What to do?
- Emergency care for superficial injuries (superficial scratches, minor bruises) can be provided at home: the injuries should be washed with soap and water, and ice should be applied to the bruised area. If blood is flowing from the wound, a tampon with hydrogen peroxide should be pressed onto the area for 3–5 minutes.
- Bleeding from the nose - in the absence of signs of fracture of the nasal bones and nasal septum - you can try to stop it yourself (by packing the nasal passage with a tight gauze or cotton swab moistened with hydrogen peroxide or cold water). If the bleeding is severe and, despite all efforts, does not stop, you must call an ambulance.
- If you suspect a fracture of the nasal bones or nasal septum, you should contact a specialized clinic as soon as possible.
Symptoms
Clinical signs of a nasal fracture:
- A nasal fracture causes severe pain. The patient is in shock or even fainting.
- Slight bleeding from the nasal slits occurs, which is blocked quickly and independently. In quite rare cases, blood flows in a stream and requires nasal packing. Such bleeding can lead to significant blood loss.
- The skin and mucous membranes are damaged, which can be manifested by the accumulation of air in the superficial fat layer. During the examination, the doctor determines whether the wound communicates with the nasal cavity.
- Then swelling of the soft tissues of the nose, eyes and cheekbones develops, bruising appears in the area of the cheekbones and eyelids. Hemorrhage under the skin occurs as a result of damage to blood vessels. After a day, swelling of the nose and surrounding tissues becomes extensive. Bruises form around the nose and under the eyes. Noticeable swelling in the impact area allows you to know whether the nose is broken. This symptom, combined with pain, deformity and bleeding, gives the characteristic clinical picture of a nasal fracture.
- Difficulty in nasal breathing is caused by displacement of bone fragments, deformation of the nasal septum, and increasing swelling.
- In case of a fracture of the bone and cartilaginous structures of the nose, the crunching of the fragments is determined by palpation - a clear sign that allows the traumatologist to make the correct diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment.
- If the nose is broken, mucus continuously leaks from it.
- In the future, infection may occur and fever, pain and redness may appear at the site of the lesion. Softening of the tissue indicates the beginning of the process of abscess formation.
Dangerous symptoms
If you suspect a fracture of the nasal bones or nasal septum, it is important to pay attention to the following signs of combined trauma and complications:
- heavy bleeding. Possible in case of damage to the nasal mucosa with bone fractures;
- lacrimation. May occur with combined trauma to the orbit and lacrimal ducts;
- release of cerebrospinal fluid. It is observed with a fracture of the ethmoid bone, which is adjacent to the upper nasal passages.
It is difficult for a layperson to distinguish between lacrimation and a cerebrospinal fluid leak, so clear or blood-stained fluid coming from the nose should raise suspicion. In such cases, you should seek qualified help as soon as possible.
Indications for surgery
Direct indications for surgical manipulation are:
- closed fractures of the nose - the outer integument is not damaged or the damage is expressed by superficial abrasions;
- open fractures, with damage to superficial tissues and bone fragments in the wound;
- fractures with displacement (there is a pronounced deformation of the nasal skeleton, disrupting the asymmetry of the face).
Fractures are often confused with severe bruises. But there are several signs that unconditionally indicate serious organ injury:
- nosebleeds (external, internal);
- pain around the nose, the intensity of which increases when trying to feel the site of injury;
- swelling of the mucous membrane and soft tissues, leading to difficulties with nasal breathing;
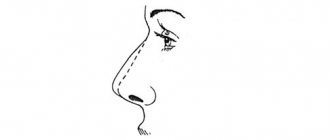
- visible change in the shape of the organ (retraction of the back, pressing inward, displacement to the side);
- crepitus of bone fragments (a characteristic crunch is heard when trying to feel the organ) - this symptom is checked only by specialists, otherwise serious damage can be caused.
If you are injured and have even one of the above symptoms, do not delay, go to the doctor immediately.
Nasal septum fracture
Nose trauma is always accompanied by swelling, which does not allow doctors to perform surgery on the same day, so treatment always begins with conservative therapy. In addition, a nasal injury can be combined with a concussion, in which surgery is undesirable, so a pause of several days is a necessary condition.
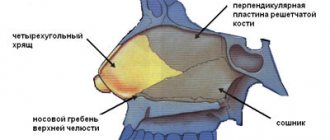
The bone of the bridge of the nose may simply sink from the blow, without a fracture. It may break, but not completely, but like a willow branch breaks: the break is only on one side, on the other - everything is intact. These types of fractures are most often observed in children, because their bone tissue contains more elastic fibers than adults. In any case, the bone must be put back in place to restore nasal breathing and the external shape of the nose.
In our country, such operations are performed in two ways.
- An old method that is still used in some hospitals. Under local anesthesia with a special instrument, similar to a long narrow spatula, the bone is lifted and fixed from below with a tight gauze swab. After a day or two they take it out, and the bone... sometimes it falls off again.
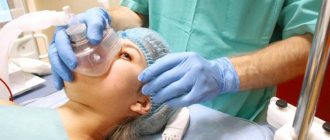
- A new method that uses anesthesia (general anesthesia). Foreign doctors have proven that fixing tampons are actually not needed. The main thing is to place the bone correctly, because there are no muscles around it that could move it. And it is more convenient to place it correctly if the operation is performed under general anesthesia: the patient does not feel anything, does not experience fear, does not interfere with the surgeon’s work... In this case, a small tampon made of perforated rubber is used, with gauze inside, which serves only to absorb moisture. It does not injure the mucous membrane as much as a tight gauze swab does, and healing proceeds faster. Within a month, a bone callus forms at the site of retraction, which firmly strengthens the bridge of the nose. Such operations are performed abroad and in many domestic clinics.
How to identify a broken nose?
How do you know if there is a fracture or not?
Trauma specialists identify the following symptoms of a nasal fracture:
- Strong, sharp painful sensations;
- Nose bleed;
- Swelling localized in the eye area, cheekbones;
- Bruising, subcutaneous hemorrhages;
- Deformation;
- Respiratory dysfunction;
- Intense lacrimation.
The listed clinical manifestations indicate that the nose is broken and require immediate assistance to the victim! Symptoms of a broken nose may vary slightly, depending on the type and location of the injury. If we are talking about an open type of injury, then there is a wound surface in which bone fragments are visible.
In this case, there is a high risk of infectious complications, as evidenced by such alarming clinical symptoms as redness of the skin, increased body temperature, fever and softening of tissue structures. A closed nasal fracture without displacement is characterized by preservation of shape. Damage can be determined by taking into account the following signs of a nasal fracture - swelling, hematoma formation, minor subcutaneous hemorrhages, ruptures of the mucous membrane, a feeling of pain and discomfort.
A characteristic sign of open/closed injury is bleeding. If the respiratory organ is broken, the bleeding is very profuse and intense. Damage with displacement of fragments is accompanied by deformation. This injury is indicated by curvature, shift of the septum, or change in the shape of the respiratory organ.
It is important to learn to identify a fracture from bruises and unpleasant symptoms that occur with other types of injury (for example, what signs appear if you simply break an organ, and not break it). This can be done by understanding the features of the clinical picture.
If the nose is injured, but not broken, then the swelling is localized only at the edges of the damaged organ, pain is present, but quite tolerable (if the integrity of the bone is broken, the pain is very strong, the likelihood of falling into a state of shock is high). Bleeding is also mild and is stopped using compresses and vasoconstrictor drops.
- After a heel fracture, the joint hurts
In general, the signs of bruises and fractures are quite similar, however, a broken organ has a more pronounced clinical picture, and only with a fracture can bone fragments be displaced!
What is the danger?
After a nasal fracture, a person needs competent, comprehensive therapy followed by rehabilitation. Otherwise, the following consequences of a broken nose are possible:
- Deviated septum;
- Sinusitis;
- Chronic rhinitis;
- Attachment of infectious processes;
- Impaired olfactory function;
- Neuritis;
- Recurrent nosebleeds;
- Hyposmia;
- Anosmia.
Infection is considered one of the most dangerous complications, significantly complicating and delaying the healing of the damaged organ. If the bone tissue of the skull and meninges were injured, then there is a high probability of developing meningitis. The consequences can be the most dire - even death! With severe hemorrhage in the area of the eyeball, visual impairment and even complete blindness are possible.
With timely provision of competent medical care, the victim can be cured, preventing the development of adverse consequences!
What to do if your nose is broken?
First aid for a broken nose is aimed at relieving pain and relieving swelling. For these purposes, it is recommended to make a cold compress or apply a heating pad with ice to the injured area. It is also necessary to take measures aimed at stopping bleeding. The basic rule is to sit or stand straight, tilt your head as far back as possible and close your nostrils. Then swabs treated with hydrogen peroxide should be placed in the nostrils.
In case of open damage, the wound surface should be treated with antiseptics to avoid infection. In case of severe pain, give the victim (if it is an adult) a painkiller tablet to reduce the risks of possible painful shock. After the initial actions have been carried out, the victim must be taken to the trauma department of the clinic, where he will be provided with professional medical care and adequate therapy will be prescribed! Under no circumstances should you try to straighten damaged bones yourself - such actions can cause serious harm to the patient’s health and provoke a number of complications!
How to treat a broken nose?
Treatment of a nasal fracture involves repositioning to restore the correct position of the bone fragments. Correction and straightening are carried out under local anesthesia. Depending on how severe the injury is, the operation can be performed manually or using a special tool - an elevator, which allows you to lift the sunken area of the bone. In more severe clinical cases, surgery—rhinoplasty—can help correct the situation.
It is possible to restore the shape of the respiratory organ surgically only after the swelling has been eliminated, 10–14 days after the injury!
Further restoration of the nose is conservative. Tampons treated with antibiotic drugs are inserted into the patient's nostrils, and sometimes a fixing bandage is applied, which should be worn for 2 weeks.
Deviated nasal septum
In case of injury, a deviated nasal septum occurs less frequently than a fracture or retraction of a bone. But the operation to restore it is more difficult. In most of our hospitals it is performed the old fashioned way, according to the Killian method, developed back in 1901. In front of the place where the curvature is located, the doctor uses a scalpel to cut the mucous membrane, peel it off and cut out the deformed area. Then he presses the mucous membrane tightly with a gauze swab. The tampon lasts up to 5 days.
The problem is that the cartilage of the nasal septum is covered on both sides by the perichondrium, from which it grows, and the mucous membrane is already located on it. In the place where the fragment of the perichondrium is removed along with a piece of cartilage, under the influence of a constant flow of air, the mucous membrane begins to dry out. A hole may form in it, which enlarges over time, while the cartilage becomes exposed and may begin to deteriorate. In such cases, repeated surgery is required to close the resulting hole.
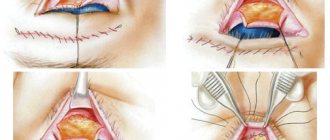
Now there are techniques that allow you to align the septum in a less traumatic way. For example, surgery using a microscope and endoscopic techniques. The doctor inserts a thin fiber-optic tube into the nasal cavity, which has a built-in light guide and a video camera that transmits the image to the monitor screen. Moreover, they reach the place of curvature of the cartilage without damaging the mucous membrane. An incision is made in the skin at the entrance to the nostril. The tissues are moved apart, the deformed section of cartilage is removed, taken out, straightened using a special apparatus, and inserted back. The nasal septum is compressed on both sides with silicone plates and stitched for fixation. A small cosmetic stitch is made at the entrance to the nostril. After a week, the silicone plates can be removed. The septum turns out smooth, the mucous membrane does not suffer or become inflamed, the nose breathes freely.
More about the operation
Nasal fractures account for almost 40% of the total number of facial injuries.
The causes of damage can be a traffic accident, a fall, household injuries, some sports, etc. Repositioning is a surgical procedure aimed at restoring the functionality and anatomy of the nose. The doctor compares bone fragments in an anatomically correct position, helping them to heal faster. The method of surgical intervention depends on the type of injury and its severity. Restoring the shape of the organ is carried out in the following ways:
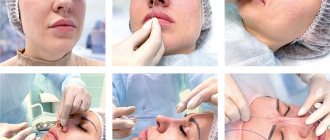
- finger – used when it is necessary to eliminate lateral deformation. The doctor presses with his fingers on the area of asymmetry until there is a click, which is evidence that the bones are in place. A control x-ray examination is performed both before and after the manipulation;
- instrumental - performed using special instruments (Volkov elevators), which the surgeon inserts into the nasal canals and lifts bone fragments with them, restoring the shape of the organ. A control x-ray examination is performed both before and after the manipulation;
- finger-instrumental – is carried out in the presence of retraction of the back of the nose and displacement of the bones to the side. The otolaryngologist expands the nasal passages with special dilators, returning the displaced fragments to their place and fixes them in their normal position with dense turundas (anterior nasal tamponade), which simultaneously perform a hemostatic function. A control x-ray examination is performed both before and after the manipulation.
In cases of severe open fractures or fractures of all lateral cartilages, open reconstruction of the nasal skeleton is used. This is a full-fledged operation that involves cutting tissue, comparing bone fragments under visual control, and applying sutures. To fix the fragments put in place, tamponade, special plate devices, metal, plastic or plaster splints, etc. can be used.
Where to treat nasal injuries?
It is best to treat a nasal injury in a clinic that specializes in oral and maxillofacial surgery. The diagnosis of a fracture of the nasal bones and nasal septum is usually made on the basis of x-rays.
Such injuries are dangerous not only because of a cosmetic defect. A change in the diameter of the nasal passages due to injury often leads to the subsequent development of persistent vasomotor rhinitis. When one of the nasal passages narrows, the child’s brain, through the neuro-reflex endings located in the mucous membrane, receives a signal about trouble (as with inflammation). In this regard, a reflex secretion of mucous fluid begins, similar to a runny nose. Such a “runny nose” can bother a person throughout his life. Sometimes in such cases, the patient is mistakenly diagnosed with “allergic rhinitis” and appropriate therapy is carried out for a long time, persistently and unsuccessfully. Meanwhile, if correction is carried out in time after an injury, nothing like this will happen.
If surgery is necessary, parents have 7-10 days after the injury (while the swelling subsides) to choose a hospital.
Clinic selection criteria:
- Find out which hospitals perform nasal septum surgeries under general anesthesia. The requirement is understandable: in such ENT departments there are specially trained anesthesiologists, doctors are proficient in modern techniques, the operation can be performed efficiently and comfortably for the child, and recovery will come faster.
- Ask how often such operations are performed in this hospital, including for children.
- If you are going to have surgery on the nasal septum, it is good if it is done under a microscope or using endoscopy.
Advantages of nasal bone repositioning at GMS Hospital
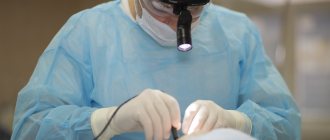
Experienced otolaryngologists at GMS Hospital perform all types of repositioning of nasal bones in case of a fracture. In our surgical center, such manipulations are carried out using minimally invasive methods, which eliminates surgical scars and scars.
A team of highly specialized specialists works on each clinical situation, which allows us to evaluate it from all sides and select the most optimal method of therapy. And the use of modern diagnostic equipment makes it possible to reliably determine the extent of damage to soft and hard tissues and carry out the procedure with precision.
The manipulation is performed within an hour if there are no contraindications (no severe swelling, concussion, etc.). The surgery center of the GMS clinic operates 24 hours a day. An appointment with an ENT surgeon can be made by phone or online.
Sources
- Yan S., Zeng N., Chen G., Chen Y., Wu Z., Pan H., Teng Y., Ma X., Li L. Presentation and management of nasal foreign bodies in a Chinese metro area. // Medicine (Baltimore) - 2022 - Vol100 - N16 - p.e25626; PMID:33879736
- Basa K., Ezzat W.H. Soft Tissue Trauma to the Nose: Management and Special Considerations. // Facial Plast Surg - 2022 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33853135
- Hamrang-Yousefi S., Kingsley-Smith H., Munroe-Gray T., Anyanechi M., Rollin M. Patterns of referral for fractured nose during major sporting events: a 10-year follow up. // Ann R Coll Surg Engl - 2022 - Vol103 - N4 - p.282-284; PMID:33682468
- Saleem SN., Hawass Z. Computed Tomography Study of the Mummy of King Seqenenre Taa II: New Insights Into His Violent Death. // Front Med (Lausanne) - 2022 - Vol8 - NNULL - p.637527; PMID:33681262
- Mo YW., Cho GY., Mo YT., Lee DL. National level data analysis of facial lacerations in Korea using the National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) database. // Medicine (Baltimore) - 2022 - Vol100 - N9 - p.e24163; PMID:33655909
- Hope N., Young K., Mclaughlin K., Smyth C. Nasal Trauma: Who Nose what happens to the non-manipulated? // Ulster Med J - 2022 - Vol90 - N1 - p.10-12; PMID:33642627
- Heichel J., Struck HG., Viestenz A. . // Laryngorhinootologie - 2021 - Vol100 - N3 - p.211-216; PMID:33636731
- Jiang Q., Liu Y., Song S., Wei W., Bai Y. Association between N95 respirator wearing and device-related pressure injury in the fight against COVID-19: a multicentre cross-sectional survey in China. // BMJ Open - 2022 - Vol11 - N2 - p.e041880; PMID:33602704
- Marofi F., Azizi R., Motavalli R., Vahedi G., Nasimi M., Yousefi M., Motavalli Y., Tahmasebi S., Gharibi T., Mohammed RN., Etemadi J., Khiavi FM. COVID-19: Our Current Knowledge of Epidemiology, Pathology, Therapeutic Approaches, and Diagnostic Methods. // Anticancer Agents Med Chem - 2022 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33563186
- Ou M., Fan W., Sun F., Li M., Lin M., Yu Y., Liang S., Liao H., Jie W., Cai Y., Chen F., Chen X., Zhao T ., Tang P., Cui L., Zhou H. Nasal Delivery of AntagomiR-741 Protects Against the Radiation-Induced Brain Injury in Mice. // Radiat Res - 2022 - Vol195 - N4 - p.355-365; PMID:33544844