- Breast reconstruction after mastectomy: what types of surgery are there?
- Methods for restoring the nipple-areolar complex
- Correction of the second breast
- Contraindications
- Preparing for breast reconstruction surgery
- Possible complications
- Rehabilitation
Mastectomy is the surgical removal of the mammary glands and soft breast tissue in women and men for medical reasons.
Cancerous tumors or a high risk of their occurrence become the reason for the removal of mammary glands in women. This operation brings psychological and physical discomfort to patients. Subsequently, the woman often experiences depression and apathy. At the bodily level, curvature of posture, stooping, and drooping shoulders may be observed. For many women who have had a mastectomy, the solution is breast reconstruction. Plastic surgery gives a woman facing cancer a chance to feel confident, attractive, and happy again. You can feel free to visit the pool and beach, return to your usual lifestyle - your breasts will look natural. Also, the reconstruction procedure will help equalize the load on the spine that has arisen due to imbalance, and will preserve the normal functioning of the heart and lungs suffering from changes in the spine.
Procedure time
3-6 hours
Hospitalization
1 day
Recovery
1-2 weeks
Anesthesia
General anesthesia
Effect
1 month
results
indefinitely
Breast reconstruction after mastectomy: what types of surgery are there?
Breast reconstruction surgery can be performed simultaneously (together with removal) or delayed. In the second case, you should wait from several months to a year.
The extent of the operation depends on the amount of breast tissue removed and the chosen reconstruction method. The shape and size of the second breast and the general health of the patient are taken into account.
Modern plastic surgery offers breast reconstruction options for any type of mastectomy: complete and partial.
1. If the patient has a sufficient amount of tissue remaining at the site of the operation to remove the gland, a method using an expander is suitable. First, a vacuum expander (expander) is installed under the skin of the breast - a special device that will help create a place for the future prosthesis and stretch the woman’s existing tissues. The device can be installed in conjunction with the mastectomy procedure or after some time.
Then, in several stages, the doctor fills the expander with saline solution through a syringe, gradually inflating it to the required size. Usually the process lasts several months. At this time, the breasts will not look very natural, but the procedure takes time. A permanent silicone implant in place of the expander will restore the aesthetics of the breast. Breast implant surgery can be combined with plastic surgery on the second breast to achieve greater symmetry.
This method of reconstructive mammoplasty is the simplest - there is no need to take your own tissue and create additional wound surfaces. Possible negative consequences: tissue necrosis, unnatural appearance of the bust, the occurrence of capsular contractures.
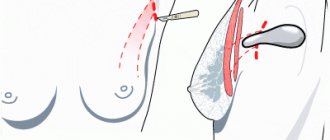
2. Transplantation of a skin flap for reconstructive plastic surgery is necessary when the remaining breast tissue is not sufficient for reconstruction. The surgeon transplants his own tissue from the abdomen, buttocks or back to the site of the removed breast.
2.1. The thoracodorsal method involves taking a flap of skin along with fat and muscle tissue from the area of the latissimus dorsi muscle. Preserved blood vessels will allow the transplanted flap to take root better. This method is usually used for those with small breasts. After surgery, a scar remains on the back, and there may be muscle displacement, which leads to a violation of proportions. However, muscle functions are preserved.
2.2. The TRAM method allows you to combine breast reconstruction with abdominoplasty. In this case, the flap is cut off from the rectus abdominis muscle and delivered to the chest area through a special internal channel. This is a good option for women with excess fat tissue in the abdominal area. After the procedure, a thin, long longitudinal suture will remain on the abdomen. There may be a downward displacement of the navel and its deformation. A plastic surgeon will correct the problem by restoring the belly button.
2.3. In very rare cases, skin, muscle and fat tissue is collected from the buttock area. The transplantation process is complicated by the need to cut off all blood vessels from the harvested flap. We need a high technical base for microsurgery to restore blood circulation. However, there is a risk that the tissue may not take root due to damage to the blood vessels.
3. The combined method consists of primary lipofilling. The surgeon first fills the reconstructed areas of the breast with his own fatty tissue. At the second stage, a musculocutaneous flap is transplanted and a silicone implant is installed.
All options for reconstructing a removed breast using skin flap transplantation allow you to achieve maximum aesthetics. The breasts look natural, feel just as soft, and in some cases, tissue sensitivity can be restored.
Treatment of arm lymphedema at the Innovative Vascular Center
The innovative vascular center has been developing the direction of conservative and surgical treatment of arm lymphostasis for more than 10 years, relying on the German experience of conservative treatment used by Dr. Shingale and microsurgical technology of lymphovenous anastomoses and lymph node transplantation.
We provide a full-fledged treatment and rehabilitation complex, which allows you to reduce swelling by 70-100% and control it. The course of treatment is 14 - 28 days.
Surgical treatment is used for stage 2-3 lymphedema of the arm and requires a preliminary course of conservative therapy. The experience of our clinic shows that the manifestations and progression of lymphedema can be significantly reduced and even reversed.
Methods for restoring the nipple-areolar complex
Often, breast reconstruction surgery is accompanied by restoration of the nipple and areola. This is a separate plastic surgery that is performed after the main reconstructive mammoplasty procedure. A prerequisite is that the patient completes the course of adjuvant therapy (taking medications after radical surgery).
It is possible to reconstruct the nipple and areola from the same tissues of the second breast. This is a painstaking process and sometimes requires re-adjustment as the nipple may become flattened. It is possible to recreate the nipple from tissue from the reconstructed breast. In this case, the simplest option for creating an areola is tattooing.
Tissue transplantation of the labia minora will allow you to achieve identical color. It is also possible to use donor material.
Get a free consultation from Dr. Granado
A unique opportunity, get a free consultation in Russian from Dr. Granado Tiagonse.
- Fill out the application for consultation
- Upload three photos of the problem area from three angles
- Describe your problem in detail
- Send your request to us
- In a few days you will receive an answer in Russian from Dr. Granado
Fill out the application
Types of Postoperative Lymphedema
- Temporary reversible lymphedema: Occurs within a few days after surgery and usually lasts a short period of time. goes away quickly enough under the compression sleeve.
- Subacute lymphostasis of the arm: appears 4-6 weeks after surgery. It is characterized by pain and high tissue density, but goes away quite quickly under the influence of compression therapy.
- Chronic arm lymphedema: This painless swelling usually appears 18-24 months after surgery.
Preparing for breast reconstruction surgery
Before undergoing breast reconstruction surgery, an examination and consultation with an oncologist or mammologist is mandatory. Blood and urine tests are required, as well as an assessment of the patient’s general health by specialized specialists.
As with any surgical procedure, it is necessary to avoid smoking and drinking alcohol. Taking any medications must be agreed with your doctor. It is advisable to monitor your weight - obese patients usually tolerate anesthesia less well. You should discuss physical activity with your doctor. Exercise will increase the elasticity of the tissues that will be needed for transplantation.
Prevention and control
Although it is impossible to predict how the disease will progress, there are steps patients can take to reduce the risk. If you already have lymphedema, it can be controlled by following some of the recommendations below:
- Perform daily stretching exercises to maintain your range of motion.
- Learn to perform lymphatic drainage self-massage.
- Lymph production is directly proportional to blood flow, so strenuous arm exercises that increase blood flow can increase the amount of lymph and therefore increase the risk of lymphedema.
- Avoid drinking alcohol.
- Avoid foods high in salt and fat. Try to eat a healthy diet that is high in fiber.
- Wear comfortable clothes and jewelry that do not constrict your hand.
- Burns can increase the risk of lymphedema, so avoid excessively hot water when bathing or washing dishes. Always use sunscreen.
- When you are sleeping or sitting, try to keep your arm elevated (for example, by placing it on a pillow).
- Take care of your skin to avoid infections. Wear gloves when doing housework or yard work. Apply moisturizer to chapped skin and use insect repellent to prevent bites.
- Watch your weight.
Your doctor may recommend a compression sleeve as a precaution. You should never buy a sleeve online or in a medical supply store and use it yourself without a doctor's advice. Choosing the right compression stocking ensures that the sleeve will perform as it should. Otherwise, the sleeve may be too tight in certain areas, which can restrict lymph flow and make the situation worse.
Possible complications
After reconstruction, complications typical of any surgical intervention are possible: the formation of edema and hematomas, the appearance of scars, infection of the suture site, loss of skin sensitivity. Deformation of tissues and implants is also possible, and the expected result does not correspond to reality, which will require additional intervention.
The most unfavorable complication is considered to be rejection of the transplanted flap, tissue necrosis. In the area of the donor site of the body, displacement of tissues and muscles and complications associated with wound healing may also be observed.
Stages of the disease
- Stage I: Spontaneously reversible. The swelling is quite noticeable; if you press on the skin with your finger, a hole remains. After rest (especially in the morning) it subsides, but in the evening it becomes the same. Patients rarely turn to specialists at this stage.
- Stage II: Spontaneously irreversible. The skin hardens (this is due to the growth of connective tissue), the swelling is no longer so soft and when pressing with a finger on the skin there is no hole left. The skin is very tight and sensitive. The patient may experience pain.
- Stage III: Irreversible. The skin is fibrous (the tissue scars), cysts or papillomas appear on it. The limb is deformed due to tissue damage. She moves poorly or even becomes motionless and becomes heavy. This is the extreme stage of lymphedema - elephantiasis.
Rehabilitation
Reconstructive mammoplasty usually takes place in several stages. The rehabilitation period depends on the chosen method and the current stage of the process. Restoration of the nipple-areola complex is a separate plastic surgery. If correction of the second breast is required, it is carried out several months later.
After the main breast reconstruction operation, the woman is under medical supervision for about two weeks. The length of hospital stay varies depending on the complexity of the intervention and the patient’s well-being.
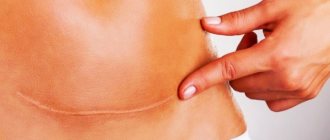
Drains and sutures are removed after 10-14 days, or they dissolve on their own.
For the first month and a half, you should avoid bending over, repetitive movements (for example, cleaning a frying pan), lifting weights of more than 1-2 kg, and raising your arms up. It is necessary to completely eliminate physical activity. You should take care in advance about comfortable clothing and the necessary living conditions for a safe and quick recovery.
The stitches will heal completely after a year. They will fade and become less noticeable, but will not disappear.
It is important to note that reconstructive plastic surgery does not in any way affect the possibility of recurrence of malignant neoplasms. But in any case, patients diagnosed with cancer are recommended to have an annual mammogram to avoid relapses.
One on one with the diagnosis
Irina (name changed) has a different cancer. Stage 2 thyroid cancer. The nodes, which she had been monitoring for half her life, turned out to be malignant after removal. In general, this type of cancer is not very aggressive and rarely metastasizes. But Irina found out about this from the Internet. The surgeon, handing her the histology results, muttered something about cancer and left.
“Then, at the clinic at my place of residence, where I was supposed to undergo regular examinations, the oncologist, from whom I expected at least some kind of explanation, did not explain anything to me. He didn't talk to me at all. It seems he didn't even look. I took a piece of paper and entered something into the computer. I wrote out directions for an ultrasound. I went to many doctors, I visited regional oncologists, I visited the oncology clinic, and I visited private clinics. Doctors don't explain anything at all. At best, they answer questions, but I didn’t always know what exactly I should have asked,” says Irina .
Reference: Clinical depression accompanies 8 out of 10 cancer patients. It often develops against a backdrop of uncertainty. A person hears his diagnosis and is left alone with it.
The doctor does not explain what is happening in the body, what you can expect, how to live with it. For some reason, doctors act as if they are embarrassed to tell a patient a diagnosis, but at the same time for them it is a common thing and, of course, they do not care. It looks like this: “Here you can wash your hands, there’s delicious borscht in the cafeteria today, and you also have cancer.”
Then there will be tears, trips to doctors, complex and difficult treatment. When the fear of the pain of death recedes a little, the moment of getting to know your new body comes. This is especially true for female cancers: breast, body and cervix.
Exposition of the exhibition “SPORKING”. Photo by Andrey Titov