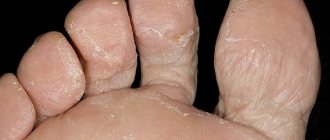
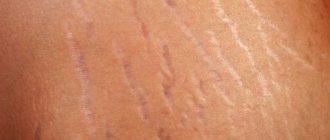
Many dermatologist patients complain of quickly, within a few days, keratinization of the skin on their fingers. Since in the first period of the disease most people try to eliminate this defect on their own, using warm baths and rich creams, they see a doctor only when deep, painful cracks form on the skin. Hyperkeratosis is a general name for a whole group of diseases that cause this symptom, some of them are very serious. This disease is characterized by disruption of the epidermis, an increase in the layer of dead cells and the formation of areas covered with the stratum corneum.
Causes of hyperkeratosis
Excessive proliferation of skin surface cells has many causes, both mechanical and pathological. Rough skin on the fingers is often observed in people whose professions involve daily pressure on these areas, for example, shoemakers or guitarists. The areas of skin that come into contact with the strings become horny, forming a layer of cells and protecting the skin. Workers who constantly deal with resins, sand or tar suffer from excessive cell growth on the fingers and palms, and this is dangerous because the degeneration of such cells can cause a malignant skin disease.
Age-related changes in hormonal levels entail keratoderma: during menopause, some women develop skin layers on the palms and fingers, they are diffusely located and have a grayish or yellowish color. Sometimes keratinization becomes covered with deep, painful cracks. Senile lumps and plaques on the hands usually do not bother their owners, but there is a risk of such cells degenerating into cancer.
Horny skin on the fingers of children and adolescents is a symptom of a serious illness, so keratoderma is most often caused by a gene mutation. Provoking factors can be various viral diseases, hormonal imbalances, a lack of vitamin A in the body, and the cause of the deficiency can be both external and internal. Poor nutrition and diseases of the digestive system, cancer and metabolic disorders are the main reasons for incomplete absorption of vitamin A, which in turn provokes keratosis.
The cause of the proliferation of epithelial cells is sometimes an allergic reaction to a cosmetic product or washing powder. Excessive consumption of food allergens also causes the appearance of horny layers of cells.
Approach to the treatment of arthritis of the fingers at the Paramita clinic
.
In our clinic, the patient is thoroughly examined using the latest laboratory and instrumental methods, including MRI, and only after that is treatment individually selected for each patient prescribed.
A special feature of treatment in our clinic is that complex therapy includes:
- modern Western methods of treatment
, allowing to eliminate the main manifestations of arthritis of the fingers; - traditional oriental methods of treating diseases
, allowing to restore balance in the body, establish the relationship of all organs and systems; this leads to the elimination of inflammation, swelling and pain in the joints and suppresses the progression of the disease.
The combination of Western and Eastern techniques makes it possible to quickly and painlessly relieve our patients of pain, and then effectively restore the function of damaged joints. The specialists at the Paramita Clinic have extensive experience in treating arthritis of the fingers. You can find out more about treatment methods in our clinic on our website.
We combine proven techniques of the East and innovative methods of Western medicine.
Read more about our unique method of treating arthritis
Symptoms of keratosis
First of all, a patient with keratoderma notices that he has rough skin on his fingers, and skin softening products do not bring the expected result. Then, after a sufficiently long period of time, the layer of cells becomes thick, the tissue underneath dies, and the edges of the stratum corneum acquire a purple tint. In the thickening itself, deep, painful, bleeding cracks form, the nails become lumpy and irregular in shape.
The symptoms of occupational or mechanical keratosis, which is the body’s response to local skin irritation, are much less pronounced. Constant pressure on the fingertips leads to the formation of calluses, and then the skin becomes coarser, the surface cells of the epidermis die off and do not slough off, as a result of which keratinization occurs. Occupational keratosis can also be accompanied by the formation of cracks in the stratum corneum, but it is limited only to those areas of the skin that are periodically injured, without spreading further.
Follicular keratosis most often forms on the flexor surfaces of the extremities, but can also be localized on the hands. The patient notices that the skin on his hands is pimply and tough. Follicular keratosis, apart from a cosmetic disadvantage, does not annoy the patient, but can spread throughout the body. One of the reasons for the occurrence of this form of the disease is heredity: according to statistics, people whose parents had a history of keratosis pilaris are most likely to develop it between the ages of fifteen and twenty-five.
Classification of postoperative sutures
How quickly the sutures heal after surgery largely depends on the nature of their application and the materials used. In this regard, post-surgical procedures are usually classified as follows.
- Bloodless (the edges of the wound are glued together with a special plaster) and bloody (a classic suture that is applied manually with a medical instrument). In turn, the latter are divided into:
- simple knots (applied at a distance of 1–2 cm from each other, after which the knot is tightened until the edges of the incision touch);
- intradermal continuous (considered the most effective, since after their healing there are no traces left);
- mattress (applied after abdominal surgery);
- purse string (used in plastic surgery, as well as in operations to reduce the volume of the stomach);
- entwining (circular sutures that are used to sew together blood vessels and hollow organs).
- Manual (applied with a needle, thread and other special tools) and mechanical (performed with a medical stapler).
- Submersible (applied during operations on internal organs with threads that are absorbable or implanted into living tissue) and removable (they are used to stitch the skin, and after the edges of the wound have fused, the threads are removed).
Absorbable sutures are made in cases where long-term fixation of the edges of the incision is required, for example, when cutting the uterus during a cesarean section. As a rule, they are performed with threads from purified connective tissue, which is subsequently rejected into the organ cavity. To apply removable sutures, threads and other fasteners made of cotton, silk, metal and other non-absorbable materials are used (more than 30 varieties in total).
Hand stitching tools
Treatment of keratoses
Keratoses associated with the professional activities of patients with exposure to toxic substances, such as arsenic or tar, are difficult to treat until the person stops engaging in this type of activity. The disease can last for years and go away completely on its own when the employee quits or changes profession.
At the first signs of causeless coarsening of the skin on your fingers, you need to carefully adjust your diet, add vitamin complexes and an oil solution of vitamin A. Locally, thoroughly clean the skin on your hands every evening, lubricate the rough areas with a nourishing cream with the addition of vitamin A. A good result is achieved by using gloves Spa Belle, they moisturize the skin, have a soft and gentle effect, releasing softening and beneficial components of the gel impregnation. You can buy silicone gloves in the online store.
If the symptoms of keratosis are severe enough, you should consult a doctor for a full examination and identify the cause of the disease. It is possible that keratinization of the skin is caused by some disease, and its treatment will help eliminate the unpleasant symptom. Ointments and creams containing healing and softening components are used locally.
At any stage of the development of the disease during the inflammatory process, it is advisable to use ointments containing antibiotics and steroids. They are used in short courses to relieve inflammation, and then use wound-healing drugs such as Panthenol or Solcoseryl, which enhance tissue regeneration. Baths with astringent herbal decoctions and compresses with plantain or aloe juice are also quite effective in the symptomatic treatment of keratoses.
How does arthritis of the fingers proceed in different clinical forms of the disease?
The symptoms of hand arthritis and the nature of its course depend on the disease that led to its development. Damage to small joints of the hands is most often found in rheumatoid, psoriatic and gouty arthritis. But it can also occur in other clinical forms of arthritis.
Rheumatoid arthritis
In most cases, arthritis begins slowly and unnoticeably. Aching pain appears in the fingers. The nature of the pain is constant, aching, exhausting. In the morning after sleep, stiffness of movement appears, which can last up to 30 minutes or more.
After some time, the patient notices that the fingers begin to swell in the joints. Most often, the metacarpophalangeal and overlying interphalangeal joints of the 2nd and 3rd fingers are affected. The lesion is symmetrical on both hands. Pain of varying degrees of intensity is constant. Over time, characteristic spindle-shaped finger deformations appear
Small, painless subcutaneous rheumatoid nodules appear on the skin of the fingers and in the elbow area. The course of the disease is slow, steadily progressing, accompanied by constant debilitating pain, deformities and loss of joint function.
Psoriatic arthritis
Pictured is rheumatoid and psoriatic arthritis of the hands
With this disease, arthritis develops in the distal (end) interphalangeal finger joints against the background of existing skin manifestations of psoriasis. But sometimes joint symptoms appear before skin symptoms or simultaneously with them. The disease in most cases begins acutely or subacutely with the appearance of redness, swelling and pain in the small finger joints. The lesion is usually asymmetrical, with the fingers resembling sausages.
The disease occurs with severe exacerbations and remissions. Nail plates are almost always involved in the pathological process. Over time, deformation of the fingertips occurs, they thicken, the nails become thinner and also deformed, and a symptom of a thimble appears - pinpoint depressions on the nail plates.
With a long course of the disease, dislocations and subluxations of small distal joints develop, as well as lysis (melting) of the bones of the fingertips (radiological sign) and shortening of the fingers.
Chondroprotectors: what are they, how to choose, how effective are they?
Joint pain at rest
Gouty arthritis
An attack of gout begins acutely, with the appearance of severe pain, swelling and redness in the affected joints. Small joints are often involved. Typically, inflammation begins with the metacarpophalangeal joint of the 1st finger, and then can spread to the metacarpophalangeal and interphalangeal joints of other fingers.
The pain is very severe, the attack can last from several hours to several weeks, and then everything goes away. But with frequent attacks affecting the same joints, their function is impaired.
Post-traumatic arthritis
This type of arthritis of the fingers can develop against the background of an acute domestic, industrial or sports injury, occur acutely with subsequent complete recovery, or (in the absence of the necessary help) be complicated by the addition of a purulent infection. Sometimes such an inflammatory process can become chronic with subsequent deformation of the affected joints.
Initially, post-traumatic arthritis of the fingers takes a chronic course with constant minor unnoticeable injury to the fingers. Most often this occurs among people in certain professions who perform minor work. Arthritis develops slowly, affecting the joints that are most injured during work. If you do not change jobs, a permanent deformity develops with impaired finger function.
Other types of arthritis
With such types of arthritis as reactive, infectious, idiopathic, damage to the small joints of the fingers practically does not occur.
Prevention of keratosis
The main treatment for keratosis of any etiology is to prevent the development of the disease. But since it is not known for certain what triggers the onset of the disease, you just need to maintain general hygiene, not subject your hands to excessive stress, and take good care of them. Sagging skin on the hands, calluses and redness are a signal for immediate action: stopping any diet, taking vitamins A and E, and cosmetic procedures.
People whose professions involve the development of this disease, or who have had cases of this disease in their family, are advised to closely monitor their health, since keratosis, although it does not threaten human life, sometimes makes it unbearable. Horny skin reduces the sensitivity of the hands, interferes with delicate work, and cracks make any movement impossible due to extreme pain. The duration and, sometimes, failure of treatment for horny growths is a reason to think about preventive measures for an unpleasant disease.
Forecast
The prognosis for eczema is most often favorable.
If you start proper treatment in time, you can curb the disease and get rid of its consequences. With adequate therapy, itching and elements of the old rash disappear, a new rash does not appear. Eczema is a chronic disease, so it is worth adhering to preventive measures and maintaining a state of remission. However, the timing of relapse is still unpredictable. Doctors give the most favorable prognosis for acute eczema. Recovery may be worse if eczema develops in young children, the elderly, or people whose bodies are weakened by infection. To enhance drug treatment, a hypoallergenic diet, physical activity, walking and hardening will help.
How long does it take for a wound to heal after surgery?
The rate of healing of a postoperative wound depends on many conditions. Among them:
- age;
- body mass;
- state of immunity;
- state of the cardiovascular system.
On average, it takes about 3 months from the moment of surgery to the formation of a scar. Depending on the complexity of the operation and if there are complications, this period may last 12 months. Tissue regeneration takes place in 4 stages.
- Inflammation (5–7 days). The body's standard defense reaction to damage. During this period, there is an increased production of substances that stimulate blood clotting.
- Polyferation (from 10 days to 1 month). At this stage, the formation of young connective (granulation) tissue, penetrated by a dense network of microvessels, occurs. At first it is bright red in color and grainy in consistency, but as the wound heals it becomes pale and smooth, and its bleeding decreases.
- Epithelization (from 1 to 3 months). The connective tissue is finally formed. Skin begins to form at the site of the wound. The number of vessels decreases, a scar forms.
- Scar formation (from 3 to 12 months). Temporary vessels completely disappear. Fibers of collagen and elastin - elements of connective tissue - form the scar.