (usually local, that is, infiltration or conduction, which allows you to anesthetize the tissues of the oral cavity).
- intravenous sedation: sedatives are administered through a catheter directly into a vein. The patient becomes drowsy (sleeping or dozing),
- general anesthesia: drugs are administered intravenously (inhalation is also possible, but this type of anesthesia is not used in dentistry). The person goes into medicated sleep for several hours.
What is local anesthesia?
Local anesthesia allows you to numb the specific area where the intervention is planned. The patient is conscious. And this is actually more than enough even for complex surgical operations.
For local administration of all types of anesthetics, special reusable syringes are used, which have a recess for inserting a carpule - this is a hermetically sealed ampoule with an anesthetic. Unlike disposable ones, carpule syringes have a thinner needle, which allows you to administer the drug slowly and thus eliminate pain. All syringes for reusable use must undergo antiseptic treatment and sterilization using modern ultrasonic and temperature sterilization equipment.
Anesthesia and anesthesia - 14 frequently asked questions
14 frequently asked questions about anesthesia and anesthesia General anesthesia - with this form of anesthesia, they sleep deeply, soundly and safely. Her response to pain is as repressed as her consciousness. Anesthetics are constantly supplied through the blood or breathing air. Therefore, this anesthesia is well controlled. Can be used in any surgery. (Masking anesthesia, laryngeal mask, anesthesia and intubation anesthesia) Regional anesthesia - covers a specific part of the body, depending on the plant. They remain conscious during the procedure or optionally choose twilight sleep, which includes spinal cord anesthesia (ankle and back anesthesia) and upper and lower limb locking. (Plexus anesthesia, knee block, etc.) Local anesthesia only makes a small part of your body insensitive to pain. This anesthesia procedure is performed by the surgeon himself.
What needs to be done before anesthesia?
Please tell your anesthesiologist about all the medications you are taking, including those you bought at the pharmacy! It is especially important to be sober, not to eat 6 hours before surgery and not to drink liquids 2 hours before surgery! (Exception: a few sips of water for taking important medications - but you should definitely check this with your anesthesiologist!)
On the day of anesthesia, refrain from smoking!
Remove makeup and nail polish!
Jewelry - including piercings - must be removed! In addition, glasses, contact lenses and hearing aids, as well as removable parts of teeth, as well as other prosthetics. Exceptions are possible only after consultation with an anesthesiologist.
Why can't you eat and drink before surgery? Anesthesia eliminates protective reflexes (such as automatic swallowing). As a result, there is a risk of stomach contents entering the pharynx and then into the respiratory tract. This can lead to severe pneumonia. The risk of swallowing (aspiration) increases the shorter the last meal. Therefore, it is in your best interest to tell the anesthesiologist exactly when you last ate and drank.
Why can't I smoke on the day of surgery? Smoking may increase stomach acid secretion and therefore has the same risk as eating before surgery. Stomach juice can drain back into the esophagus and into the lungs (aspiration), causing pneumonia there.
What are the risks and complications of general anesthesia?
- Nausea after surgery (usually caused by drugs). It only occurs in patients with a certain predisposition and can be treated very well with medication.
- Hoarseness (after intubation) usually resolves within 24 hours.
- Aspiration (which means foreign bodies entering the trachea or lungs when swallowed). If the patient adheres to the prescribed preoperative behavioral rules (“sober”!), aspiration is practically impossible. This hazard is most common in acute procedures (unplanned surgeries).
- Cardiovascular disorders (dangerous in pre-existing cardiovascular diseases) can be caused by the stress of surgery.
- Cooling (today very rare: during surgery the patient is warmed up accordingly) is manifested by postoperative tremor.
- Damage to teeth can occur during intubation - but is very rare.
- Malignant hyperthermia (extremely rare, 1:250,000, but life-threatening) is caused by the patient's genetic predisposition. This complication begins with a significant increase in body temperature and can lead to kidney failure. If there is a known history of malignant hyperthermia in the family, be sure to tell your anesthesiologist!
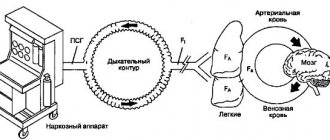
How quickly does anesthesia work? Whether the anesthesia begins through the bloodstream or the breathing air, you will fall asleep within seconds.
Is it possible to wake up during surgery or hear something? After you fall asleep, your anesthesiologist constantly checks the depth of anesthesia in addition to vital organ functions. With the medications available today, especially gaseous anesthetics, you can almost completely eliminate the possibility of waking up or listening during surgery. In addition, modern devices make it possible to measure the depth of anesthesia.
Will there be any pain after the operation? About 25% of patients complain of nausea after surgery. Reasons include personal predisposition (eg, motion sickness), type of surgery, and ultimately the anesthesia procedure chosen. You can counteract nausea with preventive medications. Although nausea cannot be completely avoided, it is less frequent and milder.
When can I eat and drink again? Depending on the type of operation, this time interval can vary greatly. It is best to wait at least 3 hours to drink and feed solid food for at least 6 hours.
Will there be pain when waking up after anesthesia? No. Although pain cannot be completely avoided after surgery, you will, of course, be given appropriate pain therapy both during the recovery phase and afterwards. The need for painkillers mainly depends on the operation being performed.
When can you go home after general anesthesia for an outpatient procedure? Discharge should always be carried out by the surgeon and anesthesiologist no earlier than 2 hours after the operation. The patient is again warned about the need to drive a vehicle during the first 24 postoperative hours, enter into any contracts, or take alcohol or sedatives (except for prescribed medications).
What is regional anesthesia? Regional anesthesia is the temporary loss of sensation of pain in a specific area of the body due to interruption of pain transmission to the brain. Typically the patient remains conscious during this form of anesthesia.
What types of regional anesthesia are there? Interruption of anesthesia is possible in several places: In the area of the spinal cord (“cross stitch”) In the area of the nerve plexus (plexus), that is, where the nerve fibers merge with the nerves after leaving the spinal cord (plexus of anesthesia) In the area of individual nerves (so called peripheral regional anesthesia or peripheral nerve blocks)
Spinal and epidural anesthesia. Both are regional spinal cord anesthesia procedures. The difference between the two methods is the depth of penetration. Unlike spinal anesthesia, with epidural anesthesia, the height of the puncture site and the amount of local anesthesia determine the location and size of the anesthesia area. "Regional anesthesia" occurs because only a specific part of the body, the "spinal cord," is anesthetized because the nerves coming out of the spinal cord are anesthetized. Unlike general anesthesia, the patient is conscious during the operation.
Spinal anesthesia can be used for all operations below the navel, that is, for operations on the legs, pelvis, perineum and lower abdomen. With epidural anesthesia, operations can be performed on the upper abdomen, pelvic and genital areas, and on the legs. Spinal anesthesia is a safe procedure using modern, state-of-the-art equipment. As with any method, complications are sometimes possible, but they are usually temporary. Permanent damage is extremely rare.
Are you awake during surgery under local anesthesia? Depending on the patient's wishes, this may be awake. But if he prefers to sleep, he can be given a mild tranquilizer.
Does the patient have to be sober before local anesthesia? As with general anesthesia, the same rules of conduct apply to regional anesthetics.
Sources:
- Anesthesiology. National leadership (ed. A.A. Bunyatyan, V.M. Mizikov). M., ed. Group "Geotar-Media". 2011.
- Levshankov A.I. Ensuring patient safety (monitoring) during anesthesia, resuscitation and intensive care. Guide to anesthesiology and resuscitation (ed. Yu.S. Polushin). St. Petersburg - 2004. – pp. 137-139
- Likhvantsev V.V., Ulitkina O.N., Rezepov N.A. Postoperative delirium: what new does the new ESA-2017 guideline offer us? // Bulletin of Anesthesiology and Reanimatology. - 2017; 14(2): 41-47)
- General anesthesia. In the book: Anesthesiology and resuscitation. Textbook for training highly qualified personnel, vol. 1 (S.A. Sumin, K.G. Shapovalov). Moscow: Medical Information Agency, 2022. P. 257-286;
- Terminology and classification of anesthesia methods. In the book: Guide to anesthesiology and resuscitation (ed. Yu.S. Polushin). St. Petersburg, 2004. Pp. 279-282
- Continuum of depth of sedation: Definition of general anesthesia and levels of sedation/analgesia. Committee of Origin: Quality Management and Departmental Administration (Approved by the ASA House of Delegates on October 13, 1999, and last amended on October 15, 2014)
Infiltration anesthesia
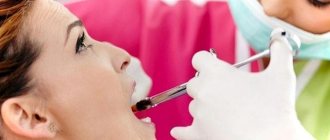
Classic “freezing”, which is used in dentistry for almost any manipulation. The drug is injected under the mucosa, into the periosteum or directly into the bone. Depending on the procedure and the patient’s pain threshold, the required dosage is selected - for example, in case of acute pulpitis or complex tooth extraction, a higher concentration of the drug is used. If the patient is afraid of injections, topical anesthesia can additionally be used to numb the site of needle insertion, or xenon sedation.
When performing the procedure, the doctor must take into account the anatomy of the jaw system. For example, in the lower jaw the alveolar bone is denser, so anesthesia is less effective. In the upper jaw, when performing manipulations in the area of wisdom teeth, there is a risk of the needle touching one of the branches of the facial nerve, which is fraught with the development of neuralgia. The clinic’s doctors have the necessary qualifications, so even the most complex anesthesia is performed completely safely for the patient.
Preparations for local anesthesia
The Smile-at-Once clinic uses modern anesthetics of the latest generation - effective, non-toxic and absolutely safe, even for pregnant women, the elderly or children. We do not use drugs based on novocaine or lidocaine due to toxicity and a high risk of allergic reactions. In addition, the articaine group of drugs, which are used today for local anesthesia, are 5-6 times more effective than lidocaine.
"Ultracaine" for all groups of patients
An original drug produced in France, which is used for both infiltration and conduction anesthesia.
It is safe, used even in the presence of allergic reactions, and is suitable for patients with heart disease and pregnant women. Its effectiveness is very high, while it is instantly eliminated from the body and does absolutely no harm. The main active ingredient is articaine, to which epinephrine is added to enhance the anesthetic and prolong its action. It provides local vasoconstriction, which significantly shortens the rehabilitation period after treatment. Depending on the concentration of epinephrine, there are three types of the drug - for different manipulations and categories of patients.
"Ultracaine-Forte" (concentration 1:100,000) is a drug with a high dose of epinephrine, used during surgical operations. "Ultracaine DS" with a low concentration (1:200,000) - is used for therapeutic treatment, including in patients with diseases of the cardiovascular system, high blood pressure, suitable for pregnant and lactating women. Ultracaine D does not contain epinephrine. The effect of the drug is short, but it can be used for allergic reactions, bronchial asthma, and pronounced cardiovascular pathologies.
"Ubistezin"
A cheaper, but no less high-quality analogue of Ultracain, produced by the German company 3M. It contains similar active ingredients: articaine hydrochloride and epinephrine. It has two forms of release, depending on the concentration of the latter (1:100,000 or 1:200,000). Use is allowed during breastfeeding and cardiovascular pathologies.
"Artikain"
An injection solution that consists directly of the main active ingredient - articaine. Inexpensive drug made in Russia. Used for infiltration or conduction anesthesia. Can be used in pure form or with the addition of epinephrine/glucose solution in a certain proportion. Not used for bronchial asthma and severe allergic reactions.
"Scandonest" for the elderly
The main active ingredient of this French-made drug is mepivacaine hydrochloride. It is not used during pregnancy and bronchial asthma, but use is allowed in patients with cardiovascular pathologies, since the drug does not contain epinephrine, adrenaline and preservatives. Suitable for older people, especially those with high blood pressure. It is one of the safest anesthetics for both infiltration and conduction anesthesia. Its disadvantage is its short duration of action, which requires repeated administration of the drug approximately every 30 minutes during long procedures.
"Orablock"
Another drug, the main active ingredients of which are articaine and epinephrine with varying concentrations of the latter, which affects the effect and duration of pain relief. Not used during pregnancy and pronounced cardiovascular pathologies.
"Naropin" for complex surgical operations
A long-acting anesthetic whose main active ingredient is ropivacaine hydrochloride. The duration of pain relief depends on the dosage. Very often, this drug is used for conduction anesthesia during complex surgical operations and the installation of a large number of implants. Among the contraindications is only individual intolerance to amide anesthetics.
Indications for use
Anesthesia is used for various surgical interventions (operations), including for pain relief for short-term operations in dentistry, gynecology, childbirth anesthesia, traumatology (fusion of dislocations, fractures).
Certain anesthetic drugs are used to eliminate severe pain and prevent pain shock in myocardial infarction, acute pancreatitis, multiple injuries (for example, car accidents, falls from a height), severe and extensive burns.
Anesthesia can also be used to relieve (eliminate) status epilepticus, a severe complication of epilepsy in which the patient’s seizures follow one another without stopping.
Indications and advantages of local anesthesia
Since local anesthesia is used everywhere, the indications for its use are very wide. Modern drugs are of very high quality and completely safe (especially if you use them thoughtfully, having first collected a high-quality anamnesis about the patient’s health condition). The level of stress from treatment without anesthesia, and especially with acute pain, can be prohibitive - very often after this, patients refuse to visit the dentist, causing dental problems. Do not be afraid of anesthesia - you will not receive such a “dose” of the drug that will harm you, even if you have to treat your teeth for several days in a row.
Indications for local anesthesia
- removal of dental plaque,
- dental treatment of any complexity,
- performing plastic surgery on gums,
- tooth extraction,
- surgical operations in the oral cavity,
- preparation and implementation of dental implantation.
Advantages
- complete relief of any painful sensations,
- safety, no toxic effects on the body,
- rapid elimination from the body,
- minimum side effects,
- the choice of drug based on the health status and age of the patient.
Are there any disadvantages to local anesthesia?
Local anesthesia has virtually no disadvantages. Unlike drugs that were used previously, modern anesthetics are absolutely safe, have a minimum of contraindications, are quickly eliminated from the body, and do not have a negative effect on the heart, kidneys and liver. With professional administration, the patient will not feel any pain even during long surgical procedures.
“Our clinic uses a strictly individual approach. We have selected several of the most effective and safe drugs - for each patient we select our own method, drug and its concentration, based on individual characteristics. Therefore, everyone who undergoes treatment, implantation or prosthetics at the Smile-at-Once clinic can feel completely safe.”
Zhilenko Evgeniy Aleksandrovich, Implant surgeon, periodontist, orthopedist Work experience over 18 years make an appointment
What if something goes wrong? Is this really safe?
Yes, it is completely safe: the administration of the anesthetic, as well as monitoring the patient’s condition, is carried out by professional and licensed anesthesiologists. The participation of professional anesthesiologists in the operation who monitor the patient’s condition allows the implant surgeon or maxillofacial surgeon at our clinic to fully concentrate on the operation. Constant monitoring of all vital indicators of the patient’s health status is mandatory.
In addition, there is an ambulance station in close proximity (up to 1 km) from each clinic. And this is an additional guarantee of your safety, because in case of complications, every second will count.
“Like you, we are sincerely interested in safe treatment and high-quality restoration of your health, so we make every effort to provide comfortable treatment: we focus on diagnosis, the correct selection of medications, and monitoring the condition during surgery.”
Namdakov Nikolay Vladimirovich maxillofacial surgeon, implantologist, orthopedist, work experience over 18 years make an appointment
Modern technologies for administering anesthesia
The pain of the anesthesia itself, as well as its effectiveness, depend 90% on the skill of the dentist. A professional doctor will make every effort and use various techniques to make the patient feel comfortable. However, all people are different, each has their own pain threshold, and that is why an individual approach not only to the concentration of drugs, but also to premedication before the direct administration of anesthesia is very important.
Today, special anesthesia devices have been developed to help doctors. Naturally, they work under the supervision of a specialist. The electronic system is equipped with special pressure sensors - to avoid pain, the anesthetic must be injected very slowly and immediately after puncturing the tissue. The device is equipped with special needles with a very thin double tip, which again reduces pain.
In addition, by administering a small dose of anesthetic, a kind of allergy test is performed - the doctor assesses the condition of the soft mucous membranes (swelling, redness, rash) and the patient’s general reaction, and the pressure force is controlled by the device.
Safe, painless and effective treatment without pain! Treatment is carried out under the supervision of anesthesiologists capable of providing first aid. Special equipment monitors indicators of the general condition of the body.
If there is any threat, the ambulance station is 800 meters from the clinics! You are under the reliable protection of professionals.
Enroll now
The use of anesthesia for health pathologies
- diabetes mellitus, bronchial asthma, allergic reactions: anesthetics without preservatives and with a minimal amount of epinephrine are used. For these problems, medications are selected strictly individually, most often based on the results of additional tests,
- high blood pressure, heart disease: with minimal or no epinephrine. It is also important that anesthetics do not contain adrenaline. For these pathologies, intravenous or xenon sedation can be used,
- pregnancy and lactation: drugs with a low content of epinephrine - in minimal dosages, the active substance does not cross the placenta and practically does not enter breast milk (only in small quantities, but this does not have any negative effect, so after dental treatment you can not skip feeding and no need to express milk). It is important that the drugs cannot be used without the addition of the vasoconstrictor epinephrine - in this case, the vessels remain open and the active substance will quickly spread throughout the body, which increases the risk of its transmission to the fetus or child through breast milk.
What do patients say about treatment under sedation?
Most of our patients sleep during surgery and wake up after the doctor has finished treatment. Many people note that they sleep well during this time. If they remain conscious (lighter sedatives are used), then they do not feel pain, but there is a feeling of a slight “crawling” in the mouth from the knowledge that the doctor is removing/treating teeth or implanting implants.
Svetlana Yurievna
“They sat me at a table, put me on an IV, then transferred me to a chair and I don’t remember anything else. Before the operation, the doctor noted that he would look at my condition and see how much medication I would need. To be honest, this scared me. Because I thought that at some point the sedative would end, it would hurt and I would feel it. But nothing like that happened, I turned my head - they put additional medicine in my IV, and everything ended well. I am immensely happy!”
- treatment WITHOUT FEAR and pain
- guaranteed safety
- minimal health risks
- with condition monitoring and professional supervision
watch a video with the patient
Sedation and anesthesia - is it safe?
Yes, if they are carried out by professional doctors who have extensive experience and have undergone appropriate training (and a license is also required to perform general anesthesia - this requires an anesthesiologist-resuscitator), then the procedure will be completely safe. In addition, for complex and long-term implantation, the use of sedation is even preferable - you are less tired, you do not need to focus on keeping your mouth open for several hours and fixing your head in a certain position. For you, 3-4 hours of surgery passes in an instant. You will be under the supervision of specialists, and before the operation you will undergo a fairly extensive list of tests for high-quality preparation for treatment and selection of the most suitable, safe drug.
1 Zoryan E.V. Errors and complications when performing local anesthesia in dentistry, 2007.
Intravenous anesthesia
This type of anesthesia refers to non-inhalation types of anesthesia, which are characterized by a long-lasting effect and a greater depth of effect compared to inhalation anesthesia. Intravenous anesthesia can be performed using the following drugs:
- Thiopental, Recofol, Oxybutyrate and Propofol - classic pain relief
- Fentathyl with diphenhydramine - neuroleptanalgesia, which can be carried out on spontaneous breathing or combined with artificial ventilation
- Sibazon with Fentathyl is ataralgesia, which provides superficial, gentle anesthesia and can be carried out with other types of anesthesia.
This type of anesthesia is used to remove abscesses and phlegmons that occur with complications; it is also possible to treat small benign tumors if their removal under general anesthesia is not possible.