Allergies to cosmetics are quite common. Most often, the mucous membranes of the eyes, eyelids, facial skin and décolleté area suffer from an allergic reaction. There are several reasons for allergies to cosmetics. At the same time, the body’s reaction to the use of cosmetics can manifest itself in completely different ways. The most common intolerance to individual components of decorative cosmetics, creams, masks and lotions.
Why allergies occur
Allergy as an essence is an overactive reaction of the body to the effects of allergens
: substances that provoke an undesirable skin reaction. A person is a complex, individual organism, which means that the causes of allergies can be different. Most often, the tendency to certain reactions is due to a whole complex of different factors. These include:
- genetic predisposition;
- hormonal levels, the presence of chronic diseases, vitamin deficiency, decreased immunity during therapy;
- stress, climate change, neglect of protection from UV radiation;
- increased sweating and skin sensitivity.
These factors create an environment for the development of dermatitis -
skin reactions to contact with a certain irritant. In this case, both household chemicals and animals, perfumes, fabrics, flowers, medicines or food can act as an allergen.
Alas, even ordinary nuts can make you sneeze and itch, just like cleansing foam, and even your furry pet. This does not mean that you need to avoid everything around you and live in a hypoallergenic spacesuit. But it’s worth drawing conclusions and becoming more attentive to the world around you and the products you consume.
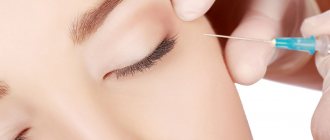
One of the possible tests for allergies is skin testing. The test is performed by an allergist
Read also
Allergic rhinitis
What is allergic rhinitis? Allergic rhinitis is caused by an immune response to certain allergens.
Pollen is the most common allergen in seasonal illness. Causes of allergic... Read more
Allergy to the sun
What is Sun Allergy Sun allergy is a reaction that causes a red, itchy rash due to exposure to sunlight. One of the common types of rash is polymorphic photodermatosis,…
More details
Drug allergy
What is a drug allergy? A drug allergy is an abnormal reaction of the immune system to medications. Any medicine—over-the-counter, prescription, or herbal—can cause this condition. However,…
More details
Cold urticaria
Cold urticaria is a condition characterized by the onset of swelling and redness 5-20 minutes after exposure to cold or subsequent warming, most often localized on the face and hands.…
More details
Allergic dermatitis
What is allergic contact dermatitis? Anyone has ever experienced skin symptoms after using various skin care products, shower gel or shampoo. Such…
More details
How to recognize allergies to cosmetics
In terms of external manifestations, an allergy to cosmetics may not differ from an allergy to a new coat or perfume. However, there is a difference. Lipstick, cream or mask is applied locally, which means a reaction will occur in this area. You should be alert to symptoms such as:
- local moderate redness at the site of application;
- mild itching and burning;
- dryness, cracks and peeling;
- local tissue swelling.
These symptoms are referred to as simple contact dermatitis.
. The reaction may appear after one application and will disappear as soon as you eliminate the cause of the irritation.
Allergic dermatitis is also distinguished
. It manifests itself in the form of severe itching, rash, bright redness and weeping rashes. It can last a long time and spread to areas of the skin that have not been in contact with cosmetics.
Another type of dermatitis is photoallergic
. It is expressed in the form of rashes on open areas of the skin not protected by clothing, redness and itching. Occurs due to skin sensitivity to the sun (photosensitization) after the use of retinoids, polyunsaturated fatty acids, natural essential oils, para-aminobenzoic (PABA or vitamin B10) and salicylic acids.
Remember: only a doctor can correctly determine the type of irritation, make a diagnosis and select an effective treatment regimen!
Symptoms and signs of the disease
As a rule, at the initial stage the signs of one or another dermatitis are the same. Redness occurs on the surface of the skin, followed by rashes, swelling, dryness and cracks. They often itch, and patients also often complain of a burning sensation and pain in the affected area. Manifestations of contact skin pathology are usually less pronounced, while the allergic form is characterized by more severe redness and swelling. Often liquid-filled blisters appear on the affected area. If they are damaged or burst, this can lead to the formation of large, weeping lesions, which can be accompanied by a secondary infection. In this case, the sites of inflammation will begin to fester, which will lead to a more severe course of the disease and its progression to a chronic form.
A clear symptom of an allergic reaction is skin lesions not only at the site of contact with the irritant, but also on other surfaces. The skin most often exposed to pathogens is the skin of the hands, face, neck, shoulders, collarbones, armpits and scalp. Allergic dermatitis rarely affects the lower limbs and torso.[3].
Natural cosmetics = safe cosmetics?
Serum with a high content of vitamin C, tonic with essential oils and lemon, sea buckthorn cream. And no “chemistry”! Sounds tempting. True, this does not mean at all that an allergic reaction will not occur to these extremely “natural”, environmentally friendly products.
This may surprise you, but the most hypoallergenic products are synthetic, since they do not contain proteins that are primarily perceived by the immune system as foreign to the body and requiring immediate destruction. If you pay attention to children's cosmetics from serious large companies, the number one component there will be mineral oil. And not because “they want to destroy children” and “bathe them in oil,” but because this is the safest component that will not cause, for example, Quincke’s edema.
In what cases is it necessary to take tests:
- the patient exhibits pronounced signs of illness upon contact with certain substances, after eating a specific food, or during seasonal changes;
- drug therapy was powerless in the treatment of bronchitis, dermatitis or rhinitis;
- hereditary predisposition;
- working in a “harmful” workshop, which results in shortness of breath, cough, and conjunctivitis.
Important: human blood contains about 0.001% immunoglobulin. If the norm is exceeded, this indicates the presence of an allergy. The extent of symptoms depends on the level of response of the immune system to the stimulus.
Allergens in cosmetics according to European standards
In January 2007, the European Scientific Committee for Consumer Safety (SCCS) approved a special “List 26”. It included 26 substances that most often cause allergies in cosmetics, which, however, can be added to cosmetics, subject to mandatory inclusion on the label. Components from “List 26” are divided into two sections depending on the frequency of allergic reactions.
LIST A
“List A” includes components with a very high frequency of allergic reactions and with a large number of documented evidence.
- Amyl cinnamal is
a synthetic fragrance.
Amylcinnamyl alcohol
is a synthetic fragrance.
Benzyl alcohol
is a component of essential oils of jasmine, hyacinth, and ylang-ylang.
Benzyl salicylate
is a component of many essential oils.
Cinnamyl alcohol
is a component of cinnamon leaf essential oil, as well as Peruvian balsam and styrax.
Cinnamal
is a component of cinnamon bark essential oil.
Citral
is a component of many essential oils with a pronounced lemon sound (from lemon itself to verbena).
Coumarin
is a component of tonka bean essential oil.
Eugenol
is a component of essential oils of bay, cloves, cinnamon, basil, and nutmeg.
Geraniol
is a component of rose, palmarosa, and citronella essential oils.
Hydroxycitronellal
is a synthetic fragrance.
Hydroxymethylpentyl-cyclohexenecarboxaldehyde
is a synthetic fragrance.
Isoeugenol
is a component of ylang-ylang essential oil.
LIST B
“List B” includes components with lower frequency and less documented evidence.
- Anisyl alcohol
is a synthetic fragrance.
Benzyl benzoate is
a component of essential oils of tuberose, hyacinth, as well as Peruvian, Tolu and Copai balsams.
Benzyl cinnamate
is a component of Peruvian, Tolu and Copai balsams.
Citronellol is
a component of rose, geranium, and citronella essential oils.
Farnesol
is a component of many essential oils (from lemongrass to neroli).
Hexyl cinnamaldehyde
is a component of chamomile essential oil.
Lilial is
a synthetic fragrance.
d-Limonene is
one of the main components of citrus essential oils.
Linalool
is a component of many essential oils and is found in 200 types of plants from lavender to cinnamon.
Methyl heptine carbonate
is a synthetic fragrance.
Alpha-Isomethyl Ionone
is a synthetic fragrance.
Oak moss
- oak moss.
Tree moss
is the collective name for mosses.
Preparing for the test
Before taking the necessary tests, the patient must comply with the following rules:
- the test is taken on an empty stomach, in the morning;
- 1.5 hours before the test you cannot smoke;
- for 3 days it is necessary to exclude from the diet all foods with a high degree of allergenicity (seafood, chocolate, nuts, honey, citrus fruits, cheeses);
- stop contact with animals 3 days before;
- avoid physical and emotional stress;
- if possible, stop using any medications;
- refusal of antihistamines;
- The test cannot be performed in case of inflammatory processes, viral or respiratory diseases.
Is it possible to prevent allergies?
A few rules to help you protect yourself:
- Study the ingredients of the products before purchasing.
The most common triggers for rashes and itching are natural fragrances (essential oils), some preservatives, dyes (mainly found in pigments in decorative cosmetics and hair dyes), honey and its derivatives. Rarely: mineral oils, plant extracts, minerals, lanolin. This doesn't mean you should avoid these remedies, but it's best to be on the lookout. Especially with severe skin sensitivity. - Test new cosmetics before use.
To do this, apply a little product to the crook of your elbow and wait up to 48 hours. - Follow the rules for storing products
and do not use cosmetics after the expiration date. - Always follow the manufacturer's recommendations.
Do not overexpose masks, do not apply creams to the mucous membranes, and do not use products intended for professionals without the appropriate skills.
heavenly fragrance
Modern cosmetics are distinguished by rich, bright aromas. Peach, violet, rose, strawberry, raspberry—our shampoos, lotions, creams, and lip glosses smell like a real blooming garden. In most cases, no flowers or berries were harmed in the creation of these violet and raspberry scents. These are all artificial flavors, and often more of them are added - not only to increase the pleasure of using such cosmetics, but also to hide the not-so-pleasant smell of the raw materials.
Unfortunately, very often such artificial fragrances cause allergies. However, you should also be careful with natural flavors: essential oils, even high-quality ones (they are used to give the product a particular aroma), can easily cause allergies. This is especially true for citrus and bergamot oils.
What to do if your skin reacts to cosmetics
If any component of cosmetics does cause an undesirable skin reaction in you, then the first thing to do is stop using this product and wash it off your skin
. After this, you should check the instructions and check the expiration dates. If you did everything correctly and the cosmetics are not expired, act according to the situation:
- Watch the dynamics. If the reaction begins to subside within an hour, it is enough not to use the product anymore.
- Take your usual antihistamine (Suprastin, Fenistil, etc.)
- If symptoms persist, consult your doctor
.
What to do next?
The first desire after purchasing unsuitable cosmetics is to return it to the store and receive compensation from the manufacturer. However, according to the consumer protection law, cosmetics are included in the list of products that cannot be returned or exchanged
(see Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated January 19, 1998 No. 55
“On approval of the Rules for the sale of certain types of goods...”
). You can get your money back only in one case: if the cosmetics you bought turned out to be of poor quality. Keep in mind: an individual allergic reaction does not prove that the product is defective.
Therefore, it is better to offer the remedy to someone else, explaining the situation honestly. Place ads on special services, in thematic groups on social networks, or share an unsuitable product with family or friends.
As for further purchases, do not rush to give up shopping! If a rash occurs with one cream, this does not mean that the same reaction will occur with another. Try to establish which component triggered the allergy.
. An allergist can help with this by prescribing the necessary tests. In the future, just avoid products containing this ingredient.
Akriderm preparations for dermatoses
Akriderm ointments and creams are combination preparations that contain several active substances at once, which provide comprehensive treatment for dermatitis of allergic and non-allergic nature. They provide:
- antipruritic effect;
- anti-inflammatory effect;
- antiallergic effect;
- vasoconstrictor effect.[6]
This therapeutic effect was achieved thanks to a thoughtful combination of glucocorticosteroids with broad-spectrum antibiotics and antifungal components. Akriderm ointments and creams not only fight redness, itching and swelling, but also protect the skin from bacterial and fungal infections.
In the fight against contact dermatitis (simple and allergic), it is advisable to use the following Akriderm preparations:
- Akriderm SK ointment contains salicylic acid, due to which it acts quickly and has a favorable safety profile.
- Akriderm GENTA ointment is used for chronic skin pathologies, in particular those complicated by secondary infection.
- Ointment or cream "Akriderm GK" - used for acute and chronic inflammation to suppress unpleasant symptoms
- Ointment or cream "Akriderm" - thanks to the thoughtful concentration of active substances, can also be used for children over 1 year of age.[7]
links to sources
- Contact dermatitis - Clinical guidelines, Russian Society of Dermatovenereologists and Cosmetologists, 2022.
- Dikovitskaya I.G., Korsunskaya I.M., Nevozinskaya Z. Contact dermatitis: clinical picture and therapy // Sovrem. problems of dermatovenerology, immunology and medicine. cosmetology. 2010. T. 4. No. 4. pp. 49–51.
- Stepanova E.V. Allergic contact dermatitis: basic approaches to diagnosis, treatment and prevention // Attending physician. - 2009. - No. 10. - P. 15-19.
- Mercedes E. Gonzalez, “Contact dermatitis” MD, University of Miami Miller School of Medicine.
- Batyrshina S.V. Glucocorticosteroids for local use in the modern strategy for the treatment of inflammatory dermatoses in pediatric practice // Practical Medicine, 2014. No. 9 (85). pp. 94–102.
- Federal clinical guidelines. Dermatovenereology 2015: Skin diseases. Sexually transmitted infections. – 5th ed., revised. and additional – M.: Business Express, 2016. – 768 p. 3. Instructions for use of the medicinal product for medical use Akriderm®. No. Reg. beat LS-002317, R N000663/01.
- Instructions for medical use Akriderm®
How we take care of our clients
pays close attention to cosmetic ingredients. We use components from trusted laboratories that have the necessary safety and quality certificates. Before release, our products are tested in laboratories. For your convenience, we place detailed information about the composition and features of the use of our products on the packaging and in product cards in the official online store aravia.ru.
In case of an undesirable skin reaction to the product, we ask you to send us an email
- photos of skin reactions;
- photographs of the product so that the batch number is visible;
- a detailed story about exactly how you used the product;
- additional contacts for prompt communication.
We will then be able to help you and determine the possible cause of the reaction, and decide as quickly as possible how to proceed.
Understanding the types of analyzes
Modern medicine offers the following types of diagnostics:
- in vivo - tests that are carried out by introducing the suspected allergen into the body's tissues. The most common is the skin test. The irritant is injected under the skin, after which the doctor observes the patient’s reaction;
- in vitro – analysis of biological material with its further study. Allergens react with blood serum, are the safest, are intended for people of any age category, and present a complete picture of the presence of allergies and the degree of its severity.
Types of allergens
For an allergic reaction to develop, the body must encounter an antigen, that is, a foreign substance. The immune system recognizes it and begins to fight. Usually there is an increased sensitivity of individuals to: • plant pollen; • pet hair; • food products; • dust mite excrement; • mold; • household chemicals; • insect poison; • latex; • medications. Food allergens are noteworthy in that not only antihistamines, but also enterosorbents (activated carbon, Polysorb, Enterodes) help neutralize their effect, and for respiratory reactions, vasoconstrictor drugs (like Allergodil or Polydex) are important. Defining a group is relatively simple: it is not difficult for a person to compare the appearance of unpleasant symptoms with specific conditions. It is more difficult to understand which substance causes hypersensitivity. This will require a blood test.
Third generation drugs
If you have an allergy, you should always have antihistamines in your home medicine cabinet.
Officially, third-generation drugs have not yet been developed, however, unofficially, improved second-generation drugs are included in this group. This group is characterized by a rapid onset of action and high efficiency. The drugs have fewer side effects. Individual intolerance is possible. They can be used both to relieve allergy symptoms and for long-term treatment of the disease. They do not affect heart rate. The best third-generation drugs include Cetrin, Erius, Xizal, and Fexofen.
- Cetrin. Available in the form of tablets (contraindicated in children under 6 years of age) and in the form of syrup (contraindicated in children under 2 years of age). The effect lasts up to 24 hours. Effective in the development of edema. Syrup as part of complex therapy relieves spasms in bronchial asthma. It has virtually no contraindications. Should be used with caution in elderly people.
- Erius. Available in the form of tablets (contraindicated in children under 12 years of age) and syrup (contraindicated in children under 1 year of age). It works almost immediately. Duration of action is up to 24 hours. Relieves and prevents the development of allergy symptoms. Should be taken with caution in case of renal failure
- Xizal (Zodak). Available in the form of tablets and drops. Has an anti-inflammatory effect. Quickly eliminates itching, swelling and redness. The effect of the drug is observed for up to 2 days. Contraindicated in renal failure. Not suitable for use by children under 6 years of age.
- Fexofen (Allegra, Fexofast). Effectively eliminates allergy symptoms, especially with seasonal rhinitis. The effect lasts for 12 hours. Can be used as prophylaxis. Not suitable for use by children under 12 years of age.
Features of skin tests
• Direct allergy tests - are done to diagnose diseases that develop due to hypersensitivity to a certain substance. In this study, allergens and the skin are in close contact: an application, a scarification test, and a prick test are performed. • Indirect skin testing is a testing method designed to detect an allergic irritant. First, the irritant is injected under the skin, then blood is taken from a vein to determine the level of antibodies. Allergens are identified after contact with the skin.
The following groups of allergenic irritants are used: 1) herbal (weeds, meadows); 2) household (presence of dust, chemicals); 3) pollen (seasonal irritant); 4) fungal; 5) animal origin (wool).
• For medications – must be carried out in a laboratory, since the examination uses the patient’s biological material (blood, saliva and others). The results of studies conducted in laboratories are the most informative; they directly depend on the medications taken and the stage of the allergic reaction.
• For urticaria – different types of studies are used: 1) blood test; 2) a smear of the mucous membrane of the nose and throat; 3) analysis of intestinal and stomach microflora; 4) the thyroid gland is examined; 5) identification of the allergen. • Provocative tests - used if information from other methods is insufficient or in case of false (positive or negative) test results. This method helps make a more accurate diagnosis when previous test results and symptoms do not match. A mandatory requirement for the test is that it be carried out in a hospital setting, since there is a high risk of a reaction occurring that requires urgent medical intervention. The allergenic solution is injected into the organ in which the strongest reaction is expected.
Commonly used types of tests: 1) Conjunctival - injected directly into the mucous membrane, a reaction is observed - redness of the eyes, lacrimation. 2) Nasal - injected into the nasal passages, a positive result in the form of difficulty breathing, sneezing, swelling. 3) Inhalation – used using an inhaler, observation is carried out over the bronchi and lungs. Difficulty breathing with whistling, wheezing indicate a positive reaction of the body. 4) Cold - allows you to detect the presence of urticaria by applying ice or cold to the forearm. The appearance of redness and blisters indicates a positive result. 5) Heat urticaria - hot water is applied to the forearm for no more than 10 minutes. 6) Food – the allergen is consumed in food. It is carried out in a hospital setting to provide timely medical care. 7) Exposure - the patient is placed in conditions under which the allergy appeared.
First generation drugs
1st generation antihistamines are able to penetrate the nervous system. This helps to quickly eliminate allergy symptoms. However, their effect does not last long, and with long-term use of drugs of this group, addiction may occur. The most common side effects of 1st generation antihistamines are drowsiness, weakness, headache, dizziness and slow reactions. Despite significant disadvantages, these drugs are low in cost and, unlike modern drugs, are available in both tablet and injection form, which allows them to be used for emergency care. Not intended for long-term treatment. In this group there are 4 most effective drugs: diphenhydramine, diazolin, suprastin and tavegil.
- Diphenhydramine. One of the very first antihistamines. Dispensed strictly according to prescription. Used in emergency situations. Not suitable for children.
- Diazolin. Does not cause significant drowsiness. Can be used for prevention purposes. Suitable for use by both children and adults. Longer lasting effect. Ineffective for severe allergic reactions.
- Suprastin. Does not cause significant drowsiness. A rapid therapeutic effect and, compared to other drugs in this group, there are fewer side effects. Has a wider range of indications. Can be used by both adults and children. Not recommended for use in bronchial asthma.
- Tavegil. Used as a treatment for both allergic and pseudoallergic reactions. Does not cause significant drowsiness. Effectively relieves allergy symptoms, especially during the flowering period. Effective for 8 hours (the longest effect from the group of first-generation drugs).
Types of hypersensitivity
The Jell and Coombs classification has been used in medicine since 1969. It shows that the mechanisms of development of allergic reactions are different.
Type I (anaphylactic) . Marker - Immunoglobulin E. Development time - from several minutes to one hour. Examples: rhinitis, conjunctivitis, asthma, Quincke's edema, urticaria, anaphylactic shock.
Type II (cytotoxic). Marker - IgM and IgG antibodies. Development time is several hours. Examples: autoimmune hemolytic anemia, transplant rejection, Rh conflict.
Type III (immune complex). Marker - Fixed immune complexes. Development time is from several hours to several days. Examples: serum sickness, rheumatoid arthritis, hypersensitivity pneumonitis, Arthus phenomenon.
Type IV (slow). Marker - T-lymphocytes. Development time - several days Examples: contact dermatitis, food gastroenteropathy, immune response to tuberculin, drug hypersensitivity.
Allergens directly cause reactions of the first or fourth type. These are usually low molecular weight proteins that, when ingested, trigger the release of immunoglobulin E or the activation of T cells.
Diagnosis of allergic diseases
Laboratory diagnostics will help identify the specific substance that causes hypersensitivity. Collecting anamnesis only helps the doctor understand in which direction to search.
Hundreds of allergens are known to medicine. Taking an analysis for each is very time-consuming and expensive, so the group of stimuli is determined by the survey method. For example, a patient notices that in spring and summer his runny nose does not go away and his eyes water. The doctor realizes that he has a pollen allergy. By comparing the periods of symptoms and the dusting calendar, you can further narrow the search area: • end of March - shrubs; • end of April - deciduous trees; • mid-May – coniferous trees, cereal grasses, dandelions; • end of June - linden, buckwheat; • from July to autumn - nettles, weeds. But the final answer to the question of which plant causes an acute immune reaction is given only by blood tests and skin tests.