Causes of skin cancer
Currently, there is no clear answer to the question of what causes skin cancer. Like many other oncological diseases, skin tumors are considered a multi-etiological pathology. There are several predisposing factors, the presence of which increases the risk of developing a tumor focus. These include:
- Excessive exposure to ultraviolet rays on the skin. A similar situation occurs with prolonged and frequent exposure to sunlight, visiting a solarium, or working outside. Residents of the southern regions are at risk of developing skin cancer.
- Having light skin. Lack of melanin production increases the likelihood of skin tumors.
- Skin burn. A high degree of burn is accompanied by scarring of the skin. This process contributes to the emergence of latent carcinogenesis.
- Irradiation. Exposure to radioactive, ionizing rays has a detrimental effect on the skin. The risk of radiation dermatitis increases.
- Presence of skin contact with toxic substances. This group of carcinogens includes arsenic, aluminum, titanium, nickel and other heavy metals.
- Immunodeficiency. Conditions in which the body's protective functions decrease predispose to the formation of a tumor focus.
- Age. Most often, skin tumors affect people over 50 years of age.
- Concomitant systemic diseases. Doctors identify a group of pathologies in which the risk of developing skin cancer increases significantly. These include systemic lupus erythematosus, leukemia, and chronic skin diseases.
- Heredity. The presence of a skin tumor in previous generations of relatives is not a major risk factor. However, family history in combination with other predisposing conditions increases the possibility of developing skin cancer.
- Tattooing. In this case, there are two risk factors. This is a violation of the integrity of the skin and the introduction of paint with carcinogenic substances. Cheap tattoo ink may contain impurities of aluminum, titanium, and arsenic.
- A large number of nevi. Doctors urge you to monitor the condition of moles and contact a specialist if there is the slightest change. Traumatization of nevi increases the possibility of developing skin cancer.
- Excessive alcohol consumption, smoking. Chronic intoxication has a detrimental effect on the body as a whole. Against this background, the risk of tumor formation increases several times.
- Eating foods high in nitrates.
Oncologists identify several precancerous conditions, the presence of which significantly increases the risk of developing skin cancer. These include:
- Xeroderma pigmentosum.
- Bowen's disease.
- Paget's disease.
- Hyperkeratosis.
- Cutaneous horn.
- Late stage radiation sickness.
- Dermatitis and dermatoses.
Why do hemangiomas appear?
The exact causes of hemangiomas have not yet been identified; It is generally accepted that their appearance can provoke disruption of intrauterine development of the fetus due to a viral illness of the mother or oxygen starvation. Additional risk factors for the formation of congenital hemangioma:
- multiple and/or late pregnancy;
- increased amount of estrogen in the mother;
- her sedentary lifestyle;
- unbalanced diet;
- alcohol or nicotine intoxication of the fetus;
- his low birth weight.
In adults, the cause of neoplasm can be a hereditary predisposition, diseases of the cardiovascular system, excessive ultraviolet radiation, and increased levels of the female hormones estrogen.
Symptoms and signs of skin cancer
The clinical picture of skin cancer development depends on its type. Often the first signs of a tumor are mistaken for other skin diseases. This results in untimely consultation with a doctor and the spread of the malignant process. Common signs for all types of skin cancer are:
- The appearance of a small spot or lump on the skin. The color of the formation can be pinkish, gray-yellow. It is noteworthy that the color of the neoplasm differs from moles and freckles.
- Uneven shape and asymmetric contours of the pathological focus.
- The appearance of itching and slight discomfort in the area of the tumor process. This symptom appears some time after the formation of cancer.
- Progressive growth of the tumor.
- Fatigue, weakness, sudden loss of strength.
- Decreased appetite, resulting in sudden weight loss.
- As cancer develops, regional lymph nodes are affected.
If any of the above symptoms appear, it is recommended to seek medical help. Depending on the type of skin cancer, the following symptoms are distinguished:
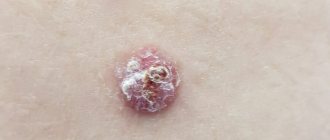
1. Basalioma. It is the most common form of skin tumor. It is characterized by a favorable prognosis when detected at the initial stage. Appears in the form of a nodule, painless on palpation. It has a grayish-pink color. The surface of the nodule is usually smooth. Scale formation is possible. As the tumor process spreads, the affected area increases. The neoplasm is covered with a bloody film. The predominant localization of basal cell carcinoma is the face, neck, and arm area. Basalioma does not cause a significant change in condition. This is the reason for late seeking medical help.
2. Squamous cell carcinoma. At an early stage, it looks like a dense red or brown nodule. A tumor of this type is prone to rapid decay, and therefore, as the process progresses, an ulcer forms. Its edges are heterogeneous, the ulcer often bleeds. Squamous cell carcinoma quickly grows into nearby tissues. If detected at a late stage, metastasis to regional lymph nodes or organs is possible.
3. Melanoma. Refers to an aggressive type of tumor. Most often, melanoma occurs at the site of an injured nevus, which increases in size, changes color and acquires uneven contours. A characteristic feature of this type of cancer is the asymmetric form of formation, as well as a tendency to bleed. The malignant neoplasm itches and increases in size. As the process progresses, the tumor turns into an ulcer. Melanoma progresses rapidly and often metastasizes.
4. Adenocarcinoma. At the initial stage of development, it looks like a dense nodule. It is most often localized in the armpit area, under the breast. With the development of the tumor process, adenocarcinoma grows into nearby tissues. This type of tumor is detected extremely rarely and is characterized by slow growth.
Melanoma, what is it?
Melanocytes synthesize pigments responsible for coloring the skin, eye color, and hair. Pigmented formations filled with melanin are called moles and can appear throughout life. Certain causative factors of an exogenous (from the Greek “exo” - external) and endogenous (“endo” - internal) nature can cause malignancy of nevi. As a result, areas of the body where there are congenital or acquired nevi are at risk of developing melanoma: the skin, less often the mucous membranes and the retina. The altered cells are able to multiply and grow uncontrollably, forming a tumor and metastasizing. Most often, among benign “brothers”, a single malignant neoplasm is discovered.
The clinical picture is varied. The size, outline, surface, pigmentation, and density of the tumor vary widely. Any changes that occur with a mole should alert you.
Types of skin cancer
Depending on the type of cells from which the tumor is formed, there are several main types of skin cancer. Determining the structure of the tumor is necessary to clarify the diagnosis and carry out appropriate treatment. In addition, the speed of its spread and further prognosis depend on the type of cancer. Oncologists distinguish the following types of skin cancer:
1. Basal cell (basalioma). Basal cell carcinoma is the most common form of skin cancer. It originates from the basal cells of the epithelium. Basalioma is characterized by slow, sudden development and a relatively favorable course. Unlike other types of skin cancer, it rarely metastasizes. Basal cell carcinoma is usually localized in the area of the nose, bridge of the nose, eyebrow, upper lip and nasolabial fold. A rare location for this type of cancer is the neck and ears. There are several forms of basal cell carcinoma:
- Nodal. The most common location of nodular basal cell carcinoma is the head and neck area. At an early stage it looks like nodules up to 5 mm in size. As the tumor process develops, the nodules merge with each other. At a late stage, nodular basalioma is a deep ulcer with necrotic areas.
- Superficial. This type of basal cell carcinoma is located on the trunk and limbs. The tumor looks like a round pink spot with ulcerations. Superficial basal cell carcinoma is considered the most favorable and non-aggressive form of skin cancer.
- Scleroderma-like. Refers to an aggressive type of cancer. Located in the deep layers of the skin. The most common location for this type of tumor is the head and neck. Basalioma has the appearance of a plaque, which in the later stages of the process has the appearance of a depressed scar.
- Cystic. A rarely detected form of basal cell carcinoma, externally similar to a cyst.
- Fibroepithelial. Located in the lumbar region. Basal cell carcinoma has the appearance of a pedunculated polyp. The fibroepithelial form is extremely rare and has a favorable course and prognosis.
2. Melanoma. Refers to an aggressive type of skin cancer that originates from melanocytes. Melanoma is characterized by rapid growth and invasion into neighboring tissues. This type of skin cancer metastasizes not only to regional lymph nodes, but also to organs. A favorable prognosis for melanoma is only possible if the tumor is diagnosed at an early stage. Women with fair skin are at risk for developing skin cancer.
3. Squamous. Squamous cell carcinoma is the 3rd most common type of skin cancer. It develops from the outer layers of the skin. It is characterized by slow development, which increases the possibility of detecting a tumor at an early stage. At the initial stage, squamous cell skin cancer looks like a red lump up to 2 cm in diameter.
The above forms of skin cancer are diagnosed most often. They account for about 90% of all detected oncological processes of the skin. In addition, there is skin appendage cancer, which is extremely rare. This type of tumor includes:
- Adenocarcinoma. Comes from the sweat and sebaceous glands. Characterized by slow growth. Outwardly it looks like a dark blue node, localized in the groin and chest area. Adenocarcinoma does not tend to grow into adjacent tissues, and metastasis rarely occurs. The tumor is removed surgically.
- Verrucous carcinoma. Refers to a very rare form of squamous cell carcinoma. Outwardly it resembles a wart, so detection at an early stage is difficult. A distinctive feature of verrucous carcinoma is its bleeding.
New growths on the skin
The term “neoplasm” implies local excessive growth of any tissue of the body. On the skin they are represented by primary and secondary tumors, nevi and hemoderma. In dermatological practice, tumors are divided into benign and malignant. A detailed photo and detailed description of each of them will be given below.
Why do they occur? The study of skin tumors is still ongoing. The exact reasons for their occurrence have not been established, but scientists put forward several theories about this. Provoking factors may be:
- family history (presence of neoplasms in relatives);
- individual characteristics of a person (light skin and hair, old age);
- exposure to ultraviolet, radiation and x-ray radiation;
- viral infection; long-term trauma to the skin;
- chronic exposure of the skin to chemical carcinogens (nitrosoamines, benzopyrene, aromatic amines, etc.);
- insect bites; metastatic processes in the presence of an oncological process in the body;
- violation of the trophism of the skin, hence chronic skin ulcers; weakened immune system (due to immunosuppressive therapy, HIV infection, etc.).
Types of neoplasms on the skin Neoplasms on the skin, according to their origin, can be divided into primary (those that are formed from the skin tissue itself) and secondary (those that metastasize into the dermis and epidermis from foci of another localization). The latter also include hemoderma. They arise due to pathological proliferation of malignant cells of the hematopoietic system. There is a division of neoplasms into benign, precancerous (precancrosis) and malignant (cancer itself). This classification allows you to determine the treatment method and life prognosis for the patient.
Nevi should be distinguished from skin tumors. These are benign neoplasms that are related to skin developmental defects.
Malignant neoplasms, neoplasms on the skin of a malignant nature in the Russian Federation in the structure of cancer incidence today account for 9.8% and 13.7% in men and women, respectively. People living in areas with high photoinsolation and having fair skin are especially susceptible to the disease. Description of new cases.
Malignant skin tumors include: basal cell carcinoma; Kaposi's sarcoma; liposarcoma; squamous cell carcinoma; melanoma, etc. Basalioma One of the most common epithelial skin tumors. It is formed from atypical cells of the basal layer of the epidermis, which is where it gets its name. The tumor is characterized by long-term progression, peripheral growth, during which the surrounding tissues are destroyed. Basalioma is not prone to metastasis. This pathology develops mainly in elderly people and the elderly, and is localized mainly on the face, neck and head (its scalp). Sometimes basal cell carcinoma is classified as a precancer, because under the influence of certain factors it degenerates into metatypical cancer.
The first manifestation of a developing tumor is a dense, hemispherical nodule that does not rise above the skin. Its color usually matches the skin color or differs slightly (light pink tint).
At the initial stage, the patient does not complain. Over the course of several years, the papule grows, reaching 1 or 2 cm in diameter. Its center gradually collapses, bleeds and becomes crusty.
Under the latter, erosion or an ulcer with a narrow ridge along the edges is found, which over time scars and grows along the periphery.
Basalioma reaches a size of 10 centimeters or more. The once pink papule turns into either a flat plaque with peeling, or a noticeably raised node above the surface of the skin, or a deep ulcer that destroys the underlying tissue (down to the bone).
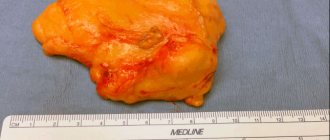
Liposarcoma This is a neoplasm on the skin from fat cells of mesenchymal origin. In the photos below you can see how big these tumors reach. The description in clinical reference books speaks of liposarcoma as a formation that tends to appear on the buttocks, thighs and retroperitoneal tissue. It is more common in men over 40 years of age.
Initially, a swelling appears, then a node appears. There are no subjective sensations yet. On palpation, the nodule is dense, elastic, and mobile. Subsequently, the tumor grows, turns red, and inflammatory processes begin. Large liposarcoma can compress nerves and blood vessels and even grow into them, causing disturbances in tissue trophism and pain.
Kaposi's sarcoma
This is a systemic multifocal disease of vascular origin with primary damage to the skin, lymphatic system and internal organs. It belongs to tumors of an endothelial nature and develops mainly in individuals with severe immunosuppression.
The morphology of skin lesions of sarcoma is quite diverse. they come in the form of spots, nodules, infiltrative plaques, etc. There are several types of sarcoma: classic (European). endemic (African). Epidemic (for HIV). immunosuppressive (immunodeficiency caused by medications and medical procedures). The first type is observed in the elderly and the elderly and has a favorable course. the elements grow for a long time, tens of years in the proximal direction and do not cause discomfort to the patient. formations are most often localized on the lower extremities, are bluish-red spots up to 5 cm in diameter with smooth edges, reminiscent of hematomas. As they grow, they transform into nodules and merge. large nodes darken and eventually ulcerate. Swelling occurs at the edges of the elements, caused by stagnation of lymph in the lymphatic channel. The African type is severe and affects young people. A fulminant course of the disease is often observed. African Kaposi's sarcoma manifests itself in several types of formations - from nodes to lymphadenopathy. The most malignant type of elements of this type of sarcoma is considered to be “flowery” (growth in the form of vegetation - in appearance it resembles cauliflower). It is characterized by deep lesions of the dermis, subcutaneous tissue and underlying tissues down to the bone. With HIV infection, the tumor can be located literally anywhere in the body, even affecting internal organs. The most typical places are the oral cavity, stomach and duodenum. The current is severe. The immunosuppressive type is similar in its manifestation to HIV-associated.
Squamous cell carcinoma
Malignant tumor of the epithelium. Formed from atypical keratinocytes that proliferate randomly. The process begins in the epidermis, gradually moving to deeper layers. The tumor is characterized by a tendency to metastatic process. Squamous cell carcinoma occurs 10 times less frequently than basal cell carcinoma. It most often affects white-skinned men whose place of residence is a sunny, warm climate.
The localization of spinocellular epithelioma varies. The most favorite place for the formation of squamous cell carcinoma is the border between the mucous membrane and the skin. These areas include the lips and genitals. At the initial stage of cancer development, an infiltrate appears with a raised hyperkeratotic (rough) surface. the color of the formation is usually gray or yellow-brown. At first, as with basal cell carcinoma, there are no complaints. As the tumor grows, it can reach a size of up to 1 cm. At this moment, a dense node that continues to grow begins to be felt. Eventually, the carcinoma approaches the size of a walnut. The tumor grows in two directions - above or deep into the tissue. The latter is usually accompanied by the formation of an ulcer, which affects not only the dermis and epidermis, but also reaches the bone and muscle tissue. An ulcer in squamous cell carcinoma does not heal. The patient suffers from excruciating pain at the site of its formation. Subsequently, the complaints are joined by disturbances in general well-being and infectious complications associated with immunosuppressive processes that accompany any oncological pathology.
Melanoma
This is a tumor of neuroectodermal origin. It consists of malignant melanocytes. UV radiation is considered the main provoking factor. Melanoma develops both from an existing nevus (mole) and on clean skin.
Signs of malignancy include: asymmetry; fuzzy edges; uneven coloring; diameter more than 6 mm; evolution of a pigment spot (any changes in a mole - sudden growth, change in color, etc.) is the most typical sign!
Benign neoplasms
New growths on the skin, classified as benign, as can be seen in the photo and their description, are not prone to rapid growth, metastasis and relapse after removal.
These tumors include:
- atheroma;
- hemangioma;
- lymphangioma;
- warts;
- moles (nevi);
- fibromas, etc.
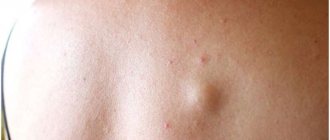
Atheroma Damage to the sebaceous gland in the form of a cystic growth. Location: face. The raised formation does not differ from normal skin in color and is tightly fused to it at one point. The contours are clear. Palpation of the atheroma is painless.
Hemangioma A neoplasm of vascular origin, refers to childhood tumors. It can be either an independent disease or a manifestation of another pathology. The course depends on the patient’s age, location, size and depth to which the hemangioma has grown. Frequent locations are the head, face, neck, but other locations are also possible. The first manifestation is a red nodule (papule) up to 5 mm in diameter. Complaints include bleeding when accidentally touched, and sometimes dysfunction of the organ where the tumor is located.
Lymphangioma There are two possible development options - a congenital defect or consequences of impaired lymph flow. The tumor can be located anywhere, but more often it is the oral cavity, neck, and upper limbs. Capillary lymphangiomas are multiple blisters with a yellowish transparent liquid inside. The same tumors that arose as a result of impaired lymph circulation look like plaques or spots, the diameter of which slowly increases.
Lipoma Tumor of adipose tissue. More often they have a nodular shape. The course is asymptomatic. It is a painless pale pink neoplasm on a stalk. The consistency is doughy. The boundaries are unclear.
Seborrheic warts Also called "senile warts". They arise as a result of impaired differentiation of cells in the basal layer of the epidermis. Appearance: Nodules or plaques raised above the skin. The surface is lumpy. The shape is often round or oval. The color of the wart varies from yellow-brown to black.
Moles or nevi are a developmental defect and consist of unchanged melanocytes. The characteristic color of the rash is from light brown to black, which is associated with different amounts of melanin (dark pigment) in the cells. More often, moles have a smooth surface and sometimes rise above the skin.
Fibroma Fibroma is a tumor that forms from connective tissue. Dense to the touch. Reaches large sizes. Malignancy (transition to malignancy) of the tumor is possible.
Neoplasms on the skin (photos and descriptions are presented above) of a benign nature, despite their relatively safe nature, can sometimes still develop into precancrosis and even cancer.
Precancerous conditions
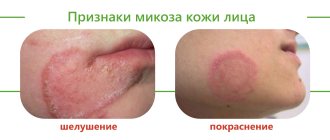
Precancrosis is a pathological condition of any tissue of the body, which, with varying degrees of probability, can contribute to the occurrence of a malignant process. The following diseases are considered precancer of the skin: Bowen's disease; Paget's disease, etc. Bowen's disease is an intraepidermal cancer that is prone to transition to squamous cell. It is a chronic inflammatory disease that is associated with excessive proliferation of atypical keratinocytes. Occurs in older people.
The tumor has invasive growth, growing not only into the epidermis, but also into deeper tissues. It can be located on any part of the skin and mucous membranes, but more often on the torso. The elements look like pink spots with fuzzy, rounded edges. Under them there is an infiltrate, due to which the formations are slightly elevated. They are rough to the touch and covered with scales. When the latter are peeled off, an erosive, bleeding surface opens.
Paget's disease is an adenocarcinoma prone to metastasis. The source of growth, as in Bouin's disease, is located intraepidermally. The typical location is the mammary glands, most precisely the area of the nipple and its areola.
Tumor growth is infiltrating (grows into underlying tissues). Clinically manifested as a unilateral itchy plaque with clear contours in women over 40 years of age. The surface is covered with scales and crusts. The element increases in size and begins to metastasize. The outcome is breast cancer.
Diagnostics
New growths on the skin, photos and descriptions of which were presented above, are diagnosed using general principles. These include mandatory medical history collection (patient complaints, clinical manifestations of the disease), examination of the patient, careful visual examination of formations and analysis of data from clinical and instrumental examination methods (MRI, radiography). The main thing in making a final diagnosis is the histological method. It is a microscopic examination of an area of pathologically altered tissue in order to identify atypical cells.
Treatment of skin tumors
Treatment methods for skin tumors include medication, radiation and surgery. The latter is radical (i.e., it allows you to get rid of the disease as completely as possible). New growths on the skin are treated medicinally with antibiotic therapy (photos and detailed descriptions of drugs can be found in clinical reference books), NSAIDs, opioid analgesics and hemostatic drugs. This method is used as a symptomatic treatment, it can alleviate the patient’s condition and somewhat improve the quality of life.
The surgical method is based on the elimination of the tumor. The goal of treatment is final relief from the disease and prevention of relapses. Radiation therapy is more often used for malignant processes, especially in cases where surgical resolution is not possible. The goal is also to prevent tumor regrowth and metastasis. Removal of skin tumors Methods for removing skin tumors are: Cryodestruction (with the help of liquid nitrogen the tumor is frozen, then it dies and disappears). The method is not used on the head, with large formations or when they are located intradermally.
Surgical excision. The scope of the operation can be different - removal of the tumor within healthy tissue (fibroma, nevi), along with the capsule (atheroma, lipoma), etc. up to excision of the surrounding skin, subcutaneous tissue, and nearby lymph nodes (squamous cell carcinoma and other malignant formations). In order not to miss the moment when skin growths become life-threatening, you need to understand what you are dealing with. After studying the photos and descriptions of common pathologies, you can guess the source of the disease and promptly contact a specialist.
What does the initial stage look like?
Symptoms of a skin tumor depend on its type. Growth rate, color, and tendency to metastasize are characteristic of each form of cancer. However, at the initial stage, several symptoms are common to all types of tumor. These include:
- The presence of a formation on the surface of the skin with unclear shapes and asymmetrical contours.
- The appearance of itching and changes in the color of the lesion as the process progresses.
- A sharp loss of strength, increased fatigue.
- Loss of appetite, sudden weight loss.
- The presence of pain in the area of the tumor.
Skin cancer develops through 4 stages. Each reflects the size of the lesion, its spread to surrounding tissues, and the presence or absence of metastases. Depending on this, the following symptoms of skin tumors are distinguished:
- First stage. At this stage of skin cancer formation, there are no specific signs. The size of the tumor focus is up to 2 mm. In this case, the general condition does not change. Detecting cancer at the first stage is possible only with a thorough self-examination of the skin.
- Second stage. The growth of the tumor leads to the appearance of the first subjective signs. These include itching and pain in the area of the pathological focus. The cancer increases in size up to 4 mm.
- Third stage. The tumor focus has a diameter of more than 4 mm. At this stage of skin cancer, the process spreads to regional lymph nodes.
- Fourth stage. Late stage skin cancer is characterized by the appearance of metastases. The tumor grows into nearby tissues. The clinical picture is accompanied by the appearance of symptoms of tumor intoxication (cachexia, weakness, lack of appetite, headache).
Lack of medical care in the early stages of skin cancer leads to rapid progression of the process. As the tumor develops, nearby organs and lymph nodes are affected. The appearance of the lesion in the form of an ulcer contributes to the addition of a secondary bacterial infection. There are often deaths due to the development of sepsis.
Are red moles dangerous?
In themselves, these formations are harmless and are not precancers.
If you have a lot of red moles on your body, the cause may be a serious liver or pancreas disease. Pay attention to this - this is a reason for examination.
Problems may arise in case of traumatization of hemangiomas. Even fairly small formations threaten heavy bleeding, which is not easy to stop.
Clinical case
Patient L, 26 years old, presented with a traumatized mass in the axillary region. According to her, she tore off a convex hemnagioma with the edge of a rigid corset of a wedding dress almost a few minutes before the start of the wedding ceremony. The hemangioma bled very heavily and a large blood stain appeared on her white dress. She had to wear the witness's jacket over her wedding dress. It was in such a strange outfit that the wedding took place.
Etiological factors of scalp cancer
The etiology of cancer is still not fully understood, but the following etiofactors are reliably known:
- Male gender. Skin cancer affects both men and women, but according to statistics, men are more likely to get it.
- Complicated family history. The risk of developing skin cancer increases when close relatives are diagnosed with this disease.
- Elderly age. Skin cancer is most often diagnosed in people after fifty years of age.
- Life history of exposure to UV rays and sunburn.
- Light skin and hair, blue eyes.
- Freckles and/or multiple nevi, etc.
Any neoplasm on the skin of the face can be dangerous, but it is necessary to undergo examination in case of asymmetry, unevenness of its edges, if its color is not uniform or it changes, and if there is a change in size.
Expert opinion
Author:
Alexey Andreevich Moiseev
Oncologist, chemotherapist, Ph.D.
Every year, 9,000 cases of newly diagnosed melanoma are registered in Russia. This aggressive malignant tumor is responsible for the death of 40% of patients. Such statistics indicate that the country's population is not sufficiently aware of the symptoms of melanoma. As a result, a visit to a doctor occurs in the later stages, when treatment is considered ineffective.
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital determine the location of melanoma and prescribe treatment appropriate to the stage of tumor development. An individual approach to the problem of each patient allows us to reduce the number of deaths. A tumor detected in time is characterized by a favorable prognosis for recovery. The later melanoma is detected, the longer the treatment process will be. Its success depends on many factors. The main treatments for melanoma are surgery, radiation and chemotherapy. Depending on the condition, symptomatic therapy is carried out.
You can diagnose the presence of skin cancer yourself at home. Doctors recommend regularly examining the skin, especially nevi, for the appearance of pathological formations.
Where can I buy Israeli medicines?
- In an Israeli pharmacy - after consulting a doctor.
If you undergo examination at the oncology center, the doctor will prescribe you the necessary medications, which can be purchased in Israel. - At your place of residence - using a telemedicine program.
As part of this program, you will also receive a consultation from an Israeli doctor - but remotely. You can order the medications prescribed by him and have them delivered to your home.
Diagnosis of skin cancer
An integrated approach to diagnosing skin cancer is the key to timely detection of the tumor process. In order to determine the presence of skin cancer, it is necessary to conduct an examination. The first signs of skin cancer can be detected on your own. For this purpose, the ACORD principle is used.
- A – asymmetry. A lesion that has an uneven and asymmetrical shape requires close attention from a doctor.
- K – edge. A malignant neoplasm of the skin is characterized by jagged edges. The appearance of such a sign requires immediate contact with a dermatologist.
- O – coloring. Skin cancer is characterized by the appearance of a red, dark blue, or black lesion.
- R – size. The tumor process often has a diameter greater than 6 mm.
- D – dynamics. The growth of education in size requires a visit to a doctor.
The appearance of any of the above symptoms requires immediate medical attention. At the appointment, the specialist examines the formation using an epiluminescent microscope, which allows him to differentiate various skin diseases.
- Collecting anamnesis of illness and life. At the doctor's appointment, complaints are collected, the time of occurrence of the pathological formation, and the presence of predisposing factors. Precancerous diseases are determined, and the rate of development of the lesion is determined.
- General analysis of urine and blood. Laboratory diagnostics allows us to determine the presence of an inflammatory process in the body.
- Blood test for tumor markers. Specific markers for the presence of skin cancer are TA 90 and SU 100. Their determination is diagnosed already in the early stages of the tumor process.
- Tissue biopsy of pathological formation. It is one of the most important methods for diagnosing skin cancer. Histological examination makes it possible to differentiate the neoplasm, determine its stage and type. In cases where there is a metastatic lesion, a biopsy of the affected areas is performed.
- MRI and CT diagnostics. Instrumental research methods are carried out to identify metastases.
- PET-CT. This diagnostic method allows you to determine the localization of metastases. The study is carried out using a contrast agent injected into the body before tomography.
- Ultrasound. Ultrasound diagnostics helps to identify damage to the lymph nodes, as well as changes in other organs if metastases are suspected.
Detection of skin cancer at the initial stage of development allows for timely treatment and provides a favorable prognosis. Therefore, if you have the first signs of the disease, you should seek medical help.
ABCDE technique for cancer detection
The first five letters of the English alphabet are a guide to help you recognize the signs of cancer.
- A is asymmetry. Most skin cancer lesions are asymmetrical. If you draw a line through the middle of the hearth, the two halves won't line up, so it looks different from round to oval.
- B is the border. The borders of cancers tend to be jagged and may have jagged edges, while regular moles tend to have smoother, more even borders.
- C is color. Multiple colors are a warning sign. While benign moles are usually one shade of brown, cancerous moles can be various shades of tan, brown, or black. Red, white, or blue colors may also appear as they grow.
- D is the diameter. It is already worth paying attention to the spring if its size is more than 6 mm. Some experts say it's also important to look for any damage, regardless of size, that is darker than others. Sometimes, amelanotic melanomas are colorless.
- E is for evolution. Any change in the size, shape, color or height of a spot on your skin, or any new symptom in your skin, such as bleeding, itching or crusting, may be a warning sign of melanoma.
If you notice these warning signs or anything new, changing, or unusual on your skin, contact your dermatologist immediately.
Surgery
Surgical removal of the tumor is the most affordable method of treating skin cancer. Surgery is most effective in the early stages of cancer development due to the lack of tumor growth into nearby tissues. The surgeon removes the tumor and all affected areas. In the presence of metastatic lesions of the lymph nodes, their removal is indicated. If an aggressive form of the tumor develops, surgical intervention alone is not enough to completely get rid of the pathological focus.
A modern method of surgery to remove skin cancer is micrographic surgery using the MONS method. In this case, tumor cells are removed layer by layer under microscopic control. Each removed layer is sent for histological examination.
Features of soft tissue tumors
Malignant soft tissue lesions are rare, accounting for no more than 1% of all cancers.
But the aggressiveness of many types of cancer of the skin or underlying tissues is very high. It is somewhat easier to identify them than lesions of internal organs, since they form quite noticeable changes in the color of the skin, its appearance or the density of the tissues under the epidermis. Sarcomas that affect soft tissue and are classified as malignant tumors can appear in the subcutaneous tissue, including stromal and fat cells, in muscle elements, blood vessels or lymphatic capillaries, nerve fibers, and connective tissue of joints. Localization of tumors is possible in any part of the body, but more than 50% of them affect the extremities (legs and arms), the rest are located in the neck and head, torso, less often internal organs or the retroperitoneal space are affected Source: Z.R. Khismatullina Skin neoplasms. Issues of epidemiology, classification, diagnostics // Creative surgery and oncology, 2010, pp. 69-73.
With early detection, radical removal of tumors and a favorable prognosis for recovery are possible.
Chemotherapy
It is carried out both as an independent method of treatment and in combination with surgical intervention. Prescribing chemotherapy before surgery is intended to reduce the pathological focus. The purpose of this method of treating skin cancer after surgery is designed to completely destroy cancer cells.
The disadvantage of this method is the inability to exclude the effects of drugs on healthy cells. The question of the need for chemotherapy is decided by the attending physician based on the individual characteristics of the development of the tumor process.
Drug treatment
As the tumor process progresses, corresponding clinical symptoms appear. The main ones include pain and itching. To symptomatically combat these symptoms, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed to relieve pain due to skin cancer.
| Stage | TNM | Treatment method |
| 1 | T1-4N0M0 | At the initial stage of the tumor process, treatment consists of surgery with excision of the pathological focus. |
| 2 | T1-4N0M0 | At this stage, the tumor does not metastasize or grow into nearby tissues. Therefore, surgical intervention is considered sufficient treatment. |
| 3 | рTN1-3M0 | The stage is characterized by growth into nearby tissues and damage to regional lymph nodes. Therefore, the scope of treatment is:
|
| 4 | pTрNM1 | The spread of the tumor process affects the lymph nodes and organs. The fourth stage is characterized by multiple metastases. The volume of therapy depends on the general condition and is selected strictly individually. Treatment is as follows:
|
What happens if you tear off a papilloma on a leg?
When a pedunculated papilloma is detached from the base, the benign neoplasm begins to become inflamed.
This creates a wound surface.
All this is accompanied by itching and increased body temperature.
There is suppuration and swelling due to the inflammatory reaction.
Remains of papilloma must be removed in a hospital setting.
Such injuries threaten the degeneration of a benign papilloma into a malignant neoplasm.
Sometimes, with good immunity, papillomas come off and new ones do not grow.
There is no negative impact.
The recovery is complete.
Forecast
The average life expectancy of patients diagnosed with skin cancer depends on several factors. These include the type of cancer, its stage, and the presence or absence of metastases. Detection of a tumor focus at the initial stage contributes to timely treatment and minimal risk of complications. In addition, each type of cancer has its own prognosis. Squamous cell and basal cell carcinomas are characterized by a favorable course and prognosis. Melanoma is an aggressive type of tumor that tends to grow rapidly and metastasize. The average five-year survival rate after skin cancer is diagnosed is:
- 80-100% when skin surface cancer is detected in the first stages.
- Up to 50% when skin cancer is detected at a late stage.
- Up to 25% in the presence of metastases in regional lymph nodes and other organs.
In order to minimize the risk of developing a tumor, it is necessary to prevent skin cancer. It is recommended to limit the time spent under ultraviolet rays and avoid excessive consumption of alcohol and nicotine. If there is an occupational hazard, it is required to undergo an annual medical examination to detect pathology at an early stage. In addition, it is necessary to wear protective suits that limit skin contact with carcinogenic substances. One of the cancer prevention measures is self-examination of the skin. Any changes require immediate medical attention to diagnose the disease.
Degeneration of papillomas into malignant pathology
We must always remember that HPV poses a risk of cancer.
Especially highly oncogenic types, for example, 16 and 18.
Typically, malignant degeneration of papillomas cells takes ten to twenty years from the moment of infection.
The process is accelerated by smoking, drinking alcohol, obesity and hormonal disorders that reduce immunity.
It is the decrease in immunity, which occurs for various reasons, that contributes to the activation of HPV and the transition of the benign state of papillomas to a malignant pathology.
The destruction of papillomas is enhanced by cytomegalovirus, genital herpes, chlamydia, syphilis, gonorrhea, and trichomoniasis.
And of course, you need to avoid frequent trauma to papillomas, which contributes to their malignancy.
A direct indication for removal of papillomas is the presence of large papillomas.
They are often hurt and hurt.
How is skin cancer treated?
The Moscow Yusupov Hospital has been diagnosing and treating skin tumors for many years. Thanks to modern equipment, skin cancer can be detected in the shortest possible time, and its type and stage can be accurately determined. This is necessary to determine further treatment tactics.
Highly qualified doctors of the medical institution select individual therapy, taking into account the obtained diagnostic data. In their work, specialists at the Yusupov Hospital use current recommendations for the treatment of skin cancer. You can make an appointment with an oncodermatologist and learn more about prices by phone.
Methods for removing papillomas
There are quite a lot of methods for removing papillomas.
Let's consider everything.
Firstly, it is the destruction of papillomas using a special liquid containing alkali.
They are purchased in pharmacies with prescriptions from the attending physician.
The disadvantage is considered:
- the need for precise local application of liquid to papillomas,
- risk of chemical burns to adjacent tissues,
- painful procedure,
- the possibility of scars appearing at the site of papillomas removal.
Usually, the method is used to remove single vulgar papillomas (warts) of the hands.
It is not suitable for filamentous papillomas.
Refrigerants are used for cryodestruction.
Basically, liquid nitrogen is used.
Although other refrigerants are possible.
The application of the coolant is painless; acute pain occurs later when “defrosting” occurs.
After a certain time, the surrounding tissues turn red and swell.
There is an active formation of a subcutaneous bladder filled with fluid.
After a week (maximum one and a half months), everything heals and is restored.
It takes three weeks for the tissue under the crust to die, while the infected tissue is reliably destroyed.
There are no scars, and any traces disappear within six months.
The intimate area and face are not treated with this method.
Firstly, the genital area is very sensitive.
And secondly, it is not suitable for the face due to post-operative swelling and redness of the surrounding tissues.
Using a special device, papillomas are removed using radio wave coagulation.
Most often they use Surgitron.
The method does not cause pain.
Several radioknives in the kit allow you to choose the most convenient one for papilloma of a given location.
The radioknife provides directed high-frequency radiation, which cuts off the papilloma, “evaporating” its tissue.
There is no rehabilitation period.
The operation is quick, painless and leaves no traces of the intervention.
But if there are acute inflammatory processes or worsened chronic ones, then radio wave coagulation is not used.
Diabetes mellitus, pregnancy, lactation and any cancer pathology in the body are also contraindications for using the method.
But if there are no contraindications, the method can be successfully used anywhere.
Patients say that the only drawback of the method is the discomfort at the time of administration of the anesthetic.
Laser beams are also used to remove papillomas without contact.
Healthy tissues are not damaged.
Infected papilloma tissues seem to “evaporate” under the action of a laser beam.
A session of laser removal of papillomas does not take long, just a few minutes.
Complete rehabilitation takes place in two weeks.
Side effects include prolonged redness of the skin and swelling of adjacent tissues.
Problems with the thyroid gland contribute to the formation of keloid scars.
Contraindications for the use of laser coagulation are the presence of:
- diabetes mellitus;
- acute inflammatory processes;
- epilepsy;
- disorders of endocrine and immune status;
- photoderomatosis;
- thrombocytopenia.
Patients who have undergone laser coagulation report pain and an unpleasant “burnt meat” smell.
Long-term rehabilitation, pain and tendency to relapse with this method.
Small papillomas are removed by electrocoagulation or cauterization.
Rehabilitation takes place within a week.
Reliable and inexpensive method.
Any localization of papillomas is suitable for its use.
To remove large papillomas or malignant neoplasms, a scalpel is used.