Both the labia majora and labia minora can be stretched. With this feature, a woman may believe that her vulva looks abnormal. And this will contribute to strengthening the feeling of awkwardness, the development of the so-called “locker room syndrome”, and certain difficulties in intimate life.
In addition, coverage of the topic of intimate plastic surgery in the media (women's magazines, Internet portals), the availability of erotic films contributed to the growing popularity of correction of the labia in particular and the anogenital zone in general. Modern women remove unwanted hair from the bikini area and have a clear understanding of the crotch and its proportions. Therefore, it is important to take into account the likelihood of dysmorphophobia that has formed in a woman against the background of the imposition of certain beauty standards relating to the genital area.
Surgical treatment of urinary incontinence
The problem that causes women moral and physical suffering comes down to involuntary leakage of urine when intra-abdominal pressure increases. It can be caused by coughing, sneezing, physical stress and even laughter. Its cause, as a rule, is the relaxation of the vaginal walls that have lost their elasticity and prolapse of the pelvic organs.
As a rule, urinary disturbances are first observed during pregnancy, and after childbirth, symptoms persist in every sixth woman.
The problem gets worse:
- during menopause;
- due to obesity;
- after operations on the pelvic organs;
- after acute and chronic inflammatory diseases;
- in women engaged in heavy physical labor and strength sports.
The most effective method of dealing with the problem is the so-called. sling or loop surgery, during which the bladder is “tied up” with special grafts - synthetic tapes.
Two methods have been developed and are successfully used in the clinic:
- TVT, in which the tape, using the included applicators (curved needles), is attached under the urethra, forming a free loop. Its ends are brought out through the anterior abdominal wall and then removed. The intervention is performed under local anesthesia using the transvaginal method.
- TOT is an improved technique in which, using special applicators, the tape is passed through the obturator foramina in the area of the inguinal fold. The intervention takes a little less time, and the surgeon has the ability to fully control the course of the needle.
The material from which the tapes are made does not dissolve over time and does not lose its original strength, reliably fixing the middle and posterior part of the urethra.
Contraindications
Like any other procedure, stretching the labia has some contraindications. These, first of all, include:
- oncological diseases;
- age under 18 years;
- severe chronic diseases in the acute stage;
- inflammation of the labia and other organs, suppuration;
- problems with the skin in the intimate area, pathological sensitivity;
- pregnancy, breastfeeding;
- phlebeurysm;
- herpes in the acute stage;
- climate change.
Vaginoplasty
Vaginal plastic surgery is performed to restore its aesthetics and functionality. Its elastic walls stretch during childbirth and do not always return to their previous shape, as a result of which the volume of the vagina increases. This reduces the quality of sensations during sexual intercourse, causes psychological problems in women and brings discord into marital relationships.
During menopause, drooping vaginal walls lead to complete or partial prolapse of the uterus, urinary incontinence and uncontrolled release of gases produced during digestion.
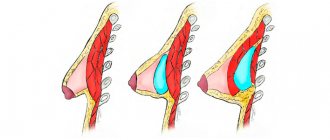
Intimate surgery offers effective techniques to reduce the vaginal opening and its volume. During colporrhaphy, excess vaginal tissue is excised, its walls, if necessary, are strengthened with a synthetic mesh to prevent prolapse of the pelvic organs, and the edges of the excised mucosa are connected with a suture. Together with the anterior or posterior, or both walls at once, the surgeon also sutures the perineal muscles.
African method
Stretching the labia in girls is traditionally performed in many African tribes. And there is a logical explanation for this. Firstly, stretched labia provide greater pleasure during intimacy, and secondly, they protect against infection entering the genital tract.
Unfortunately, the approach in this case is truly barbaric. At an early age, the girl is given heavy clips, which she wears until the stretched labia reach the required length.
However, in a number of African countries another, more humane method is used.
In this case, the procedure is carried out in the following order:
- Olive or any other vegetable oil is mixed with a few drops of vitamin E and then heated (it should be barely warm and never hot to avoid burns).
- Before retracting the labia, hands and genitals are thoroughly washed with detergents. To cleanse the latter, it is better to use a special gel or baby soap. They contain a minimal amount of alkali and will not dry out sensitive areas.
- The genitals are treated with oil and stretched with your hands (the labia should be pinched between your fingers). When performing these actions, it is necessary to observe moderation. If you simply stroke the genitals, there will be no effect, but if, on the contrary, you apply too much force, you can feel severe pain and even get injured.
These manipulations are recommended to be carried out within 10 minutes. At the end of the procedure, the genitals and hands should be washed again.
Stretching the labia in a similar way is done in the morning and evening. The duration of the course is until the desired result is achieved. As a rule, this takes several months.
Thus, it can be understood that the African method is quite safe. It can be safely used to stretch the labia at home. This method gives the best results in young women. For mature ladies, the effect may not be so impressive.
Labiaplasty
Labiaplasty or surgery to correct the labia can improve their appearance and relieve physical discomfort that occurs when playing sports. Enlarged, asymmetrical labia make a woman insecure about her sexual attractiveness, prevent her from establishing contacts with men and destroy her personal life.
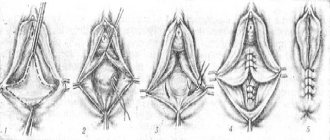
During a simple operation, excess tissue is excised and absorbable sutures are placed. The intervention has no effect on excitability and the ability to experience orgasm.
Advice from expert gynecological surgeon Ivanov A.V.
The labia can be affected by herpes, fungal diseases, HPV infection or even cancer. Therefore, when you feel itching, pain or burning in the vulva, you need to consult a gynecologist. You should also see a specialist if you notice any unusual tissue growth, ulceration, warts, nodules, or discoloration of the labia.
Regarding the size of the labia, modern plastic gynecology can solve almost any problem, so do not hesitate to contact our specialized Intimate Plastic Center in St. Petersburg with such questions.
You can see photos of labia disorders here ⇒.
Advantages of visiting our clinic “Polyclinic+1”
- Competence of doctors. Services for the correction of asymmetry and deformation of the perineum are provided by gynecologists R. A. Sasunova, V.S. Rigas. Our doctors have a certificate that confirms the right to practice aesthetic gynecology.
- Use of proven drugs. We use safe and effective products from well-known pharmaceutical companies.
- Caring for every patient. Before prescribing the procedure, we will make sure that the woman has no contraindications. Fillers are introduced carefully, in small doses, so that the drug is distributed evenly.
- Anonymity. We maintain complete confidentiality, so we do not require passport information.
- Convenience. To make an appointment, just call or leave a request on the website. We are waiting for you any day from 9 am to 9 pm. The clinic is located at the same distance from the Novokuznetskaya and Tretyakovskaya metro stations.
Diagnostics
To undergo an examination, you must contact a specialized medical center. During the consultation, the doctor will ask the woman about her complaints and examine her medical history. A thorough examination of the skin of the vulva in a gynecological chair reveals specific symptoms of kraurosis. To confirm the diagnosis, instrumental and laboratory examinations are prescribed.
Additional diagnostic methods:
- Vulvoscopy is a method of high-precision visual examination of the external genitalia. The gynecologist uses an optical device to magnify the image many times. If necessary, before the examination, the skin is treated with special solutions. Vulvoscopy allows a specialist to confirm the diagnosis and exclude signs of malignant tissue degeneration.
- Taking a smear from the mucous membrane. The doctor uses a special swab to collect the material and sends the sample to the laboratory. Cytological examination makes it possible to exclude the presence of abnormal cells. Nutrient media are also used to identify the causative agent of a bacterial infection (if indicated). Cytological examination of papilloma helps detect signs of HPV infection.
- Blood analysis. A nurse is drawing blood from a vein in the treatment room. The purpose of a blood test is to determine the ratio and quantity of formed elements. An immunogram is necessary to detect signs of an autoimmune process. To more accurately diagnose an infection, serological tests are carried out: specialists look for antibodies in the patient’s blood that are produced by the immune system to fight pathogenic microorganisms. Polymerase chain reaction is used to identify the type of HPV infection. If necessary, the concentration of sex hormones is determined.
- Biopsy - removal of a small area of affected tissue. First, the gynecologist injects local anesthesia into the tissue and treats the skin with an iodine solution. The resulting material is examined in the laboratory to determine the cause of dystrophic changes and detect malignant cells. A biopsy is the most reliable method to exclude vulvar cancer.
Carrying out several diagnostic procedures at once allows the doctor to prescribe the most effective treatment. If necessary, the gynecologist prescribes the patient a consultation with a dermatologist, venereologist or immunologist.
Risk factors
The etiology of kraurosis is not limited to the mechanisms of skin damage listed above. Doctors are also aware of various forms of predisposition to this condition associated with a woman’s lifestyle, health status and heredity.
Known risk factors:
- Unfavorable hereditary history. Skin and reproductive diseases identified in close relatives indicate an increased risk of the disease. Vulvar atrophy may be caused by genetic mutations that are inherited.
- Type 1 diabetes mellitus, Crohn's disease, rheumatoid arthritis and other diseases caused by autoimmune pathologies.
- Chronic infections of the skin and organs of the reproductive system.
- Carrying out diagnostic and therapeutic interventions in the area of the external genitalia.
- Constant trauma to the skin of the vulva, such as cuts, sprains and burns.
- Psychogenic factors: persistent depression of mood, anxiety and chronic stress.
- Obesity and metabolic pathologies.
- Hypersensitization of the immune system, manifested by allergic reactions.
The exact causes of dystrophic changes in the external genitalia in women are unknown. Eliminating the main risk factors for the disease is an excellent way of prevention.
Causes
Kraurosis of the vulva is a polyetiological disease. Dystrophic changes in the skin represent a specific tissue response to external and internal factors. This may be an independent disease or a complication of other pathological conditions, such as an endocrine system disorder or infection.
Possible reasons:
- Pathologies of endocrine organs. Endocrine glands secrete hormones that control the development and function of organs. A lack of sex hormones can lead to degeneration of the skin of the vulva. Also, this disease is often diagnosed against the background of diseases of the adrenal glands, thyroid gland and ovaries.
- Human papillomavirus or HPV infection. This is a sexually transmitted disease. Invasion of the virus into the epithelium of the skin and mucous membranes of the genital organs (mainly the cervix) leads to tissue dysplasia and the formation of papillomas. Kraurosis may be a consequence of long-term HPV infection. The combination of degenerative changes in the vulva with invasion of the human papillomavirus significantly increases the risk of tissue malignancy.
- Other infectious diseases including herpes virus and gonorrhea. Pathogenic microorganisms damage tissue and cause chronic inflammation. Some studies indicate a connection between vulvar kraurosis and hepatitis C and Lyme disease.
- Autoimmune diseases in which the body's defense system attacks its own tissues.
Clarifying the cause of dystrophic changes is important for treatment.
Prognosis and prevention
In most cases, doctors are unable to completely restore the condition of the skin of the vulva, but complex treatment slows down the degenerative processes in the tissues. Physiotherapy helps improve the appearance of the external genitalia. Even after treatment, it is necessary to undergo regular examinations by a gynecologist to exclude malignant tissue degeneration.
Methods for preventing the disease:
- safe sex;
- timely treatment of inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system;
- careful hygiene of the external genitalia;
- prevention of skin trauma;
A consultation with a dermatologist and gynecologist will help a woman learn more about methods of prevention and treatment of vulvar kraurosis.