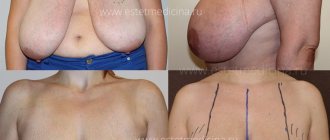
Men look at women with large breasts with admiring glances, but those with a cup size D and above often experience difficulties. Impressive and heavy breasts cause difficulties even in youth, and over the years the number of complaints only grows. The situation can be corrected with reduction mammoplasty. We tell you what kind of operation this is and who needs it.
According to the anatomy of the female breast, the bust cannot remain elastic throughout life, especially if nature has generously endowed you with forms. This area of the body, even with normal dimensions, is most susceptible to change under the influence of various factors. Her condition depends on hormonal levels, constitutional characteristics, pregnancy, lactation, weight fluctuations and health problems. The mammary glands enlarge not only during pregnancy, lactation or excess weight gain, sometimes this happens due to gynecomastia - the growth of glandular or fatty breast tissue, noticeably exceeding the norm. The reasons for this growth lie in an unbalanced diet, hormonal imbalances and other factors.
Indications for reduction mammoplasty
Back pain
Large breasts shift the center of gravity forward and down, forcing the back muscles to overexert in an attempt to provide balance to the body.
As a result, osteochondrosis or curvature of the spine develops. Over time, gait inevitably becomes disturbed and posture worsens. In addition, under the weight of the mammary glands, the bra straps dig into the shoulders and cause chronic pain (including headaches).
Difficulties when playing sports
A large bust, even with well-chosen underwear, causes discomfort or pain when running, jumping, and other active exercises.
Uncomfortable sleep
Even if a woman doesn't like to sleep on her stomach, sleeping without a bra can be a challenge, especially during intense turns.
Wearing underwear around the clock is dangerous to your health. Studies have shown that women who wear a bra most of the time are at risk of developing breast cancer.
Difficulties with choosing underwear
Finding the perfect bra for large breasts is extremely difficult. Manufacturers usually increase the cups in proportion to the girth under the bust. If you are skinny and curvy, finding suitable underwear will take a lot of time.
Increase after childbirth
For many women, after the birth of a baby and breastfeeding, the mammary glands increase by one or two sizes, and if it was initially large, the problem gets worse.
Ptosis
Any breast sag with age, after breastfeeding or with weight fluctuations. The constitutionally large mammary glands can stretch under their own weight even in youth, stretch marks form, and the shape and, as a result, the contours of the figure deteriorate.
Figure imbalance
It happens that large breasts look disproportionate in relation to the rest of the body, especially if the woman is quite petite.
Preparing for surgery
If you are planning to resort to surgery, the first thing you need to do is consult a plastic surgeon and find out what options for mammoplasty he can offer you.
At your appointment, discuss in detail with your doctor the desired results: not only the shape and size of the breast, but also the appearance of the nipple and areola - as a rule, they also need correction.
The choice of a specific technique will depend on the severity of aesthetic problems. If a woman is only concerned about large breast size, then reduction mammoplasty or breast reduction is performed.
But most often, owners of large busts, in addition to size, also complain about deformation - a condition when the main volume of the mammary glands is concentrated below the nipple, and in the upper part there is a shortage and sagging of tissue. In this case, a combination of reduction mammoplasty and mastopexy (breast lift) will be needed.
What is an axillary approach?
In another way, this method is called “axillary”. The surgeon makes 3-4 cm incisions in the folds of the armpits. Thus, there are no scars on the chest itself. The operation is performed using an endoscope.
Advantages
- Good cosmetic effect;
- There is no risk of damage to the mammary glands;
- The doctor can install an implant either under the pectoral muscle or under the gland.
Minuses
- The surgeon’s control over the course of the operation decreases: the risk of asymmetric installation of implants and damage to nerve endings increases;
- It is difficult to make a correction;
- Not suitable for breast augmentation with large implants;
- Not suitable for women with severe ptosis and breast asymmetry.
Who might suit it?
Axillary access is popular among patients due to its excellent cosmetic effect and the ability to install an implant under a muscle or mammary gland. However, its aesthetic benefits come with risks and limitations. Most often, mammoplasty through the axillary approach is performed by women who have poorly defined mammary glands and fatty tissue and who are planning breast augmentation with small-sized implants.
Thus, there is no clear answer to the question of which type of access is better for augmentation mammoplasty. Each of them has advantages and is associated with some limitations. The optimal option for installing breast implants can only be selected after an examination and conversation with a doctor.
Center for Plastic Surgery at the N.I. Clinic Pirogov opened in 1999. During this time, we performed more than 10 thousand plastic surgeries. Our professionals are recognized as the leading plastic surgeons in St. Petersburg, according to the ratings of independent experts and leaders in the medical industry. The clinic also offers patients:
- modern technical equipment of the clinic;
- promotional offers for mammoplasty and initial consultations;
- comfortable conditions of hospital stay;
- personal support of out-of-town patients at all stages of examination, surgery, rehabilitation;
- installments for operations.
Call the number and we will answer your questions.
How is reduction mammoplasty performed?
In the absence of ptosis and with slight hypertrophy of the mammary glands, their volume can be reduced through minimal intervention - with one incision and without moving the nipple-areolar complex to a new position.
Reduction mammoplasty
The operation is performed through a small access (6–10 cm), located in the natural crease under the breast. Thus, no one will notice any traces of the operation, even if you sunbathe topless on the beach. Excess glandular tissue and fatty tissue in the lower part of the breast are removed through the incision. Since this operation cannot significantly affect the shape of the breasts or correct sagging, it can only be recommended for young women with elastic skin. In other cases, simultaneous breast reduction and lifting is required, which can be done in various ways. This operation is considered the most difficult of all types of surgical breast correction. In the process of bust reduction, you need to remove a noticeable amount of fat and glandular tissue, as well as excess skin, but do this in the most gentle way possible in order to maintain sensitivity and normal blood circulation.
If a woman wants to only slightly reduce the volume of her breasts and at the same time she has moderate tissue sagging, then the operation is performed through the periareolar approach, that is, through an incision around the areola of the nipple.
The breast tissue is carefully redistributed, excess fat and skin are removed, and the nipple is moved to a higher position. This method is considered the least traumatic, since it does not affect the mammary gland itself, and the incision then becomes almost invisible. However, it is not suitable for severe ptosis and excess glandular tissue.
Lift and reduction with vertical incision
The most popular method.
With its help, you can give your breasts a natural shape, reduce stretched skin, reduce the size of the areola and the volume of the mammary glands. A skin incision is made around the nipple and vertically down to the inframammary fold. This lifting scheme makes it possible to work with significant sagging of the mammary glands. After the operation, the scar around the nipple is almost invisible, but the thin vertical scar remains visible, although it fades over time.
T-shaped (or anchor) mastopexy
This method is used for severe ptosis and large breasts.
The incision is made in the form of an anchor: around the areola of the nipple, then vertically down to the inframammary fold, in which a horizontal incision is also made. Through the created access, excess fatty and glandular tissues, as well as skin, are removed. Additionally, it is necessary to move the nipple to a new, higher position and reduce the circumference of the areola. A certain difficulty may arise here when moving the nipple-areolar complex, when the nipple has to be raised by 15–20 cm. Firstly, it must be returned to its anatomically ideal position, and secondly, it must not damage the vessels and maintain normal blood supply to the area.
After reduction and lifting, the upper pole of the breast becomes rounded and seductive again, the volume of the mammary glands is reduced, and they acquire a neat, clear shape.
When it comes to breast augmentation, mammoplasty is performed using implants or your own fat. But when reducing mammary glands, these techniques are not used.
Consequences after breast surgery
After the operation, when the anesthesia wears off, the patient may feel pain and discomfort in the chest area.
This is due to swelling after breast surgery, which is a completely normal phenomenon and occurs in all cases to one degree or another, depending on the individual characteristics of the body and the intervention technique. Immediately after the operation, special compression garments are put on, the purpose of which is to provide the least stress on the swollen tissues and stabilize the installed implants. The pain lasts for up to a week. Patients wear compression garments for up to 4 weeks. All parameters are individual and determined by the attending physician.
How often do complications occur after breast surgery? Surgeons answer negatively to this question. This is due to the fact that the operation is not performed for emergency reasons and all parameters of the patient’s health are taken into account. In addition, modern techniques allow operations to be performed with a high degree of predictability.
Condition after surgery
Reduction mammoplasty on average takes about 2.5 hours and is performed under general anesthesia. The type and extent of the operation depends on the specific case and is selected by the surgeon.
The patient is observed in the hospital for the first few days, then, after examination by a specialist, she can go home. The sutures are removed two weeks after surgery. Primary healing takes about a month, during which it is necessary to wear compression garments.
At first, the breasts after mammoplasty may hurt. Bruising and swelling are possible. Restrictions on physical activity apply for the first three months. During the rehabilitation period, visiting the solarium, bathhouse, and swimming pool is also prohibited.
After three to four months, the desired aesthetic result is already visible, and complete restoration of all internal structures of the mammary glands occurs in about a year.
How to eliminate risks?
To be sure of the success of the operation, you need to choose a good clinic and an experienced specialist. Also, before correction, you must undergo a full examination to make sure there are no contraindications.
Before and after surgery, it is important to carefully follow all instructions and recommendations of your doctor. Do not remove compression garments ahead of schedule. You should protect yourself from stress, ultraviolet rays, sports, etc.
This approach allows most of the potential risks of mammoplasty to be minimized or completely eliminated. The remaining potential complications are highly individual and very difficult to predict or prevent. But these complications are so rare that they occur in one case per thousand patients. Therefore, you should not be afraid of mammoplasty and possible consequences.
Possible risks of reduction mammoplasty
In rare cases, complications may occur after surgery in the form of hematomas, inflammatory processes, tissue necrosis, and scar formation.
Approximately 10% of patients experience impaired sensitivity of the nipples up to complete anesthesia, as well as circulatory disorders in the breast tissue.
If the problem is not solved in the first months of rehabilitation, then it is necessary to surgically eliminate the factors that led to the disruption of blood supply.
Sometimes postoperative flattening and subsidence of the mammary gland occurs. This may be due to insufficient tissue removal or perhaps the surgeon did not secure the nipple-areolar complex well. In both cases, revision breast surgery is required. On average, the incidence of complications with reduction mammoplasty does not exceed 3%.
Other types of risks
In extremely rare cases, various specific complications may occur, for example, “dubble bubble” (the so-called “double breast”) or synomastia. These situations occur due to incorrect installation or an error in the choice of implants, less often due to unique anatomical features.
It is also possible that an allergic reaction to the implant may occur. Unfortunately, it is impossible to predict the individual reaction of the body. The implant itself is made of a material that does not cause allergies, but medications, suture materials, and consumables can lead to a reaction. Allergies are usually controlled with medication.
Very rare, but no less unpleasant, are such phenomena as thinning of the integumentary tissue (as a result of which the implant becomes visible), double folding or calcification. In most cases, the risks increase from the incorrectly selected size or type of implants during breast augmentation.