Botulinum therapy in cosmetology and medicine is actively developing. The method is highly effective and has minimal side effects. In cosmetology it is used for:
- smoothing facial wrinkles;
- preventing the formation of facial wrinkles, including age wrinkles;
- correction of the shape of individual parts of the body (for example, the face);
- healing wounds and reducing the likelihood of scar formation in areas of increased muscle activity;
- reducing sweating.
Botulinum therapy - what is it?
Botulinum therapy in cosmetology and medicine is actively developing. The method is highly effective and has minimal side effects. Botulinum toxin was discovered back in the 19th century and is the cause of death in patients with botulism. In large doses, this substance has been found to cause vomiting, difficulty swallowing, convulsions, paralysis and can be fatal. But in the 70s of the last century, Alan Scott conducted animal studies proving that botulinum toxin can be used for medicinal purposes in small doses. The scientist proposed using this substance to treat strabismus. This aroused interest in the new technique, which is why new studies and articles on botulinum therapy appeared.
Cost of botulinum therapy procedure
The cost of botulinum therapy in Moscow is influenced by factors such as the dose of botulinum toxin, the total area of the correction zone, and the manufacturer of the drug. At the International Hemostasis Clinic, the price for botulinum therapy using modern drugs ranges from 250 to 350 rubles. Before prescribing the procedure, our cosmetologists will conduct a thorough diagnosis, excluding any contraindications, select an effective drug, and provide regular monitoring after injections. To clarify prices and make an appointment with a cosmetologist, request a call back or call the phone number listed on the website. Our consultants will contact you and be happy to answer all your questions.
You can make an appointment with a cosmetologist, find out the cost of botulinum therapy (Botox) and ask any questions you may have by phone or through the feedback forms on the website.
Biorevitalization
Treatment of hyperhidrosis
Mesotherapy
Botulinum toxin and its properties
This is a protein substance, which is considered one of the most powerful poisons of natural origin. But scientists have found that in small doses it is safe for the body and allows you to relieve muscle spasms. Initially, botulinum therapy was used to treat neurological diseases, but one interesting side effect was noticed after the injections: facial wrinkles were smoothed out on the patients’ faces. This was especially noticeable in the folds between the eyebrows and in the corners of the mouth.
This aroused interest among wealthy middle-aged and older women who were ready to do anything for beauty and youth, so there was a high demand for an anti-aging procedure. The effect of botulinum therapy was amazing, so the innovative rejuvenation procedure began to be widely used in cosmetology.
The very first and most famous botulinum therapy drug based on botulinum toxin A (BTA) is Botox.
. For a long time it was the only one, but now there are drugs that include botulinum toxin type B (BTV). Other types of this toxin are not used for botulinum therapy.
To treat diseases associated with muscle spasms, botulinum therapy has been officially used since 1989. The use of Botox in cosmetology was approved in 2002. Since then, cosmetologists have achieved excellent results in the field of rejuvenation. After botulinum therapy, most small facial wrinkles disappear, the face acquires a more welcoming expression due to the smoothing of the folds between the eyebrows.
The effect of botulinum toxin during botulinum therapy
Botulinum toxin is an A-type neurotoxin that disrupts the transmission of nerve impulses from nerve endings to muscles. The essence of botulinum therapy is the injection of botulinum toxin type A into soft tissues. Once penetrated, the substance blocks the transmission of nerve impulses to the muscles, causing temporary paralysis and relaxation. Since the blocked muscles stop contracting and take an active part in facial expressions, the skin in this area gradually smoothes out, as a result of which wrinkles, deep folds, and creases disappear.
Mechanism of action
Botulinum toxin is a neurotoxin. It blocks the release of acetylcholine, which is involved in the transmission of nerve impulses at neuromuscular synapses. Thus, if the nervous system sends a signal to the muscles, it does not reach the point of application. Consequently, the muscle remains in a relaxed state. Local administration of the substance in small concentrations allows for relaxation of certain muscles. That is why botulinum therapy for spasticity can achieve a positive result.
The direct effect of botulinum toxin is to influence motor and parasympathetic nerve fibers. Acetylcholine is blocked and does not leave the presynaptic part of the neuron, so the transmission of nerve impulses becomes impossible. The introduction of Botox and other drugs into the muscle leads to a decrease in the cross-section of muscle fibers and the number of myofilaments. Thus, the volume and strength of the muscle decreases. This process is reversible.
BEFORE
AFTER
The indirect effect of the substance is also described. At the level of the central nervous system, botulinum toxin leads to inhibition of alpha motor neurons and normalizes reciprocal inhibition between antagonist muscles (flexors and extensors). This makes it possible to combat such phenomena as skeletal muscle dystonia.
The analgesic effect of drugs for botulinum therapy was also revealed. This property was discovered by accident when using the toxin for anti-aging purposes. Doctors noticed that botulinum therapy for migraines reduces the intensity of pain, so they began to actively study this property. To date, it has been proven that BTA has an analgesic effect for dystonia, spasticity, tension headaches, trismus, migraines, and chronic pelvic pain. This is explained by several theories. The first is decompression of pain receptors due to the elimination of muscle spasm. The second is the normalization of muscle spindle contraction. The third theory is a reduction in neurogenic inflammation.
Headache treatment
Separately, it is worth noting the use of botulinum toxin for the treatment of headaches. Scientists have found that Botox can help relieve chronic headaches caused by migraines. According to statistics, they bother every fifth adult.
Botox is administered to all areas from which sensory impulses go to the central nervous system. Thanks to this, it is possible to achieve complete muscle relaxation. After a few hours, the drug penetrates the sensory nerves and blocks the transmission of pain impulses from them.
With the help of a pronounced relaxing effect on the muscles of the head and neck, it is possible to restore the quality of life of patients. Botulinum therapy allows you to forget about regular headaches.
Botulinum therapy: pros and cons
Let's talk about the pros and cons of botulinum therapy in cosmetology and medicine. This question worries many who want to use the technique. On the one hand, there is extensive experience in the successful use of drugs based on BTA and BTV, but on the other hand, this is a strong poison.
The benefits of botulinum therapy include:
- high efficiency
- quick result
- minimal trauma to the skin
- safety of registered drugs
- duration of effect
- painlessness
- minimum list of contraindications
The content of botulinum toxin in drugs used in botulinum therapy is minimal. The dangerous dose of the toxin is tens or hundreds of times greater than the amount injected during the session, so the injections are completely safe for the body. If you go to a licensed clinic for botulinum therapy and use only registered drugs, you should not be afraid of complications and the development of life-threatening conditions. The result of botulinum therapy will please you, and the general condition of the body will not worsen.
The main disadvantages of botulinum therapy:
- The effect lasts 6-8 months. After this period ends, the procedure must be repeated.
- Only a qualified doctor can perform botulinum therapy correctly. Any mistake can lead to facial asymmetry.
- After injections, swelling may persist for the first days. It is especially noticeable on the eyelids. Swelling after botulinum therapy goes away on its own.
- Facial muscles located next to muscles immobilized by botulinum toxin may become excessively mobile. This leads to the appearance of new facial wrinkles.
- duration of effect
- If injections are abused for rejuvenation, the face can become unnatural and devoid of facial expressions. In everything you need to maintain moderation, because a motionless face without emotions can hardly be called beautiful and natural.
Is botulinum therapy harmful?
If you entrust it to a professional and observe the measure, then no. Some patients, in pursuit of youth, become dependent on beauty injections, try stubbornly to overcome even minor wrinkles, and as a result get a face that resembles a mask. Fortunately, this is reversible.
Preparations for botulinum therapy
Modern cosmetology clinics use the following drugs for botulinum therapy:
- Xeomin (“Xeomin”). Does not contain any protein compounds, which reduces the risk of allergies and side effects. The product acts locally, only on the desired muscle, so after the injection, natural facial expressions are preserved and the face looks alive. Well smoothes horizontal wrinkles on the forehead, in the area between the eyebrows, and corrects the lower third of the face. Thanks to its unique composition, it is not addictive. The effect after use lasts for 3 – 4 months.
- Dysport. The composition contains stabilizing proteins, so patients prone to allergies may develop an acute immune response after injections. This is an analogue of Botox, but Dysport acts faster, so fewer injections are required per session, which is a definite advantage. The drug smoothes expression lines and age-related wrinkles, helps get rid of hyperhidrosis and chronic migraines.
- Botox (“Botox”). The composition includes botulinum toxin with associated proteins and stabilizing proteins, so after administration an acute allergic reaction may develop. Botox contains the highest concentration of onabotulinumtoxin. The product is best suited for correcting the eyebrow line and corners of the eyes. The effect lasts for 3 – 6 months.
Contraindications to botulinum therapy
Despite the safety of the method of treatment and rejuvenation, it has contraindications. Botulinum therapy cannot be performed if:
- pregnancy and breastfeeding
- malignant neoplasms
- hemophilia
- acute infections
- duration of effect
- renal dysfunction
- taking anticoagulants and antibiotics
- individual intolerance to drug components
- inflammation of the skin at injection sites
- high myopia
- generalized movement disorders
There are also relative contraindications to botulinum therapy. In such cases, the possibility of using botulinum toxin is determined on an individual basis. The procedure is not recommended for people under 18 and over 60 years of age, with increased fragility of blood vessels, as well as for people who regularly drink alcohol. For medicinal purposes, preparations based on botulinum toxin can be used in children at least 9 years of age.
What is botulinum therapy in cosmetology
Botulinum therapy is an injection cosmetological rejuvenating procedure, the essence of which is the subcutaneous administration of drugs from the botulinum toxin group. After penetration into soft tissues, the substance blocks the transmission of nerve impulses to muscle structures, providing a relaxing, blocking effect. As a result, the skin at the site of Botox injection gradually smoothes out, facial and age wrinkles disappear, and new ones no longer appear. The technique has its own indications and contraindications, so before performing it, consultation with a specialist and a comprehensive diagnostic examination are required. The International Hemostasis Clinic uses only safe, proven, certified drugs, so clients who use our services never experience side effects or complications. The clinic’s cosmetologists individually select a treatment regimen, taking into account the nature of the problem and the desired effect. Results after botulinum therapy last for an average of 10 – 12 months.
Are there any side effects of botulinum therapy?
Side effects of botulinum therapy are not dangerous to health and quickly disappear without additional intervention. After the procedure, the patient may feel slight malaise, weakness, dizziness, and nausea for 1-2 days. These phenomena resolve on their own and do not affect the final result of the procedure.
Another problem that is encountered after a course of rejuvenation with Botox and other drugs is the lack of lip mobility, drooping of the eyebrows and upper eyelid. Drooping of the corners of the mouth occurs if the patient does not comply with the recommendations to be in an upright position for the first hours after the procedure. Drooping of the eyebrows and upper eyelid is associated with the incompetence of the doctor. These problems go away after 1-2 months.
Another possible consequence of botulinum therapy is the formation of compactions at the injection sites. This is due to its uneven distribution. In this case, after 2-3 weeks you need to go to the clinic for correction using additional injections. After botulinum therapy, the load on the muscles is redistributed, so creases may form on the forehead and under the eyes. After 14 days, you need to visit a cosmetologist and, if necessary, make a correction.
The most common side effect of botulinum therapy is swelling at the injection site. Despite the use of fine needles, soft tissue damage is still present and the body responds accordingly. Swelling can persist from 2 to 10 days, disappearing without a trace without additional intervention.
Some patients experience headaches after the procedure. This is often due to violation of doctor’s recommendations after botulinum therapy. Also, headaches can be associated with a redistribution of the work of facial muscles and an individual reaction. An unpleasant symptom usually goes away after a few hours, in some cases it can persist for 10-14 days.
A competent cosmetologist recommends starting botulinum therapy with minimal doses. If the effect is insufficient, a correction can be made. If the dosage is higher than necessary, the facial muscles become immobilized and the face becomes unattractive. In this case, you will have to wait until the effect of the substance wears off. If you want to smooth out wrinkles, don't try to do it quickly. It is better to undergo an additional corrective procedure and get a natural result.
Possible complications
Two decades of observation by clinicians prove that botulinum therapy has a high safety profile. Complications are extremely rare. They are few in number and completely reversible. Possible side effects are divided into general and local reactions.
Common complications are caused by the immune response. These include:
- anaphylactic shock;
- generalized weakness;
- flu-like syndrome;
- autonomic dysfunction - drooling, decreased blood pressure.
Local reactions include:
- pain, swelling at the injection site;
- ptosis of the upper eyelid;
- dry eyes;
- lowering of the inner or lateral corner of the eyebrows;
- pseudohernia of the infraorbital region;
- transient diplopia;
- impaired swallowing (during correction of the neck area);
- weakness of the upper lip;
- headache;
- facial asymmetry.
Exceeding the dose of botulinum toxin can cause a mask-like effect on the face. Long-term use of BTA in high concentrations and without interruption is fraught with the development of resistance to treatment.
The likelihood of complications depends on the mastery of the methodology and skill of the doctor, as well as the patient’s disregard for recommendations during the recovery period.
Indications for botulinum therapy in medicine and beauty
The technique is widely used not only for rejuvenation, but also for therapeutic purposes. It is actively used not only by cosmetologists, but also by neurologists. Botulinum toxin therapy is also used for spasticity after a stroke. Let's take a closer look at what problems can be solved with the help of drugs based on BTA and BTV.
The use of drugs for botulinum therapy in cosmetology
The main effect of botulinum therapy is the smoothing of facial wrinkles
b>. Thanks to local relaxation of muscle fibers, it is possible to successfully combat age-related changes. Botox injections can get rid of wrinkles on the cheeks, forehead, folds between the eyebrows, crow's feet, folds on the sides of the mouth, and on the nose. Photos of the results of using botulinum therapy in cosmetology before and after are the best proof of the effectiveness of the method. Beauty injections are an alternative for women who want to prolong their youth, but do not dare to undergo plastic surgery or have contraindications to surgical intervention.
With the help of botulinum therapy, you can correct the oval of the face, cope with drooping corners of the lips or the tip of the nose, asymmetry of the eyebrows, reduce cords on the neck, and rejuvenate the décolleté area. For those who want to improve their appearance, Botox is an excellent solution.
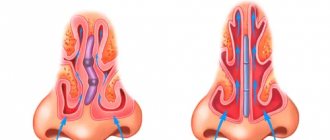
Another pressing problem that can be solved with injections is increased sweating.
. Botulinum therapy for hyperhidrosis is safe and gives excellent results. The toxin blocks the transmission of nerve impulses to the sweat glands and inhibits their work. The effect occurs 1-1.5 weeks after the procedure and lasts up to 8 months. The technique allows you to forget about wet spots on clothes in the armpit area, the smell of sweat and feel confident in any clothes. Also, with the help of botulinum therapy, you can fight hyperhidrosis of the palms, feet, gluteal and inguinal folds, as well as other parts of the body. The procedure lasts about an hour, is easily tolerated and allows you to completely block the work of the sweat glands.
Another cosmetic problem that can be solved with botulinum therapy is rosacea.
. This is an inflammatory lesion of small vessels of the skin, manifested by spider veins, redness of the cheeks, chin and other areas of the skin. The introduction of BTA into problem areas leads to persistent vasospasm and allows you to eliminate a cosmetic defect.
How is botulinum therapy used in neurology?
In neurology, botulinum therapy is widely used for spastic processes, impaired muscle tone, and also for pain. The treatment is well tolerated and gives positive results.
Botulism toxin type A in the treatment of pain syndromes
Botulinum toxin is a protein that is a potential neurotoxin produced by the anaerobic bacterium Clostridium botulinum. In large doses, botulinum toxin can cause diffuse muscle paralysis, vegetative disorders with a possible fatal outcome, which is observed with botulism. However, the toxin, introduced as a drug in very low doses into individual muscles or local skin areas, turns out to be a unique means of treating various motor and autonomic disorders, as well as correcting facial wrinkles. In 2000, the global neuroscience community dubbed botulinum toxin the “mysterious molecule of the century,” due to its effective use in treating a wide variety of diseases in recent decades, and perhaps at the same time recalling its millennia-long history of combating it. There are 8 known serological subtypes of botulinum toxin (A, B, C1, C2, D, E, F, G). Serotypes A, B, E, F and G can cause botulism in humans, but the most powerful toxin is type A. Therefore, botulinum toxin type A (BTA) is the first and most widely used serotype in clinical practice. The main point of application of BTA is the presynaptic terminals of cholinergic synapses, including neuromuscular ones. In the injection zone, the toxin blocks the release of acetylcholine from presynaptic axon terminals by cleaving synaptosomal transport proteins (type A blocks SNAP-25) and causes dose-dependent local muscle relaxation. The process of presynaptic cleavage of transport proteins by botulinum toxin is irreversible and takes an average of 30–60 minutes, and muscle relaxation occurs after a few days. 1–2 months after the injection, new terminals begin to grow from blocked axons and new functionally active synapses are formed (sprouting), and the original synapse is gradually restored. This explains the reversibility of the therapeutic effect of BTA injections after 2–6 months. The complete end of the effect occurs when neuromuscular transmission is restored and sprouting ceases. The local effect of BTA, the possibility of injection into any accessible muscle, good tolerability of treatment, safety, absence of systemic side effects and long duration of action, proven on the basis of rigorous scientific studies, determine the therapeutic value of botulinum toxin [6,14]. Today, more than 100 potential indications for the therapeutic use of BTA are known. Hundreds of scientific articles and manuals have been published on the clinical use of botulinum toxin, primarily in the treatment of diseases and conditions involving increased skeletal and smooth muscle tone or spasm. The most studied use of BTA is for focal dystonia, spasticity, cerebral palsy, hyperhidrosis, hyperfunctional facial wrinkles [6,14,15]. Although BTA was originally used for diseases manifested by increased muscle tone, its analgesic effect has long been noted [7,11]. In many patients, the analgesic effect appears earlier and lasts longer than the effect on muscle hyperactivity. A decrease in pain can also be observed in the absence of a muscle relaxant effect. Recent studies have shown the effectiveness of BTA for various pain syndromes, including various types of primary headaches, back pain, pain from whiplash injuries, myofascial pain syndromes, myogenic dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint, chronic pain in large joints (intra-articular administration of BTA) , with local alopecia syndrome with cephalalgia (cephalalgic alopecia areata), secondary headaches with cervical and cranial dystonia, trigeminal and postherpetic neuralgia, chronic facial pain with hyperactivity of the masticatory muscles, chronic pelvic pain in women with spasm of the pelvic floor muscles, etc. [2 ,9,12,15,16,17,30,41,43,46]. The nature of the analgesic effect of BTA in pain syndromes remains not entirely clear. The following mechanisms of action of BTA are discussed. 1) Weakening of prolonged muscle contraction of muscles in the area of BTA injections leads to decompression of the afferent endings of muscle nociceptors (pain receptors) and muscle blood vessels; the release of various substances leading to sensitization of muscle nociceptors is reduced [23]. As a result, muscle triggers of pain attacks are eliminated - local painful muscle areas that “work” as permanent or potential triggers of attacks. This mechanism is very important, especially for such a common chronic disease as migraine, since constant excessive impulses from the pericranial muscles (muscle stress) are today considered one of the provoking factors of headache attacks, along with known sensory stimuli (noise, light, odors). 2) Reduction (normalization) of muscle spindle activity while eliminating excessive muscle contraction and, as an indirect consequence, reduction in pain. In this case, a change in the activity of supraspinal projections of muscle spindle afferents leads to a change in the activity of sensory systems at the level of the central nervous system. This mechanism is discussed as a manifestation of neuroplasticity of the central nervous system in response to “damage” of afferent input. 3) Retrograde transport of BTA and/or its metabolites in the central nervous system. Experiments on animal models have shown modulation of the release of methionine-enkephalin-like substances in the striatum, substance P and enkephalin in the spinal cord and raphe nuclei (in vitro) and glutamate (in vivo) [10]. 4) Suppression of the release of not only acetylcholine, but also other neurotransmitters, such as CGRP, substance P, which allows modulation of sensory afferent flow. 5) Suppression of neurogenic inflammation – an important factor in the pathogenesis of pain syndromes. Thus, local administration of botulinum toxin type A leads to long-term muscle relaxation, the pathological “chain” of muscle spasm–pain–spasm is broken. When the muscle relaxes, activation of peripheral nociceptors and, accordingly, impulses along pain C-fibers and Ad-fibers stop, which leads to a decrease in the hyperexcitability of peripheral nociceptive neurons in the trigeminal ganglion or spinal ganglia, thus affecting peripheral sensitization. During muscle relaxation, the afferent flow from muscle spindles along non-pain sensitive Ab fibers also decreases. This reduction in afferent flow along pain and non-pain sensory fibers leads to a decrease in the excitability of neurons in the trigeminal nucleus (headaches and facial pain) or the dorsal horn of the spinal cord and the nuclei of the thin and cuneate fasciculus of the medulla oblongata (somatic pain syndromes), thus affecting central sensitization. That is, as a result of ultra-long-term muscle relaxation, BTA indirectly affects the state of peripheral and central nociceptive systems. Headaches Headaches are one of the most common reasons for seeking medical help. The first question that the doctor must resolve is: is the headache primary, secondary (symptomatic) or mixed? Fortunately, in only 8% of patients the cause of headaches is severe organic diseases, often life-threatening: tumor, aneurysm, traumatic brain injury, infection and others. In the vast majority of cases, patients suffer from primary headaches - diseases not associated with structural lesions or systemic diseases of the nervous system, the main clinical manifestation of which is headache. According to the 2004 International Classification of Headache Disorders, these include migraine, tension-type headache, cluster headache and other trigeminal autonomic (autonomic) cephalalgias, as well as other rare primary headaches [25]. The most common forms of primary headaches are migraine and tension-type headache (TTH). The history of the use of BTA for the treatment of headaches begins with aesthetic medicine. In 1992, plastic surgeon William Binder first drew attention to the regression of headaches in patients who were injected with BTA to correct facial wrinkles. This was the start of a new direction in the therapeutic use of BTA - the treatment of headaches. For medicine, such a case is unique, when an initially “neurological” drug, which over time became popular as a highly effective means of aesthetic medicine, “returned” to neurology with new indications for its use. To treat headaches, botulinum toxin type A drugs are usually injected into the m. Procerus, bilaterally in mm. Frontalis, Corrugator supercilii, Temporalis, Occipitalis and less commonly mm. Trapezius, Splenius capitis, Sternocleidomastoideus. Two techniques are used: 1) “fixed points”; 2) “following the pain”, when the choice of injection points depends on the location of pain or muscle tension. Sometimes a combination of techniques is used. The choice of technique depends on the patient’s complaints and medical examination data. The “fixed point” technique is most often used for migraine, and the “following the pain” technique is more often used for tension headaches and chronic migraine, both approaches are used for mixed headaches [1,2,13]. BTA preparations are diluted with sterile saline according to standard methods. The prepared solution is injected with a syringe with a needle with a diameter of 0.3 cm. For injections into the face, head and neck, it is better to use syringes with non-removable needles. The total dose of BTA is always determined individually and depends on the type of headache, severity of symptoms, body size, size of injection areas (head or head and neck area). The total dose per procedure for one patient varies from 1/3 to 2 bottles of the drug. Over the past 13 years, 57 clinical studies have been carried out, including 28 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies of the effectiveness of BTA in various forms of tension-type headache and migraine, which involved more than 7500 patients [19,22,35,36,40 ]. Thus, BTA is one of the most studied drugs for the preventive treatment of various types of primary headaches. Migraine. Migraine is one of the most well-known neurological diseases; it occurs in the adult population with an average frequency of 12% (6% in men and 18% in women) and 4% in childhood [28,39]. Migraine has a characteristic clinical picture. It manifests itself as repeated attacks of pulsating headache of moderate or severe intensity, lasting 4–72 hours, predominantly unilateral localization (hemicrania), which intensifies with normal physical activity and is necessarily accompanied by nausea (less often vomiting) and/or photophobia, phonophobia. Transient neurological symptoms are possible, which usually precede the attack and last no more than 60 minutes (migraine aura). For convenience, this type of course in the literature is conventionally called “episodic” migraine. Although there is no such nosology in the 2004 International Classification of Headache Disorders, this term formally corresponds to two classification positions – migraine without aura and migraine with aura [25]. Migraine is not a life-threatening disease, but it significantly reduces the quality of life of patients. The World Health Organization includes migraine in the list of 19 chronic diseases that most disrupt the social adaptation of patients. To identify predictors of a favorable response to BTA, features of the clinical picture of migraine and injection parameters (doses, schedules and frequency of administration) were studied. It turned out that the predictors are the duration of the disease (if the duration of migraine is up to 30 years, the treatment results are better), as well as the qualitative characteristics of headache (squeezing/squeezing pain - imploding or pain in the orbital area - ocular) [20,26]. Tension headache. Tension headaches are the most common form of primary headaches. The clinical picture of tension headaches is not as clear and specific as migraines, but has its own characteristics. As a rule, headaches are monotonous, pressing, bilateral, weak or moderate intensity, without vegetative accompanying symptoms, and do not interfere with daily activities. The history of studying the possibilities of BTA in the treatment of headaches began with tension-type headaches [37,45]. However, controlled studies in recent years have shown a relatively low effectiveness of BTA for this nosology [19,35,40]. That is why the selection of patients with TTH must be carried out with special care. Patients with a chronic form of tension-type headache who have tension in the pericranial muscles, without pronounced comorbid psycho-vegetative and insomnia disorders, respond to treatment. Chronic daily headaches. The main reason for patients visiting specialized headache clinics is not the “classical” forms of migraine and tension-type headaches with episodic attacks, but daily or almost daily headaches, which make up from 40 to 80% of all visits. In the population, chronic daily headaches are observed in 3–5%. However, according to a recent study conducted in Russia, this percentage turned out to be significantly higher and amounted to 16.9% [3]. The term chronic daily headache (CDH) refers to a heterogeneous group of diseases whose main characteristic is very frequent headaches (more than 15 days per month). There are primary and secondary forms of CEHD [38]. Most patients in this group have severe daily headaches, often refractory to treatment; typically the presence of anxiety and depressive disorders, which together determines a significant decrease in the quality of life of these people. More than 90% of patients with CEHD initially had episodic primary headaches. The abuse of analgesics and other drugs to relieve headaches, which is observed in the majority of patients in the CEHD group (up to 80%), is today considered one of the most important factors in the transformation of episodic headaches into chronic daily ones [18]. The most common forms of CEHD are chronic migraine (25–55%) and chronic tension headache (47–70%). The potential of botulinum toxin in the treatment of CEHD has increasingly attracted the attention of researchers recently. 17 large-scale studies were conducted, including 6 double-blind placebo-controlled studies with a total number of patients of more than 4800 people. Patients with chronic migraine who have predominantly unilateral headaches and tension in the pericranial muscles respond better to BTA treatment [19,21,40]. The best results are shown with repeated injections (a course of three injections at intervals of 3–6 months). Other rare primary headaches. There are isolated reports of the effectiveness of BTA in the preventive treatment of chronic cluster headache, hypnic headache and coin-shaped headache, refractory to drug treatment [32,33,42]. Thus, at present, BTA is most often used in the treatment of various forms of primary headaches in the following cases: • ineffectiveness of standard preventive drug therapy regimens; • severe migraine (more than 8 attacks per month); • chronic migraine and combined CHB; • if the patient refuses to take daily preventive medications; • tension of the pericranial and cervical muscles. It should be noted that each of the above indications separately is sufficient for the use of BTA. Cervicogenic headache. Among the secondary forms of hypertension that practitioners most often encounter, cervicogenic hypertension occupies one of the leading positions. This type of headache occurs with various pathologies in the cervical spine and is often associated with a history of whiplash injury to the neck. Injections are made in m. Splenius capitis, m. Semispinalis capitis, m. Levator scapulae, m. Trapezius on one or both sides at trigger points. Side effects include impaired neck extension due to excessive weakening of the occipital muscle group [31]. HD in cranio-cervical forms of focal dystonia. BTA is safe and highly effective in the correction of hypertension associated with craniocervical dystonia when the drug is administered in doses and according to schedules determined by the main diagnosis - a specific form of focal dystonia of the craniocervical region [6,34]. The use of BTA drugs is a fundamentally new direction in the preventive treatment of headaches. Controlled studies have shown significant effectiveness of the method in comparison with placebo, and various forms of migraine respond to BTA therapy better than TTH. Neuralgia: trigeminal, postherpetic, occipital nerve. Patients with various types of neuralgia resistant to pharmacological treatment have shown a positive effect from treatment with BTA. For trigeminal neuralgia, the drug was administered in large doses on the side of pain in the area of the jaw arch (zygomatic arch); for postherpetic neuralgia - in the area of pain; for neuralgia of the occipital nerve - using the method of analgesic blockades. An additional introduction to the traditional drug treatment for BTA injections made it possible to achieve positive dynamics and reduce the severity of pain [27,29,43]. Miofascial pain syndromes (MFBS) MFBS is one of the most common causes of pain. The acute or chronic local muscle pain associated with one or multiple trigger points (TT) is characteristic inside the “tight -legged” in the muscle detected during palpation. TT is a local area of exceptionally high sensitivity, the mechanical irritation of which causes intense local and reflected pain. In the treatment of MFBS, injections are carried out in TT, determined by palpation, according to anatomical landmarks, sometimes using instrumental control (EMG, ultrasound, CT), which is especially important for regions with complex anatomy (forearm), with a deep location of the muscles (pear -shaped, illegal- Lumbar muscles), at the risk of developing side effects (proximity to larynx, trunk vessels). Miofascial pain syndrome. Myogenic pain dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint. Patients suffering from facial pain due to MFBS are introduced into the temporal, chewing, pore muscles, as well as the facial muscles. As a rule, the injections are bilateral, a large dose is administered on the side of the pain, but the dosage must be calculated with caution, since excessive asymmetric weakening of chewing muscles can aggravate articular dysfunction and occlusal disorders [4,41]. Thoracic outlet syndrome. BTA is introduced into the anterior staircase (into the central part) or into a small chest muscle (two TT). The simultaneous introduction of local anesthetics is recommended. Injections are performed in a lying position with a reserved hand. The main TT is located closer to the cooperative process. Additional inactivation of TT in the large breast muscle is required [6]. Syndrome of the shoulder - flip periartropathy. In myofascial syndrome with shoulder -pave periartropathy, as a rule, m. Supraspinatus, m. Deltoideus, m. Subscapularis, m. Teres Major. BTA injections are carried out in 2-5 of the most interested TT, perhaps the simultaneous administration of up to 5 ml of local anesthetic. When involving a sublopate muscle with a limitation of the shoulder divert, injections are performed in 2-3 tt [6,24]. In injections in the TT of a small breast, large round, lifting shoulder blade and rhomboid muscles, the best effect with adhesive capsulitis is indicated than with the spinning cuff of the shoulder [8]. "Tennis elbow." This term denotes damage to the muscles of the forearm or lateral epicondilite that occur due to chronic trauma during sports. The one -time introduction of BTA in m. Extensor digitorum can significantly reduce pain manifestations for more than a three -month period, however, some patients develop the weakness of the extension of the fingers of the hand [5,46]. Lumbodynia. In case of myofascial pain in the lumbar region, BTA is introduced into the pear -shaped, iliac -lumbar, square muscle of the lower back. It is recommended to carry out BTA injections in large dilution (usually in 4 ml of physiological solution) and at the same time administer up to 8 ml of anesthetics [6]. Chronic pain in plantar fascia. The introduction of BTA in two points on the foot with plantar fascia leads to a significant relief of pain and improving the function of the foot for a period of 3 to 8 weeks. [12]. Pain syndromes with local muscle cramps Trisma, bruxism, chronic facial pain with hyperactivity of the chewing muscles. Patients suffering from grinding with teeth and squeezing the jaws during wakefulness and/or during sleep are found in the practice of neurologists, dentists, orthodontists and maxillofacial surgeons. In the chronic course, a prolonged contraction of the muscles of the jaws causes the development of myofascial pain in the chewing muscles and muscles of the bottom of the oral cavity, erasing and destruction of teeth, degenerative -dystrophic changes in the temporomandibular joint, and the restriction of opening of the mouth. Typically, BTA is injected in bilaterally into three muscles: m. Temporalis, Masseter, Ptyrygoideus Lateralis [44]. Chronic pelvic pains in women with tape muscles spasm. The use of BTA injections in women with spasm of the pelvic floor muscles and chronic pelvic non -constructions resistant to traditional conservative therapy led not only to the weakening of pain and tension of the pelvic floor muscles, but also to significant reduction of dysparaunia (sexual coldness) [9]. Chronic pain in the joints of the limbs (intra -articular administration of BTA) has unit reports about the prolonged analgesic effect of BTA in patients with osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis, resistant to traditional drugs of therapy (oral and/or intra -articular), suffering from chronic the average chronic pains and a severe degree in the affected joints; as well as the effectiveness of re -injections of BTA. The duration of the analgesic effect of the single administration of the BTA was from 3 to 12 months [30]. In this review, far from all the data proving the analgesic effect of BTA are transmitted. I would like to emphasize once again that BTA injections as a therapeutic effect are rarely used as monotherapy, more often as part of complex treatment, which allows you to expand the possibilities of traditional medicinal and non -valley techniques (therapeutic physical education, massage and manual therapy, acupuncture, physiotherapeutic treatment, bos/biological feedback , psychotherapy and others). The results of controlled clinical studies and the authors' own experience shows that the treatment of BTA is well tolerated by patients, has minimal side effects. BTA injections should be conducted by a qualified doctor who has special training and permission from the manufacturer. It is important that injections can be carried out on an outpatient basis in the conditions of the procedural office. For practicing doctors who regularly face the problem of chronic pain, BTA drugs are a new valuable drug in the treatment of patients with severe pain syndromes. Literature 1. Artemenko A.R., Orlova O.R. Botox (toxin type a) in the preventive treatment of migraine. Treatment of nervous diseases. - 2004. - Volume 5. - N. 2 (14). - S. 14-18. 2. Artemenko A.R., Orlova O.R. Botulin therapy is a new approach to the preventive treatment of primary headaches. Practical neurology (Appendix to the Journal of Neurology and Psychiatry named after S.S. Korsakova). - 2007. - Issue 2. - P. 45–49. 3. Kutsutselov I.B. Clinical and epidemiological analysis of primary headaches of the adult urban population. Author's abstract. diss. ...cand. honey. Sci. - M., 2005. - 25 p. 4. Mingazova L.R. Clinical and physiological analysis and treatment of myofascial pain syndrome. Author's abstract. diss. ...cand. honey. Sci. - M., 2005. - 25 p. 5. Mozolevsky Yu.V. Botox returns to the court. Magazine "Tennis and Golf". - 2000. - No. 3 (6). - S. 5. 6. Orlova O.R., Yakhno N.N. The use of Botox (toxin type a) in clinical practice. - M.: Catalog, 2001. - 201 p. 7. Orlova O.R. Focal dystonia: pathogenesis clinic, treatment using botulism toxin. Author's abstract. diss. … the doctors. honey. Sci. - M., 2000. - 48 p. 8. Solokha O.A. Neurological aspects of the syndrome of shoulder -pave periartropathy. Author's abstract. Diss ... Cand. honey. Sci. - M., 2004. - 20 p. 9. ABBOTT JA, Jarvis SK, Lyons SD, Thomson A., Vancaille TG Botulinum Toxin Type A for Chronic and Pelvic Floor Spasm in Women: A Randomized Controlled Trit. Obstet. Gynecol. 2006; 108 (4): 915–923. 10. Aoki Kr Evidence for Antinocial Activity of Botulinum Toxin Type a in Pain Management. Headache 2003; 43 (SUPPL 1): S9–15. 11. Arezzo JC Possible Mechanisms for the Effects of Botulinum Toxin on Pain. Clin. J. Pain 2002; 18: 125–132. 12. BabCock MS, Foster L., Pasquina P., Jabbari B. Treatment of Pain Attributed to Plantar Fasciitis with Botulinum Toxin a: a short - tarm, randomized, Placesbo - Controlled, DUUble, DUUBLELE –Blind study. Am. J. PHYS. Med. Rehabil. 2005; 84 (9): 649–654. 13. Blumenfeld am, Binder W., Silberstein SD, Blitzer A. Procedures for Administering Botulinum Toxin Type Migraine and Tension - Type Headache. Headache 2003; 43 (8): 884–891. 14. Brin Mf, Jankovic J., Hallett M. (EdS). Scientific and Therapeutic Aspects of Botulinum Toxin. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2002. - 507 p. 15. CHENG CM, CHEN JS, Patel RP Unlabeled Uses of Botulinum Toxins: A Review, Part 2. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2006; 63 (3): 225–232. 16. Cutrer FM, Pottelkow Mr Cephalgic Alopecia Areata: A Syndrome of Neuralgiform Head Pain and Hair Loss Responsive to Botulinum a Toxin Injection. Cephaalgia 2006; 26 (6): 747–751. 17. De Andres J., Cerda --olmedo G., Valia JC, Monsalve V., Lopez --larcon, Minguez A. Use of Botulinum Toxin in the Treatment of Chronic Myofascial Pain. Clin. J. Pain. 2003; 19 (4): 269–275. 18. Dineer H - C., Limmroth V., Katsarava Z. Medication --Overuse Headache. In: Beadsby Pj, Silberstein SD, Dodick DW (EdS.). Chronic Daily Headache for Clinicians. London: BC Decker Inc. 2005: 117–128. 19. Dodick DW, Mauskop A., Elkind AH, Degryse R., Brin Mf, Silbertein SD Botulinum Toxin Type a for the Prophylaxis of Chronic Daily Headache: Subgroup Analysis of Patients not Rece. Iving Other Prophylactic Medications: A Randomized Double - Blind, Placebo –Controlled study. Headache 2005; 45 (4): 315–324. 20. Eross EJ, Gladstone JP, Lewis S., Rogers R., Dodick DW Duration of Migraine is a Predictor for Response to Botulinum Toxin Type A. Headache 2005; 45 (4): 308–314. 21. Freitag FG Botulinum Toxin Type a In Chronic Migraine. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2007; 7 (5): 463–770. 22. Gobel H. Botulinum Toxin in Migraine Prophylaxis. J. Neurol. 2004; 251 (SUPPL. 1): 8–11. 23. Gobel H., Heinze A., Heinze - Kuhn K., Autermann K. Botulinum Toxin A in the Treatment of Headache Syndromes and Pericrangal Pain Syndromes. Pain 2001; 91: 195–199. 22 Syndrome: Results from a Randomized Double - Blind Placebo - Controlled Multicentre Study. Pain 2006; 125 (1–2): 82–88. 25. Headache Classification Subcommittee, International Headache Society. The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 2nd Edition. Cephalalgia 2004; 24 (SUPPL. 1): 1–160. 26. Jakubowski M., Mcallister Pj, Bajwa ZH, Ward TN, Smith P., Burstein R. Exploding vs. Imploding Headache in Migraine Prophylaxis with Botulinum Toxin A. Pain 2006; 125 (3): 286–295. 27. Kapural L., Stillman M., Kapural M., Mcintyre P., Guirgius M., Mekhail N. Botulinum Toxin Occipital Nerve Block for the Treatment Occipital Neuralgia: A Case Seeris . Pain Pract. 2007; 7 (4): 337–340. 28. Lipton Rb, Stewart WF, Diamond S. et al. Prevalence and Burden of Migraine in the United States: Data from the American Migraine Study II. Headache 2001; 41: 646–657. 29. Liu Ht, Tsai SK, Kao MC, Hu JS Botulinum Toxin a Relieved Neuropathic Pain in A Case of Post - Herpetic Neuralgia. Pain Med. 2006; 7 (1): 89–91. 30. Mahowald ML, Singh Ja, Dykstra D. Long Term Effects of Intra - Articular Botulinum Toxin A for Refractory Joint Pain. Neurotox. Res. 2006; 9 (2-3): 179–188. 31. Martelletti P., Van Suijlekom H. Cervicogenic Headache: Practical Approaches to therapy. CNS Drugs 2004; 18 (12): 793–805. 32. Marziniak M., Voss J., Evers S. Hypnic Headache Successfully Treed with Botulinum Toxin Type A. Cephalgia 2007; 27 (9): 1082–1084. 33. Mathew NT, Kailasam J., Meadors L. Botulinum Toxin Type a Treatment of Nummular Headache: Four Case Studies. Headache 2007; . 34. ONDO WG, Gollomp S., Galvez - Jimenez N. A Pilot Study of Botulinum Toxin a for Headache in Cervical Dystonia. Headache 2005; 45 (8): 1073–1077. 35. Rozen D., Sharma J. Treatment of Tension - Type Headache with Botox: a Review of the Literature. Mt. Sinai J. Med. 2006; 73 (1): 493–498. 36. Schulte - Mattler WJ, Krack P. Treatment of Chronic Tension - Type Headache with Botulinum Toxin a: a radoMized, Double - Blind, Placebo -Controlled MultiCenter Study. Pain 2005; 109 (1–2): 110–114. 37. Schulte - Mattler WJ, Wieser T., Zierz S. Treatment of Tension - Type Headache with Botulinum Toxin: a Pilot Study. Eur. J. Med. Res. 1999; 4 (5): 183–186. 38. Silberstein SD Chronic Daily Headache. JAOA 2005; 105 (SUPPL. 2): 23–29. 39. Silberstein SD Practice Parameter: Evidence - Base Guidelines for Migraine Headache (An Evidence - Bassed Review): Report of the Qualeity Standards Subcommitte of the American Academy F Neurology. Neurology 2000; 55: 754–762. 40. Silberstein SD, Stark SR, Lucas SM, Christie Sn, Degryse Re, Turkel CC Botulinum Toxin Type A for the Prophylactic Treatment of Chronic Daily Headache: a Randomized, Double - Doulle - Doulle - Doulle - Doulle - Doulle - Doulle - Doulle - Doulle - Doulle - Doulle - Doulle - Doulle - Doulle - Doulle - Double -BLLIN D, Placebo - Controlled Tial. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2005; 80 (9): 1126–1137. 41. Song PC, Schwartz J., Blitzer A. The Emerging Role of Botulinum Toxin in the Treatment of Temporomandibular Disorders. Oral Dis. 2007; 13 (3): 253–260. 42. Sostak P., Krause P., Forderreuther S., Reinisch V., Straube A. Botulinum Toxin Type - aPy in Cluster Headache: An Open Study. J. Headache Pain 2007; 8 (4): 236–241. 43. Turk U., Ilhan S., Alp R., Sur H. Botulinum Toxin and Intractable Trigeminal Neuralgia. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 2005; 28 (4): 161–162. 44. Von Lindern JJ, Niederhagen B., Berge S., Appel T. Type a Botulinum Toxin in the Treatment Facial Pain Associated with Masticatory Hyperaactivity. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2003; 61 (7): 774–778. 45. Wheler AH Botulinum Toxin A, Adjunctive Therapy for Refractory Headachens Associated with Pericrangal Muscle Tension. Headache 1998; 38 (6): 468–471. 46. Wong SM, Hui AC, Tong Py, Poon DW, Yu E., Wong LK Treatment of Lateral EpicONdylites with Botulinum Toxin: A RANDOMIZED, DOBLE - BLIND, PLACEBO - Controlled Trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2005; 143 (11): 793–797.
Main indications for botulinum therapy:
- involuntary contractions of facial muscles
- bruxism
- lagophthalmos
- multiple sclerosis
- spasticity of the limbs after head injuries
- muscular torticollis
- blepharospasm
- tension headaches
- migraine
- tremor
- strabismus
- trigeminal nerve dysfunction
- pain syndrome of neurological origin
- tics
Botulinum therapy after a stroke can successfully combat spasticity, so it is actively used for the rehabilitation of such patients. Treatment is carried out under myography control. This allows you to objectively evaluate the results obtained and, if necessary, adjust the dosage.
How is botulinum therapy performed?
Before treatment, the patient is examined by a doctor, assesses the scale of the problem, the possibility of solving it using the method, and studies medical documentation to identify possible contraindications. The botulinum therapy protocol is drawn up individually, the number of units is calculated, and injection sites are selected. To correct wrinkles on the forehead and between the eyebrows, around the eyes, 10-30 units of botulinum toxin are needed, to lift the corners of the lips - 3-6, to correct the oval of the face - 40-60. To rejuvenate the entire face and neck, cosmetology uses the full-face technique, affecting all areas of the face.
The patient does not require special preparation for botulinum therapy. On the day of the procedure, you need to give up alcohol and thoroughly clean your face of makeup.
For botulinum therapy, drugs are used that are officially registered and approved for use in medicine and cosmetology.
These include:
- Botox
- Dysport
- Xeomin
- Relatox
- Lantox
- Botulax
The drugs are basically identical and differ from each other in the concentration of the substance, stabilizers and cost.
Amount of drug
The amount of the drug is calculated individually by a cosmetologist depending on:
- drug administration zones;
- type of drug;
- gender of the patient (men usually require a larger amount of the drug than women)
- characteristics of the human body.
For example, as practice shows, the number of units of a drug injected, say Botox, into one part of the face (forehead, nose, chin, etc.) does not exceed 80 units per procedure.
How is botulinum therapy done?
Before the session begins, the doctor determines the injection points and marks them on the skin. This will allow you to precisely target specific muscles. For patient comfort, an anesthetic gel is applied to the skin. Injections are made with a syringe with a thin needle. This makes it possible to minimally injure the skin. After the session, the treatment area is treated with an antiseptic. A re-examination is recommended after 2 weeks. If necessary, the doctor will make a correction.
Botulinum therapy after a stroke can successfully combat spasticity, so it is actively used for the rehabilitation of such patients. Treatment is carried out under myography control. This allows you to objectively evaluate the results obtained and, if necessary, adjust the dosage.
Botulinum therapy after a stroke can successfully combat spasticity, so it is actively used for the rehabilitation of such patients. Treatment is carried out under myography control. This allows you to objectively evaluate the results obtained and, if necessary, adjust the dosage.
Carrying out the procedure
At the initial consultation, the doctor analyzes the patient’s requests, collects the necessary information about his life and previous diseases. Next, he conducts an examination - assesses the individual characteristics of the face, the activity of facial expressions, identifying asymmetries, and motor functions. In accordance with the wishes of the patient, clinical condition, indications and contraindications, the cosmetologist draws up a treatment plan. Provides comprehensive information about the mechanism of action of the pharmacological agent, the expected effect of botulinum therapy, and possible complications.
Before the procedure, the doctor prepares the drug - diluting the BTA powder with physiological solution until the required dose is obtained. The number of units depends on the depth and area of wrinkles and skin thickness. The intramuscular method of administering anesthesia does not require. Superficial anesthesia is used only for subcutaneous injections to treat hyperhidrosis.
The procedure is carried out according to the following scheme:
- the skin is treated with a disinfectant;
- the solution is injected with a syringe with a thin needle intramuscularly or subcutaneously into pre-designated areas;
- An ice pack is applied to the treated skin.
The duration of the correction takes from 20 to 60 minutes. It is recommended to maintain a vertical position for the first 4 hours; during the day, do not massage the injection areas.
After 2 weeks, the doctor prescribes a repeat examination at the clinic. If necessary, makes corrections.
How is the rehabilitation period after botulinum therapy?
The doctor will tell you what not to do after botulinum therapy. If you follow these recommendations, you can avoid complications. It is recommended to remain in an upright position for the first 4 hours after injections. This promotes uniform distribution of the drug and reduces the likelihood of swelling.
Recommendations after botulinum therapy:
- Do not take a horizontal position for 4-5 hours
- eliminate alcohol
- do not take anticoagulants
- don't be in the sun
- do not visit the sauna, swimming pool, solarium
- no exercise for two days
- do not touch the treatment area with your hands
- do not take antibiotics for a month
- eliminate spicy foods from the diet
- do not massage the areas where the drug was administered
- Don't sleep face down on your pillow for the first 2 weeks
Following these simple rules will help avoid complications of botulinum therapy.
What result should I expect?
The effect after botulinum therapy can be assessed after 7-10 days. If the purpose of the session was rejuvenation, the patient will notice the smoothing of deep folds and the disappearance of fine wrinkles. When correcting the contours of the face, its oval becomes symmetrical and the lines become smooth. The effectiveness of botulinum therapy in neurology can be assessed using myography, as well as by the patient’s subjective feelings, the degree of restoration of lost functions, and a decrease in the intensity of pain.
The doctor will tell you what not to do after botulinum therapy. If you follow these recommendations, you can avoid complications. It is recommended to remain in an upright position for the first 4 hours after injections. This promotes uniform distribution of the drug and reduces the likelihood of swelling.
Should I try botulinum therapy?
If you have problems that can be solved by Botox injections, and there are no contraindications to the procedure, you should try this method. Is there any harm from botulinum therapy, is the toxin dangerous? This question worries many. The lethal dose of the toxin is more than 2 thousand units, and in medicine and cosmetology dosages are used that are at least 10-20 times less. This makes the development of dangerous complications completely impossible.
If you follow the recommendations after botulinum therapy, and don’t do what you shouldn’t do during the rehabilitation period, recovery will go quickly and without problems, and the result will live up to expectations.
Trust botulinum therapy only to professionals. The clinic of dermatocosmetology and endocrinology “Trinity” employs doctors with experience in performing the procedure, only high-quality drugs that have been officially registered are used, and anti-epidemic standards are observed. Thanks to an individual approach to each patient, doctors manage to achieve a pronounced effect after botulinum therapy, which will last for a long time.
Botulinum toxin injection is a well-studied, proven technique that is widely used throughout the world. If you decide to take a course in our clinic, you will be able to look attractive, feel confident, and also avoid complications after botulinum therapy thanks to the professionalism of the doctors.
Effect of the procedure
To eliminate facial wrinkles, botulinum therapy is the main method in cosmetology; it is considered the gold standard throughout the world.
The first result of the procedure is noticeable on days 5-7. Complete smoothing of wrinkles is observed after 2 weeks. The maximum effect of BTA is manifested in the upper third of the face - between the eyebrows, forehead, and area around the eyes. Facial expressions are not turned off completely. The natural appearance of the face is preserved.
Clinical effects of the procedure:
- pronounced rejuvenation - the skin is smoothed, the oval of the face is tightened;
- psychological discomfort caused by aesthetic defects is eliminated;
- self-esteem increases;
- social activity is expanding;
- quality of life improves.
The effect of the drug lasts for 3–6 months. During this time, the muscles get used to being in a relaxed state, new wrinkles do not form. With repeated applications of botulinum toxin, the cosmetic effect does not decrease.
Dissatisfaction with the result may be caused by an insufficient dose of the active substance, incorrect choice of target points, or inflated patient expectations.
In some cases, resistance to botulinum therapy is observed , which is confirmed by the lack of results after repeated administration of the active substance in the same dose.
FAQ:
Is the procedure painful?
Answer: The pain of this procedure can be compared to waxing the legs.
Is it possible to increase the volume of any parts of the body (for example lips) using botulinum toxin?
Answer: no.
Will it be necessary to increase or decrease the dosage with repeated procedures?
Answer: It all depends on the characteristics of the patient’s body. It is possible that subsequent procedures will require an increase in the dosage of the drug (usually in small volumes), but it may not be necessary. During the repeated procedure, the doctor will observe the body’s reaction to the administered dosage and, in order to achieve a positive result, will increase it if necessary.
What will happen to the skin after the injected drug expires?
Answer: During the action of the drug, the patient’s skin is renewed and the skin is smoothed. After regaining the previous muscle activity, wrinkles begin to form again
Recovery after botulinum therapy
Following the cosmetologist’s recommendations is a necessary condition for quick recovery and maximum aesthetic effect. The rehabilitation period after the procedure takes 1–2 weeks. After the procedure it is recommended:
- for 2 days, avoid bending face down and medications that affect blood clotting, do not use decorative cosmetics;
- For 2 weeks, avoid ultraviolet, heat exposure, excessive physical activity, stop drinking alcohol and smoking.
If adverse reactions occur during the recovery period, consult a doctor!
Taking some antibiotics and physiotherapy (microcurrents, massage) reduce the duration of the drugs. A course of botulinum therapy will help to effectively cope with the first signs of aging and maintain youth for a long time.
Cosmetic procedures are contraindicated during pregnancy and lactation.