Separation of the rectus abdominis muscles, or diastasis, is a common problem affecting mostly women. According to statistics, 70-100% of women develop this pathology in the third trimester of pregnancy. Normally, after childbirth, the structures should return to their original position, but in approximately 30% of cases this does not happen. A gap remains between the muscle tissues, which causes a bulging, flabby abdomen and provokes more serious consequences. That is why it is important to know how to determine diastasis of the abdominal muscles at home, which doctor can help, and what treatment methods modern medicine offers.
What is diastasis
To understand this concept, it is necessary to briefly outline the structural features of the abdominal muscles. In the center of the abdomen is the rectus muscle. It begins in the lower abdomen and extends to the pubic bone. Consists of two sections that are connected in the center by loose fabric. This connective tissue is called the linea alba.
As a result of prolonged and strong tension of muscle structures, intra-abdominal pressure increases. Weak tissues of the white line cannot withstand the load and begin to diverge. At the same time, the distance between the sections of the rectus muscle increases, they diverge to the sides and move several centimeters away from each other. A kind of furrow is formed, and when tense, the stomach protrudes unnaturally. Pathological discrepancy can form under the navel, above it, or have a mixed form.
The pathology should not be confused with a hernia of the white line or with an umbilical protrusion. It does not threaten to infringe on internal organs. But at the same time, even at an early stage it represents an aesthetic problem, since diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscle is much more often determined in women than in men.
Depending on the degree of discrepancy and the size of the formed distance, diastasis is divided into three degrees:
- first - the distance between sections is from 2.5 to 5 cm;
- second - the discrepancy reaches a gap of 5-8 cm;
- third - the size of the furrow between the sections exceeds 8 cm.
This classification allows you to understand how to determine the degree of muscle diastasis even at home.
Pathology can also affect other muscle structures of the anterior abdominal wall. Depending on what surrounding tissues are involved in the process, four types of diastasis are distinguished:
- A - classic form, in which only the rectus muscle diverges;
- B - loss of tone in the inferolateral muscle sections;
- C - appearance of expansion in the area of the xiphoid process, ribs;
- D - curvature of the waist line.
Service
Suturing of diastasis without incisions using the SCOLA method
The SCOLA (subcutaneous onlay laparoscopic approach) technique is suitable for patients who have diastasis, local fat deposits, but no large excess skin.
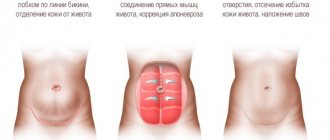
During the operation, a special device is used - a laparoscope, which is inserted into the abdominal cavity through punctures of 5 mm in size in the bikini line area. The device is equipped with a miniature video camera, the image from which is transmitted to the screen in an enlarged size, which allows the doctor to perform complex manipulations with the highest precision. The surgeon sutures the rectus muscles using special threads, and a soft mesh implant made of inert material is used. Made in 3D weaving, the mesh implant grows with connective tissue, and its external coating prevents the adhesion of organs. Thus, the sutured tissues remain in the desired position, and the development of relapse is excluded.
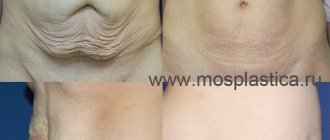
As a result of such an intervention, the patient receives a stomach without traces of the incision, without wrinkling of the skin, with a corrected shape of the navel.
Suturing of diastasis
Diastasis is a condition in which the distance between the rectus abdominis muscles increases. There are two methods of performing the operation - tension and non-tension. The rehabilitation period is relatively easy. At first there is swelling, hematomas, and pain. The first ones gradually go away on their own, and the pain is relieved with a drug prescribed by the doctor. Cost of the operation:
from 170,000 rubles Make an appointment with a doctor
More about the operation
Causes of abdominal muscle diastasis
The main reason for the discrepancy is the excessively high pressure that occurs in the abdominal cavity. At the same time, the prerequisites for increased intra-abdominal fluid are of different nature. These include:
- Loss of muscle elasticity as a result of rapid weight loss.
- Excessive physical activity.
- Dysplasia is the abnormal development of tissues and organs. In addition to diastasis, it is accompanied by many additional manifestations: hernia, varicose veins, hemorrhoids, etc.
- Pregnancy. As a result of hormonal changes, collagen production is reduced, tissues lose elasticity and become loose. At the same time, the enlarged uterus significantly increases pressure on weakened muscle structures and the linea alba.
In 60% of cases, diastasis in women is associated with pregnancy. Pathology begins to develop in the middle of the second trimester. It is at this time that the muscles are stretched under the influence of increasing abdominal pressure. Normally, after childbirth, the uterus restores its previous size, and the width of the white line returns to its normal value of up to 2 cm.
However, in many cases, the recovery process is complicated by concomitant factors that prevent the tissues from returning to their previous position. These factors include:
- mature age of the woman in labor;
- excess weight before and during pregnancy;
- the fruit is too large;
- number of previous pregnancies and births;
- type of pregnancy (one fetus or several);
- complications during pregnancy;
- too rapid return to active physical activity after childbirth.
Diastasis can also occur in children, especially premature babies. The key prerequisite for the development of pathology is the failure of the child’s muscles and tendons. In this case, most often the defect is eliminated on its own during the first year of the baby’s life. During this period of time, the muscles acquire tone, the ligaments become strong. Only children with Down syndrome are at risk of maintaining the discrepancy.
In only 1.5% of cases, diastasis is diagnosed in men. The basic prerequisites are the same as for women: obesity, dysplasia, sudden weight loss. Also, men are more likely to be overly involved in strength training, which not only causes hernias and varicose veins, but also provokes the formation of diastasis.
Signs of abdominal muscle diastasis
For a long time, the pathology has an asymptomatic course. Manifestations increase as the discrepancy develops and complications appear. And if in women the signs of diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles are maximally manifested after pregnancy and childbirth, then in men - only when the pathology is already in an advanced state.
The main and most noticeable manifestation of the pathology is a rounded vertical protrusion of the abdomen. If you deliberately tense your abdominal muscles, a groove between the right and left halves of the body becomes visible. At the same time, in men, even with intense strength training, the abs are not sufficiently worked out and do not acquire the desired relief.
If the disease progresses, the pathological structure of muscle tissue and disturbances in muscle function become the cause of other, more dangerous characteristic manifestations. There are:
- pain in the spine, lower back;
- posture disorders;
- increased fatigue;
- dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract, which is accompanied by heartburn, belching, pain, constipation, flatulence.
At the third stage of the pathology, dangerous complications are possible, which manifest themselves in the form of:
- ptosis, prolapse of internal organs;
- intestinal obstruction;
- urinary incontinence;
- renal colic;
- feeling of heaviness in the legs while walking;
- muscle atrophy in the abdominal area.
Surgical treatment of diastasis
The only method that actually eliminates diastasis and the negative aspects that accompany it is surgical. Of course, we do not recommend surgery for all patients with diastasis recti.
Diastasis is not a hernia; there is no defect in the anterior abdominal wall in which internal organs can be pinched; therefore, diastasis of the rectus muscles does not threaten the life and health of the patient.
There are certain indications for performing the operation:
- The presence of clinically significant diastasis of the rectus muscles (>3 cm according to ultrasound or CT/MRI), worsening the quality of life (severe aesthetic defect, lumbar and pelvic pain, urinary incontinence, etc.)
- Combination of diastasis with hernia of the anterior abdominal wall
Contraindications, in addition to the usual contraindications for any surgery and anesthesia, include:
- Planned pregnancy - diastasis plastic surgery in such a situation does not make sense, the risk of its re-formation is extremely high
- Less than 12 months have passed since birth - the anterior abdominal wall can still return to a state that suits the patient, especially when performing the above exercises
How does a doctor determine the presence of diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscle?
If any of the listed symptoms appear, as well as if there are predisposing factors such as recent pregnancy and childbirth or increased physical activity, you should consult a doctor for examination. You can’t delay your visit; it’s better to see a specialist for prevention than to wait until dangerous complications appear.
Many people do not know which doctor determines the presence of diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles. You need to contact a surgeon. In most cases, an experienced specialist will be able to determine the pathology using only palpation examination.
For diagnosis, the patient lies on his back, slightly bends his knees and rests his feet on the surface. After this, the surgeon asks you to tighten your abdominal muscles. At the same time, you need to raise your shoulder blades and head. The doctor feels the abdomen, measures the width of the discrepancy, and determines the presence and stage of the pathology. In this case, pronounced diastasis of the third degree is noticeable even in a standing position.
In some cases, the study of the width of the white line is complicated by excess body weight. The doctor refers such patients for an ultrasound examination. This procedure is also prescribed if there is a suspicion of the development of complications: hernial protrusions, displacement of internal organs. In rare cases, radiography or computed tomography is necessary.
How to treat diastasis?
There are a few studies that indicate self-correction of diastasis within a year after childbirth. Despite the insufficient evidence base, during the first year we do not recommend surgical correction of diastasis, giving preference to physical exercises. And only if there is no sufficient aesthetic effect, we plan the operation.
It should be noted that physical education can visually improve the shape of the abdomen, make it flatter, but it is impossible to reduce the width of the white line with its help - connective tissue, unlike muscle tissue, is not capable of hypertrophy, it cannot be “pumped up”.
What exercises cannot be done with diastasis? Again, there are no high-quality studies on this issue to date. “Classical” exercises that strengthen the abdominal muscles are not recommended: crunches, leg or body lifts, “bicycle”, etc., as they can even contribute to an increase in diastasis.
The main muscle that should be strengthened during diastasis is the transverse abdominal muscle (transversus abdominis). This is the deepest muscle of the anterior abdominal wall, whose function is to maintain a flat abdominal shape. Basic exercises that use this muscle:
Abdominal retraction
Lying on your back with your legs bent, draw in the lower half of your abdomen as much as possible. Hold in this position for 10 seconds at first, gradually increasing the time to 30. 10 repetitions 3 times a day
Abdominal pulsation
Rapid alternation of retraction and relaxation of the abdomen. 5 times a day, 100 pulsations
"Cat"
In the “on all fours” position, as you exhale, arch your back upward, rounding it like a cat, while straining and pressing your stomach to your back. Keeping your muscles tense, inhale and slightly arch your back in the opposite direction. 10-15 repetitions 3 times a day.
Also, for diastasis of the rectus muscles, the Kegel exercise is recommended, which strengthens the pelvic floor muscles and a number of others. Let us repeat that their regular implementation is quite capable of improving the shape of the abdomen, but, unfortunately, the exercises are unable to eliminate diastasis, and even more so the hernia of the anterior abdominal wall that often accompanies it.
Wearing bandages during and after pregnancy, according to some data, reduces the risk of developing diastasis and reduces the intensity of pain. However, to date, there are no high-quality studies devoted to this aspect.
How to determine the presence of abdominal muscle diastasis yourself
Diastasis can be determined at home. A simple test will help you do this, during which you need to measure the distance between the edges of the rectus muscle.
To do this, you need to lie on your back on a hard surface, bend your knees. Place one hand under your head and the other on the white line, just above your navel. Then you should relax and raise your chest. In this case, you need to feel the discrepancy between the muscles with your fingertips. The gap is most pronounced between the navel and the xiphoid process. If the discrepancy is greater than the width of two fingers, this should alert you and be a reason to contact a specialist.
This technique is as similar as possible to the approach that a surgeon uses for diagnosis. This is the easiest way to determine diastasis at home without the help of a doctor and instrumental examinations.
How to remove diastasis
The treatment regimen for the pathology depends on the stage of its development and the degree of manifestation. At the first stage, it is enough to follow the doctor’s recommendations, which will help strengthen the muscles of the abdominal wall and reduce their discrepancy:
- reduce weight to normal levels;
- maintain a balanced diet with limited consumption of fatty and sweet foods;
- adhere to the daily fluid intake;
- wear a bandage that supports the stomach;
- undergo massage and other physical procedures;
- do swimming, yoga, Pilates or physical therapy.
Physical therapy should be carried out under the supervision of a specialist. He creates a program with the correct load level. Particular attention is paid to the deep transverse and oblique abdominal muscles, which, with an appropriate level of tone, reduce the degree of stretching of the linea alba.
A set of therapeutic exercises is useful even for pregnant women. With its help, you can prevent the development of pathology and speed up the process of postpartum recovery of the body.
Such training takes place without straining the abdominal muscles. It is also not recommended to do exercises while standing, including on your knees or elbows. Such loads are permissible only after restoration of the normal width of the lumen.
In later stages, the discrepancy can no longer be corrected with exercise or massage. Surgical intervention is necessary to return the muscle corset to its place and relieve complications and symptoms. It could be:
- Tensionplasty using patient tissue. The surgeon removes excess connective tissue and stitches the edges of the muscles together. This method is the least preferable, since relapses occur quite often after it.
- Tension plastic using a prosthesis. It involves the same removal of excess tissue and suturing of muscle layers, but is accompanied by additional strengthening using a mesh polypropylene prosthesis.
- Tension-free plastic surgery with installation of a prosthesis. An endoprosthesis is inserted under the stretched area, which serves as a barrier and replaces the weakened structures.
- Combined approach. It involves a combination of tension and non-tension plastic surgery.
The specialist selects the surgical method taking into account the characteristics and degree of development of the pathology, as well as individual factors and the patient’s health status. Full recovery after the intervention occurs within 1 to 3 months. At this time, it is necessary to avoid excess tension, adhere to a diet and wear a special bandage that relieves stress from the operated muscle structures.
Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation is an important stage in the completion of the patient’s treatment and his full recovery. It depends on many factors: age, the presence of chronic diseases, the development of complications of the underlying pathology and many other reasons.
Our main goal is the health of our clients. Therefore, in the early postoperative period, the patient is under round-the-clock supervision of doctors and nursing staff who provide all the necessary assistance.
We strive to ensure that our patients begin mobilization as early as possible in order to prevent thromboembolic complications, such as stroke, myocardial infarction, and pulmonary embolism. It must be remembered that heavy physical activity is prohibited for up to 6 weeks after surgery.
It is important to follow a diet for 2-4 weeks, which will contribute to the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Exclude foods rich in fiber from your diet, as they promote active peristalsis and gas formation.
After discharge from the clinic, you must remember and follow all the recommendations of your doctor. Your doctor may recommend that you take pain medications and also stop some medications that you take regularly during the recovery period.
Prevention of diastasis
To reduce the risk of developing pathology, it is extremely important to systematically follow preventive recommendations. To do this you need:
- adhere to a proper balanced diet;
- lead an active lifestyle, walk more;
- strengthen all muscle groups, especially the muscle structures of the abdomen and lumbar region;
- eliminate excessive physical activity;
- do not lift weights, especially for women;
- strengthen the diaphragm;
- monitor your weight and prevent obesity.
During pregnancy, you need to use special oils, creams, ointments that increase the elasticity and firmness of tissues. After childbirth, it is necessary to carefully monitor the condition of the press in order to detect pathology in a timely manner and, if necessary, seek help from a doctor before complications develop. Treatment of the initial stages of discrepancy is successful and does not require excessive effort from the patient.
Diagnosis of diastasis
The easiest way to determine the presence of diastasis is to raise your head while lying on your back with your legs bent. In this position, the rectus muscles tense, and the extended linea alba protrudes forward in the form of a protrusion. It can also be felt between the rectus muscles. If two fingers pass freely between the rectus muscles, this is a sign of clinically significant diastasis. In this case, you should seek help from a specialist who will conduct an ultrasound examination and determine the exact width (degree), localization of diastasis, stage of the process, the possible presence of hernias and other features in order to decide on the optimal method of correcting this problem.
In some situations, for example, when diastasis is combined with hernias, it is preferable to use computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging. These studies provide complete information about the condition of the tissues of the anterior abdominal wall and make it possible to determine the optimal method of surgical treatment.
In addition to the aesthetic defect, 20% of patients with diastasis have chronic lumbar or pelvic pain. The reason is the dysfunction of the anterior abdominal wall and the redistribution of excess load on the muscles of the pelvis and lower back. In 10% of women, pain can be quite intense, affecting quality of life and interfering with daily activities. Another delicate problem that is more common in women with diastasis is urinary incontinence and other manifestations of pelvic floor dysfunction (according to Spitznagle et al. (2007) - in 66% of observations).