Types of operations
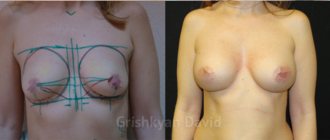
Breast augmentation is one of the most common cosmetic surgeries. To change the size, prostheses (gel-based silicone elastomers) are used, the entire surface of which is covered with a special textured material. Implants have different sizes and shapes to fully satisfy all the wishes of patients.
Implants are installed in the breast in three ways:
- Podgrudny. This is the safest and most convenient option. Surgeons make an incision under the breast of no more than 6 cm. The resulting scar either disappears on its own soon after the operation or is removed cosmetically.
- Through the halo. An incision of approximately 2.5 cm is made along the border of the lower areola. Through it, access to the gland is provided. The disadvantages of the method are: decreased sensitivity of the nipples and the risk of damage to the milk ducts. Pros: almost invisible seams.
- Through an incision in the armpit. This is the most aesthetically attractive method, since it does not cause external damage to the breast itself.
Before breast augmentation surgery, the surgeon examines the chest, together with the patient selects the type of implant and, based on the results of the consultation, determines the method of performing the operation and announces the price.
Breast augmentation (breast replacement) “Isabella”
Breast augmentation (breast replacement)
Breast augmentation surgery, known in terminology as augmentation mammoplasty, is used:
- to increase the volume and improve the shape of the breast while maintaining function (the possibility of breastfeeding);
- to restore breast volume after pregnancy or after sudden weight loss;
- to eliminate differences in breast size;
- as a reconstructive operation after removal of a breast tumor.
The effect is achieved through the placement of a special prosthetic implant.
The goal of the surgery is to give the breasts an improved shape and size that is proportional to the figure. The effect is achieved by placing under the breast tissue or even deeper (under the pectoralis major muscle) a special prosthetic implant having a silicone or polyurethane shell filled with semi-liquid content in the form of a gel.
Who is rhinoplasty indicated for?
Rhinoplasty can be performed for both aesthetic and therapeutic purposes. There are no special restrictions on this procedure, however, it is believed that it is undesirable to do rhinoplasty until the process of facial formation is finally completed (by the age of 14 for girls, a little later for boys).
Indications for surgery
Breast augmentation is usually performed for both aesthetic and reconstructive purposes (for example, after breast surgery).
Carrying out the operation
Rhinoplasty is performed only in a hospital setting under general anesthesia in combination with local infiltration anesthesia. The operation usually lasts 1.5-2 hours, although more complex procedures may take longer. The operation consists of separating the skin of the nose from the bones and cartilage, which will be brought to the desired shape. After this, the skin is restored.
Some surgeons perform rhinoplasty from the inside, making an incision on the inside of the nostrils. In difficult cases, the “open” method is preferable, when a small incision is made across the skin part of the septum. The minimum inpatient stay is usually 1-3 days, depending on the extent of the surgical intervention.
Planning your operation
At the consultation stage with the surgeon, it is important to discuss your wishes and listen to his opinion. Every patient, like every doctor, has a different idea of the desired breast size and shape. The doctor will examine your breasts and take the necessary measurements and explain the specifics of the operation in relation to your age, skin condition, breast shape and size. If your breasts have a saggy appearance, your surgeon may also recommend performing a breast lift at the same time.
The surgeon should describe the procedure in detail, explaining any possible limitations and uncertainties. Be sure to discuss all your questions with him.
Preparing for surgery
— the patient must be healthy (no colds or other diseases);
— it is necessary to undergo an examination (blood tests, urine tests, sugar levels, ECG, oncologist’s report), as well as an examination by an anesthesiologist;
— 10 days before surgery, you should not take medications containing aspirin, vitamin E, or lecithin;
- if you smoke, you will have to abstain from smoking;
- the night before you should take a bath, a light dinner is allowed;
— you must bring a soft bra without a metal base;
- no cosmetics, nail polish, etc.
Carrying out the operation
Breast augmentation surgery is usually performed under general anesthesia and lasts about 50 minutes. There are several methods of performing the operation.
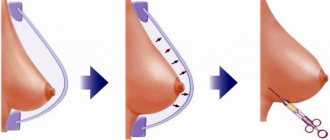
The method of inserting the implant and its location will depend on your body anatomy and your surgeon's recommendations. An incision may be made in the lower inframammary fold, around the areola, or in the armpit. Through an incision, the surgeon separates your breast tissue and skin to create a “pocket” just behind the breast gland or under the pectoralis major muscle.
Some surgeons believe that placing the implant behind the pectoral muscle may reduce the possibility of capsular contracture. This placement is less disruptive to breast examination than placement directly under the breast.
Features of the operation
— an inconspicuous scar remains (usually under the breast) about 5 cm long;
— over time, natural sagging of the breast occurs;
- absolute symmetry is impossible;
— the operation does not affect the likelihood of developing breast cancer;
— difficulties for medical examination usually do not arise;
— 1 year after surgery, mammography is recommended.
Postoperative period
— discharge from the hospital is carried out on the 2nd or 3rd day after the operation, but you will be able to return to work
- start no earlier than in a week (depending on your well-being);
- during the first 3 weeks, especially in the first five days after implantation of prostheses, hand movements should be limited;
- a slight increase in temperature may be observed for several days;
- once a week for a month you must come for examinations;
- stitches are removed after 10-14 days;
— the final result appears after 2-3 months.
Possible side effects
Temporary:
- discomfort or pain when moving;
- decreased sensitivity of some areas of the skin;
- swelling of tissues and associated asymmetry of the mammary glands.
Permanent:
— postoperative scars are formed;
- in some cases, the sensitivity of the nipples decreases or increases;
— the rarest complication, which manifests itself quite late (after 6 months or more), is an increase in volume and unwanted thickening of the mammary gland. This occurs as a result of the formation of fibrous contracture, which worsens the achieved aesthetic effect and, in some cases, requires repeated surgical correction.
Early postoperative complications (bleeding, infection, severe scarring) are rare.
Scars after mammoplasty remain forever. They typically appear pinkish for six weeks, after which they become less noticeable, sometimes appearing as fine white lines. Fortunately, the scars are usually positioned so that you can wear low-cut clothing.
The final result of the operation depends not only on the skill of the surgeon, but also on the individual characteristics of the patient and his compliance with all the instructions and recommendations of the doctor.
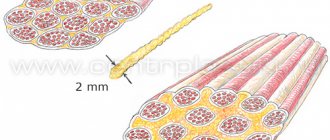
Types of implants
In the manufacture of prostheses, medical silicone is used, which has undergone multi-stage chemical processing. Thanks to this, implants are highly durable and are not damaged by physical impacts. They do not have any special wearing conditions and do not require preventive procedures.
With a slight change in size, hemispherical implants can be used. If breast surgery involves a significant change, anatomical implants are recommended. Such breasts will look natural.
Indications and contraindications
In addition to resizing, mammoplasty can be used for:
- Asymmetrical arrangement of glands, differences in size.
- Removal of one or both breasts.
Contraindications to surgery are:
- Diseases and glands of unknown etiology.
- Neoplasms before completion of therapy (for benign tumors, implant installation is possible simultaneously with tumor resection).
- Pregnancy, lactation.
- Age up to 18 years.
Also, breast surgery is not performed against the background of inflammatory and infectious diseases or exacerbation of chronic pathologies. In this case, the operation is postponed until the patient's condition stabilizes.
According to the declaration of the international committee EQUAM, modern implants do not cause any side effects during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Postoperative period
Modern techniques for applying cosmetic sutures minimize the visible consequences of the operation. Over time, the seams become invisible.
- If the operation is successful, the woman is discharged home after 1-2 days.
- It is not recommended to wet the seams for a week. For hygiene reasons, you should not take a quick shower, soap or rub in the area of the seams. The bath can be taken 2 weeks after surgery.
- For 1.5 months, you should avoid physical activity, especially on your hands.
- Until complete healing and adaptation, it is not recommended to sleep on your stomach.
- It is recommended to wear compression garments until your doctor allows you to switch to regular ones.
To speed up the healing of sutures, you can use anti-scar creams and ointments.
More detailed information about changing the shape and size of the breast in Nizhny Novgorod will be provided to you by the surgeons of our medical center during a consultation. Sign up by phone and on the website.
Mammoplasty
The concept of “mammoplasty” (lat. mammoplastica) includes various types of plastic surgery on the mammary gland, aimed at changing its shape and (or) size of the mammary gland (increase or decrease).
In case of sagging glands, excess skin is removed, and the breast tissue is fixed to the soft tissues of the chest in a typical position.
Breast replacement is indicated for asymmetry of the mammary glands and for breast reconstruction after mastectomy (breast removal).
Mammoplasty is indicated for:
Macropathies (breasts are sharply increased in size, location and firmness are preserved)
Micromastia (small breast size)
Ptosis of the mammary glands (size is preserved, but the mammary glands are omitted)
Post-lactation involution of the mammary glands (the glands are significantly reduced in size, occurs in some cases after the end of natural feeding of the child with breast milk)
Gynecomastia (hypertrophied breasts in men)
Contraindications for mammoplasty are:
Oncological diseases
Infectious diseases
Impaired blood clotting
Mental illness
Severe diseases of internal organs
Incomplete lactation (on average, a child is breastfed for 1 year)
Age up to 18 years
Before surgery, it is necessary to undergo a study of the functions of internal organs, ultrasound of the mammary glands and blood tests.
14 days before the date of surgery (provided that the patient is clinically healthy), you should not take products that contain salicylates or use hormonal contraceptives.
7 days before the operation, you must stop using cigarettes (nicotine entering the body seriously impairs blood flow), otherwise the sutures will take a very long time to heal.
The operation is performed under general anesthesia and, depending on the type of surgery, lasts from 1.5 to 4 hours.
Types of mammoplasty
Breast replacement (augmentation mammoplasty)
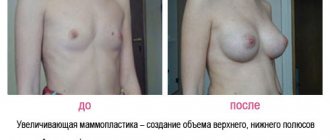
The purpose of this operation is to increase the volume of the mammary glands and (or) improve its shape and give elasticity. In addition, endoprosthetics can be carried out to correct the asymmetry of the mammary glands, to eliminate the reduction and sagging of the breasts in the postpartum period (post-lactation atrophy). To correct post-lactation involution and micromastia of the mammary glands, it is necessary to use surgical interventions using special implants (prostheses). They vary in shell texture, shape, size and filling. The material from which it is made is resistant to pressure and tearing, and the gel filler ensures long-term retention of the shape and the feeling of natural fabric. Prostheses of this kind can remain in a woman’s body throughout her life without requiring replacement. In most cases, the choice of incision site is left to the patient. Depending on the anatomical features of the patient, the implant can be installed either under the pectoralis major muscle or between the pectoral muscle and the gland. At the end of the operation, cosmetic stitches are applied to the skin. For 1-1.5 months after surgery, it is necessary to constantly wear compression garments.
These operations include reduction mammoplasty (in case of breast hypertrophy) and mastopexy (breast lift).
T-shaped or anchor cut. This is a classic method of breast reduction. It is recommended to be used when a large volume of resection is planned. There are two disadvantages here: the length of the sutures and the time-consuming operation.
Reduction mammoplasty, as a rule, is performed with simultaneous breast lift, since its main goal is to form the optimal shape of the mammary glands, with a minimum number of stitches and incisions. During the operation, excess breast tissue and subcutaneous fat are removed, then a new shape and size is formed. Once macromastia and breast ptosis are diagnosed, surgery is often performed using tissue from the patient.[2] With a slight sagging of the breast, it is usually enough to limit yourself to endoprosthetics. When applying skin cosmetic sutures, absorbable and non-absorbable materials are used, which provide not only good healing but also an excellent aesthetic effect. When sutures are applied using traditional materials, they are removed 12-14 days after surgery.
Resection of excess mammary gland tissue, which is carried out during reduction mammoplasty, significantly reduces the risk of malignant degeneration of the gland, since as a result of mastopathy the tissue is often changed.
Correction of the shape of the areola (nipple) in breast surgery
A significant increase in the areola in women occurs during pregnancy or during the postpartum period of breastfeeding. In addition to increasing the areola, the nipple may change its shape. For some women, an elongated nipple and a large areola can bring certain inconveniences into life, especially with regard to their psychological state. In addition, if the nipple is elongated, breastfeeding the baby becomes difficult. The correction is as follows: the pigmented area of the areola is reduced, without affecting the gland tissue and deep layers of the skin. The operation does not require hospitalization and is performed under local anesthesia. Correction of nipples and areolas belongs to a special group of operations, since when the nipple-areolar complex is transplanted, breastfeeding in most cases becomes impossible, but at present, special microsurgery methods are used for nipple correction and the ducts of the mammary glands are often preserved. The length of the incision is one centimeter, which makes it possible not only to carefully straighten the nipple, but also not to leave noticeable marks.
Rehabilitation period
In the standard course of the operation, the patient is discharged the day after the operation; in some cases, the patient may leave the hospital on the day of the operation. In the first few postoperative days, the patient may experience a feeling of skin tension in the area that was affected during surgery. This is due to postoperative swelling. It is considered normal to experience moderate pain in the surgical area during the first two to three days. Swelling completely subsides 5-7 days after surgery, and there are usually no bruises.
By strictly following the doctor’s recommendations and prescriptions, the risk of complications is minimized. The most common complications are subcutaneous hematomas, hypertrophied scars, inflammatory changes in soft tissues, and contracture of prostheses.
It should be noted that 12 months after the operation, with the condition of implantation of high-quality prostheses, the patient retains the possibility of lactation and breastfeeding.