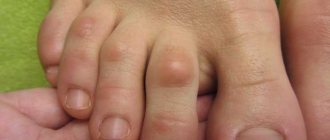
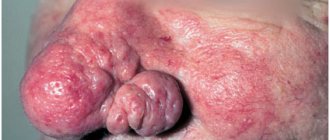
Causes of ingrown toenails
The main causes of ingrown nail plates include:
· valgus deformity (curvature of the big toe at the joint level) associated with flat feet, and other anatomical changes in the foot: improper placement of the toes, their pressing on each other inside the shoe can lead to ingrown toenails
genetic predisposition: hereditary deformation of the nail plate and lateral periungual skin ridges
· circulatory disorders caused by diseases such as varicose veins, diabetes mellitus and other endocrine disorders: diseases are accompanied by swelling of the legs, feet, fingers, which leads to ingrown nails
· inflammatory processes - fungal and bacterial diseases: the nail becomes thicker, may lose its previous shape, crumble, thereby damaging the nail fold and causing inflammation
· incorrectly selected shoes: narrow or smaller, squeezing the toes; without a backdrop, leading to the toes resting on the toe of the shoe when walking; high heels, increasing the load on the fingers; on a hard sole, leading to a lack of softening while walking
· incorrectly performed pedicure: trimming nails too short, cutting off the corners of the nail plates
· injury to the toes: bruises leading to damage to the nail and its further abnormal growth
· high load on the legs: physical activity, excess weight, pregnancy, hormonal changes
Ingrown nail
- a problem that causes pain and discomfort, and inaction leads to more severe consequences. Constant pain, the inability to wear any shoes, purulent formations and inflammation around the nail plate are only part of the unpleasant complications associated with onychocryptosis. If you notice the first signs of an ingrown toenail, be sure to schedule a consultation with a specialist.
Why do nails grow ingrown?
The most common cause of the disease is improper pedicure technique. The nail grows into the skin if you use scissors with rounded edges and cut off its corners.
The second most common cause is a fungus (onychomycosis). It leads to delamination of the plate, so it becomes brittle and can bend and “cut” into the roller.
Other causes of ingrowth may be:
- pressing shoes, narrowed toes of shoes, boots;
- hereditary predisposition;
- blow, bruised finger.
These are key factors in the disease, but not the only ones. Inflammation of an ingrown toenail can also develop with flat feet, diabetes, and obesity.
Symptoms of onychocryptosis
With onychocryptosis, the lateral part of the nail abuts the periungual fold and continues to grow inside it. At first, the patient feels general discomfort, redness of the skin around the nail is observed. It is also possible to change the shape of the nail. Preferences in shoes are gradually changing, the choice is given to open options, wearing tight, narrow, and over time, any closed shoes becomes difficult. In case of inaction, the symptoms of the disease become more pronounced, complications appear, and over time, surgical intervention becomes inevitable.
The main symptoms of an ingrown toenail include:
Painful sensations in the toe area resulting from injury, after wearing shoes, or for no apparent reason
· swelling and hyperemia (overflow of blood vessels of the circulatory system of any area of the body) of the periungual fold
formation of pus in the area of the nail plate
formation of excess connective tissue protruding from the wound, visually reminiscent of raw meat
In medicine, the development of onychocryptosis is characterized by three main stages - mild, moderate and severe.
Stages of onychocryptosis
First (mild) stage
characterized by redness of the periungual fold and moderate swelling. At this stage, the nail plate has no visual changes, and painful symptoms usually appear while walking in shoes.
Second (moderate) stage
accompanied by signs of inflammatory processes: the periungual fold becomes red, purulent discharge appears, and in some cases painful pulsation is observed. The nail becomes denser and dull.
Third (severe) stage
caused by hyperemia (increased blood supply) of the periungual ridges, the formation of hypergranulation (tissue growth in areas of inflammation), an increase in the volume of the phalanx, and the presence of purulent discharge. The nail becomes brittle and mobile, the skin around it visually resembles raw meat (this symptom is called “wild meat” in medicine).
Complications of onychocryptosis
Prolongation of the disease leads to the development of infections, which certainly aggravates the situation. Wounds that are open for a long time and do not heal are an excellent breeding ground for bacteria. An infected wound heals slowly as the body tries to heal the affected area, resulting in bright red granulation tissue forming at the site of the ingrown nail. If you do not start treatment or start the wrong treatment, the granulation becomes dense, the phalanx changes shape, and it becomes impossible to solve the problem with conservative methods. In addition, inflammation of the soft tissues of not only the fingers, but also the entire foot is likely to develop, which, if left untreated, can spread to the bones and lead to osteomyelitis.
Complications of onychocryptosis are associated mainly with the development of infectious and inflammatory processes and include:
· abscess
(limited inflammatory purulent focus causing intoxication) fingers. It is characterized by the presence of pronounced swelling and redness of the skin. Surgery required.
· lymphangitis
(acute or chronic inflammation of the lymphatic trunks and capillaries, occurring secondarily against the background of purulent-inflammatory processes). It is characterized by the spread of infection throughout the lymphatic system, affecting blood vessels. Complex treatment is required, including anti-inflammatory and antibacterial therapy.
· gangrene
(death of living tissue) of the finger. Characterized by processes leading to irreversible necrosis of soft tissues. Amputation of the affected phalanx or the entire finger is required.
· osteomyelitis
(purulent - inflammatory process that develops in the bones, bone marrow and surrounding soft tissues) of the finger. The infection affects the bones. Drug therapy is required. Amputation of the phalanx of the finger is possible if the patient comes too late.
The risk of complications increases in the presence of concomitant diseases associated with disruption of blood vessels, for example, diabetes mellitus and atherosclerosis. The risk group also includes people who are overweight and over the age of 60.
Types of orthonic plates
B/S plates
The material for the manufacture of B/S structures is elastic, biocompatible plastic, which transfers its tension to the nail. Devices are selected individually and attached after antiseptic surface treatment.
After a certain time of fixing the plate on the ingrown nail, excessive pressure on the periungual fold is significantly reduced or completely eliminated. As a result, the symptoms of inflammation (redness, swelling, pain) go away and the physiological growth of the stratum corneum is restored.
For optimal correction, the plate is replaced with a new one every 2-6 weeks.
Onyclip
They are steel structures coated with plastic, with two rigidity options. To regulate the tension force, a special tool is used, with which the size and shape are varied, and the most optimal effect is selected at all stages of treatment.
The device is disposable. Replaced as correction occurs.
Podofix
Presented in the form of a wire frame covered with a soft silicone shell. Fixed with measured tension, the orthonic device works like a spring.
The plate on the toenail does not cause discomfort when wearing regular shoes and can even be covered with decorative varnish. After a certain period of time, inflammation and pain from pathological pressure disappear, and the normal physiology of the nail is restored.
Podofix is a disposable design that needs to be replaced if necessary.
Podological staples are presented in the form of curved wire rods. Designed to correct more complex disorders, they are securely fixed to the side edge of the nail using hypoallergenic fastening hooks or medical glue. Steel structures, having optimal hardness and shape memory, make it possible to level out various degrees of deformation without the use of traumatic surgical interventions.
Treatment of an ingrown toenail with staples can be carried out at all stages of the development of onychocryptosis, including in the presence of pathological tissue granulation.
Types of staples
Combiped (COMBIPED)
Designed to eliminate unilateral ingrowth and curling of the nail plate.
Consists of one hook and a plastic pad that sticks to the nail.
Installation of a disposable structure is almost painless.
In case of diabetes mellitus, the brace should be worn with extreme caution, only with the permission and under the supervision of the attending physician.
3-TO
It is a three-component correction system, consisting of two “shoulder” brackets with hooks, and a fastening clamp. Made from inert, non-allergenic, chromium-nickel steel.
Installing a 3-TO staple on an ingrown toenail is possible at any, even the most advanced stages of onychocryptosis. However, its fastening requires a fairly high qualification level. Patients with diabetes must use extreme caution when fixating and wearing an orthonic device. The design is disposable, can be replaced with a new one if necessary.
Fraser bracket
The most successful system in therapeutic terms is the invention of Ross Fraser, the founder of orthonyxia, created in 1946. Consists of one piece of wire, with two arms and hooks. As the nail grows, it is adjusted once or twice (without removal), which significantly reduces the cost of the procedure. Thanks to the central bend in the "omega" shape Ω, the maximum tensile force observed in the first day after installation gradually weakens.
It is produced in two stages. First, a plaster cast is taken from the nail phalanx, and then a staple is selected based on it. The selection of wire is carried out on an individual basis, taking into account the thickness of the nail in need of correction. After attaching a staple to an ingrown toenail, relief occurs almost immediately due to the reduction in pressure.
The Fraser brace, like any other medical device, has a number of contraindications for wearing:
- children up to 6 years old
- fungal and psoriatic nail infections;
- diabetes mellitus (as determined by the doctor).
ERKI technology
An innovative development by Erkodent Erich Kopp GmbH (Germany). The device looks like a wire ring and plastic hooks that are glued to the lateral periungual ridges. By changing the diameter of the ring, the traction force is adjusted.
ERKI - technology can be used on short nails when it is not possible to install a staple.
Correction is made every 3 – 4 weeks.
Diagnosis of the disease
First of all, a visual examination and history taking are necessary. It is important to identify the presence of concomitant diseases - to exclude or confirm fungal infections and diseases that are associated with disruption of blood vessels (diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis).
Diagnosis of onychocryptosis includes
:
· collecting anamnesis (full collection of data about the patient and his diseases): identifying the causes of the disease, collecting complaints
· visual examination of the patient (diagnosing the stage of the disease and identifying complications): the condition of the nails, periungual ridges, skin of the fingers and feet; the presence of deformation of the fingers, swelling, purulent inflammation, granulation; comparison of two limbs
· general blood test (if complications are detected): carried out to identify or exclude a general inflammatory process. A blood glucose test is also performed to confirm or rule out diabetes.
· bacteriological examination of discharge from wounds (analysis of purulent discharge): the study is carried out to determine the type of pathogen and the severity of the inflammatory process
· X-ray examination (study of the internal structure of the foot): carried out to study the anatomical changes in the structure of the foot and to identify or exclude the transition of inflammatory processes to the bones
Treatment of ingrown toenails
The tools for treating onychocryptosis are conservative methods
in the initial stages (load reduction, compression treatment, foot hygiene, etc.) and
surgical methods
in later stages (nail resection, complete removal of the nail plate, laser techniques).
There are also modern non-surgical methods
that involve the use of various plates, staples and springs (orthonyxia methods).
Which doctor should I contact?
A podiatrist is the doctor you should contact when the first signs of an ingrown toenail appear. In certain cases, treatment requires the participation of a surgeon (in late stages, when conservative treatment is ineffective), a dermatologist (in the presence of fungal and other infectious diseases) and a laser therapist (when treating the disease with methods associated with the use of laser therapy).
It is very important to prescribe competent, most effective treatment to restore pain-free mobility to the patient.
Treatment methods for onychocryptosis
This or that method depends on the stage of onychocryptosis, as well as the presence of complications and concomitant diseases. At the initial stage, the problem can be solved using conservative methods. When a patient presents at a late stage of the disease, there is a high probability of surgery.
Non-surgical methods:
· medical hardware pedicure (a treatment procedure that is performed by a pedicurist with a higher medical education and is aimed not only at the aesthetic beauty of the feet and toes, but also at their health)
· tamponing (installation of a special thin gasket between the nail and the periungual ridge, which prevents contact of the nail with the ridge; therefore, the process of ingrowth is impossible)
· installation of corrective systems: staples, plates (the device is placed on the nail plate in various ways depending on the type of problem and helps to lift the nail, thereby reducing pressure on the roller and preventing ingrowth)
A positive effect can only be achieved if the treatment is prescribed by an experienced doctor - a podologist with higher education. Contact only professional specialists in trusted clinics with extensive experience and a good reputation.
Surgical methods for treating onychocryptosis:
· resection of the nail plate. Resection is a surgical operation aimed at removing part of an organ.
· complete nail removal
Today, classical surgical methods of nail removal are inferior to modern methods that involve the use of laser.
Laser therapy has a number of advantages - it is low in trauma, short recovery time and reduces the risk of re-ingrowing (relapse) of the nail. Using a laser, it is possible to painlessly remove: the nail fold, nail plate, part of the nail, hypergranulations, inflammatory and purulent formations.
Laser treatment is painless, safe and most effective; the procedure is carried out by experienced specialists using modern high-tech equipment.