Human skin color depends on melanin, a pigment produced by melanocytes - cells that lie mainly under the basement membrane. The natural color of not only our skin, but also our hair and eyes depends on the amount of melanin.
The main factor stimulating increased melanin production and the formation of pigmentation is ultraviolet radiation. By and large, this is the skin’s response to the sun’s rays - it produces more melanin for protection purposes.
But it’s one thing when the pigmentation is represented by an even, beautiful tan, the so-called physiological pigmentation, and another when the uniformity is spoiled by the appearance of elements of a different color on the skin. Where are they from?
Hyperpigmentation is excessive coloring of certain areas of the skin. This is a kind of violation, and why it occurs is a question. The reasons may be harmless. For example, this is a congenital anomaly that manifests itself in a certain area of the skin and does not cause trouble to its owner.
The most common example of an increased concentration of pigments is the already mentioned elphids.
Disruption of melanin production is also possible due to hormonal changes. For example, during pregnancy we often observe the development of so-called chloasma. The same elements may appear when taking contraceptives. After childbirth, the spots disappear on their own.
Age-related pigmentation may be associated with changes in hormonal levels. If in youth melanin is distributed evenly, then after 30 years, when the antioxidant protective properties of the skin decrease and antitumor immunity falls, there may be more of it in one place and less in another.
Skin defects must be treated from the inside
But still, don’t forget about the sun. It ages the skin and increases the risk of melanoma. It also leads to the appearance of unsightly age spots, which are most often associated with old age and unkemptness.
Sun marks on the skin are not only aesthetically unattractive, but also indicate problems in the body. And although pigment spots themselves are not considered a disease, they are a signal that something has gone wrong somewhere inside.
One of the most likely reasons for their appearance is hormonal disorders. For example, thyroid diseases, genital dysfunction, even pregnancy. In addition, hyperpigmentosis can be a symptom of a gynecological disease (primarily endometriosis).
According to dermatovenereologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences Maria Shirshakova, an experienced cosmetologist refers women who complain about pigment spots first of all to a gynecologist to rule out possible health problems. After all, any defects on the skin must be treated from the inside.
However, there may be other reasons for the appearance of “sun marks”. For example, some fungal diseases cause such a reaction on the skin. Or, for example, liver pathology (and in this case, alas, you need to prepare for long-term treatment). Acupuncturists always pay attention to the places where age spots appear, noting that they can be used to determine which specific organ is at risk.
Treatment with antibacterial drugs (especially from the tetracycline family) sometimes leads to the appearance of hyperpigmentation. In addition, the skin may react with unsightly brown spots to too intense cosmetic treatments (especially aggressive chemical peels or skin cleansing).
Allergy to the sun - photodermatitis (photodermatosis) and its prevention
The sun's rays not only warm us with their warmth in spring and summer and make us happy in winter, but also help strengthen our immune system. But, unfortunately, exposure to the open sun can cause an allergic reaction in some people.
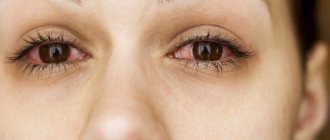
Sun allergy, photodermatitis (photodermatosis) are diseases caused by increased sensitivity of the skin to sunlight. This is not at all a rare occurrence. Statistics show that about 20% of people worldwide experience this disease.
Sun allergy actually refers to photodermatitis or photodermatosis. The toxic or allergic effect of the sun occurs when the sun's (ultraviolet) rays interact with any substance located on the skin (exogenous photodermatitis) or in the skin (endogenous photodermatitis).
Allergy to the sun in the form of exogenous photodermatitis
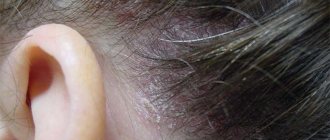
The most striking example of exogenous photodermatitis is the so-called meadow dermatitis. In summer, during the flowering period, many meadow plants secrete special substances - furocoumarins, which settle on the skin when a person is in these places. With simultaneous exposure to ultraviolet radiation, some sensitive people may experience skin redness and blisters (erythema, vesicles, bullae). The rash is accompanied by severe itching. Subsequently, long-term pigmentation remains on the affected areas of the skin.
An allergy to the sun or photodermatitis can also occur if, before going out into the sun, a person sensitive to it applied cream or ointment, or used perfume and deodorant. Substances contained in various cosmetics or perfumes can react with ultraviolet rays and cause an allergic reaction. Such properties are possessed, for example, by eosin, which can be contained in lipstick, and para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA), which is part of some sunscreens. In addition, polyunsaturated fatty acids, retinoids, bergamot oil, St. John's wort, rose, musk, sandalwood, dill juice, parsley, boric acid, salicylic acid, phenol, and mercury preparations have a similar effect.
More often than others, people with fair skin and young children, whose skin defense mechanisms are much weaker, suffer from sun allergies.
Photodermatitis is often caused by many medications. This effect is exerted, in particular, by sulfonamides, barbiturates, aminazine, some antibiotics (doxycycline, tetracycline), antihistamines, some cardiovascular drugs (amiodarone, Trazicor), cytostatics, some non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (ibuprofen, aspirin), and oral contraceptives.
In addition, an increased reaction of the skin to the sun's rays appears when the skin is “weakened” by some additional influence - peeling, tattooing using cadmium salts.
Allergy to the sun in the form of endogenous photodermatitis
This group of photodermatitis includes quite rare diseases, in the development of which disturbances in the functioning of the body’s immune system, as well as various metabolic disorders (metabolic disorders), play an important role. Endogenous photodermatitis includes, in particular, porphyria, xeroderma pigmentosum, solar eczema, solar prurigo, Hydroa vacciniformia, polymorphic photodermatosis.
Typically, these reactions can occur by two mechanisms: 1) a phototoxic reaction and 2) a photoallergic reaction. Phototoxic reactions are much more common than photoallergic reactions.
How does sun allergy or photodermatitis usually manifest?
The main symptoms of photodermatosis:
- redness and inflammation of the skin,
- peeling of the skin,
- often accompanied by intense itching and burning,
- rashes can be in the form of folliculitis (pustules) or papules.
Often this condition does not develop immediately. Unlike a burn, it can occur several hours after you leave the beach, and in some cases even after returning from the resort. A phototoxic reaction can occur within a few hours of sun exposure, while a photoallergic reaction can occur even days after sun exposure.
Increased risk of developing sun allergies:
- in people with naturally light skin;
- in pregnant women;
- in young children;
- a number of medications can make skin burns faster - these include tetracycline antibiotics, sulfa drugs, painkillers, etc.;
- who has relatives with sun allergies. There is a greater chance of having a sun allergy if you have a sibling or parent with a sun allergy;
- also, the presence of atopic dermatitis or another type of dermatitis increases the risk of developing an allergy to the sun;
- Some skin allergy symptoms are triggered when your skin is exposed to a certain substance and then sunlight. Some common substances responsible for this type of reaction include fragrances, disinfectants, bleach, and even some chemicals used in sunscreens;
- those who abuse tanning beds;
- In addition, an allergic reaction from exposure to the sun can also develop in those who the day before performed cosmetic procedures using cadmium salts (tattooing, chemical peeling).
Photosensitizers are the cause of sun allergies
Some vegetables and plants can cause sun sensitivity when they come into contact with the skin. Mango peels, lime juice, parsnips, and celery may cause temporary discoloration (darkening) of the area of skin exposed to the sun. The main phototoxic fruits and vegetables: celery, carrots, rice, parsley, parsnips, and all types of citrus fruits. Therefore, before going to the beach, you should not eat oranges, tangerines or grapefruits. Swelling, redness and itching may occur on the surface of the skin where drops of juice from these fruits remain. And the more active the sun is, the more acute the body’s reaction will be.
Prevention of sun allergies (photodermatitis and photodermatosis)
Unfortunately, there are not many methods for preventing such allergies.
If you have very sensitive skin, make it a rule to sunbathe under a tent or umbrella. Avoid exposure to the sun during peak sun hours (11:00 a.m. to 4:00 p.m.). Protect yourself with a hat and loose clothing made from natural fabrics: linen, cotton. Children have a very weak protective skin reaction, so children under three years old are generally not recommended to be in direct sunlight.
Use sunscreens with high photoprotection from well-known brands, and regularly, at least every two hours. Please note that the cream contains protection against UVB rays (SPF) and UVA rays (PPD) - they are the ones that affect the occurrence of photodermatosis.
It should be noted that wavelength plays an important role. Try not to go to resorts where the sun is especially active.
Recommendations for preventing photoallergy on the beach:
- Before going to the beach, you should not use cologne, perfume or regular moisturizers. They contain alcohol, which can cause sunburn in the sun.
- In your case, you need to use sunscreen as often as possible. Just pay attention to its composition. Fat-based products can cause allergies. It is better to choose a hypoallergenic spray with a protective SPF factor.
- It is better not to use waterproof sunscreen - it clogs the pores, as a result of which ulcers may appear on the skin. When going to the beach, you should opt for a water-soluble product.
If it is not possible to see a doctor, how to relieve acute manifestations of sun allergy?
No way. Only a doctor will be able to understand: the manifestations on the skin relate to phototoxic reactions or are they a manifestation of another disease. Often, “folk” methods only aggravate the course of toxic and allergic reactions.
Sun marks - hyperpigmentation
We have figured out the underlying causes of hyperpigmentation. But the main provocateur for the appearance of such spots is sunlight. They cause increased production by the body of cells that are responsible for skin coloring, injecting melanin pigment into it. In fact, its main task is to protect the skin from harmful UV rays. But when there is an excess of it, its protective functions are reduced. Therefore, cosmetologists never tire of repeating how important it is to use sunscreen, especially for fair-skinned and red-haired people. At the same time, it is better for Russians to buy creams or sprays with an SPF of at least 30. But many rely on chance and neglect them and like to sunbathe until black.
Any hyperpigmentation provokes early skin aging and the appearance of deep wrinkles. But this is not even the worst thing - in some cases, pigment spots can degenerate into melanoma.
Main reasons
Despite the existence of the term “sun allergy,” sunlight itself is not an allergen. On the contrary, sunlight in safe quantities has a beneficial effect on the human body - it improves mood, promotes the absorption of vitamin D, and stimulates the immune system. Only when the ultraviolet component of sunlight interacts with any substance located on or in the skin do compounds with antigenic properties appear. It is these compounds, not the sun's rays, that cause sun allergy symptoms. Doctors call this disease “photodermatitis.”
Typically, photodermatitis can occur during periods when a person is exposed to significant sun exposure by spending a lot of time outdoors, that is, in the spring and summer. But this disease can also be provoked in winter: after all, some begin preparing for the beach season in advance by visiting a solarium, while others go to the south or to tropical countries for additional sun during the cold season. Therefore, sun allergy has become a year-round disease for many.
What to do to prevent age spots from appearing
Prevention scheme:
Antioxidant preparations
Why we shouldn’t forget about the effects of free radicals: pigment cells also react to their excess by increasing melanin production.
Causes of excess free radicals:
- age over 30-35 years
- solar radiation
- bad ecology
- dietary violations, etc.
Residents of megacities and hot sunny regions experience a special load of free radicals, and therefore their own antioxidant defense system is depleted ahead of time and cannot cope.
Lightening agents
Starting in early spring, the use of agents that normalize and balance the work of melanocytes. These are non-aggressive lightening agents that do not thin the skin or increase sensitivity.
Example: DermaQuest SkinBright lightening line is designed specifically to work with pigmentation of any severity. Combined formulations and the absence of aggressive and dangerous ingredients make therapy not only effective, but also comfortable.
DermaQuest SkinBright serum and cream are a combination that enhances each other’s effectiveness. Advantages:
- rich composition of safe brightening ingredients
- do not require additional skin care products
- moisturize, nourish, have an antioxidant effect
- prevention of age-related changes
Contains:
- Stem cells of Lily Snow White
- Melanostatin-5 (brightening peptide)
- Chromebright
- Bakuchiol A (Vitimon A simulator without the irritating effects of retinoids)
- Hexylresorcinol – 4 times more active than hydroquinone in lightening effect
- Emblica – plant extract
- Kojic acid dipalmitate
- Bearberry, licorice root and white mulberry extract
- Arbutin
- SkinBright preparations do not contain Hydroquinone!
They do not have an irritating effect, have a moisturizing and nourishing effect, making them a complete treatment used morning and evening for the entire face.
There is no need for local application and the purchase of additional care products!
Treating sun spots
Before you begin to treat stains, you need to find out the source of their appearance.
If it is tinea versicolor, then it is better to get rid of this disease in advance by using medications recommended by your doctor.
If it is vitiligo, then you also need to visit a doctor who will prescribe a full examination of the body. But since there is no complete confidence in the treatment of this skin defect, you can resort to folk remedies. They will help make white spots after tanning more invisible. But this is usually a temporary effect.
The easiest way to get rid of stains is those associated with excessive sweating or taking medications. To do this, it is enough to use special means or replace medications with their analogues.
If there are no particular reasons to worry about the appearance of spots after tanning, you can get rid of them with your own means. For example, take hot baths using a washcloth with stiff bristles. This will help exfoliate the top layer of the skin, which after a while will lead to an even tan. This can be facilitated by scrubs purchased in a store or made by yourself.
When treating pigment spots after sunbathing, you should use more serious means, such as special whitening creams, which should be used as prescribed by a doctor.
Use extreme caution when using products containing mercury. Since this element has toxic properties, it should not be used by pregnant women or those suffering from kidney or liver disease.
In the beginning, when using such creams, in order to avoid severe irritation, you should not wash your face with water, cleansing your face with special cleansers. As an alternative to products containing mercury, you can use creams containing salicylic alcohol, perhydrol or lactic acid.
To get rid of sun spots, beauty salons will offer chemical and ultrasound peeling and laser therapy.
Dark spots after sunburn
Dark spots are caused by prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation on the skin, which results in burns. It may appear as reddened skin or appear as blisters. These phenomena are accompanied by headache and nausea, which disappear after some time.
KK Adapt. 5 paragraph
Sometimes dark spots against tanned skin appear due to diseases of the internal organs - liver, thyroid gland. Before sunbathing, you should not use perfume, take antibiotics or sedatives and hormonal medications.
Doctor, is this forever?
Treatment of sun allergies involves eliminating exposure to ultraviolet radiation. In the case of solar urticaria, antihistamines help, and there are special medications that thicken the skin and reduce its sensitivity to sunlight. Treatment in this case consists of gradually accustoming the skin to the sun while taking medication.
To relieve exacerbation of photodermatitis, local treatment is prescribed in the form of ointments, sometimes hormonal, and internal treatment: vitamins B, E, C, nicotinic acid, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory and antihistamines. Usually the course of treatment continues for several days or weeks. During this time, it is recommended to spend less time in the sun, wear a wide-brimmed hat, clothes with sleeves and sunglasses.
If sun allergy is left untreated, repeated episodes will lead to the development of photodermatosis. When you have managed to stop the allergy attack by carefully taking care of protecting your skin, eliminating provoking factors and strictly following the sunbathing regime, you have the opportunity to bask in the gentle rays. Sun allergies can be controlled and prevented, and children may even outgrow this disease.
medkrug.ru