Breast cancer is the most common cancer in women in the world. In Russia, this type of cancer accounts for 20.9% of all malignant diseases. In 2015, more than 66,600 new cases of breast cancer were identified in the country, and the incidence rate was 49.75 per 100,000 population.
Advances in surgery, pharmacology, diagnostic methods, and new knowledge about breast cancer have increased the chances of detecting a tumor at an early stage. Thanks to this, surgical treatment of the disease with preservation of the mammary glands has become much more common. The tactics of examining patients after primary treatment are also changing - now it helps to most effectively and promptly identify possible relapses.
The number of patients who have undergone primary treatment and are under dynamic control is increasing every year. This is why breast cancer recurrence and methods of preventing it are becoming increasingly discussed medical topics.
Recurrence of the disease must be diagnosed at an early stage. Actively monitoring patients helps reduce the risk of relapse and determine the most effective treatment if it does occur. In addition, the recurrence of the disease can be prevented by proper prevention.
Follow-up after breast cancer treatment
In the first 5 years after primary cancer treatment, the risk of breast cancer recurrence is greatest. Therefore, during this period it is necessary to visit the oncologist 1 to 4 times a year (depending on the specific clinical situation). During the appointment, the doctor examines the patient and identifies possible complaints. After 5 years, it is advised to contact a specialist once a year, unless, of course, there are any complaints about the condition.
During the appointment, in addition to the examination, the oncologist will prescribe instrumental research methods that will allow timely detection of breast cancer recurrence or progression of the disease:
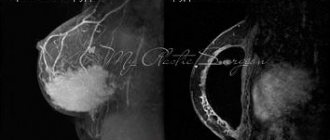
- bilateral (in the case of organ-preserving surgery) or contralateral mammography in combination with ultrasound of regional zones and the area of the postoperative scar - once a year;
- scintigraphy of skeletal bones, ultrasound of the abdominal and pelvic organs, radiography of the chest organs - as prescribed by the oncologist.
In addition, women taking adjuvant tamoxifen in the presence of a intact uterus should undergo a routine examination by a gynecologist annually. The fact is that the drug can cause the development of endometrial hyperplasia, and a specialist will notice this in time.
Women taking aromatase inhibitors for a long time are recommended to undergo annual densitometry. This diagnostic method helps assess bone density and the risk of developing osteoporosis.
What else should you do to make the stitches on your chest heal faster?
To make the stitches on your chest heal faster, you need to:
- do not load the shoulder girdle - avoid lifting heavy objects, active movements of the limbs until scar tissue forms (from 15 to 20 days);
- monitor the condition of the wound, treat it with antiseptics, lubricate it with cream as prescribed by the surgeon;
- take a shower in the first month, covering the seam with a bandage;
- be sure to wear underwear with a slimming effect, and you should have at least 2 sets to change to clean ones every day;
- prevent pressure on the seam, do not sleep on your side.
Watch this video about caring for stitches after breast augmentation:
Why do relapses occur after mastectomy?
Recurrence of breast cancer after mastectomy in a postoperative scar can occur as a result of poor-quality treatment, chemotherapy, or incomplete tumor removal.
Period when relapses may occur after treatment
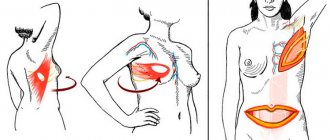
The first 10 years after initial treatment are considered the most dangerous for the development of local relapses. Moreover, more than half of cases of recurrent disease occur in the first 5 years. The task of patients during this period is to immediately contact an oncologist if there is any suspicion of a relapse. It is necessary to conduct an independent examination of the breast and postoperative scar, as well as know your risk group and the main symptoms of relapses.
Risk groups for breast cancer recurrence
The likelihood of breast cancer recurrence after mastectomy depends on the following factors:
- the presence of metastases in regional lymph nodes;
- molecular genetic profile of the tumor (presence of receptors for estrogen and epidermal growth factor HER/2neu);
- size of the primary tumor;
- patient's age. Breast cancer relapse occurs more often in young patients.
In this regard, there are 3 risk groups.
High risk
- metastases in 1-3 lymph nodes in the absence of HER2/neu overexpression in the tumor;
- metastases in 1-3 lymph nodes in the presence of overexpression;
- HER2/neu in tumor;
- metastases in 4 lymph nodes or more.
Medium risk
The absence of metastases in the lymph nodes in combination with at least one of the following signs:
- tumor size more than 2 cm;
- degree of malignancy 2-3;
- presence of vascular invasion;
- the presence of HER2/neu overexpression in the tumor;
- age less than 35 years.
Low risk
Absence of metastases in the lymph nodes in combination with all of the following:
- tumor size less than 2 cm;
- tumor grade 1 (low);
- no vascular invasion;
- no overexpression of HER2/neu;
- age over 35 years.
How long after breast surgery can the suture be wetted?
It is possible to wet the suture after breast surgery only after a while - usually on the 2-3rd day, since the drainage must be removed. The doctor may then allow the patient to take a warm shower, but the wound must be covered with a bandage. The water temperature should be moderately warm; it is better to use regular baby soap or gel with a neutral pH.
It is important to consider that if there are signs of inflammation, surgeons prohibit water procedures; then you should wipe the body with wet wipes in the area of the mammary glands. Bathing is not recommended for at least 1 month.
Symptoms of relapse
To detect recurrence of breast cancer in a timely manner, it is necessary to regularly visit an oncologist and undergo examinations. However, it is equally important to independently monitor the condition of the chest and mammary glands.
Symptoms of cancer returning may not be obvious. Regular breast examination and understanding of its normal condition will help to identify unwanted changes as early as possible and begin treatment.
Among the most common symptoms of breast cancer recurrence are:
- the appearance of a lump under the skin of the mammary gland (during organ-preserving surgery) or in the area of a postoperative scar;
- change in the structure of breast tissue (during organ-preserving surgery);
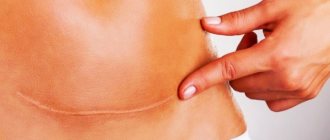
- recurrence of breast cancer in a postoperative scar can cause a change in skin color in the scar area (redness).
If you notice signs of breast cancer recurrence, you should immediately contact an oncologist.
How to care for seams: brief instructions
For a speedy recovery, it is important that postoperative sutures scar normally. Even if the material was self-absorbable, they need care, because the tissues injured during the intervention will not heal instantly. This will take time, during which you need to ensure that no infection gets into the wounds and that the edges remain securely fastened.
Proper care will ensure not only a quick recovery, but also the absence of obvious signs that the woman had plastic surgery. What does it consist of:
- On the first postoperative day you need to rest in a semi-sitting position . This will help to avoid heavy load on the seams, hence their possible divergence.
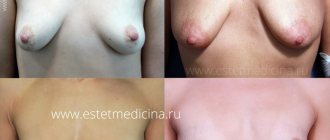
- It is necessary to control the appearance of scars . At first they are red, but as they heal they turn pale and shrink in size.
Change in color of scars after mammoplasty within a year
- Sometimes the attending physician recommends treating the seams after mammoplasty with antibiotic ointments , in other cases they insist on simply wiping them with sterile wet wipes. Experts prescribe using brilliant green and other solutions to prevent infection.
- In each case, you need to follow the recommendations, since the material used for suturing varies, as do the individual characteristics of tissue healing. Therefore, you should not be arbitrary in choosing care products, ignoring the doctor’s opinion.
- After removing the sutures, you can smear them with absorbable creams and ointments , after consulting with the surgeon. Contractubex will help improve the appearance of scars by applying a silicone strip to the incision site overnight.
- It is mandatory to wear compression garments for 30 days . It will help to avoid excessive tension of the skin in the area of the seam, that is, it will not allow it to hurt longer than expected and, moreover, will not allow it to separate. And to prevent infection, you should change your underwear daily.
Compression garments are put on the patient immediately after surgery.
- You can wash only 3-4 days after surgery , avoiding getting water and shower gel on the suture areas. It is best to do this with a bandage, removing it after the procedure. You cannot rub the body in the area of the mammary glands with a washcloth for 3-4 weeks.
- You need to avoid physical activity for at least 2 - 3 weeks . Rest helps damaged tissues heal faster and relieve pain in the suture area. This is also important for their correct formation without hypertrophy.
- You will have to sleep on your back , without turning on your side or stomach, for at least 2 - 3 weeks. This way, it will be possible to relieve the skin of excessive tension, therefore, avoiding increased blood supply in the area of the sutures, the risk of their damage and hypertrophic development.
To learn how rehabilitation after mammoplasty should proceed, watch this video:
Diagnosis for suspected recurrence of breast cancer
If you suspect a relapse, you should immediately consult a doctor. The specialist will conduct diagnostics: examination, palpation, mammography, prescribe ultrasound of the postoperative scar and regional areas and morphological (cytological and histological) examination.
Morphological examination of a recurrent tumor should be carried out similarly to the diagnosis of a primary tumor, including the determination of estrogen receptors (ER), progesterone receptors (RP), HER2/neu, Ki67. Based on the data obtained, further tactics and treatment methods will be determined. If necessary, the oncologist will prescribe additional studies and tests.
How is the operation performed?
Here's how breast resection is performed:
- Immediately before the operation, the doctor uses a special marker to mark on the chest which areas of the mammary gland are to be removed.
- The woman is given anesthesia.
- The skin is carefully treated with an antiseptic.
- The doctor makes an incision along the previously marked lines: from the periphery to the center. The incision passes through healthy tissue; a distance of at least 10 mm is maintained between the affected and healthy areas.
- The doctor removes the affected area and, if necessary, nearby tissues.
- Then drainage is installed and sutures are applied.
- Biological material that was removed during surgery is sent for histological examination.
- At the end of the operation, the doctor applies a sterile bandage.
Prevention of recurrence of the disease
After a long and difficult treatment, all patients are interested in the question “how to avoid recurrence of breast cancer.” The following methods help prevent recurrence after breast cancer or reduce its risks:
- comprehensive treatment in accordance with international standards;
- for hormone-positive cancer, long-term use of tamoxifen/aromatase inhibitors;
- dynamic observation after completion of the main stage of treatment;
- prevention with agents based on indole-3-carbinol and epigallocatechin-3-galate (Promisan) to restore the activity of tumor-suppressing genes (the gene whose product ensures the prevention of tumor transformation of cells) and BRCA proteins.
In addition to regular monitoring by specialists and systemic therapy, a healthy lifestyle will help prevent breast cancer recurrence. Walking in the fresh air, physical activity, and proper nutrition are the basis of any person’s health. But this is especially important for those who have suffered a serious illness.
You also need to maintain your weight at an optimal level. The fact is that excess adipose tissue is a source of estrogen production. It has been proven that excessive estrogen stimulation negatively affects breast tissue, stimulating the development of proliferative processes. Thus, reducing excess estrogen stimulation also leads to a reduction in the risk of relapse, especially for hormone-dependent types of breast cancer.
Before mastectomy
Before the operation, the woman receives specific instructions that describe restrictions and other things she needs to know. The patient should tell her doctor about any medications, vitamins, or supplements she is taking. Taking certain substances may negatively affect the course of surgery. For a week or more before surgery, you should avoid taking medications that may increase the risk of excessive bleeding. These include aspirin, ibuprofen and other pain relievers and blood thinners (anticoagulants).
Immediately before the operation, 8-10 hours, you should stop eating and drinking. It is also worth preparing in advance for your stay in the hospital. Find out how long you plan to stay there. Pack a bag with a toothbrush, robe, and slippers to make your hospital stay more comfortable. Also, prepare something that will help you pass the time, such as a book.
A mastectomy without reconstruction usually takes one to three hours. This usually requires one extra day in the hospital, although more and more women are choosing to go home on the day of surgery.
If you have surgery to remove both breasts (double mastectomy) or breast reconstruction after a mastectomy, the surgery may take longer and your hospital stay after surgery may increase to several days.
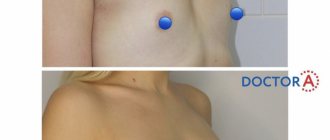
To perform a sentinel node biopsy, a radioactive substance or blue dye is injected near the tumor before surgery and deposited in the sentinel lymph node. This will allow the surgeon to identify and remove the affected lymph nodes during surgery.