Mammary cancer
is a malignant tumor that can grow into the surrounding tissues, destroy them and create metastases - additional foci of the disease in other organs. Fighting it is not an easy task, since its cells develop rapidly, multiply uncontrollably and move throughout the body through the circulatory and lymphatic vessels. The lymphatic system complements the cardiovascular system. The lymph circulating in it - the intercellular fluid - washes all the cells of the body and delivers the necessary substances to them, taking away waste. In the lymph nodes, which act as “filters,” dangerous substances are neutralized and removed from the body. systems Unfortunately, it is impossible to completely destroy an already formed tumor using medical methods alone.
Most patients with this diagnosis undergo surgery as part of treatment. Such interventions may have several goals:
- Removing as many changed cells as possible.
- Assessing the spread of oncology to the lymph nodes - tiny organs of the lymphatic system that retain and neutralize dangerous substances.
- Reconstruction – restoring the shape of the breast after tumor removal.
- Relief of symptoms of advanced cancer that has damaged a large amount of tissue and created metastases - additional tumors in various parts of the body.
Breast cancer surgery
There are 2 types of such interventions:
- Mastectomy is
resection, or removal of the entire breast, including the nipple, and sometimes other normal tissue nearby. - Organ-conserving operations
, during which only the part of the mammary gland in which the tumor is located and a small amount of healthy tissue surrounding it are excised. These include lumpectomy - removal of a small area of cancer, quadrantectomy - about ¼ of the breast, as well as partial or segmental mastectomy, which involves removing more than ¼ of the organ.
Which is better, breast-conserving surgery or mastectomy?
As a rule, at an early stage of the disease, there are 2 options for surgical intervention - partial or complete removal of the mammary gland. The main advantage of the former is the ability to preserve most of the breast, and therefore the usual appearance. Psychologically, such interventions are perceived much easier, but they have a disadvantage - in most cases, after their implementation, a course of radiation therapy is required. Some women worry that less extensive surgery may increase the risk of recurrence—the cancer coming back. Research conducted over more than 20 years has shown that long-term survival of patients who can be recommended for both procedures is the same if additional radiation treatment is provided.
If the tumor grows to a large size and the cancer damages other tissues, a mastectomy is prescribed.
Removal of lymph nodes
Non-invasive - research methods that do not damage the skin and other tissues, such as ultrasound, CT or MRI, do not always make it possible to understand whether the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes. To study the condition of these important organs, one or more of them are excised during removal of the mammary gland or part thereof, or during a separate operation:
- Sentinel lymph node biopsy
is the removal of the organ of the lymphatic system closest to the tumor. As a rule, it is he who is affected by oncology first. Removing just one or a few lymph nodes reduces the risk of serious side effects such as lymphedema, a gradual increase in the volume of the arm due to impaired drainage of lymph, a colorless fluid that bathes all tissues and cells of the body. - Dissection
is the removal of a large number, usually less than 20, of axillary lymph nodes. The procedure is quite traumatic and is not used often, but in some cases it may be the best way to detect cancer cells.
What can they do
Do your usual housework.
Play sports (as soon as the lymph stops accumulating). In this condition it is good to swim in the pool. Now they produce swimsuits with prosthetics inserted into the cups; they do not even allow one to suspect that the woman has undergone surgery.
Have an intimate life immediately after discharge from the hospital.
Give birth to. But it is better to first discuss this decision with an oncologist and gynecologist.
Oncologist Igor Khatkov: our operating rooms are no worse than American ones Read more
Breast reconstruction after cancer treatment
Women who have undergone surgical treatment for cancer can resort to the help of plastic surgeons and return to their usual appearance, or leave everything as is and use special underwear with pads. If the patient is ready for reconstructive procedures, she needs to discuss this point with doctors in advance. Specialists will offer her recovery options - immediate, carried out simultaneously with the removal of the mammary gland, or delayed, prescribed some time after breast resection.
Preparing for surgery
A mastectomy is prescribed by an oncologist if there are indications for surgery. The first stage of preparation for surgery to remove the mammary gland with a diagnosis of cancer is a consultation with the surgeon, who decides to perform the operation. When the date of mastectomy is determined, the doctor refers the patient for diagnostics necessary to possibly identify contraindications to the operation.
Diagnostics include:
- general analysis of urine and blood;
- specific blood tests (biochemistry, coagulogram, blood group, etc.);
- fluorography;
- electrocardiogram.
To determine the clinical features of the pathology and characteristics of tumor development, ultrasound of the mammary glands, biopsy and histology of the tumor, and mammography are performed. A consultation with an anesthesiologist is required to select the method of induction of anesthesia and the anesthetic drug.
The patient is recommended to stop smoking and drinking alcohol 14 days before the mastectomy, and stop taking medications that thin the blood. Stop eating 10–12 hours before, and do not drink any liquid on the day of surgery. Such restrictions are associated with the use of general anesthesia.
Surgeries for advanced breast cancer
It is unlikely that it will be possible to completely cure oncology that has spread to other parts of the body through surgical interventions. In such situations, surgery is prescribed to slow the progression of tumors and to prevent or relieve the symptoms they cause. Similar interventions are used to:
- Destroying a small number of metastases - additional foci of the disease in other organs, for example, in the brain.
- Removal of tumors that lead to the appearance of open wounds on the mammary gland.
- Removal of tumors pressing on the spinal cord.
- Removing blockage of the hepatic ducts, through which the bile necessary for digestion enters the gallbladder.
- Relieving pain and other symptoms.
In such cases, the doctor explains that the purpose of the operation is not to treat cancer, but to prevent or alleviate its consequences, and the patient makes a decision and agrees or refuses the intervention.
Oncology specialists provide all types of breast cancer treatment, including surgery, hormonal, targeted, immunotherapy and chemotherapy.
We employ truly professionals in their field - candidates and doctors of medical sciences with extensive experience in the fight against oncology. We prescribe all possible interventions only by decision of a council of doctors of various specialties. This approach allows us to take into account all the characteristics of each patient and avoid mistakes.
What determines the choice of treatment?
The selection of treatment is carried out individually for each patient and is drawn up in the form of a plan. It is composed of a council of doctors; the term “multidisciplinary team” is also used abroad. According to Russian clinical guidelines, the team includes a surgeon, chemo- and radiotherapists, and, if necessary, an anesthesiologist, radiologist and doctors of other specialties are involved.
The treatment plan is drawn up taking into account all the data about the patient. With their help, doctors will be able to determine the stage of cancer and its malignancy - further therapy is based on them.
Doctors determine the stage and malignancy using the TNM system and the Grade scale. Using the first parameter, you can understand how big the tumor is and how far it has spread from the original site of development. The second is determined by the appearance of tumor cells under a microscope. If the cells are more similar to normal and do not reproduce much or do so slowly, the cancer is considered non-aggressive. The less the tissue resembles normal and the more its cells divide, the more aggressive the disease.
In addition, it is important for doctors to know whether hormones or certain proteins in the body stimulate tumor growth. If so, patients may benefit from hormonal and targeted therapies.
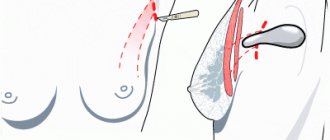
Organ-conserving surgery for breast cancer
Lumpectomy, quadrantectomy, partial or segmental mastectomy is the removal of the tumor, surrounding tissue and lymph nodes, while preserving as much breast volume as possible.
Important facts about the operation:
- It is not suitable for all patients.
- The amount of tissue removed depends on the size and location of the tumor, breast size and other factors.
- Such manipulations allow you to save most of the breast, but in most cases involve subsequent radiation therapy.
- In some situations, other types of treatment, such as hormonal or chemotherapy, may be prescribed after the procedure.
- The long-term prognosis of women who agree to complete mastectomy and partial breast removal in combination with radiation therapy is the same.
- If the patient is planning reconstruction, she needs to tell the doctor about this in advance, before the start of surgical treatment.
- After such interventions, pain is often felt, scars, hard scars or pits remain at the site of tumor removal, lymphedema develops - a gradual increase in the volume of the arm due to a violation of the outflow of lymph - a colorless liquid that washes all tissues and cells of the body.
Who is suitable for breast-conserving surgery?
A lumpectomy, or partial mastectomy, may be suitable if:
- The patient is extremely concerned about the upcoming changes.
- I am ready to undergo a full course of radiation therapy.
- The mammary glands have not yet been exposed to radiation and such interventions have not yet been performed on them.
- A woman has been diagnosed with one or more adjacent tumors, the removal of which will not critically affect the appearance of the breast.
- The neoplasm is up to 5 cm, accounting for the minimum volume of the organ.
- The patient is not pregnant or does not require immediate radiation therapy.
- The risk of developing cancer in the second mammary gland is not high, and mutations - changes in the BRCA genes The BRCA gene protects the cell from becoming a tumor cell. When changes occur in it, the risk of developing breast cancer increases significantly. or ATM The ATM gene carries information about a protein that recognizes and corrects damage to DNA, the repository of our hereditary information. If it “breaks,” the risk of developing breast cancer increases significantly. There are no increases in this probability.
- There are no connective tissue diseases such as scleroderma. Scleroderma is a rare incurable disease that affects any systems and organs, the normal tissue of which is eventually replaced by thick connective tissue. or lupus Systemic lupus erythematosus is an inflammatory disease of connective tissues that affects any organ: kidneys, lungs, heart, walls of blood vessels, kidneys, blood cells, skin, joints and lungs. which complicate the side effects of radiation.
- The woman does not have an inflammatory cancer that causes redness of the skin of the breast and possibly a rise in body temperature.
- The edges of the tissue removed along with the tumor are clean, that is, they do not contain cancer cells.
Mastectomy for breast cancer
Doctors perform several types of such operations:
- During a subcutaneous mastectomy
, the mammary gland is removed, but the skin, nipple and surrounding areola are preserved. This intervention allows for immediate or delayed reconstruction - restoration of shape, but it is not suitable for patients with large tumors or neoplasms located close to the surface of the skin. - During a radical mastectomy,
the breast, underlying muscles, lymph nodes and vessels, skin, nipple, areola and subcutaneous fat are completely removed. Possible less traumatic variations of this procedure, while maintaining: - According to Madden
: parts of the fiber, pectoralis minor and major muscles. - Amputation
is the removal of only the mammary gland, without muscles and lymph nodes.
According to Peity-Dysen
: pectoralis major muscle.
both breasts are removed. The operation is suitable for women with a high risk of developing cancer, for example, with a mutation - a change in the BRCA gene. The BRCA gene protects the cell from becoming a tumor cell. When changes occur in it, the risk of developing breast cancer increases significantly.
Indications and contraindications
Mastectomy is indicated for various types of breast cancer.
The operation can also be performed for other pathologies, for example, for gangrene of the mammary gland. There are a number of medical contraindications to mastectomy:
- severe diseases of internal organs;
- severe swelling of the skin of the chest;
- numerous metastases in the lymph nodes.
At the time of the operation, the patient should be as stable as possible; for this purpose, special therapy may be prescribed.
How is breast cancer surgery performed?
Before the intervention, the patient undergoes a full examination, during which it becomes clear whether he can tolerate the procedure and whether he has any contraindications. Based on the results of such diagnostics, the most gentle of the suitable mastectomy techniques is selected. The operation is performed under general anesthesia, which puts the person into deep sleep with loss of consciousness. Its drugs are delivered into the body intravenously or using a mask, after which a special tube is inserted into the throat to make breathing easier. During surgery, doctors monitor the patient's heart rate, oxygen supply, and blood pressure. During the intervention, the doctor makes an incision in the skin and removes tissue affected by cancer in accordance with the chosen technique.
After the operation, the doctor will apply stitches and, if necessary, install a drain - a plastic or rubber tube attached to a soft container that collects fluid produced during wound healing. The drain is removed after 5-7 days and the sutures are removed after approximately 3 weeks, after which patients requiring additional treatment are individually prescribed a subsequent therapy regimen.
Treatment after surgery for breast cancer
In some situations, surgical intervention is not enough - some patients are prescribed radiation, hormonal, targeted or chemotherapy. This treatment destroys the cancer cells remaining after surgery, reduces the risk of relapse - re-development of the tumor, inhibits the growth of the tumor or reduces its size.
results
Typically, pathology results should be available within a week or two after mastectomy.
If a woman has a large tumor, extensive lymph node involvement, cancer that has spread to the skin or nipple, or cancer left behind after a mastectomy in addition to surgery, other treatments may be needed. These treatments may include hormone therapy, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. All of them have their side effects and the choice of further treatment should be discussed with your doctor.
Consequences of surgery for breast cancer
The number of side effects depends on the type of intervention performed - as a rule, the more tissue that has to be removed, the more severe the consequences, which may include:
- Pain in the area where the operation was performed.
- Edema.
- Hematoma is an accumulation of blood in a wound.
- Restriction of arm or shoulder movement.
- Their numbness.
- Seroma is the accumulation of tissue fluid in the subcutaneous tissue of a sutured wound, which is formed when small blood vessels rupture.
- Postmastectomy syndrome is prolonged or persistent burning or shooting pain in the chest wall, armpit and arm.
- When axillary lymph nodes are removed, lymphedema often develops - a gradual increase in the volume of the arm due to a violation of the outflow of lymph - a colorless liquid that washes all tissues and cells of the body.
- As with any surgery, there may be bleeding or infection at the surgical site.
First days
The patient is in the hospital for 15 days. On the first day, in order to avoid complications - the formation of blood clots in the vessels of the legs or the development of pneumonia (older people are especially susceptible to complications) - the patient should sit down, and then get out of bed and walk. The patient does not feel pain. At first she receives painkillers, but not very strong ones. During such operations, narcotic drugs, which are prescribed after surgical interventions on the abdominal cavity or chest, are never prescribed. And by the time of discharge there is no longer any need for painkillers. During all the days of her stay in the hospital, the patient has a drainage in the armpit for lymph drainage and the chest is tightly bandaged with an elastic bandage so that the skin at the operated site fits tightly to the muscles and lymph does not collect here.
Sometimes lymph continues to accumulate after the stitches and drainage are removed, after discharge from the hospital. It has to be removed from time to time using a puncture by a surgeon at the place of residence. How long the lymph will flow depends on the individual characteristics of the body. For overweight people this happens a little longer than for thin people.
Oncology in numbers. Breast cancer from 2 to 5 cm can be completely cured Read more
Rehabilitation after surgery to remove a breast tumor
The recovery time after surgery varies from person to person. They mainly depend on the amount of tissue removed and overall health. Typically, it takes about 2 weeks to return to your normal lifestyle after a lumpectomy, about 4 after a mastectomy, and breast reconstruction increases this time to several months.
Before discharge, the doctor or medical staff tells you how to care for the surgical area, what stress to avoid and when to start doing it. A special diet is usually not required during rehabilitation - it is advisable to simply follow the principles of a healthy diet, rest, get enough sleep, do not overexert yourself and take care of the wound. A very important point for recovery is special exercises with which you can develop the arm and shoulder, restore flexibility and mobility to them, and also reduce the risk of developing lymphedema. Lymphedema is a gradual increase in the volume of the arm due to a violation of the outflow of lymph - a colorless liquid that washes all tissues and body cells...
Before you leave the hospital, be sure to ask your doctor some important questions:
- How to care for the wound and bandage?
- What do you do with a drain - a plastic or rubber tube attached to a soft container that collects the fluid produced as the surgical area heals?
- How to recognize signs of infection?
- When and how can you shower?
- When to call a doctor or go to an urgent appointment?
- When to start using your hand and how to do special exercises?
- When can I wear a bra again?
- What medications can and should be taken, including painkillers and antibiotics?
- What not to do and what stress to avoid?
- How should the sensations in the arm, shoulder and chest area change?
- When should I go for a scheduled follow-up examination?
Recovery
After the operation, the patient is transferred to the inpatient department. The length of stay in the clinic depends on the type of surgery performed and the general health of the patient. Usually it is no more than a week.
During the rehabilitation period, the patient must wear special compression garments, take care of the drainage system, and regularly come for preventive examinations to the attending physician.
Many women are frightened by the very possibility of having a mastectomy. However, it should be noted that in case of breast cancer, this is the only opportunity to cope with a serious illness. If you are a candidate for a mastectomy, we recommend that you do not delay the operation. The sooner the surgical procedure is performed, the higher the chances of cure. An appointment with a medical oncologist can be made by phone or through a special form on the website.