Non-invasive carboxytherapy is a technique for restoring intracellular respiration of the skin! It is a non-injection transdermal injection of carbon dioxide under the skin. A special product is applied to the skin, which contains carbon dioxide molecules obtained by mixing certain ingredients.
With age, skin trophism deteriorates significantly, vascular tone and, accordingly, oxygen saturation of tissues decrease.
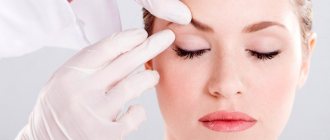
The program includes the use of the original mask. The main component of this mask is carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide is formed as a result of mixing the components of the active mask: granules and gel. Molecular CO2 very quickly penetrates the epidermis of the skin and reaches the blood vessels, due to which there is an instant dilation of blood vessels, increased blood circulation, and an influx of oxygen and nutrients to the skin cells. This process stimulates collagen production, which provides a natural face lift (lifting), improving the color and appearance of the skin.
Service information
Non-invasive carboxytherapy is an effective method of combating age-related changes in the skin.
Cosmetologists apply a special mask to the facial skin, saturating the tissue with carbon dioxide. The subsequent release of oxygen by the cells causes the positive effects of the procedure, including improved blood supply and epithelial renewal. Carboxytherapy is most often used in the facial area, but sometimes specialists perform similar therapy to treat cellulite. Unlike the injection method of introducing carbon dioxide, non-invasive carboxytherapy can be carried out on an ongoing basis. Adverse factors directly affect the chemical composition of tissues. A lack of oxygen in the skin is observed with constant exposure to cold, vascular diseases and age-related changes. As a result, the skin becomes flabby and bags appear under the eyes. Also, weakened blood flow causes a decrease in local immunity, so many women with this problem suffer from chronic inflammatory ailments. Seeing a cosmetologist will help improve your skin condition.
Non-invasive carboxytherapy ECO2 GEL THERAPY NeoChemir
NeoChemir was founded in May 2001. The company's headquarters are located in Japan in Minato-ku District, Kobe.
NeoChemir works closely with five departments at Kobe and Osaka Research Universities.
One of the main achievements of the company's research department was the development of DDS technology for transporting therapeutic substances using hydrogels and non-invasive carboxytherapy eCO2-Gel Therapy.
This carboxytherapy system is the only one in the world and has a huge evidence base - numerous officially registered research works, tests and experiments.
This is a patented and only system in the world for delivering CO2 to tissue to a depth of 2 to 7 cm.
This brand is the result of numerous studies and experiments, during which it was revealed not only the therapeutic effect of CO2 on healing processes, but also amazing results when the CO2 system is exposed directly to the skin.
Skin covering
The main area of effect of carboxytherapy is the skin. This superficial organ is necessary for humans to protect against adverse external factors, form vitamin D, maintain metabolism and store blood. Healthy skin preserves the beauty of the face and prevents the development of diseases. Unfortunately, many pathologies of internal organs and external influences worsen the condition of the integumentary tissues.
Departments of the organ:
- The epidermis is the most superficial part of the organ, consisting of several layers of epithelium. The horny cells of the epidermis protect the body from bacteria, viruses, harmful substances and physical influences. The inner layers of cells ensure constant renewal of the keratinized epithelium.
- The dermis is the middle part of the organ in which active metabolic processes occur. Important structures of the dermis include hair follicles, nerve fibers, blood vessels, sweat and sebaceous glands.
- Subcutaneous tissue is the deepest part of the organ. First of all, this is a reserve of adipose tissue. The body can use fat to replenish energy and fluid deficits. In addition, subcutaneous tissue protects the body from hypothermia. Excessive amount of adipose tissue is observed with metabolic disorders.
Proper skin care helps eliminate vascular and metabolic pathologies. As we grow older, the amount of elastin and collagen in the surface tissues decreases, causing the skin to become loose. Another problem is insufficient oxygen supply to the epithelium. Women often do not notice the progressive deterioration of their skin until complications arise. Carboxytherapy makes it possible to eliminate negative changes even in advanced cases.
This unique system runs:
- Processes of activation of intracellular respiration;
- Increases the energy potential of the cell and its level of viability;
- Energy and information exchange (signal peptides) between cells;
- Launches the system of “exploding” the smallest sclerotic capillaries of the cell, ensuring a high level of trophism of skin cells on all, including the highest layers of the skin;
- Improves blood rheology and optimal blood supply to tissues;
- Increases the strength of smooth and transverse muscles several times;
- Powerful anti-inflammatory, antiseptic and antioxidant effects.
Mechanism of action
The blood vessels of the skin contain a large number of red blood cells containing hemoglobin. This protein carries oxygen to tissues and removes carbon dioxide from the body. At the same time, a metabolic stimulus is required to release oxygen from red blood cells. Blood cells must receive a signal indicating a lack of this substance in the skin. Using masks containing carbon dioxide helps release oxygen from red blood cells.
After applying the mask to the skin, carbon dioxide is quickly absorbed into the epithelium. An increase in carbon dioxide levels in tissues leads to a response from the blood vessels. As a result, the hemoglobin of red blood cells releases oxygen and binds to carbon dioxide molecules. Vasodilation leads to additional changes in the organ and improves cell nutrition.
Invasive ventilation
An endotracheal tube is inserted into the trachea through the mouth or nose and connected to a ventilator.
With invasive respiratory support, the ventilator provides forced pumping of oxygen to the lungs and completely takes over the breathing function. The gas mixture is supplied through an endotracheal tube placed into the trachea through the mouth or nose. In particularly critical cases, tracheostomy is performed - a surgical operation to dissect the anterior wall of the trachea to insert a tracheostomy tube directly into its lumen.
Invasive ventilation is highly effective, but is used only if it is impossible to help the patient in a more gentle way, i.e. without invasive intervention.
Who needs invasive ventilation and when?
A person connected to a ventilator can neither speak nor eat. Intubation is not only inconvenient, but also painful. Because of this, the patient is usually placed in a medically induced coma. The procedure is carried out only in a hospital setting under the supervision of specialists.
Invasive ventilation is highly effective, but intubation involves placing the patient in a medically induced coma. In addition, the procedure is associated with risks.
Traditionally, invasive respiratory support is used in the following cases:
- lack of effect or intolerance of NIV in the patient;
- increased drooling or production of excessive sputum;
- emergency hospitalization and the need for immediate intubation;
- coma or impaired consciousness;
- possibility of respiratory arrest;
- presence of trauma and/or burns to the face.
How does an invasive ventilator work?
The operating principle of devices for invasive ventilation can be described as follows.
- For short-term mechanical ventilation, an endotracheal tube is inserted into the patient's trachea through the mouth or nose. For long-term mechanical ventilation, an incision is made in the patient's neck, the anterior wall of the trachea is dissected, and a tracheostomy tube is placed directly into its lumen.
- A breathing mixture is delivered through a tube into the lungs. The risk of air leakage is minimized, so the patient is guaranteed to receive the right amount of oxygen.
- The patient's condition can be monitored using monitors that display breathing parameters, the volume of supplied air mixture, saturation, cardiac activity, and other data.
Features of equipment for invasive ventilation
Equipment for invasive ventilation has a number of characteristic features.
- Completely takes over the breathing function, i.e. actually breathes instead of the patient.
- It requires regular checking of the serviceability of all valves, because... The patient’s life depends on the performance of the system.
- The procedure must be supervised by a doctor. Weaning the patient from the ventilator also requires the participation of a specialist.
- Used with additional accessories - humidifiers, cough cleaners, spare circuits, suction units, etc.
Positive effects
Carboxytherapy is a safe method of rejuvenating the skin of the face, neck, hips and other parts of the body. Violation of the integrity of the skin is not a side effect of the procedure, since cosmetologists use topical products instead of needles. Many of the positive properties of this therapy are not immediately noticeable, but within a few hours after applying the mask, a woman can see results.
Key effects:
- Restoration of blood flow in the surface epithelium. As a result, the stratum corneum begins to renew itself faster.
- Strengthening oxidative processes in cells. The additional amount of energy required by tissues to perform important functions is released.
- Stimulation of synthetic processes. The cells produce more protein, which is necessary to maintain the strength and elasticity of the skin.
- Cleansing. Dilated vessels remove harmful metabolic products from the epithelium.
The oxygen saturation technique is useful for any skin type. A consultation with a cosmetologist in Moscow will help the patient clarify the conditions of the procedure and prices. You can read reviews in advance on the Internet.
Patient A., 49 years old, was admitted to the Federal State Budgetary Institution "National Medical Research Center of Cardiology" of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation COVID-19 Center with complaints of cough with difficult sputum, shortness of breath, shortness of breath, chest pain, headache and fever up to 39.4 o C , SpO2 93-94% in atmospheric air. The patient had a positive nasopharyngeal swab for SARS-CoV-2.
Over the course of several days, the patient's symptoms of respiratory failure increased; according to computed tomography, the percentage of lung damage increased to 90% (CT-4).
The patient was on antibacterial therapy, anticoagulant therapy, specific therapy: hydroxychloroquine, azithromycin, lopinavir-ritonavir. Subsequently, due to the development of a cytokine storm, the patient was administered tocilizumab.
Considering the increasing severity of the condition, with insufficient effectiveness of respiratory support (NPV up to 40/min, SpO2 - 90% per 13 l/min of oxygen through a nasal cannula), the patient underwent escalation of respiratory support using non-invasive pulmonary ventilation (NIV) using a device for the treatment of breathing disorders during sleep, by creating positive pressure in the airways with a ventilated oronasal mask. The device was configured in CPAP (continuous positive airway pressure) mode: constant positive pressure at 10-12 cmH2O with 5-10 l/min of oxygen connected to the circuit. To reduce the risk of aerosolization, the device was used without a humidifier, with the autostart function turned off; for the same purpose, the original insulation of the exhalation valve of the oral-nasal mask was used for the first time by double wrapping it with a medical surgical mask.
Against the background of NIV with oxygen support (up to 12 l/min): there was an improvement in the condition, a decrease in shortness of breath, a feeling of congestion in the chest, a gradual decrease in respiratory rate to 24-28/min, stabilization of SpO2 - 94-96%. The patient subjectively tolerated this type of therapy well, breathing was synchronized with the device, and no additional medications were required to reduce agitation.
The patient stayed in the intensive care unit for 6 days and subsequently, given the stabilization of the clinical condition - there was no need for respiratory support using CPAP therapy, the patient was transferred to the department.
During the control CT study: pronounced positive dynamics in the form of partial resolution of viral pneumonia, new areas of infiltration in the lung parenchyma are not detected. Moderate to severe degree, the percentage of lung tissue damage is 50-60% (CT2).
Considering the stabilization of the condition, the absence of signs of respiratory failure and good health, the patient was discharged from the hospital.
During CPAP therapy, doctors and medical personnel used the following protective equipment: FFP3 respirator, goggles, face shield, waterproof personal protective suit, gloves (2-3 pairs). During the patient’s use of CPAP therapy and for 14 days after, not a single employee fell ill, and no positive nasopharyngeal smears for SARS-CoV-2 were recorded.
After discharge, the patient expressed his gratitude to the entire team of the National Medical Research Center of Cardiology.
The full clinical case is planned for publication in the journal “Anesthesiology and Reanimatology”; a link to the issue will be posted on the website.
The case was provided by Alexander Yurievich Litvin and Evgenia Mikhailovna Elfimova.
Carrying out
Non-invasive carboxytherapy is carried out in beauty salons and medical centers. Before starting the procedure, the specialist assesses the condition of the patient’s skin and specifies which dermatological ailments need to be eliminated.
Stages of implementation:
- Remove makeup, sebum and impurities using lotion or gel.
- Steaming the integumentary tissue to expand the pores.
- Applying the mask using a spatula.
- Waiting for the mask effect. All carbon dioxide penetrates the epithelium in about 20-25 minutes.
- Removing the mask and treating the skin with a soothing ointment.
Immediately after the procedure, redness or swelling of the skin may develop, but after a few hours all side effects go away on their own.
Indications for artificial ventilation of the lungs
Artificial ventilation is performed for acute or chronic respiratory failure caused by the following diseases or conditions:
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD);
- cystic fibrosis;
- pneumonia;
- cardiogenic pulmonary edema;
- restrictive lung pathologies;
- lateral amyotrophic syndrome;
- obesity-hypoventilation syndrome;
- kyphoscoliosis;
- chest injuries;
- respiratory failure in the postoperative period;
- respiratory disorders during sleep, etc.
Carboxypil procedure protocol
Stage 1. Cleansing
Cleansing
Cotton Clean Cleansing Milk and Toner
(northern cotton and chamomile extracts, Candida saitoana, lactic acid).
Remove makeup, cleanse and tone skin.
Stage 2. Degreasing
Degreasing
Degreaser Solution
(glycolic acid, premium solution of witch hazel, salicylic acid, chlorhexidine gluconate).
Thoroughly degrease the skin to ensure uniform penetration of AHA peels.
Step 3: Protect sensitive areas
Moisturizing Protector
(silicon polymers, bisabolol, vitamins A, C, E, mimosa and aloe extracts).
Using a cotton swab, apply moisturizing protector to sensitive areas.
Stage 4. Intensive care
Intensive care
AHA peels with mandelic acid
Almond peeling Mandelic A40 (pH 1.5) in alcohol form
(40% mandelic acid, sweet almond extract). Weakens the cohesion of corneocytes, loosens the stratum corneum, normalizes the proliferation and differentiation of keratinocytes, activates the synthesis of the main structures of the dermal matrix. Has anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects.
Apply 1-2 layers of peeling to the face and neck, avoiding the eye area. Do not rinse off.
Almond peeling Mandelic A40 (pH 2.0) in gel form
(40% mandelic acid). Blocks free radicals, improves trophic processes in the skin, inhibits the activity of melanocytes, stimulates intradermal synthesis of protein molecules.
Apply one layer of peeling to the skin of the face and neck, gently rub until completely absorbed. Wash off after 5 minutes.
Carboxytherapy
Active phyto-gel CO2 Carboxy Pro
(sodium bicarbonate, extracts of licorice, chrysanthemum, sophora, rose, centifolia, rosehip, angelica, furrow, pine, oak; eucalyptus oil, glucose).
Plant extracts dissolved in an alkaline environment have an antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and dermoprotective effect.
Evenly distribute the gel (30 ml) on the skin of the face and neck, excluding the eye and lip area. Mask-activator with citric acid CO2 Carboxy Pro.
Place the mask, gently pressing it with your hands for better contact with the skin. The mask should be evenly saturated with gel. Leave for 25–30 minutes. Every 5 minutes, the mask must be pressed against the skin or an elastic bandage should be used to bandage the oval and cheeks for more intense oxygen release.
GF Global Renewal Concentrate
Rejuvenating con
(ferulic and hyaluronic acids, oat extract, SOD, growth factors (EGF, IGF, aFGF, bFGF, VEGF). Enhances cellular metabolism and functional activity of skin cells, increases the synthesis of collagen and elastin, increasing the firmness and elasticity of the skin, protects cells from aggressive exposure to free radicals.
Apply the contents of the ampoule to the face and neck, gently rub until completely absorbed.
Stage 5. Final care
Final care
Aloe PRO cream-gel Aloe V Pro
(aloe leaf extract, glycolic acid, rose hip oil, calendula extract, vitamin E). Restores the hydrolipid balance and pH of the skin after the procedure. Soothes and regenerates.
Apply a small amount of cream-gel to the skin and distribute it evenly over the entire surface of the face.
Preventive course:
4–5 procedures performed once a week.
Intensive course:
8–10 procedures, 1–2 times a week.
Integrated technology schemes may vary depending on the condition of the skin, age, and individual skin characteristics. One of the intensive carboxytherapy regimens, Carboxy PRO Intensive, recommended for patients of mixed morphotype after 35 years, is given below.
Contraindications
- Patient's reluctance to cooperate with medical personnel;
- Impaired consciousness (coma, stupor or agitation);
- Severe hypoxemia, resistant to oxygen therapy;
- Respiratory arrest or likelihood thereof;
- Abundant tracheal secretion and the patient’s inability to cough it up (for example, in the presence of brochiectasis, abscess);
- Tumors of the head and neck;
- Damage to the facial skeleton;
- The inability of the face mask to fit tightly, leading to significant air leaks.
Indications
- The presence of several or one of the signs of ARF: reversible hypoxemia, shortness of breath at rest > 25/min, participation of auxiliary respiratory muscles in breathing, PaCO2 > 45 mm Hg. Art., pH 7.20-7.35, PaO2/FiO2 < 200 mm Hg. st;
- The presence of a clear consciousness in the patient and his willingness to cooperate with the doctor;
- There are clear prospects that NIV will stabilize the patient’s condition over the next few hours or several days.
- Patient's reluctance to cooperate with medical personnel;
- Impaired consciousness (coma, stupor or agitation);
- Severe hypoxemia, resistant to oxygen therapy;
- Respiratory arrest or likelihood thereof;
- Abundant tracheal secretion and the patient’s inability to cough it up (for example, in the presence of brochiectasis, abscess);
- Tumors of the head and neck;
- Damage to the facial skeleton;
- The inability of the face mask to fit tightly, leading to significant air leaks.