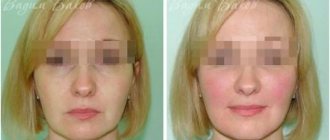
Oleg Stasevich, together with the plastic surgeon of the Blagoveshchensk City Hospital, Victoria Alekseevnina, performs a complex reconstructive operation to restore the patient’s nose. Photo: Sergey Petrukhin
— Oleg Valerievich, reconstructive rhinoplasty operations affect the sense of smell - won’t it turn out that the nose has become smoother and more beautiful, but the sense of smell has disappeared?
— Before any operation on the nose, we always ask about the person’s professional activity - what kind of work he does. If this is a professional smell taster, then we do not recommend touching the nose in principle - the sense of smell may change. I have not encountered this in my practice, but I can say with confidence that the sensitivity of the skin on the nose definitely changes in the first year after surgery. It may become dull or, conversely, worsen. When it’s +1 or +3 degrees outside, you and I are unlikely to feel small changes in temperature with the tip of our noses. And a person after rhinoplasty for the first year and a half or two will clearly distinguish how many degrees there are outside the window.
— Who is more difficult to do rhinoplasty - Europeans or Asians?
— I wouldn’t put the question that way, although there are ethnic characteristics. Even men and women of the same race have different nose shapes. One of the most common rhinoplasty operations in the world is to make a Caucasian nose for people of the Mongoloid race. But sometimes patients come and don’t know what they want. They say: I don’t like my nose, what can you offer me or how can you change it? You look, and the nose is quite normal and proportional, following common sense, you shouldn’t touch it.
— Did you have to dissuade anyone from the operation?
“I inform each patient as fully as possible not only about the external result that he hopes to get by contacting a plastic surgeon, but also about possible negative consequences, including complications. And only the patient himself makes the final decision on the advisability of the correction. Otherwise, problems cannot be avoided. It also happens that after a conversation a person decides to refrain from interfering.
— Over the 19 years that you have been in plastic surgery, has the patient’s portrait changed much?
— Previously, there was little information; only a few had access to plastic surgery. Nowadays, many people come to a consultation already very savvy. Moreover, the approach of men and women is somewhat different. Men are more interested in health. For example, when doing plastic surgery of the nose or ears, they first of all ask whether it will become easier to breathe, or whether the operation will worsen hearing. And women are more concerned about how long the swelling will last, when the scar disappears...
400
plastic surgeries were carried out in 2016 at the Blagoveshchensk City Clinical Hospital, where aesthetic surgery is put on stream: the queue is scheduled for three months in advance. People come to us from Yakutia, Kamchatka and Sakhalin for plastic surgery
Beauty is an elusive and very individual thing, on the one hand, and very global and standardized, on the other. Modern man is dependent on the Internet and the images that are imposed by the media. More and more people are deciding to undergo plastic surgery in order to look better on social networks - for the sake of a beautiful selfie on Instagram or Facebook, they are ready to go to great lengths. For us plastic surgeons, globalization allows us to use some common approaches in operations to follow the trends that patients ask for. I go to Milan, where representatives of the beauty industry from all over the world share their experiences to learn and see trends.
— And what’s trending now?
— Talking about trends in plastic surgery, on the one hand, is strange: medicine is not fashion, where everything changes twice a season. There is no denying that beauty standards are changing. Exaggerated femininity and an appearance reminiscent of a Barbie doll are no longer in fashion. But in general, there have been no global changes; the main request of patients is sexuality.
— Dreaming of adjusting the size or shape of their breasts, many people worry whether plastic surgery will cause cancer?
— According to studies, the incidence of breast cancer in both women operated on for aesthetic reasons and those not operated on is exactly the same. If there was a risk of breast cancer, endoprostheses would be banned throughout the world. It is impossible to say that breast correction surgery has no effect on a woman’s health, but it is absolutely certain that it does not increase the likelihood of cancer. These women are at the same risk as everyone else.
— Does the operation affect lactation? Will the woman then be able to breastfeed her baby?
— The technology of breast augmentation surgery does not involve damage to the mammary glands, therefore, the woman will be able to breastfeed her child.
— What problems do patients most often come to you with?
— If we talk not about the popularity rating of “plastic surgery” in general, but specifically about my practical activities, then more often I have to do rhinoplasty, breast surgery, and anti-aging surgeries on the face. We are talking about plastic surgery of the upper and lower eyelids, various options for lifting facial tissues, plasma lifting, lipofilling, that is, transplanting specially treated adipose tissue of the patient himself into problem areas. By the way, lipofilling gives a very good effect on the face area, when the tissues seem to be “overwhelmed” due to age-related atrophy.
The problem of many modern people with our physical inactivity and poor nutrition is swollen figures: fat folds at the waist, the “breeches” area on the hips, a bulging belly. All this spoils the silhouette. Not only women, but also men are also increasingly deciding to undergo liposuction in order to get rid of excess fat without exhausting themselves with painful diets and workouts. Of course, you won’t be able to lose several sizes at once, but removing excess fat from the back, abdomen, thighs or chin is a feasible task for a plastic surgeon. A very fashionable procedure now is laser-assisted liposuction.
If we are talking about otoplasty, surgeons advise performing such an operation before the age of 5-6, so that later, when children go to school, they do not become an object of ridicule because of their strongly protruding ears.
— How is it different from regular liposuction?
— The principle is this: a laser beam “melts” adipose tissue, which allows it to be sucked out using thin tubes. The punctures are almost invisible. To carry out the laser liposuction procedure in certain areas, general anesthesia is not required; it is enough to use modern local anesthesia.
To be honest, the popularity of laser liposuction is most likely due to the fact that distributors are actively working to sell the relevant equipment. This also needs to be understood. Aesthetic medicine - in addition to some purely medical aspects, it is also a business. Even in Soviet times, such interventions were performed only on a paid basis. Although there are situations when “beauty surgery” has to be done for medical reasons. This is one of the sections of my dissertation.
— After liposuction, does fat grow again?
— No, because adipose tissue is completely replaced by scar tissue, but there are so-called fat traps. They can appear in the most unexpected places. After such an operation, the patient will have to change his lifestyle, because it is impossible to lose weight with liposuction.
— What kind of beauty operations are women booming in now?
— This is a change in facial sculpture to more clearly emphasize the cheekbones and lower jaw line, dimples and sunken cheeks, and removal of fat deposits in the cheek area. Among older patients, fat injections (fan distribution of own fat tissue over the face) are most popular. This improves the quality of the skin, rejuvenates it, and leads to the disappearance of age spots.
— As a microsurgeon, you also perform sex reassignment operations. But you don’t say anything about this in your interviews?
“This is largely due to the sensitivity of the issue. Such operations are multi-stage and very complex work. In addition, it is difficult to communicate with such patients. They often feel inferior. Transsexualism is an officially registered disease that belongs to the field of psychiatry. First, a person must go through a long medical and legal chain, and then we perform surgical correction for gender reassignment. I deal with gender reassignment from female to male and mostly communicate with such patients.
- And they don’t regret it later?
“For many years, I don’t remember a single case where a patient came and asked to change their gender back. This is precisely the section of plastic surgery where the cost of a mistake is human life.
Age category of materials: 18+
- Irina Voroshilova
- Amurskaya Pravda from 04/13/2017
Education and career
01.09.2002 - 24.06.2008 - Faculty of Medicine, Belarusian State Medical University. Diploma in General Medicine.
01.08.2008 - 30.06.2009 - internship in the specialty "Surgery".
04.08.2009 - present - surgeon at the Republican Center for Plastic and Reconstructive Microsurgery (microsurgical department of the Minsk Regional Clinical Hospital).
04/08/2010 — Master class “Laser surgery and sclerotherapy in the treatment of varicose veins” (Minsk, Belarus).
04/08/2011 — Republican seminar “Endovascular methods of treatment of varicose veins of the legs” (Minsk, Belarus).
05/14/2011 - awarded the second qualification category in the specialty “surgeon”.
06.06.2011 - 17.06.2011 - internship in plastic surgery at the Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery of the Clinic of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences (Kaunas, Lithuania).
12/11/2011 - IV international scientific and practical conference “1. Medical trichology. 2. Modern methods of diagnosis and treatment. Anatomical rationale for volumetric contouring. Volumization. Theory and practice." (Minsk, Belarus).
06/07/2013 - 06/09/2013 - III International ISAPS Course in Plastic Surgery (St. Petersburg, Russia).
03.03.2014 - 01.04.2014 - advanced training courses at BelMAPO under the program “Modern aspects of plastic and reconstructive surgery” (Minsk, Belarus).
05/30/2014 - awarded the first qualification category in the specialty “surgeon”.
07.10.2014 - 09.10.2014 - 23rd European ESPRAS Course in Plastic Surgery (Helsinki, Finland).
10.25.2014 - 10.26.2014 - course “Breast reconstructive surgery and aesthetic improvements” (Minsk, Belarus).
04.11.2014 - 05.11.2014 - program “Breast Augmentation Surgery” (Riga, Latvia).
12/10/2014 - 12/13/2014 - 6th European Symposium “Aesthetic Breast Surgery” (Milan, Italy).
04/28/2015 - 04/29/2015 - modern course “Augmentation using polyurethane implants” (Riga, Latvia).
05/29/2015 - 05/31/2015 - international congress on plastic surgery “Anti-aging facial contouring” (Gardone Riviera, Italy).
10.22.2015 - course “Complicated cases of aesthetic breast surgery” (St. Petersburg, Russia).
10.23.2015 - 10.25.2015 - international symposium on aesthetic surgery “Advanced aesthetic rhinoplasty, otoplasty and facial contouring” (St. Petersburg, Russia).
12/04/2015 — republican seminar “Human Face. Aesthetics and functions” (Minsk, Belarus).
03/15/2016 - 03/19/2016 - 5th open course on rhinoplasty (Bergamo, Italy).
05/19/2016 - 05/21/2016 - international congress on aesthetic and reconstructive breast surgery (Paris, France).
05.26.2016 - 05.28.2016 - 12th international symposium on aesthetic medicine “Beauty through science” (Stockholm, Sweden).
10.21.2016 - 10.23.2016 - international symposium “Advanced aesthetic surgery of the breast and body” (St. Petersburg, Russia).
11/19/2016 - modern medical aesthetic training program in augmentation mammoplasty (Moscow, Russia).
08/22/2016 - 12/16/2016 - retraining as a plastic surgeon at the Department of Plastic Surgery and Combustiology of BelMAPO (Minsk, Belarus).
01/02/2017 - member of the Society of Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery of Belarus.
02/09/2017 - 02/10/2017 - master class on primary breast augmentation at the Viktoriakliniken base under the guidance of Professor Charles Runquist (Stockholm, Sweden).
03/30/2017 - 04/01/2017 - master class “Composite SMAS lifting. Plastic surgery of the face and neck - answers to all questions" under the guidance of Dr. Sam Hamra (Moscow, Russia).
03/16/2018 - 03/17/2018 - international congress on plastic surgery and aesthetic medicine (Kyiv, Ukraine).
05/13/2018 - 05/15/2018 - 5th International School of Mammoplasty (Kazan, Russia).
05.25.2018 - 05.28.2018 - international congress on aesthetic breast surgery “Botti's Breast Best” (Gardone Riviera, Italy).
05.31 – 06.01.2018 – 1st National Congress “Plastic Surgery and Cosmetology” (Minsk, Belarus).
06/29/2018 - awarded the highest qualification category as a doctor.
10.31.2018 - 11.04.2018 - 24th World Congress of the International Society of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery (Miami, USA).
02/08/2019 - 02/09/2019 - ISAPS international training course “Face and Rhinoplasty” (Moscow, Russia).
04/18/2019 - 04/19/2019 - intensive course “Modern aesthetic surgery of the breast and body contours” (St. Petersburg, Russia).
05/30/2019 - 05/31/2019 - Republican scientific and practical conference with international participation, master class “Male reproductive health and surgical methods for correcting some of its disorders” (Gomel, Belarus).
03.11 - 04.11.2019 - master class on breast augmentation with Motiva implants at the Akademikliniken, led by Dr. Paolo Montemuro (Stockholm, Sweden).
11.15.2019 - 11.17.2019 - ISAPS international training course “Body plastic surgery. Aesthetics and reconstruction” (Moscow, Russia).
Training
- 2010 - Second Course on open rhinoplasty in Bergamo: aesthetics, function, treatment of complications. Course directors: E.Robotti, R.Mazzola. Bergamo, Italy.
- 2009 — Thematic improvement in the sections of burn surgery at the Department of Emergency Surgery of BelMAPO.
- 2008 — Thematic improvement in the sections of vascular and endoscopic surgery at the Department of Surgery of BelMAPO.
- 2008 - Internship in plastic surgery at the Department of Plastic Surgery at the University Hospital of Ghent (Belgium), supervisor Prof. S. Monstrey. Phalloplasty, vaginoplasty, breast reconstruction, mastopexy, rhinoplasty;
- 2006 - Thematic improvement in the sections of plastic and reconstructive surgery at the Department of Surgery BelMAPO (Minsk, Belarus);
- 2003 - Internship in plastic surgery at the Department of Plastic Surgery at the Central Hospital of the University of Helsinki (Finland), head prof. S.Asko-Seljavaara. Breast reconstruction, plastic surgery of the hard and soft palate, upper lip for congenital clefts, injuries of the maxillofacial area, plastic and reconstructive surgery of the maxillofacial area;
- 2003 - Internship in plastic surgery at the Department of Plastic Surgery at the University Hospital of Ghent (Belgium), supervisor Prof. S. Monstrey. Phalloplasty, vaginoplasty, breast reconstruction with perforator flaps;
- 2001 - Thematic improvement in sections of general surgery at the Department of Surgery of BelMAPO (Minsk, Belarus).
Scientific and practical conferences and intensive courses in selected areas of plastic reconstructive and aesthetic surgery, hand surgery at the Clinics of Reconstructive Surgery of Vilnius University (Vilnius, Lithuania) and the Russian Scientific Center for Surgery of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences (RSCH RAMS), (Moscow, Russia) in 2003 , 2004, 2005, 2006, 2007, 2008, 2009, 2010
Hand surgery. How torn and severed body parts are sewn back into place in Belarus
To what extent are surgeons and traumatologists able to restore hand function? Pavel Pashuk, head of the City Center for Hand Surgery in Minsk: In factories where there is press equipment, serious injuries occur more often. After a few days, necrosis occurs. Such injuries most often result in amputation of the fingers or hand.
Even minor hand injuries can be fatal. That is why the victim needs to quickly and efficiently provide first aid.
Alexey Igorevich Volotovsky, Associate Professor of the Department of Traumatology and Orthopedics of the Belarusian State Medical University, Scientific Director of the Department of Hand Surgery of the City Center of Traumatology and Orthopedics of the 6th City Clinical Hospital of Minsk: Any injuries are divided into open and closed. In case of open injuries, everything must be done to close the wound with sterile material. The dressing allows you to seal the wound and prevent secondary microbial contamination. When the injury is closed, the main measures are, of course, immobilization and pain relief. The most effective pain reliever is cold.
Pavel Pashuk: You can use various available means: a board, wire. Under no circumstances should the “breaks” be set, as important anatomical structures may be damaged. By setting the fracture, we introduce infection deep into the wound.
After providing first aid to the victim, you must immediately transfer him to the hands of a specialist. To do this, you can go to the clinic, and if the injury occurred on the weekend or at night, call an ambulance or come yourself to the 6th City Clinical Hospital in Minsk.
Alexey Volotovsky: We use all technologies known in the world. If we take tendon injuries, then options for surgical interventions are possible: from tendon suture in the acute period to plastic surgery for chronic injuries. Damage to soft tissues is divided into three types: fresh, stale, old. Fresh means damage in the first 3 days. Stale - from 3 days to 21 days. 21 days is a criterion for the oldness of damage, since during this time a scar forms, which means that changes have begun in the patient’s tendon tissue. Therefore, less than 3 weeks is the period of time when we can more effectively use a person's own tissue and repair his damaged tendons. But ideally, this is, of course, the first day.
Pavel Pashuk: If there is no separation of the fingers or hand, then first aid is to stop arterial bleeding. And in order for the severed area to be sutured or implanted, we must maintain its viability. It is placed in a special bag, then in a bag of ice. There it cools and biochemical processes occur. This allows you to sew on the tassel later.
Replantation allows the patient to restore the integrity of the limbs . But this does not mean that every traumatic amputation ends with a similar intervention.
Oleg Stasevich, surgeon of the Republican Center for Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery: When it is possible to restore blood circulation to the amputated segment, but there is no way to restore the bone base, then there is no point in doing microsurgery .
Sergei Mechkovsky, surgeon at the Republican Center for Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery: When a very small segment of the hand is cut off, in which there are no structures to be restored, and the hand is functioning, then we no longer fight for it.
But for some patients, microsurgeons make an exception.
Sergei Mechkovsky: If a person needs it for his profession, he is a pianist or a programmer (we had such cases), then, of course, we will sew it on. If the profession is not associated with any scrupulous activity, then we talk with him about whether it makes sense to sew on a finger, we explain what awaits him ahead. Sewing a finger is technically possible, but then it needs to be designed so that the finger helps and is not just a warm prosthesis.
Sometimes replantation is not possible due to the patient’s severe general condition, his age, or the presence of other serious injuries to the body.
Sergei Mechkovsky: We have had cases when a patient was delivered with two cut off legs. He got hit by a train, it seems. We managed to save one of his legs, but the other had to be amputated. In this case, we were not concerned about reattaching the limb, but about saving the person’s life.
Over the years, surgeons have developed a database of special patients whose stories are rather tragicomic.
Sergei Mechkovsky: We operated on a person twice. He lost his fingers. Only the first one remains. We transplanted two toes from his foot to restore grip on his hand. He returned to his old job. After 7-10 years, he cuts off the ones we transplanted and his thumb. A young man, 38-39 years old, wanted to work actively physically. I had to take a finger from the other hand and another from the foot and again create a grip on the hand. Now he works there.
To save a person from disability, doctors have to restore structures of the hand that are invisible to the naked eye. And that’s why surgeons look at their patients through the prism of magnifying optics , holding miniature instruments in strong male hands.
Podgaisky Vladimir Nikolaevich, head of the Republican Center for Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, professor of the Department of Surgery of BelMAPO, Doctor of Medical Sciences: Microsurgery is simply a method that helps surgeons perform various types of reconstructive operations. Since the 70s, replantation of fingers and limbs . In the Soviet Union, the first replantation was performed in 1976. We sent patients to Moscow. Since the 80s, microsurgery began to be used in Belarus. It was initially used in the vascular surgery department of the Regional Hospital, and already in 1985 a microsurgery department with 40 beds was opened, which was then given the functions of the Republican Center.
Dmitry Batyukov, surgeon at the Republican Center for Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery: One of the patients was admitted to us on Monday evening. He had been injured the day before by a circular saw. He was sent with a diagnosis of an incised wound of the hand with tendon damage, but the injury turned out to be somewhat more serious. The operation took 4.5 hours. After the operation, we diagnosed “incomplete traumatic amputation of a segment of the left hand.” Currently, this patient is undergoing conservative treatment - vasoactive therapy , that is, treatment aimed at dilating blood vessels, improving blood supply to the replanted segment in order to maintain its viability.
Vladimir Podgaisky: Circular saws. They can already erect a monument in front of the microsurgery department. They provide us with the main flow of patients. When everyone starts to “get themselves this nail file,” someone will definitely fit in there: a child who helps push the board, or the owner himself.
Sergei Mechkovsky: Most often this is an injury, of course, to the hands: either it’s the fingers, or it’s the hand, or the shoulder, forearm.
During the Soviet Union, the main suppliers of victims were industrial enterprises. Round-the-clock operation and safety precautions gave microsurgeons 150-200 patients a year. Now there are fewer such emergency cases.
Pavel Pashuk: Losing a hand is tragic. Firstly, this is a cosmetic, visible defect, and secondly, the center located in the head of the brain is responsible for the function of the hand, which means a person who had the gift of playing and drawing will lose it.
Oleg Stasevich: We often neglect safety rules. Accordingly, we get injured. Sometimes these injuries are so severe that people are disabled for life. And there is absolutely no one to blame for this but yourself.
The contribution of surgeons to the recovery of a patient with a hand injury is certainly significant. But they themselves consider it no more significant than the contribution of a rehabilitation doctor and a physiotherapist. Only the professionalism of these doctors, coupled with the efforts of the patient himself, can return the hand to its capabilities.
The rehabilitologist and traumatologist together create an individual recovery program for each patient. It includes various physical procedures and physical therapy classes.
Daria Gerasimchuk, physical rehabilitation methodologist at the 6th City Clinical Hospital in Minsk: The injury was sustained with a circular saw: tendon rupture, bone fracture. Osteosynthesis was performed. After removal of the pins, stiffness (contracture) , as the patient walked in a plaster cast for a month. Since the hand cannot be developed without movement, and the patient feels very sorry for himself, this cannot be done without outside help. Unfortunately, this is a painful procedure. We help you do passive exercises, that is, we stretch the ligaments, teach you to do active exercises so that the tendon moves independently along its channel, and use biomechanical stimulation to more quickly and effectively stretch the organ along the muscle fiber.
Sergei Mechkovsky: The main thing is for a person to adequately perceive that a lot depends on him. If he does not actively engage with his hand, then all our work will go down the drain.
Vladimir Podgaisky: When the fracture heals, as a rule, for fingers it is 2-3 months, repeated operations begin. I feel sorry for the efforts spent during transplantation and replantation.
Children have the best chance of successful rehabilitation after replantation, so microsurgeons often make favorable prognoses for them.
Daria Gerasimchuk: I know why. After their cast is removed, the children begin to run. They don't carry this hand around like a doll. They are not afraid of pain when stretched.
Oleg Stasevich: We restore almost all anatomical structures at the level of the forearms or hands for children of primary school and preschool age. After 4 years, it can even be difficult to see where the scar from this injury is, although the injury was very serious. And an adult would become disabled.
But the return of function of the restored limb segment depends not only on age, but also on compliance with all doctor’s recommendations and active rehabilitation work on oneself.
Sergei Mechkovsky: No surgeon can say with a 100% guarantee that everything will be very good. Something in the person himself sometimes prevents recovery. I operated on a patient with a severed finger 7 times, trying to replant it. Thrombosis occurred and we repeated the operation again. As a result, this finger had to be amputated.
Dmitry Batyukov: We can judge the end of rehabilitation and the absence of prospects for recovery if a change in sensitivity or motor activity does not occur within 6 months. If the result is functionally insufficient, then we begin to plan another operation.
Alexey Volotovsky: Sewing a tendon or restoring a bone is sometimes even easier than restoring movement in the patient later. For hand surgery, treatment is prescribed individually. We then try to leave patients for 1-2 courses of rehabilitation in our department under the supervision of our specialists, which allows us to increase efficiency.
Yulia Ostrovskaya, head of the rehabilitation department: From the first day of the patient’s admission to the hospital, rehabilitation measures begin: full physical therapy, electrotherapy, ultrasound therapy, heat therapy, massage, hydrotherapy, underwater shower-massage. It is very important to follow the necessary principles: early start, complexity in the application of methods and means, phasing and continuity of treatment. We work taking into account the patient’s condition, his age, functionality, and develop an individual complex. It was not for nothing that I said “individual”, because even with the same disease, the complexes may differ. A lot depends on the patient himself, on his mood. You need to understand that this process is sometimes painful, we set up our patients in a certain way, that is, we also work a little as psychotherapists. We cope, and most patients are very happy with us.
The construction season is becoming a real hot time for trauma surgeons and microsurgeons, and this trend cannot be called pleasant. If you look at it, the reasons are quite banal: human self-confidence, carelessness and violation of basic safety rules. As a result, the sad result: severe injury with the threat of disability. Take care of your hands and the hands of surgeons who correct your mistakes.
Plastic surgery
- Breast augmentation, reduction and lift
- increase in the volume of the legs
- abdominoplasty
- autologous hair transplantation (HFE)
- otoplasty
- blepharoplasty
- liposuction and lipofilling
- mastectomy in men with gynecomastia
- subcutaneous mastectomy
- removal of Bisha lumps
- intimate plastic surgery
- hand surgery
- phalloplasty, endophalloprosthetics
- surgical correction for penile deformities
- plasmolifting
- injection correction with botulinum toxin and hyaluronic acid preparations
Certificates