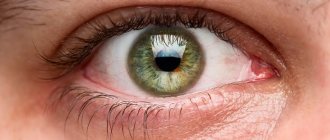
The eyelid appears very thin and soft to the touch; This is one of the most delicate areas of skin on the human body. Meanwhile, in order to fulfill their protective (including) functions, the eyelids must have at least minimal strength, elastically maintain a certain shape and ensure a tight fit of their inner mucous membrane (conjunctiva) to the eyeball. This minimum rigidity of the eyelid is given by one of its inner layers, consisting of cartilage tissue and playing the role of a kind of mechanical corset.
If for some reason - and these reasons are always pathological - the “stiffening rib” is broken or the eyelid loses its elasticity, the contact of the conjunctiva with the spherical surface of the eyeball weakens, becomes partial or is lost completely. The eyelid “sags”, turning outward with the conjunctiva, like a pocket that is too large or a piece of fabric that is not secured at one end. This condition of eversion in medicine is called “ectropion of the century” (the term is used not only in ophthalmology; there is, for example, the concept of “cervical ectropion”).
For anatomical reasons, ectropion affects the lower eyelid, since the upper one is naturally adjacent to the eyeball. In addition to a pronounced cosmetic defect, ectropion of the eyelid leads to the development of numerous and very unpleasant symptoms, therefore it is an absolute reason to contact a specialist at the first manifestations.
Symptoms of eyelid inversion
One of the most characteristic symptoms of ectropion is increased lacrimation (the medical term is “epiphora”). Normally, the tear fluid produced by special glands (and also, partly, by the lacrimal glands of the conjunctiva) serves to cleanse small particles, moisturize and lubricate the outer surface of the eye, primarily the cornea, which prevents it from drying out when exposed to oxygen in the air. Removal and drainage of used tear fluid is carried out through special tubules located on the conjunctiva (i.e. on the inner surfaces of the eyelids) - the so-called. "tear points" Almost the entire volume of lacrimal substance is thus excreted through a special duct into the nasal mucosa - in other words, it enters the nose.
But with ectropion, when the above-described drainage tract is grossly destroyed, the lacrimal fluid cannot naturally enter the lacrimal openings. Accumulating in the gap formed between the eye and the eyelid, at a certain volume it begins to overflow.
It should be emphasized that with the gradual formation of the organs of vision, evolution “had” to solve two opposing problems: drying out and souring of tissues due to constant excessive wetting. That is why the composition of tears is balanced in such a way that it contains not only purely liquid, moisturizing components, but also a certain mucous “lubricant” that maintains the moisture balance necessary for the outer eye membranes. With eversion of the eyelid, such balance is impossible; the lower part of the cornea and sclera dries out without the constant washing movement of the blinking eyelid, the lacrimal glands try to compensate for this and reflexively increase the secretion of fluid.
The inverted conjunctiva and the outer skin of the eyelid, on the contrary, are constantly in a stream of flowing tears, and in a heterogeneous stream: some areas dry out, others get wet. The result is a feeling of discomfort, itching, a foreign body (the most eye-specific reactions to any problem), as well as a corresponding urge, sometimes irresistible or realized unconsciously, to rub the eye. As a result, the dermis and mucous membrane of the lower eyelid quickly become inflamed.
Externally, this is manifested by redness, swelling, and the characteristic appearance of “sick meat.” Obviously, under such conditions, a direct path opens for the penetration of all kinds of pathogenic microorganisms (viruses, bacteria, fungi, parasites). With such an invasion, the pathology easily acquires an acute purulent character and can spread to adjacent ocular tissues, sometimes leading to very serious complications and consequences, including panophthalmitis (total inflammation of the eyeball) and the initiation of atrophic processes in the retina and optic nerve, resulting in blindness.
Prices for lower eyelid inversion surgery
| № | Service name | Price in rubles | Make an appointment |
| 2013008 | Surgery for lower eyelid inversion of various etiologies and minor degrees (without the cost of consumables and anesthesia) 1st category of complexity | 30 000 | Sign up |
| 2013009 | Surgery for lower eyelid inversion of various etiologies and a large degree (without the cost of consumables and anesthesia) 2nd category of complexity | 44 000 | Sign up |
| 2013010 | Surgery for lower eyelid inversion of various etiologies and a large degree using alloplastic materials and skin grafts (without the cost of consumables and anesthesia) 3rd category of complexity | 68 000 | Sign up |
Making an appointment Today registered: 21
Types of eyelid eversion
According to the etiological (cause-and-effect) criterion, ectropion is classified into the following categories:
- senile (caused by age-related degradation of muscle and skin tissues, their stretching; pathology usually develops symmetrically in both eyes and, in the absence of adequate treatment, steadily progresses with age);
- scar (forms as fibrous tissue grows after burns, ulcerative inflammation, trauma, etc.; since scar tissue is much larger than functional tissue, the contact of the conjunctiva with the eye is mechanically disrupted - the eyelid simply “moves away” from the eyeball, gaps appear, and lacrimal secretion increases fluids, etc. The dynamics and clinical picture of cicatricial ectropion largely depend on the localization of primary scarring);
- paralytic (due to neuropathology and functional failure of the facial nerve, which controls the entire facial muscular system - from facial muscles to the motor system of the eyelid);
- mechanical (occurs as a result of the progression of various oncopathologies; as in the case of cicatricial ectropion, as the tumor grows, mechanical contact with the eyeball is disrupted. In addition, cellular degeneration distorts the system of forces and mechanical stresses in the eyelid itself, as a result of which the resultant of these forces begins to increase pulls the conjunctiva away from the eye - instead of pressing it against it - and eventually turns the eyelid outward).
1.General information
The term “ectropion” refers to a pathological inversion of the eyelid, i.e. its loose fit to the eyeball. Most often, ectropion affects the lower eyelid. This is due to the slightly different anatomical structure of the upper and lower eyelids: the lower one has a much smaller cartilaginous frame, which gives the eyelid the necessary level of rigidity and maintains its correct shape.
Eversion of the eyelid, even with a moderate degree of severity, creates a significant cosmetic defect, but the main danger is different: the conjunctiva is exposed, access for various types of infections is facilitated, the natural processes of wetting the eyeball with tear fluid are disrupted, which leads to dryness of the eye and inflammation.
Ectropion affects mainly elderly and senile people, but this is far from an absolute rule: among those affected, there are persons of both sexes from all age categories, including newborns.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Diagnostics
The clinical picture in this case is so obvious that the patient usually makes the primary diagnosis for himself - simply by looking in the mirror. The main diagnostic task of an ophthalmologist is, in fact, not to ascertain or exclude ectropion, but to identify its immediate causes, since they determine both the further prognosis and the response therapeutic tactics.
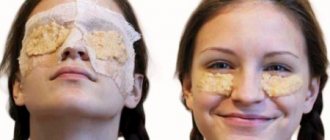
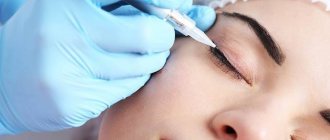
Surgical treatment (blepharoplasty surgery)
For any variant of entropion, conservative treatment, unfortunately, has no effect; physiotherapeutic or laser procedures, which are very popular today, are also ineffective. The natural anatomy, dynamics and kinematics of the eyelid can only be reconstructed by ophthalmic surgery, the specific techniques of which, however, are quite well developed and not too complicated.
Thus, with senile (senile) entropion, the natural disposition of the eyelid is restored, the tight fit of its internal conjunctiva to the surface of the eyeball, the exact closure of the edge with the edge of the opposition eyelid during blinking and sleep. To do this, it is necessary, in particular, to reduce the volume of skin that has stretched and weakened with age (“tighten” it, as they say in aesthetic surgery).
Similar tasks are set for cicatricial entropion, but here it is necessary, first of all, to remove the overgrown connective (scar) tissue.
Mechanical entropion, since it is caused by a tumor process, requires, first of all, the involvement of an oncologist, and cosmetic problems in this case fade into the background. Only after specialized oncological treatment (whether surgery, chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy) is the question of restoring normal statics and mechanics of the eyelid raised.
Finally, with congenital volvulus, it is necessary to diagnose the situation in all details and accurately establish the immediate causes of entropion (abnormal size of the eyeball, irregular shape or hypertrophy of the eyelid itself, pathological development of motor muscles, deficiency of cartilage tissue, etc.), after which action is taken decision and restoration surgery is planned.
Treatment of ectropion
Etiopathogenetic, – i.e. aimed at eliminating the causes of the disease, therapy for ectropion varies depending on its specific variant. However, almost always, eversion of the eyelid requires some kind of surgical intervention (blepharoplasty), since it is impossible to restore the anatomical and mechanical structure of the tissues with medication.
Thus, senile ectropion requires restoration of the natural contact of the inner surface of the eyelid with the eye by tightening (reducing in volume) stretched skin that has lost strength and elasticity. One of the key tasks is to restore natural blinking function with complete closure of the eyelids.
Cicatricial ectropion is eliminated in a similar way: scar tissue is surgically removed, and the natural geometry and mechanics of the eyelid are restored.
Ectropion of the mechanical type requires, first of all, the intervention of oncologists and/or dermatologists: removal of the tumor, biopsy and prevention of relapses come to the fore. After this, if necessary and according to indications, a repeat reconstructive operation may be prescribed to reconstruct normal fit and closure.
Learn more about blepharoplasty surgery >>>
Only with paralytic ectropion, the role of the ophthalmologist is, in fact, limited to palliative, purely symptomatic treatment. Etiopagenetic therapy here is to eliminate the causes of nervous paralysis - as far as possible in each case - and such treatment should, of course, be carried out by a neurologist. As the conductive activity of the facial nerve is restored, the functions it regulates are gradually restored, in particular, the position, tone and mobility of the eyelid.
To eliminate subjective discomfort, for the prevention and treatment of an infectious component (if one has already been introduced), for any type of ectropion, anti-inflammatory, antibiotic, immunostimulating drugs in various pharmaceutical forms, as well as eye moisturizing drops (artificial tears) can be prescribed. However, the appropriateness, form, frequency, and dosage of any medications must be determined by a doctor; self-medication is contraindicated in all cases.
2. Reasons
Eversion of the eyelid can be congenital and, in this case, represents an anomaly in the intrauterine development of the visual organs. Cicatricial ectropion is a consequence of healing of wounds and other damage to the eyelid (for example, thermal or chemical burns). The paralytic version of inversion develops against the background of serious damage to the facial nerve and, in particular, paralysis of the orbicularis muscle. Spastic eversion sometimes accompanies inflammatory processes. In some cases, inversion is purely mechanical in nature and is associated with the growth of a neoplasm in the area of the ciliary edge of the eyelid.
Finally, age-related (atonic) ectropion progresses with the natural aging of the body and the development of degenerative processes in the eyelid, which leads to a decrease in muscle tone and stretching of increasingly dehydrated tissues of the eyelid.
Visit our Microsurgery page
Other Treatment Options for Entropion
For entropion of any type, keratoprotectors can be symptomatically prescribed - literally translated, this means “cornea protectors”, which is fully consistent with the objectives and action of such drugs: first of all, it is necessary to preserve the integrity, thickness and transparency of the corneal layer to the maximum extent possible, preventing its inflammation or ulceration.
To stimulate natural regenerative (self-healing) processes, epithelializing drugs are also used. Medicines of both groups are prescribed, as a rule, in the pharmaceutical form of an eye ointment or gel. In some cases, during the period of preparation for radical intervention, it is recommended to wear a special soft contact lens, which serves the cornea as a reliable mechanical shield from traumatic contact with the eyelashes.
In some cases, when the lower eyelid is inverted, retraction with a patch can be used, however, this measure is aimed at reducing trauma to the cornea and alleviating the patient’s condition until blepharoplasty.
Treatment options
Elimination of pain under the upper eyelid require symptomatic therapy, but complete treatment of the underlying disease , therefore, after examination by an ophthalmologist, additional diagnostic measures are possible from other specialists.
In cases where the cause of pain is a foreign body getting under the eyelid , you can cope with the problem yourself if you follow this simple algorithm:
- A clean scarf or napkin is folded into a triangle to form a sharp edge. After which, with this sharp edge, the foreign object is gently pushed towards the inner corner of the eye (if the object has not dug into the conjunctiva to a great depth, it can be immediately picked up with the corner of a napkin);
- when the speck reaches the corner of the eye, you can remove it from there with a cotton swab ;
- After the procedure, antibacterial drops can be dropped into the eye .
At home, you can take emergency measures for chemical burns.
Prevention
Prevention involves compliance with hygiene standards , which will eliminate the risk of infections in the eyes.
It is necessary to keep your hands clean (especially after going outside or visiting public places), but even with clean hands you should not rub your eyes too much.
You should also follow a sleep schedule, avoid getting too cold, and include more healthy foods in your diet (including fruits and vegetables).
This is necessary to maintain immunity at a high level and will avoid the development of diseases even when pathogenic microflora enters the body.