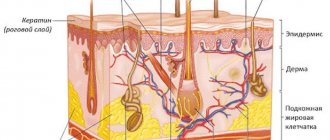
- Initial appointment with a dermatologist
1200 ₽ - Calling a dermatologist to your home
4000 ₽
The disease occurs as a result of weak immunity. After recovery in patients, the body is able to produce antibodies to the pathology. Pityriasis rosea is an infectious disease. Rashes form on the skin, they are curable if therapy is prescribed in a timely manner.
Women are susceptible to deprivation much more often than men; it occurs in children aged 10 years. Pregnant women are susceptible to pathology as a result of hormonal changes. The peak of the disease occurs in the off-season, with weakened immunity.
Clinic specialists treat the disease. They will identify the causes, conduct research and prescribe therapy.
Varieties of pityriasis rosea
- Typical form. It is formed from the mother's plaque.
- Antitypical shape. There is no redness, but vesicles and blisters appear on the body. Itching appears and spreads to the face; this is not typical for a typical pathology. A rash is observed, small bubbles form, which merge into one whole, the size is 10 cm.
The flaky atypical form has several stages:
- itching on the skin, small rashes;
- the formation of papules that have a rough, fine-grained surface;
- Whole lesions are observed, they are noticeable among uninfected areas of the skin.
Symptoms of pityriasis rosea
The patient has a large pink spot. Its diameter is 20 mm or more. After a few days, the plaque becomes pale and yellow in color. The skin begins to peel off in the infected area. After the formation of spots, 3-5 days later they are observed on the body, arms, their diameter is 1 cm. The spots are pink, round or cylindrical in shape. The rashes begin to dry out and scales appear in the form of folds.
The patient's health worsens. Weakness, fever, headache, drowsiness, myalgia, redness of the throat, and poor appetite are observed. Based on the symptoms, pityriasis can be mistaken for an allergy. In this case, self-medication will lead to a deterioration in the patient’s health. The symptoms of the pathology are similar to other dermatological diseases.
The spots cover the back, thighs, arms and cause itching. They form within 3 weeks, then slowly disappear. The total duration of the pathology is up to 2 months. Dermatologists at the medical clinic treat patients with severe and initial forms of the disease.
Publications in the media
Pityriasis rosea is an acute dermatosis characterized by abundant, finely scaly pink spots on the trunk, neck and proximal extremities, most often occurring in the autumn-winter period. One of the most common skin diseases; usually resolves spontaneously. Risk factors: infectious diseases, prolonged hypothermia. Frequency. 5% of patients who consulted a dermatologist. It is observed mainly in middle-aged women, rarely in children and the elderly.
Clinical picture • The process begins with a primary maternal plaque, which is much larger in size (2–6 cm) than subsequent rashes, and is often located on the trunk, in the area of the collarbone and shoulder blades. After 7–10 days, sometimes later, many spotted or macular-urticarial elements appear, up to 1–2 cm in diameter, pale pink or slightly brownish in color with pronounced pityriasis-like peeling. The long axes of the spots are located along Langer's lines, indicating the direction of maximum extensibility of the skin • The rashes are localized in the axillary and groin areas, on the inner surface of the thighs and the flexor surface of the forearms. In adults, the skin of the face, scalp, hands and feet, and mucous membranes are usually not affected • Itching is mild or absent altogether • Along with typical manifestations, there are other types of pityriasis rosea •• Urticarial form •• Vesicular form •• Papular form •• Lichen annulare bordered Vidal or pityriasis rosea giant is a rare variant of pityriasis rosea, characterized by single large rashes (up to 8 cm in diameter) of red or pink color with small pityriasis-like peeling along the periphery in the form of a ring, as well as a long course; may occur independently or together with typical rashes.
Test methods • Blood test: slight leukocytosis and eosinophilia • Serological test to rule out syphilis • Skin biopsy: inflammation with cytolytic degeneration of keratinocytes adjacent to Langerhans cells. Differential diagnosis • Toxidermia • Trichophytosis • Syphilitic roseola • Psoriasis • Parapsoriasis • Eczema • Lichen planus • Dermatomycosis of the trunk.
TREATMENT General recommendations • Avoid water treatments, hypothermia • Maintain good hygiene to prevent the development of secondary infection • Diet with limited pickles, spices, marinades, concentrated broths • Insolation • Drug therapy is symptomatic only.
Drug therapy • For an inflammatory reaction and itching - topically: ointments with menthol (0.25–1%) • For very severe itching - prednisolone 10 mg 4 times a day orally until the itching disappears (if discontinued, the dose is reduced gradually) • Antihistamines • Anti-inflammatory drugs (salicylates, indomethacin) • Calcium pantothenate. Complications • With irrational therapy, the development of eczema is possible • Secondary infection. Forecast. Recovery is usually within 4–6 weeks. Very rarely, rashes persist for more than 3 months and, as a rule, are due to irrational therapy. Synonyms • Tinea rosacea Giberta • Giberta disease • Roseola exfoliating
ICD-10 • L42 Pityriasis rosea [Gibera]
Diagnosis of pityriasis rosea
The doctor will perform a diagnosis. At the first examination, he identifies the presence of a maternal plaque and determines the extent of the spread of rashes on the surface of the skin. Rarely, the pathology is similar to measles, eczema, rubella. The rash is similar to syphilis and is one of the signs of the disease.
Research is needed to confirm the disease. A urine and blood test will be required. If syphilis is suspected, a Wasserman test is performed. Also, a scraping is taken from the infected dermis and an examination is performed under a Wood's lamp. Diagnosing the disease in its early stages is difficult because maternal plaque is similar to other diseases. Doctors have extensive experience in treating pityriasis and will quickly identify it.
Diagnosis is prescribed by a dermatologist. Research is required to detect antibodies to the virus in a patient.
What you need to know about diagnosis and treatment
Diagnosis of pityriasis rosea is based on taking the patient's medical history. To confirm or refute and analyze complex cases, a number of laboratory tests are prescribed. They include clinical examination of blood and urine. It is necessary to exclude syphilis and mycosis, therefore serological and microscopic studies are additionally carried out. If these methods do not provide enough information to verify the diagnosis, the patient is referred for a biopsy (biopsy histology).
Treatment for pityriasis rosea is not always required. The disease is prone to voluntary self-healing within 5 weeks. However, dermatosis should not be considered harmless. First of all, antipruritic therapy is required. For this purpose, topical glucocorticosteroid drugs and antihistamines are used externally. Ointments, gels, pastes cannot be used without a dermatologist's prescription. Otherwise, the rash may increase the extent of skin damage, covering new areas. Antibiotics and antiviral drugs may be prescribed depending on the indications. Ultraviolet therapy has a good effect.
Differential diagnosis of pityriasis rosea with other diseases
The disease is differentiated from psoriasis, parapsoriasis, seborrheic eczema, syphilis, trichophytosis. The pathology differs from seborrheic eczema by the maternal plaque, the location of rashes that are not characteristic of eczema. Among other things, with seborrheic eczema the scales are often greasy.
Unlike psoriasis, lichen is spotty; it does not appear on the feet, hair, or hands. Difficult diagnosis is observed in the first stage of the disease.
There is a similarity between the disease and parapsoriasis; the spots may be similar. However, peeling and identical spots are not characteristic of lichen.
Lichen differs from syphilitic roseola in its brightness and the presence of peeling, since this is rarely found with syphilis.
Treatment of pityriasis rosea
To eliminate the disease, the dermatologist prescribes ointments, creams and tablets. These include:
- Acyclovir. It is used to inhibit pathogens. Experts advise applying cream or ointment every 4 hours. You can take the medicine in tablets.
- Flucinar. Reduces the formation of allergies, used for external use.
- Sinaflan. The medicine is an antihistamine, it is prescribed when lichen appears in children from 3 years of age and in adults. It is not recommended to use it for more than 7 days.
- Lokoid. Helps with allergies for women and when breastfeeding.
- Lorinden. Restores immunity, renews sleep, speeds up the healing process.
- Salicylic and zinc ointments. They have an antiseptic effect, prevent new skin rashes, and the spots dry out very quickly.
Dermatologists prescribe antiviral and antihistamine medications for therapy. If the pathology appears as a result of infection, antibacterial drugs are prescribed. Hormonal medications are prescribed in severe cases, if the disease is complicated by other chronic diseases.
For prolonged lichen, patients are prescribed antiviral drugs, it is recommended to treat stains with salicylic alcohol, as well as the use of ointments.
For symptoms of intoxication, the doctor prescribes activated charcoal as an auxiliary medicine.
The doctor prescribes antihistamines during therapy. These include Claritin, Tavegil, Loratadine, Suprastin. Taking medications is possible only on the recommendation of a doctor.
Why should you contact our clinic?
Dermatologists of the highest category
Experienced dermatologists in Moscow. Experience of specialists from 15 years.
Modern equipment
Modern equipment from the world's best manufacturers.
Expert class equipment
Ultrasound is performed using expert-class equipment manufactured by General Electric, SONY, Mindray.
Tests and ultrasound on the day of treatment
Tests, x-rays, ultrasound with interpretation, dressings on the day of treatment in Moscow.
Consultations for adults and children
A network of dermatological clinics in Moscow. Clinics near the metro.
Experienced doctors
Our experienced doctors with over 15 years of experience. Candidates of Medical Sciences.
Most frequently asked questions from patients
What causes pityriasis rosea?
There is no clear answer to this question. Research continues. Presumably, the cause may be herpes virus type 6 or 7. When immunity decreases, it becomes more active, which triggers the process of various types of rashes (plaques, vesicles, blisters). The disease can be triggered by stress, poor ecology, hormonal fluctuations, and chronic diseases.
Is pityriasis rosea contagious?
Pityriasis rosea in humans is considered non-contagious, but rare cases of the disease affecting entire families are known. Much depends on the state of the immune system and the body’s defenses, which can resist viruses, bacteria and infections.
Is it possible to sunbathe with pityriasis rosea?
One type of therapy for this dermatological disease is light therapy. Moderate exposure to ultraviolet radiation has a positive effect on the condition of the skin, stimulating its regeneration. Combustion must not be allowed. This will lead to increased itching in the area of the spots.
Prevention of pityriasis rosea
- regular walks;
- reduce consumption of fatty foods and foods containing dyes;
- include multivitamins in your diet only on the recommendation of a dermatologist;
- change bed linen and clothes regularly;
- Perform water procedures regularly;
- undergo preventive examinations;
- avoid stress;
- Do not use hard washcloths that irritate the skin.
The diet should be balanced; our doctors will recommend that the patient monitor the amount of carbohydrates and proteins. It is better to include fermented milk products, cereals, bread, and lean beef in the menu. Vegetables and berries are useful for treating the disease.
How to avoid infection
Due to the fact that the nature of the occurrence of Gibert's disease has not been thoroughly studied, there are no methods to prevent this disease. The main recommendation is to monitor the state of the immune system, as it will help avoid infection.
Complications
The disease itself in most cases goes away without leaving a trace. However, sometimes complications arise in the form of eczema, staphylococcus or streptococcus; ring-shaped lichen can develop, which quite often becomes chronic and even after a few years a relapse can occur. Then treatment is done with antibiotics. To prevent such problems, we strongly recommend that you undergo comprehensive treatment in our clinic. Don't forget about your health and the health of your family!
Complication of pityriasis rosea
Relapses do not occur very often, but in some cases there are complications. These include folliculitis, eczema, osteofolliculitis and others. Re-infection can occur as a result of wearing uncomfortable clothes, not following therapy, or in people who suffer from allergies.
Secondary disease is typical on skin that is subject to stretching: thighs, groin, forearms. Infection appears in the sweat glands or on the skin of the face. If you notice the appearance of lichen, immediately contact a specialist. Timely treatment will avoid negative consequences.
Help from a dermatologist in Moscow
Diagnosis and treatment of pityriasis rosea is the field of activity of a dermatologist. Depending on the form of the disease and the extent of skin damage, the patient is provided with recommendations. With lichen, the emotional and psychological background of a person is important, so promptly making a correct diagnosis allows you to quickly overcome the disease.
You can make an appointment with a dermatologist at Meditsina JSC (academician Roitberg’s clinic) by phone. You should not self-medicate. The reason is that, according to external signs, skin rashes may turn out to be differential diseases, for example, toxicerma, psoriasis, mycosis, secondary syphilis. In these cases, it is necessary to prescribe another therapy, taking into account the specific clinical picture and medical history of the patient.
Pityriasis rosea in children
Pityriasis is diagnosed in children over 5 years of age. The dermatologist prescribes antihistamines and multivitamins to patients, which restore the immune system. For children under 2 years of age, the doctor prescribes antiseptics and zinc ointment.
Children with weak immunity are susceptible to pathology in the fall and spring. The disease is diagnosed more often in girls, less often in boys. Rashes are rare in infants. The reason is overheating or hypothermia of the baby.
Causes of skin disease:
- allergic reactions to foods or fabrics;
- intestinal disorder;
- depression, emotional turmoil;
- insect bites.
The specialist will recommend medications to speed up recovery. The disease period is up to 2 months. To destroy microorganisms, it is necessary to take antibiotics, and for allergies - antihistamines. At high temperatures, the doctor prescribes antipyretic tablets.
Pityriasis rosea during pregnancy
The appearance of pityriasis is frequent with hormonal changes in the patient’s body or with a reaction to any foods. The pathology can be dangerous for the health of mother and baby, but it causes discomfort, itching and spots appear. The cause of the disease is weak immunity.
During lactation, women are not prescribed hormonal or antiviral drugs. When itching occurs, the dermatologist prescribes antihistamines, taking into account the woman’s condition. Ointments containing zinc are prescribed as external agents.
In pregnant women in the early stages, lichen has a negative effect on the fetus, since the disease is infectious. The child will not be able to become infected, but there is a possibility of miscarriage or the birth may be premature. Patients who are up to 15 weeks pregnant are susceptible to infection.
If lichen appears, you should consult a doctor. He will prescribe antihistamines in case of swelling, antibiotics if the disease causes complications. He will also prescribe vitamins C, A, B. Sedatives will need to be taken if there is a risk to the fetus. Taking medications on your own is not recommended, as this may have a negative effect on the child.
Methods of infection and risk groups
At the moment, there is no reliable evidence of the transmission of this disease from a sick person to a healthy one. There are only infrequent cases when someone in the environment fell ill with lichen upon contact, but in all cases there were provoking factors. These include:
- presence of herpes virus in the body;
- weakened immune system;
- recently suffered viral and colds;
- frequent hypothermia of the body.
The risk group mainly includes women under 40 years of age and children. Men suffer from this disease much less frequently. Almost no cases of infection are detected in infants and people over 40 years of age. In order to reduce the risk of contracting Gibert's disease, it is worth strengthening your immune system. It is reliably known that in most cases the disease appeared against the background of a weakening of the body’s protective functions.