Photoaging is the aging of the skin of the face, body, and hands under the influence of ultraviolet rays. This is a completely different type of skin aging, different from natural ageing. Photoaging is a type of skin “damage” that depends on external factors - excessive exposure to UV radiation.
The main signs of photoaging: loss of skin tone, dryness, solar lentigo, wrinkles, pigmentation, rosacea, visible dilated capillaries, spider veins.
How does it appear? UVA rays penetrate deep into the skin, reducing elasticity and firmness, causing the formation of wrinkles, age spots and freckles. UVA rays cause much more serious and profound changes in the skin than UVB rays and can provoke the development of skin cancer.
Photoaging occurs at any age, starting from 20 years.
Today, photoaging is classified according to the Glogau scale. There are 4 stages of skin aging depending on age and the signs that appear. Depending on the condition, the Beauty Practice Clinic doctor will provide appropriate treatment.
Ages 20 to 35 years : no wrinkles, light pigmentation, no visible deep wrinkles and no keratoses.
Age from 35 to 50 years : moderate aging, manifested by the formation of facial wrinkles around the mouth and eyes, pronounced changes in skin pigmentation.
Age over 50 years : pronounced photoaging, characterized by an abundance of wrinkles, visible even at rest, the presence of obvious symptoms of telangiectasia, as well as dyschromia.
Age from 60 to 80 years : extreme photoaging, the skin becomes yellow-gray in color, pronounced wrinkles appear on the entire surface of the skin, there may be pre-malignant changes in the skin. Risk groups: fair skin, pregnancy, menopause, period of hormonal disorders.
What is photoaging
Photoaging is the deterioration of skin caused by sun exposure, which causes signs of aging. It is estimated that 75 to 90% of wrinkles and lack of skin elasticity are associated with exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
Exposure to UVA and UVB rays is a determining factor in the appearance of signs of premature aging. It is believed that photoaging begins to appear around the age of 20, and the damage is directly proportional to the time spent in the sun without protection.
Photoaging is a long process. Experts say that damage caused at age 15, for example, does not become apparent until age 40. So, visible skin changes are a direct result of the cumulative “sun damage” to which we are exposed throughout our lives.
Table of contents
- Etiology and pathogenesis
- Clinical manifestations
- Principles of treatment
- Cosmetological methods
- Invasive methods
- Hardware treatment methods
Chronoaging (genetic aging, programmed aging, age-related skin changes, intrinsic aging) is the result of gradual changes in the appearance and functional characteristics of the skin over time.
In our company you can purchase the following equipment for the correction of chronoaging:
- M22 (Lumenis)
- Fraxel (Solta Medical)
- AcuPulse (Lumenis)
- UltraPulse (Lumenis)
- Clear+Brilliant (Solta Medical)
- Thermage (Solta Medical)
- Maximus (Pollogen by Lumenis)
- GeneO+ (Pollogen by Lumenis)
Signs of healthy skin
With international trends such as "glass skin" and models' seemingly natural, perfect faces, any "imperfection" on the face is viewed with concern. However, this is not necessarily a really serious problem.
Here are some signs of healthy skin:
Skin hydration.
Drinking enough water is vital not only for your internal organs, but also for maintaining the health of your body's largest organ, your skin. If you drink enough water (about 3 liters for men and about 2 liters for women), then your skin is probably adequately hydrated.
If so, your skin should have a slight sheen to it - take a close look at your face while slowly rotating it in natural light. Do you see shine or dryness and dullness? Draw conclusions.
Get into the habit of wearing sunscreen.
Many people believe that they only need to protect their skin from ultraviolet radiation on sunny days or on the beach. But the truth is that we need to do this even when we are driving a car, flying on a plane, or running errands.
If you actively use sunscreen (with SPF) every day, you protect yourself from harmful UV rays, allowing your skin to remain its healthiest.
No tightness or dryness.
Ideally, the skin should not experience any discomfort. Moreover, regardless of whether you used makeup or skincare products or not.
Any unusual sensations, such as itching or burning, may prompt you to consult a dermatologist or change your usual skin care routine.
Even complexion.
An even skin tone is a positive sign that you do not suffer from common dermatological diseases.
If you have a lot of dark spots or redness, it could be a sign of eczema, psoriasis, or rosacea. If you suddenly notice a change in color that is outside the normal range for your skin, consult a dermatologist.
Adaptation-regulatory theory
In the 60-70s, scientists V.V. Frolkis developed a theory that proves the genetic programming of aging and death. The main premise of this theory is that human life expectancy and age-related changes are determined by two processes: along with the irreversible aging process, a reverse process also develops, which is aimed at increasing life expectancy, maintaining the vitality and adaptive properties of the body.
A special place in this theory is also occupied by the hypothesis that the main mechanisms of human aging may be disturbances in the functioning of genes that are responsible for the activity of structural genes. Due to age-related gene dysregulation, changes in the ratio of synthesized proteins in the body occur, as well as the appearance of proteins that were not previously synthesized.
The scientist also put forward a hypothesis confirming that the aging mechanisms he described underlie such age-related pathologies as cancer, diabetes, atherosclerosis, Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases. Depending on which function of a particular gene was activated or suppressed, a certain pathology of aging develops.
This group includes theories that prove that aging is the result of a number of random processes occurring at the molecular level. Namely, many scientists have proposed many hypotheses confirming that aging is the result of the accumulation of mutations in chromosomes due to wear and tear of the DNA repair mechanism.
Signs of skin photoaging
The effects of photoaging can appear in a variety of ways, from cute freckles to melasma and changes in skin texture.
For example, sun exposure (and hormonal changes) can cause the following signs of photoaging:
- Loose skin (loss of elasticity);
- Dark spots;
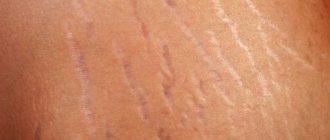
- Broken blood vessels (telangiectasia);
- Yellowish tint;
- Change in skin texture;
- Favre-Racouchaud syndrome (sun-related milia, rashes and cysts).
UV exposure also causes fine lines and wrinkles around the eyes, mouth and forehead, as well as liver spots. An age spot is pigmentation caused by sun exposure. They can appear not only on the face, but also on the body, including the hands, chest and back.
Photoaging is skin damage caused by prolonged exposure to the sun, and its main danger is that it can lead to skin cancer.
Free webinars on anti-aging medicine Learn about the features of the Anti-Age Expert International School, as well as the opportunities for improving your medical practice every day.
The webinar program also includes fascinating reviews of innovations in anti-aging medicine and analyzes of the most complex clinical cases with recommendations that really work. Find out more
Natural and premature aging
Scientists have proven that the type of human aging is determined by nature itself. However, several periods of skin aging can be distinguished. The aging process starts at the age of 25, which is caused by hormonal changes in the body and slower cell regeneration. Of course, at this age the body’s functional reserves are still quite high, so metabolic processes in it proceed quite quickly. The appearance of the first wrinkles at the age of 25 is usually associated with the influence of negative environmental factors on the skin.
Histological signs of photoaging
Photoaging is accompanied by quantitative and qualitative changes in the skin.
The severity of skin damage depends on the strength and duration of ultraviolet radiation. It affects all layers of the epidermis and can be expressed by atrophy of the stratum corneum or hyperkeratosis.
At the histological level, photodamage is manifested by the destruction of collagen fibers, as well as the replacement of normal collagen fibers by damaged ones. Elastin fibers are also subject to destruction. In this case, damaged fibers can occupy different parts of the dermis.
Upper face wrinkle removal
• Vertical and horizontal wrinkles of the glabella • Horizontal wrinkles of the forehead • Wrinkles in the outer corners of the eyes (“crow’s feet”) • Horizontal wrinkles in the lower eyelid caused by hypertrophy of the orbicularis oculi muscle
The injection technique in these areas depends on the location of the problem area, so in the treatment of glabella wrinkles, injections are mainly performed intramuscularly, with the injection points always located above the brow ridge.
When removing horizontal forehead wrinkles and crow's feet, botulinum toxin preparations (Botox, Dysport, Lantox) are most often injected subcutaneously at several points along the muscle or even intradermally, so as not to lead to drooping of the eyebrows. It should be remembered that men have more muscle mass, so the dose of drugs administered to men is usually also higher.
When removing horizontal wrinkles in the lower eyelid area caused by hypertrophy of the orbicularis oculi muscle, as a rule, one subcutaneous injection is performed into the central part of the muscle, 3 mm below the edge of the lower eyelid.
Photoaging: how it works
The skin consists of three layers: epidermis, dermis and subcutaneous fat. The dermis contains collagen, elastin and other fibers that support the structure of the skin. It is these elements that give the skin a smooth and youthful appearance and are damaged by UV radiation.
Ultraviolet radiation consists of UVA and UVB rays. To put it schematically, UVB rays burn, and UVA rays age the skin.
UVB rays are shorter than UVA rays and are the main cause of sunburn. UVA rays, with their longer wavelengths, are responsible for much of the damage we associate with photoaging. UVA rays penetrate deep into the dermis, where they damage collagen fibers, a protein responsible for the strength of all body tissues, including the skin. And this leads to an increase in elastin production. This abnormal amount of elastin triggers the production of enzymes known as metalloproteinases, which repair damaged collagen.
However, these enzymes usually end up doing more harm to collagen than good by not repairing the skin properly. Since it is exposed to UV rays on a daily basis, this process is repeated, which at a minimum results in wrinkles.
Although sunlight is the main cause of skin aging, about 10 percent is due to HEV radiation and infrared light. HEV, or high-energy (blue) visible light, comes from the sun and devices such as phones or computers and can be seen by the human eye. This light doesn't go out when the sun goes down. Infrared light is invisible to the eye and feels more like heat, such as in a microwave oven.
Fortunately, none of them are associated with skin cancer, but observations have shown that they destroy collagen and elasticity of the skin. According to a 2014 study published in the journal Photodermatology, Photoimmunology & Photomedicine, non-solar radiation significantly contributes to photoaging and should be taken into account when developing skin protection measures.
Mechanism of wrinkle formation
The mechanism of wrinkle formation is genetically programmed. The facial muscles are attached to the skin at one end and to the bones of the skull at the other. Their contraction determines our facial expressions. Wrinkles form in areas of constant muscle activity. When it contracts, the muscle shortens and wrinkles the skin, and when it relaxes, it returns to its original position and pulls it back with it. In young people, the skin is elastic and expands quickly. With age, the elasticity of the skin decreases, and constant contractions of the facial muscles contribute to the formation of wrinkles on the forehead, in the corners of the eyes, on the bridge of the nose, bridge of the nose, upper and lower lips. Unfavorable external factors provoke increased activity of the facial muscles and contribute to the progression of the skin aging process, which also affects the formation of wrinkles.
Who is most susceptible to photoaging?
No one is 100% protected from ultraviolet radiation, however, people with a certain skin type are more vulnerable to photoaging of the face, and the degree of susceptibility to sunlight depends, among other things, on the climate zone in which the person lives.
In general, lighter skin is more susceptible to photoaging and skin cancer.
Dermatologists use the Fitzpatrick scale to determine skin phototype (or skin color) and assess the risk of photodamage:
- Type 1 - pale skin, light eyes, blond or red hair. Always burns, never tans.
- Type II - fair skin, light eyes. Burns easily, but can also tan.
- Type III - Medium-light skin that first burns and then tans.
- Type IV - light brown skin that tans with minimal burn.
- Type V is medium brown skin that rarely burns.
- Type VI is dark brown or black skin that tans easily and never burns.
Darker skin can also be damaged by UV light and be diagnosed with cancer, but the more likely outcome is that the skin will develop uneven dark patches (melasma).
Elevation (ontogenetic) theory of aging
In the 50s of the twentieth century, scientist V.M. Dilman promulgated the idea of the existence of a special regulatory mechanism that is responsible for age-related changes in various body systems. According to this hypothesis, the main link in the development and aging of the body is the hypothalamus. The scientist decided that the main reason for the aging of the body is a decrease in the sensitivity of the hypothalamus to signals that come from the endocrine glands and the nervous system.
Over the next decades, scientists have proven that this process is the cause of age-related changes in the functionality of the reproductive system. Dilman's theory implies that aging and the diseases caused by it are a side process of the body's development. It is important that this model of understanding aging has helped to discover new approaches to the prevention and treatment of many age-related diseases such as malignant neoplasms, strokes, heart disease, metabolic immunosuppression, obesity, diabetes, and mental depression. Scientists have proven that some of these diseases can be inhibited if homeostasis is stabilized at the level that the body reaches towards the end of its development.
Alternative tanning methods
Tanning is essentially a protection that our body produces when it is exposed to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. To avoid the risks associated with sun exposure, you can “tan” artificially. For example, using one of these methods:
- Bronzing. This salon method allows you to instantly achieve a chocolate shade. Using a special apparatus that resembles a shower, tanning lotion is applied to the body. Afterwards, it is not recommended to shower or bathe for 10 hours to allow the tan to set and develop.
- Self-tanning. Self-tanning products, often DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) based, cause oxidation of the top cells of the skin. They come in the form of creams, sprays or even tablets. Most effective when combined with regular skin exfoliation.
Please note that none of these procedures protects from the sun and therefore using a protective cream with SPF afterwards is also necessary.
Theories of skin aging
- Molecular genetic theories
The mechanisms of skin aging are quite complex, so today there are many theories that explain them. One of the most recognized and widespread hypotheses is based on the fact that the cause of skin aging is changes occurring in the genetic apparatus of cells. In science, it is customary to divide molecular genetic theories into two large groups: the first includes theories that consider aging as a hereditarily programmed change in the genome, and the second includes theories that prove that aging is the result of the accumulation of mutations.
How to protect your skin from photoaging
Quitting tanning is just the first step in the right direction. If you want to live a more skin-friendly lifestyle, here are helpful tips you can use to maximize photoaging prevention.
- Use SPF protection every day. Even on cloudy days, up to 80% of solar radiation reaches the Earth and possibly your skin. So if you're serious about preventing photodamage, choose a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF30 or higher and reapply it every two hours.
- Use shade, a sun hat and umbrellas. Whenever possible, use additional accessories to avoid direct sunlight.
- Minimize sun exposure between 10:00 and 14:00. During these hours, ultraviolet rays are most active and dangerous.
To effectively protect against photoaging, it is advisable to start applying these recommendations right now, without delaying until later.
Free radical theory
In the 50s of the twentieth century, almost simultaneously the ideas of scientists D. Harman and N.M. were presented to the public. Emanuelema. These theories explain both the mechanism of aging of the body itself and a large range of pathological changes associated with it (cardiovascular diseases, brain dysfunction, weakened immunity, cancer, cataracts). According to scientists, the cause of aging is free radicals, which are reactive oxygen species synthesized in mitochondria.
If a chemically active and aggressive free radical leaves its place for any reason, it can lead to damage to proteins, lipids, RNA and DNA. It is worth noting that nature has developed a system for protecting the body from free radicals - for example, many substances that enter the body with food have antioxidant properties. Therefore, it is believed that regular consumption of such foods provides the necessary daily dose of antioxidants. However, it must be remembered that an overdose of such substances can lead to an acceleration of oxidative processes in cells.
How to fight photoaging
The gold standard for treating mild to moderate photoaging is the use of vitamin A products such as retinol and retin-A.
Products containing them were first used for acne and were later found to reduce the formation of wrinkles, especially fine lines and wrinkles. Retinoids work by activating cell renewal. However, it may take several months before changes are noticeable.
Light technologies are also used to treat photoaging, including:
- Photodynamic therapy is a method in which a light-sensitive drug is applied to the skin. Once it penetrates the skin, the affected area is exposed to light, which activates the medication to promote collagen growth, giving the skin a more youthful, elastic appearance.
- Intense pulsed light (IPL) is a light therapy technique that is effective in reducing the appearance of uneven pigmentation and broken blood vessels over several sessions.
- Laser therapy is used to treat a variety of skin conditions, depending on the wavelength of light hitting the skin. Different wavelengths are used to contract blood vessels, eliminate age spots, reduce wrinkles and remove hair.
Treatment of signs of photoaging will be more effective the sooner you pay attention to this problem.
Removal of wrinkles from the middle and lower parts of the face
• Radial wrinkles around the lips • Labiomental folds (“sadness folds”, “marionette lines”) • Chin wrinkles • Neck wrinkles
Unlike the upper third of the face, where expression wrinkles predominate, the lower part of the face has both expression and static wrinkles. The causes of the formation of static wrinkles (for example, nasolabial folds) are primarily genetics, atrophy of fatty tissue associated with aging, gravitational ptosis of tissues and, to a lesser extent, contractions of facial muscles. Therefore, botulinum toxin (Botox, Dysport, Lantox) is much less effective in combating static wrinkles than in combating expression wrinkles. In addition, it should be remembered that the effect of botulinum toxin injection in the middle and lower part of the face may be less lasting due to the high functional activity of the muscles (chewing, speech).
When treating radial wrinkles around the lips with botulinum toxin (Botox, Dysport, Lantox), the drug is usually injected subcutaneously into 4 points on the upper lip and 2 points around the lower lip. In this case, there may be a slight increase in volume (this can be especially useful for those who wish to enlarge the upper lip at the same time as rejuvenation) and some protrusion of the upper lip, which may be associated with partial paresis (decreased muscle strength) of the orbicularis oris muscle.
The presence of labiomental folds or “folds of sadness” gives the face a sad, angry or dissatisfied expression. To eliminate these wrinkles, botulinum toxin preparations (Botox, Dysport, Lantox) are injected directly into the middle and lower thirds of the depressor angle oris muscle. As a rule, as a result of such therapy, the corners of the mouth are slightly raised.
With hypertonicity of the mentalis muscle, there may be wrinkles or numerous irregularities on the chin, which can give the face an unattractive appearance. To improve the appearance of the chin, an injection of botulinum toxin is administered intramuscularly into the central part of the mentalis muscle.
When rejuvenating the neck, correction with botulinum toxin (Botox, Dysport, Lantox) best responds to vertical “cords” of the subcutaneous neck muscle and horizontal neck wrinkles.
[/td]
Prevention of skin photoaging
The appearance of signs of photoaging can be prevented by following just a few recommendations:
- Avoid exposure to the sun when it is at its strongest, usually between 10:00 a.m. and 2:00 p.m.
- If possible, sit under umbrellas and in the shade.
- Wear a wide-brimmed hat to protect your face.
- For example, wear loose clothing with SPF.
- It is also important to apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen (protects against UVA and UVB rays) daily to sun-exposed areas: face, neck, chest, arms, hands and legs.
- Wear sunglasses, or not wearing them can speed up macular degeneration, a leading cause of blindness as we age.
Note that daily use of sunscreen can also reduce the risk of developing skin cancer. Dermatologists recommend a cream containing zinc oxide and/or titanium dioxide, which has broader coverage for UVA rays. SPF must be at least 30.
If signs of photoaging appear, you should also use skin care products designed to neutralize sun damage. Some ingredients, such as vitamins C and E and green tea, are antioxidants that stabilize the skin and help lighten dark spots. Retinol, used at night, accelerates cell turnover, giving skin a healthy, youthful appearance.
Anti-Aging Medicine Seminars Gain knowledge based on evidence-based medicine first-hand from the world's leading experts. As part of the Anti-Age Expert Modular School, in-person two-day seminars are held every month, where the intricacies of anti-age medicine are revealed to doctors of more than 25 specialties
Find out more
Apoptosis theory
This theory was proposed by scientist V.P. Skulachev. It is based on apoptosis, a process of cell death that has been programmed in advance. It is believed that, like trees shedding parts to preserve the whole, over time, each cell, after completing its life cycle, must die. The destruction of a cell can be triggered by infection with a virus or the onset of mutation processes in it, which provoke its malignancy. A cell can die because its life has reached the end of its life. The death of the cell occurs so that it does not infect the entire body.
Moreover, this process differs significantly from necrosis, in which cells die violently due to poisoning, injury, burn, or lack of oxygen due to blockage of blood vessels. On the contrary, as a result of apoptosis, the cell independently disassembles into separate parts, after which neighboring cells use these parts as building material.
Similar self-destruction occurs with mitochondria. The reason for this is the formation of excessive amounts of free radicals. When the number of dead mitochondria becomes quite large, their breakdown products provoke cell poisoning and apoptosis. According to scientists, aging is a consequence of the fact that more cells die in the body than are born. In this case, the dead cells gradually begin to be replaced by connective tissue. Old age is a real disease that can be cured if the aging program that shortens a person's life expectancy is disabled.
Hydration
The cause of early wrinkles is often poor facial skin moisture. Skin loss of moisture occurs due to the negative impact of various external factors - atmospheric and climatic phenomena. In addition, air polluted with aggressive chemical compounds has a detrimental effect on the epidermis. Excessively low humidity usually causes the body to lose water. Increased humidity provokes the production of sebum.
It is believed that even with very high humidity, the skin should still be protected from drying out, so it constantly needs good hydration. Low temperatures and low humidity also pose serious dangers to facial skin. Often the skin becomes dry due to exposure to wind. As a result of this impact, it becomes thin and begins to peel off. That is why, to prevent skin loss of moisture, it is necessary to regularly use moisturizing cosmetics.
However, it must be remembered that the older a woman is, the drier her skin becomes. Even if a woman had oily skin at a young age, by the age of 50 it will turn into dry. Therefore, over time, additional effective moisturizing of the skin is necessary, which will be very difficult to achieve with conventional creams. The most effective way to completely moisturize the skin is to inject hyaluronic acid into it.
To eliminate signs of skin aging, a biorevitalization procedure is ideal, during which the patient is injected into the epidermis with hyaluronic acid, the concentration of which is as close as possible to the most natural for the body. It is for this reason that this substance is not rejected by the body, and also has a beneficial effect not only on the problem area, but also on the tissues adjacent to it.
The results of this procedure are simply amazing: the skin becomes more elastic and tightened, then shallow wrinkles disappear, and more pronounced wrinkles become less noticeable. It has been proven that just one molecule of hyaluronic acid can hold at least a thousand molecules of water. Therefore, after introducing the substance under the skin, it is very powerfully moisturized, which has a prolonged effect.
Please note that hyaluronic acid injections are a completely painless procedure. At a young age, this acid is actively produced by the body, but over the years the process of its accumulation slows down. It is for this reason that many women over 30 years old experience the first signs of skin aging - sagging and wrinkling. In modern cosmetology, there are also non-invasive methods of introducing hyaluronic acid. These include hardware techniques - ultrasound, aquaphoresis, laser.