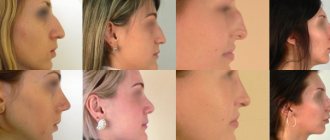
Correction of the shape of the nose, or rhinoplasty, is a very popular aesthetic operation. This is not surprising, because at least half of people think about somehow improving this part of their face! However, few of them resort to the help of a plastic surgeon, because surgical intervention is still a drastic measure. And if you don’t like the result, then “returning it the way it was” may no longer be possible!
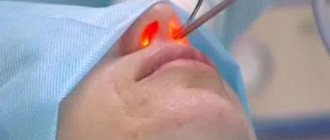
Non-surgical rhinoplasty using special fillers is a temporary change in the shape of the nose. In this case, the changes will be quite persistent and will last for about two years, after which the procedure can be repeated. Filler injections will help straighten the bridge of the nose, make its tip less pointed or remove its bifurcation, and eliminate unsightly bulges or depressions on the nose. However, it is not possible to achieve a radical change in the shape of the nose or reduce its size in this way.
Indications for non-surgical rhinoplasty
When will rhinoplasty of the nose using fillers help make a person’s face more harmonious and attractive? Here are the main indications for the operation:
- asymmetry of the left and right half of the nose;
- irregularities of the nose - “dips”, depressions, tubercles on it;
- ugly - excessively sharp or forked - tip of the nose;
- “predatory”, pointed shape of the bridge of the nose;
- almost not rising above the face, flat shape of the bridge of the nose, or the presence of a hump on it;
- nasal deformities due to previous injuries;
- correction of defects after unsuccessful surgical rhinoplasty;
- age-related changes in the skin of the nose - its sagging and sagging.
Nose surgery (rhinoseptoplasty)
Prices for rhinoseptoplasty
The final cost of rhinoseptoplasty is determined only at a face-to-face consultation based on the complexity of surgical treatment and can be changed either upward or downward.
Anesthesiology and resuscitation
| Service code | Internal code | Name | Price, rub |
| B01.003.004.007 | 37.1.1 | Spinal anesthesia lasting up to 1 hour | 8 000 |
| B01.003.004.006 | 37.1.2 | Epidural anesthesia lasting up to 1 hour | 14 000 |
| B01.003.004.008 | 37.1.3 | Spinoepidural anesthesia lasting up to 1 hour | 20 000 |
| B01.003.004.009 | 37.1.4 | Total intravenous anesthesia up to 20 minutes | 6 000 |
| B01.003.004.009 | 37.1.5 | Total intravenous anesthesia from 20 minutes to 60 minutes | 12 000 |
| B01.003.004.010 | 37.1.6 | Endotracheal anesthesia from 1 hour to 2 hours | 20 000 |
| B01.003.004.010 | 37.1.7 | Endotracheal anesthesia from 2 hours to 3 hours | 26 000 |
| B01.003.004.010 | 37.1.8 | Endotracheal anesthesia from 3 hours to 4 hours | 34 000 |
| B01.003.004.010 | 37.1.9 | Endotracheal anesthesia from 5 to 6 hours | 58 000 |
| B03.016.011 | 37.1.10 | Express analysis of blood gases and electrolytes | 2 000 |
| B03.016.011 | 37.1.11 | Advanced express analysis of blood gases and electrolytes | 2 500 |
| B03.016.011 | 37.1.12 | Artificial ventilation for 12 hours | 7 200 |
| B01.003.004.010 | 37.1.13 | Endotracheal anesthesia up to 1 hour | 14 000 |
| B01.003.004.010 | 37.1.14 | Endotracheal anesthesia from 4 to 5 hours | 40 000 |
| B01.003.004.002 | 37.1.15 | Conduction anesthesia of the 1st category of complexity | 4 000 |
| B01.003.004.005 | 37.1.16 | Infiltration anesthesia (large volume or area) up to 30 minutes | 3 000 |
| B01.003.004.005 | 37.1.17 | Infiltration anesthesia up to 15 minutes | 1 400 |
| B01.003.004.004 | 37.1.18 | Application anesthesia | 1 000 |
| B01.003.004.009 | 37.1.19 | Drug sedation with hemodynamic monitoring | 3 000 |
| B01.003.004 | 37.1.20 | Prolonged regional anesthesia (days) | 8 000 |
| A11.12.001 | 37.1.21 | central vein catheterization | 10 000 |
| A11.23.002 | 37.1.22 | TAP TEST | 12 500 |
| A11.23.001 | 37.1.23 | Diagnostic spinal (lumbar) puncture | 3 500 |
| B01.003.004.007 | 37.1.1.2 | Spinal anesthesia from 1 hour to 2 hours | 14 000 |
| B01.003.004.007 | 37.1.1.3 | Spinal anesthesia from 2 hours to 3 hours | 17 000 |
| B01.003.004.007 | 37.1.1.4 | Spinal anesthesia from 3 hours to 4 hours | 20 000 |
| A11.23.003.001 | 37.1.2.1 | Placement of an epidural catheter | 8 000 |
| B01.003.004.006 | 37.1.2.2 | Epidural anesthesia from 1 hour to 2 hours | 17 000 |
| B01.003.004.006 | 37.1.2.3 | Epidural anesthesia from 2 hours to 3 hours | 21 000 |
| B01.003.004.006 | 37.1.2.4 | Epidural anesthesia from 3 hours to 4 hours | 24 000 |
| B01.003.004.006 | 37.1.2.5 | Epidural anesthesia from 4 hours to 5 hours | 28 000 |
| B01.003.004.008 | 37.1.3.1 | Spinoepidural anesthesia from 1 hour to 2 hours | 22 000 |
| B01.003.004.008 | 37.1.3.2 | Spinoepidural anesthesia from 2 hours to 3 hours | 26 000 |
| B01.003.004.008 | 37.1.3.3 | Spinoepidural anesthesia from 3 hours to 4 hours | 27 000 |
| B01.003.004.008 | 37.1.3.4 | Spinoepidural anesthesia from 4 hours to 5 hours | 30 000 |
| B01.003.004.009 | 37.1.5.1 | Total intravenous anesthesia from 1 hour to 2 hours | 20 000 |
| B01.003.004.009 | 37.1.5.2 | Total intravenous anesthesia from 2 hours to 3 hours | 24 000 |
| B01.003.004.010 | 37.1.9.1 | Endotracheal anesthesia from 6 to 7 hours | 65 000 |
| B01.003.004.010 | 37.1.9.2 | Endotracheal anesthesia from 7 to 8 hours | 70 000 |
| B01.003.004.002 | 37.1.15.1 | Conduction anesthesia of the 2nd category of complexity | 5 000 |
| B01.003.004.002 | 37.1.15.2 | Conduction anesthesia of the 3rd category of complexity | 6 000 |
General hospital services
| Service code | Internal code | Name | Price, rub |
| S01.001.001 | 37.0.1 | Stay in a hospital ward (daily) | 6 000 |
| S01.001.002 | 37.0.2 | Stay in a hospital ward (daytime until 21:00) | 3 000 |
| S01.001.003 | 37.0.3 | Stay in the ward for accompanying persons (daily) | 6 000 |
| S01.001.004 | 37.0.4 | Stay in hospital room VIP 1 (daily) | 10 000 |
| S01.001.005 | 37.0.5 | Stay in hospital room VIP 2 (daily) | 16 000 |
| S01.001.006 | 37.0.6 | Stay in a hospital ward (daily, without meals) | 3 400 |
| S01.001.007 | 37.0.7 | Stay in the intensive care unit from 6-24 hours | 8 000 |
| B01.047.009 | 37.0.9 | Supervision by a therapeutic physician (1 visit) | 2 500 |
| A11.12.003 | 37.0.10 | Infusion therapy of expensive drugs | 4 000 |
| A23.01.001 | 37.0.11 | Extraction of surgical material using delivery means (calculated price) | 1 000 |
| A18.05.013 | 37.0.22 | Treatment using blood products (calculation, price) | 1 000 |
| A11.12.003 | 37.0.23 | Treatment using additional drug therapy (calculation, price) | 1 000 |
| A23.01.001 | 37.0.24 | Selection of implants (calculation, price) | 1 000 |
| S01.002.001 | 37.0.25 | Selection of compression garments (calculation, price) | 1 000 |
| B01.057.001 | 37.0.28 | Appointment with an operating specialist | 0 |
| A11.01.014 | 37.0.29 | Hemostasis using local hemostatic agent Zhelplastan 2.5 g | 6 600 |
| A11.01.014 | 37.0.30 | Hemostasis using local hemostatic agent Zhelplastan 5.0 g | 12 700 |
| A11.12.003.002 | 37.0.31 | IV drip infusion of Ferinject 500 mg (Ferinject, 50 mg/ml, 2 ml No. 5 in ampoules or 50 mg/ml, 10 ml in a bottle), duration up to 30 minutes | 8 000 |
| А11.12.003.003 | 37.0.32 | IV drip infusion of Ferinject 1000 mg (Ferinject, 50 mg/ml, 10 ml in bottle No. 2), duration up to 30 minutes | 15 000 |
| S01.001.008 | 37.0.1.1 | Stay in a hospital room (overnight) | 3 000 |
| S01.001.009 | 37.0.4.1 | Stay in hospital room VIP 1 (no more than 12 hours) | 5 000 |
| S01.001.010 | 37.0.5.1 | Stay in hospital room VIP 2 (no more than 12 hours) | 8 000 |
Rhinoplasty
| Service code | Internal code | Name | Price, rub |
| A16.07.062 | 37.10.2 | Aesthetic rhinoplasty (1 category) | 90 000 |
| A16.07.062 | 37.10.3 | Aesthetic rhinoplasty (2 categories) | 140 000 |
| A16.07.062 | 37.10.4 | Aesthetic rhinoplasty (3 categories) | 180 000 |
| A16.07.062 | 37.10.5 | Plastic surgery of the tip of the nose (1 category) /CORRECTION OF THE TIP OF THE NOSE | 50 000 |
| A16.07.062 | 37.10.6 | Plastic surgery of the tip of the nose (2 categories) | 80 000 |
| A16.07.062 | 37.10.7 | Reconstruction of the tip of the nose (category 3) | 150 000 |
| A16.07.062 | 37.10.8 | Rhinoseptoplasty (1 category) | 110 000 |
| A16.07.062 | 37.10.9 | Rhinoseptoplasty (2 categories) | 140 000 |
| A16.07.062 | 37.10.10 | Rhinoseptoplasty (3 categories) | 180 000 |
| A16.07.062 | 37.10.11 | Secondary rhinoseptoplasty (1 category) | 130 000 |
| A16.07.062 | 37.10.12 | Secondary rhinoplasty after 2 or more operations (2 categories) | 170 000 |
| A16.07.062 | 37.10.13 | Functional septoplasty | 90 000 |
| A16.07.062 | 37.10.14 | Reconstruction of the nose for post-traumatic and iatrogenic deformities, (stage 1, stage 2) | 270 000 |
| A16.07.062 | 37.10.15 | Reconstruction of the nose for post-traumatic and iatrogenic deformities, (2nd stage, 2nd stage) | 215 000 |
| A16.07.062 | 37.10.16 | Reconstruction of the nose for post-traumatic and iatrogenic deformities using rotated flaps, (1st stage, 1st stage) | 205 000 |
| A16.07.062 | 37.10.17 | Post-traumatic reconstruction of the nose using rotated flaps, (2nd stage, 1st stage) | 250 000 |
What fillers are used for rhinoplasty in Ryazan in our clinic?
There are several types of drugs that are injected into the tissue to improve the shape of the nose and eliminate its aesthetic defects:
- based on hyaluronic acid. Such fillers are widely used in contour plastic surgery and have proven themselves to be excellent. After one and a half to two years from the date of administration, the effect may become less pronounced - in this case, simply repeat the procedure;
- based on collagen;
- persistent fillers that do not dissolve for a long time and are not removed from the body for 3 or more years. These are “Radiesse”, “Sculpture”, etc.;
- a long-lasting effect can be achieved by using gels based on synthetic substances, the most popular of which is silicone;
- Increasingly, the patient’s own adipose tissue is used for non-surgical rhinoplasty – this is the so-called lipofilling. This procedure can be combined with liposuction. The latter, in turn, is indicated for patients who cannot get rid of excess fat in problem areas of the body by playing sports and following a diet. This happens, for example, in patients after a hormonal imbalance.
Specialists at our private clinic in Ryazan strongly recommend choosing the first type of drugs for rhinoplasty. The result is less stable and long lasting than in the case of using gels, but such fillers not only improve the shape of the nose, but also have a positive effect on the skin of the entire face. The fact is that “hyaluronic acid” is a natural moisturizer, an analogue of a sponge that attracts precious moisture and retains it, keeping the skin young, beautiful and elastic.
Rhinoplasty: all about the method of nose correction
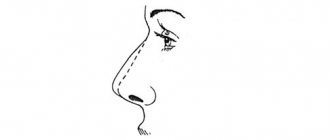
The operation allows you to correct defects in appearance, such as the shape of the nose and its absence. Along with restoring aesthetics, rhinoplasty normalizes impaired nasal breathing. Technically, this is not the simplest procedure, and therefore requires high professionalism from the doctor. When performing rhinoplasty, two correction methods are used:
- Open rhinoplasty is performed under general anesthesia. The surgeon makes an incision in the internostril area (at the base of the columella) with a marginal exit into the nostrils. The skin is separated from the cartilage, after which the correction itself is carried out with the removal and movement of cartilage tissue and bones, and the installation of implants (if necessary). At the end of the operation, the doctor applies thin sutures. After rehabilitation there are no visible marks left. The result of the operation is fixed with a hard plaster cast, which is removed after 10 days.
- Closed rhinoplasty - endonasal surgery does not involve making open incisions. The surgeon chooses the option of access to the correction zone individually. His movements are precise and controlled, and no bleeding is observed during the intervention. The recovery period is short.
It is recommended to undergo the procedure at a young age, since at this time the tissues are more elastic and the body’s ability to regenerate is higher.
Features of rhinoplasty at ON CLINIC Ryazan
As part of a preliminary consultation with a specialist, the result of the procedure and the drug that will be used as a filler are discussed. In addition, it is necessary to find out whether the patient has any contraindications to non-surgical rhinoplasty. These include:
- endocrine diseases such as diabetes mellitus and thyroid diseases with impaired thyroid function;
- hemophilia;
- any malignant tumors;
- some autoimmune diseases;
- tendency to form keloid scars on the skin;
- pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- recovery period after anti-aging procedures such as peeling or laser skin resurfacing;
- inflammation of the skin in the intervention area;
- ARVI;
- Women should not schedule rhinoplasty during their menstrual period.
Fillers are injected using local anesthesia. Typically, the duration of the procedure does not exceed 30-40 minutes, and after its completion the patient can go home. The very next day you can return to your daily routine. The effect of non-surgical rhinoplasty can be fully assessed within a week after the procedure.
Indications for rhinoplasty
Surgical intervention is recommended for congenital and trauma-induced nasal deformities, as well as for respiratory disorders (nasal breathing). The operation can also be performed at the request of the patient:
- if you have a saddle-shaped nose;
- to correct a hump or a hooked tip;
- to smooth out the sharpness or eliminate excessive length of the nose;
- with asymmetrical lines (deviated septum) and wide nostrils.
For aesthetic reasons, rhinoplasty surgery is performed only on adult patients. Contraindications to its implementation are age over 40-45 years, disorders of the hematopoietic apparatus, severe pathologies of the liver and kidneys, diabetes mellitus, oncology and mental illness.
Indications for mammoplasty:
- Micromastia (small breasts and is a congenital pathology);
- Macropathy (breasts are sharply increased in size, while the location and elasticity are preserved);
- Post-lactation involution (significant decrease in size after breastfeeding);
- Ptosis of the mammary glands (breasts are drooping, but the size is preserved);
- Gynecomastia (hypertrophied breasts in men).
It is forbidden to eat or drink less than 12 hours before surgery.
The doctor's consultation
At the appointment, the doctor listens to the patient, conducts an examination and takes the necessary measurements of the nose (length, width, etc.). Having ruled out contraindications for rhinoplasty, he gives a referral for tests and additional examinations (consultations of related specialists). Patients with body dysmorphic disorder need to meet with a psychologist. People with high blood pressure and heart pathologies require permission from a cardiologist for surgery.
List of mandatory tests:
- ECG at rest and with stress.
- X-ray examination of the pulmonary system (fluorography).
- Nomogram (study of bone structures and structure of the sinuses, for the presence or absence of various diseases).
- Rhinomamometry (screening of nasal breathing characteristics).
- Biochemistry, complete blood count (CBC), determination of sugar and coagulation characteristics (coagulation), absence of infections.
- General urinalysis (UCA).