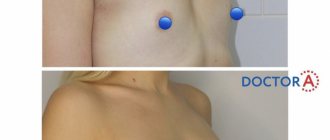
Recently, the journal Expert Opinion On Drug Safety published an article by gynecologists from Taiwan who reviewed the use of BTA in pregnant women, and the doses of botulinum toxin were therapeutic and used in patients to treat neurological diseases1.
All of these conditions were successfully treated both before and during pregnancy with BTA injections, which allowed doctors to monitor the effect of botulinum toxin on the course of pregnancy and the effect on the fetus. Scientists say BTA injections have shown relative safety during pregnancy.
Below we provide excerpts from the material.
Botulinum toxin in the systemic circulation
To begin with, we should remember: in order to act on the myometrium or reach the placenta and negatively affect the fetus, the active substance must enter the systemic circulation.
Some reports indicated that, at high doses, BTA could diffuse from facial muscle tissue into the arm, as measured by single-fiber electromyography (EMG)2, 3. However, this effect appeared to be subclinical because no muscle weakness was detected in the affected individuals. If the dose of the drug did not exceed the recommended one, then during intramuscular injection BTA did not enter the systemic circulation4.
BTA is classified by the FDA as a Category C drug, which means that animal studies have shown adverse effects of the drug on the fetus and there have been no adequate studies in pregnant women, but the potential benefits associated with the use of this drug in pregnant women may justify its use despite existing risk.
In addition, studies have shown that molecules larger than 500 Daltons cannot cross the placenta5. The molecular weight of BTA exceeds 500 D, so BTA is unlikely to cross the placental barrier and is unlikely to be present in fetal blood.
To date, animal studies have found no evidence for transmission of toxins to the fetus. In rabbits, BTA was not detected in the placenta or in embryos when high (lethal) doses of the toxin were administered intravenously. Malformations and abortion were recorded only if rabbits received high-dose injections of BTA daily; conversely, pregnant mice treated with BTA did not show similar adverse outcomes6.
How the drug works
Years have a detrimental effect on the condition of the skin, and even cosmetic preparations and gels stop working. This is the reason why women choose different ways to combat age-related changes.
The use of a protein neurotoxin, which is part of the drug discussed in the article, will be effective in the fight against age-related deformations. What is its effect on the skin?
The neurotoxin contains a special poison. This is a strong component that exists in the world of cosmetology. It has also found its application in the medical field and in the development of biological drugs. In cosmetology, for rejuvenation procedures, a minimum dose is used.
The neurotoxin is injected into the upper ball of the skin and blocks the nerve fibers, the muscle is temporarily paralyzed. This leads to its relaxation, unevenness and minor folds on the face are smoothed out, the skin is significantly tightened, returning its previous appearance and condition. Typically, the effectiveness of the procedure lasts for at least six months.
Dystonia
Dystonia is a syndrome in which there is a constant spasmodic contraction of muscles, spasms are often unpredictable, change the normal position of the body, can be chronic and cause significant discomfort, pain and disability.
Article 1 examined the use of BTA in the treatment of idiopathic torsion dystonia, oromandibular dystonia, and spastic dystonia (Table 1).
As a rule, the disease begins before the onset of reproductive age and persists throughout life. Common in pregnant women. Currently, BTA injections are the preferred treatment option. Moreover, in 10% of patients the disease began suddenly in connection with pregnancy and childbirth. Ankola showed (a study of 350 patients) that pregnancy or pregnancy-related hormonal changes may be a risk factor for the disease7. Morgan found that in a survey of 396 doctors, nine pregnant women received a BTA injection during pregnancy. One patient had a spontaneous abortion, but the other eight patients gave birth to healthy children8. Blitzer11 summarized the data of 1300 patients with dystonias such as adductor and abductor dysphonia, and over 24 years, according to his data, the effectiveness of BTA was 91.2% and 70.3%.
Table 1.
Use of BTA for the treatment of dystonia during pregnancy (according to Wu Li, Min Tang1)
| Study | Number of BTA injections | Dosage/Duration of treatment | Result |
| Newman, 20049 | 3 | 15 weeks / 200 units. 21 weeks / 100 units. 32 weeks / 300 units | BTA improved the symptoms, which recurred approximately every 3–4 months. Over the next 9 years, the patient became pregnant three times and received BTA several times during each pregnancy. The injections gave good results in all three pregnancies, the patient gave birth to healthy children |
| Aranda et al.10 | 1 time in the second and third trimesters | The injection site and dose were identical to those used before pregnancy: 40 IU into the left sternomastoid muscle, 150 IU, and an additional 60 IU divided between the trapezius and right elevator scapula muscles. The total dose during pregnancy is 500 IU. | At the 40th week, the patient gave birth to a healthy baby (weight 3400 g). |
| Morgan8 | _ | _ | The patient experienced relief of symptoms and gave birth to a healthy baby20. |
Strabismus
Deviation of the visual axes from the direction towards the object in question, in which the coordinated work of the eyes is disrupted and it becomes difficult for both eyes to fixate on the object of vision. BTA is considered an alternative to surgery.
Table 2.
| Study | Number of BTA injections | Dosage/Duration of treatment | Result |
| Morgan, 20048 | Two patients with strabismus received BTA during pregnancy | 1.25 to 300 IU | The therapeutic effect did not cause complications or fetal abnormalities |
| Lee Yim12 | 17 year old woman. The drug was administered before the patient knew she was pregnant | 2.5 IU | A healthy baby was born |
Alternative rejuvenation options
During pregnancy, it is difficult to find a worthy alternative to Botox. Most interventions are prohibited. Chemical peeling, biorevitalization, and deep massage will have to be abandoned. All that remains is careful care. Don't forget about cleansing, superficial peeling, and masks. An important aspect will be the selection of suitable cosmetics. You can learn about popular products from an experienced cosmetologist.
During pregnancy, it is especially important to organize healthy sleep, proper nutrition, and oxygen supply. This will support your health and have a positive effect on your appearance. At home, you can perform light massage and gymnastics. The procedures will maintain muscle tone and help reduce the number of wrinkles. A cosmetologist will always tell you how to maintain a decent appearance.
Botox during pregnancy is a procedure that requires serious consideration. Taking care of your health is the most important component of an “interesting situation.” There cannot be a choice between the well-being of pregnancy and increasing the attractiveness of appearance.
Esophageal achalasia
Functional obstruction of the esophagus. Characterized by loss of lower esophageal sphincter (LES) activity and esophageal motility; the main symptoms are dysphagia, chest pain and reflux.
Treatment options include diet, calcium channel blockers, and Heller myotomy. BTA can be injected locally into the stomach area. The procedure does not require deep anesthesia, and can relax the LES and relieve esophageal obstruction.
Table 3.
| Study | Number of BTA injections | Dosage/Duration of treatment | Result |
| Wataganara et al., 200913 | From 18th week | 80 U BTA | A healthy infant was born at 36 weeks' gestation and no swallowing problems were noted until 6 weeks postpartum. |
| Hooft 201514. | BTA at 14 weeks of pregnancy | 100U | Healthy baby |
| Holliday 201615 | BTA at 31 + 3 weeks of pregnancy | – | Eclampsia and childbirth at 37 + 4 weeks of pregnancy |
Chronic pelvic pain (CPP)
A common syndrome with various causes: the main and only symptom is pain, sometimes accompanied by defecation disorders. In addition to daily pain, patients often complain of dyspareunia and dysmenorrhea. In women, pain was significantly reduced after BTA injections.
Table 4.
| Study | Number of BTA injections | Dosage/Duration of treatment | Result |
| Abbott 200616 | 30 | 80 IU | Two women became pregnant 4 and 5 months after the injection; One woman (41 years old; complex medical history) had an elective caesarean section at 40 weeks and the baby had a ventricular septal defect that required surgical correction. However, it is unclear whether it was caused by BTA administration. |
| Abbott 200917 | Two cases during pregnancy | – | Both mothers had good results. |
Migraine
Some migraine medications are considered unsafe for pregnant women18.
In 2000, Binder et al were the first to report that BTA was successfully used in patients with headache19. In a meta-analysis of 17 studies involving 3646 patients with chronic migraine, Brula et al found that BTA significantly reduced chronic migraine symptoms after 3 months of treatment compared with placebo; therefore, BTA was considered safe and well tolerated20.
Preparation
Botox injections in the neck are carried out provided that the patient is completely healthy and feels well. The procedure requires simple preparation. A week before the manipulations, it is necessary to exclude from the diet salty, spicy, fatty foods that contribute to the formation of edema. In 2–3 days, you need to completely give up alcohol, limit physical activity, stop taking hormones, antibiotics and other medications prescribed by your doctor.
Immediately before administering botulinum toxin, the cosmetologist conducts a thorough examination of the problem area, assessing:
- type of wrinkles and the specifics of their location;
- Tugor;
- anatomical features.
Complication statistics
Wu Li, Min Tang1's findings on complications showed that rates of spontaneous abortion and fetal malformations in pregnant women treated with BTA were similar to those reported for the general population.
Tan reported 28 cases occurring before 2013 in patients who received BTA during pregnancy; including 25 normal births, 1 therapeutic abortion and 2 spontaneous abortions21.
In 2016, Brin et al. reported results in pregnant women who had received local injections of BTA within the previous 24 years. Of the 137 births (139 fetuses), 110 (79.1%) were live births, 29 (20.9%) were fetal loss (21 spontaneous abortions) and 8 abortions22. Among the live births, 106 (96.4%) were normal, only 4 patients had a poor outcome, two had minor fetal malformations and one congenital complication; the overall incidence of fetal malformations was 2.7%. They may not have been related to BTA treatment.
Recovery period
The rules of the rehabilitation period are announced by the cosmetologist after the procedure. It is important to strictly follow the specialist’s recommendations in order to consolidate the result and prevent negative consequences:
- In the first 4 hours after botulinum therapy, do not take a horizontal position. You can only sleep on your back with a high pillow under your head.
- For 4–5 days, stop using decorative cosmetics.
- For 2 weeks, exclude salty, spicy, fatty foods from the menu, stop drinking alcoholic beverages, coffee, and strong tea.
- Limit sports activities.
- Refuse to visit the solarium, swimming pool, sauna, bathhouse, and do not take hot baths.
- Do not massage, peel, or scrub until complete recovery after Botox injections.
Botulinum poisoning
There have been cases in the literature where high doses of BTA could cause symptoms of systemic botulinum poisoning.
However, a report by Brin et al. (2016) states that clinical botulism has no adverse effects associated with pregnancy or the fetus22. Badell studied maternal and fetal outcomes associated with botulinum poisoning in 16 women during pregnancy (11 cases in late pregnancy) and 1 woman after injection23. Although the pregnant women showed signs of poisoning, all babies were born healthy and only six patients experienced premature birth. Newborn blood tests did not show the presence of BTA in the systemic circulation; these findings also supported the hypothesis that BTA does not enter the fetal circulation24,25.
Effect of the toxin on the unborn child
Botox is essentially poison. Although the toxin is administered in small doses for cosmetic and medicinal purposes, this does not change its nature. A dangerous substance entering the body of a pregnant woman inevitably reaches the fetus. Whether it is possible to inject botulinum toxin while carrying a child is a controversial issue.
Studies of the negative side of the toxin's action were carried out exclusively on pregnant animals. Similar experiments are not carried out on humans. Taking into account the available data, it is possible to state the facts of the influence of Botox administered during pregnancy on:
- increased frequency of miscarriage;
- the birth of offspring with various defects (deviations from the norm, deformities).
Most often, non-standard development of the nervous and cardiovascular systems was observed. The general deterioration of the condition is known - endurance, life expectancy. The data suggest that the pattern of human fetal development under the influence of the toxin will have similar consequences.