- What is inside a pimple, full answer
- What's inside black and white pimples?
- What is inside a pimple, papules and pustules?
- What is inside pimple cysts and nodules?
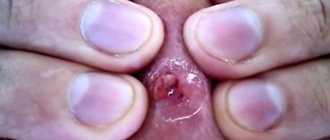
Pimples inside under the skin contain oil, acne bacteria, dead skin cells and white blood cells. A pimple appears when sebum, an oily substance produced by the skin, gets into the pores. Bacteria begin to replicate in this sebum, leading to the formation of pimples.
Causes of carbuncle
The appearance of a carbuncle is preceded by an inflammatory process in the soft tissues, which usually begins with an inflammatory disease of the hair follicle - staphylococcal folliculitis, less often - with streptococcal folliculitis.
The development of inflammation can lead to the formation of a boil, which is an acute purulent-necrotic inflammation of the hair follicle. When several such boils form in one area of the body, they can merge with each other.
The product of the merger of several boils is a carbuncle. A sharp bursting pain occurs in the area of infiltration. The skin over the infiltrate becomes purple, tense, and swollen. Large amounts of gray-green pus are released from the pustules.
The tissues become necrotic. There are clear signs of general intoxication: tachycardia, nausea, vomiting, severe headache, hyperthermia up to 39-40 ° C, leukocytosis, shift of the blood count to the left, lack of appetite, insomnia. If the carbuncle is localized on the face, the symptoms of intoxication are much more pronounced, even to the point of fainting.
After exfoliation of necrotic tissue and removal of pus, the severity of signs of intoxication weakens significantly.
Risk factors for carbuncle formation:
- the presence of a chronic source of infection in the body;
- lack of vitamins;
- diabetes mellitus and other metabolic disorders;
- exhaustion of the body;
- psychological overload;
- immunodeficiency states;
- recent operations or serious illnesses;
- skin contamination, poor sanitary culture;
- nutritional deficiency;
- obesity;
- prolonged friction of the skin with clothing;
- increased sweating.
Carbuncle mainly affects teenagers and young adults. Men get sick more often than women.
What is inside a pimple, papules and pustules?
What is inside a pimple, papules and pustules?
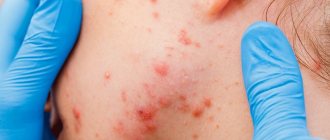
Sometimes clogged pores become so irritated that their walls break down, and the body sends out white blood cells—your immune system's warriors—to begin repairing the damage caused by the pimple. As a side effect, the skin becomes red, painful, and inflamed.
This is when you may get pimples called papules or pustules. Papules are covered with red bumps that are hard and sometimes painful to the touch. Pustules are red and inflamed pimples with a white head in the center. These pimples contain pus inside and also contain dead white blood cells. cells.
Symptoms of carbuncle
Clinical signs of a carbuncle are:
- suppuration and wound formation;
- hyperemia of the skin around the lesion;
- severe pain in the entire affected area.
The appearance and development of a carbuncle is usually accompanied by the following symptoms:
- elevated temperature, which often reaches 40 degrees;
- major intoxication;
- vomiting;
- nausea;
- loss of appetite;
- headache;
- general malaise.
These signs are especially pronounced when the carbuncle appears on the face or neck.
There are 3 stages of carbuncle:
Stage 1: infiltrate (folliculitis)
During this period, nodes form under the skin, which will be represented by inflamed hair follicles. The infiltrate contains adipose tissue, pus, lymph and lymphocytes. Nodules rise above the surface of the skin.
Since the nutrition of the dermis is disrupted, it acquires a bluish color. After a few days (from 9 to 12), the infiltrate reaches impressive sizes. It can be about 10 cm in diameter. The skin is swollen, tense, and hot to the touch. The more swelling there is, the more intense the pain will be.
Stage 2: purulent formation
At the stage of suppuration, the carbuncle reaches maturity. Blisters form on it, which are filled with pus. They open, so the surface of the carbuncle resembles a sieve. Through these small holes, pus leaks out, mixed with blood and dead epithelium.
The suppuration stage lasts about 14-21 days. During this period, the patient’s general health deteriorates.
Stage 3: necrosis and tissue rejection
During this period, pus from the carbuncle stops oozing. At the site of inflammation, ulcers are formed that will have rods. They merge with each other, forming one large defect. Tissue damage is very intense and often involves muscles. The affected area is black.
The wound heals slowly, gradually filling with granulations. A scar remains in its place. The necrosis stage lasts about 21 days.
What's inside black and white pimples?
Poll: When did your acne appear? (Number of votes: 4295)
I've been suffering all my life
It's been a couple of years now
About a few months
Recently
To vote, click on the desired answer. results
What's inside black and white pimples?
Black and white pimples are clogged inside with the same dead skin cells (which your skin always produces when exposed to acne bacteria) form on the skin, and sebum (an oily substance secreted by tiny glands) is found inside your pores.
Many people think that black pimples are clogged with dirt inside, but that's not true. The difference in color between these two types of pimples is actually due to the effects of oxygen, as the National Institutes of Health explains.
In whiteheads, the blockage is below the surface of the skin and therefore remains white. But in blackheads, the seal opens when exposed to air. It turns brownish-black when they are exposed to oxygen.
Methods for diagnosing carbuncle
Carbuncle is diagnosed based on clinical symptoms.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with the following pathologies:
- rupture of an epidermal cyst;
- hidradenitis (if the carbuncle is localized in the perineum or armpit);
- anthrax;
- chronic ulcerative herpes.
Laboratory diagnostics
Microscopy of the smear reveals staphylococci. Bacterial culture allows identification of the pathogen and assessment of sensitivity to antibiotics.
Sign up for diagnostics To accurately diagnose the disease, make an appointment with specialists from the Family Doctor network.
Treatment methods for carbuncle
Small carbuncles that occur without noticeable intoxication and deterioration of the patient’s general condition are treated on an outpatient basis.
In cases where
- the patient is severely intoxicated,
- the carbuncle is large and localized on the face,
- the patient suffers from uncompensated diabetes mellitus or other serious diseases,
treatment is carried out in a hospital.
Conservative treatment
If treatment of the carbuncle was started at the stage of its maturation, then conservative methods are used, which in most cases leads to regression of the disease, that is, resorption of the infiltrate.
Antibacterial drugs with a broad spectrum of action are indicated for oral administration to the patient.
At the same time, the carbuncle itself is injected with antibiotics. To reduce pain, analgesics (Novocaine, Lidocaine) are used.
The surface of the carbuncle is treated with ethyl alcohol or other alcohol-containing antiseptics. An aseptic dressing is applied. Syntomycin or streptomycin emulsions are also used.
Surgery
If the carbuncle enters the necrotic stage, then this is an indication for surgery, which is performed while using antibiotic therapy.
The operation consists of dissecting the carbuncle and removing necrotic tissue from it.
Then a tampon with a hypertonic sodium chloride solution and proteolytic enzymes is inserted into the wound.
To clean the postoperative wound and completely remove necrotic tissue, the dressing is changed daily.
Physiotherapy
At the maturation stage, as well as in the postoperative period, UHF therapy and local ultraviolet radiation are prescribed.
To stimulate the body's defenses, intravenous laser and ultraviolet irradiation of blood can also be performed.
More information about the treatment method
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Rate how useful the material was
thank you for rating
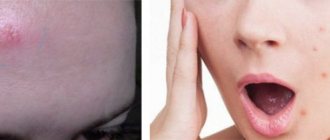
Acne marks
Post-acne is the unpleasant marks that acne can leave behind: lumps and scars, changes in skin color in certain areas, red spots from acne, enlarged skin pores, the appearance of a vascular pattern (rosacea), sometimes even deep scars. Dermatologists combine all these skin changes under the term post-acne (“post” - after, “acne” - pimples, blackheads). The more severe the acne disease, the more pronounced the signs of post-acne will be. Even after non-acute, but long-term processes, quite noticeable scars and depressions can remain. The main reasons for the occurrence of post-acne are improper treatment or lack thereof during the period of skin lesions with acne, mechanical removal of contents, lack of proper facial skin care, and also if the patient did not turn to specialists for help and did not use specially selected treatment products, then the likelihood of that scars and spots form after acne increases several times. If the form of acne is severe, the rashes are deep, for example cysts, nodules, then during healing there will always be scars, so it is very important to start proper acne treatment on time so that as few such forms of acne form as possible.
The most common acne marks are:
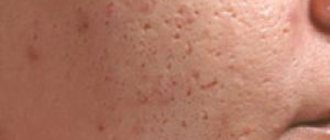
- Scars . Acne scars usually remain after inflammatory processes that affected the deep layers of the skin and were accompanied by abundant formation of pus, with long-term difficulty in the release of pus from the inflamed area to the surface of the skin. In this case, the inflammatory reaction develops for quite a long time in a confined space, gradually spreads to nearby areas of the skin and ultimately seriously deforms them. Often the cause of scars is inept attempts to squeeze out pimples, resulting in deep skin damage that heals with the formation of a scar (most often atrophic). The color of acne scars changes over time: from the pink color of fresh scars to the color of normal skin about a year after appearance, but can also become hyperpigmented or, conversely, paler than the base color of the skin.
The following types of acne scars are known:
Atrophic scars - resemble a small rectangular or oval hole, the color of which is usually flesh-colored. This type is divided into rounded, chipped and rectangular scars.
Physiological scars are almost completely invisible on the skin and heal quite quickly.
Keloid scars - cause itching and other painful sensations, similar to hypertrophic scars. They form quite rarely on the surface of the face.
Hypertrophic scars are convex, pink, dense formations. They arise due to a huge amount of scar tissue.
- Vascular spots. Prolonged inflammation of the skin leads to disruption of blood microcirculation in these areas. An additional factor in their appearance is crude attempts to squeeze or open pimples. As a result, areas of burgundy, crimson, and bluish redness may appear. Without treatment, these acne spots can remain on the skin for a long time (sometimes more than a year). It is also possible that telangiectasia (visible vascular networks on the surface of the skin) may appear, which do not tend to go away on their own.
- Changes in skin pigmentation - dyschromia. Dyschromia is a disorder of skin color. With dark skin, acne marks may appear as light spots against the background of dark skin. With fair skin, dark spots appear at the sites of resolved rashes. The immediate causes of changes in skin pigmentation are prolonged inflammation and trauma to the skin due to inept attempts to squeeze out or open pimples. Areas of dyschromia can appear both under the influence of ultraviolet radiation and without it.
Registration for consultation
Post-acne treatment methods:
- Chemical peels - various acids are used to dissolve the stratum corneum of the epithelium. As a result, increased division of young cells begins and, as a result, the upper layer of the skin is leveled. With their help, you can make the transition of the surrounding skin into an atrophic, receding scar less noticeable or make a hypertrophic, protruding scar flatter. Peels are most effective on fresh acne scars (pink in color).
- Mesotherapy is a fairly effective modern method that allows you to saturate the skin with the most necessary substances and microelements. Its principle is to introduce into the skin compositions that include biologically active substances, vitamins, hyaluronic acid and various enzymes. For different types of scars and different stages of their growth, different drugs are used.
- Biorevitalization – hyaluronic acid is very important for proper skin healing. The use of biorevitalization in the early stages of scar formation allows you to avoid the formation of coarse scar tissue.
- Laser skin resurfacing allows you to minimize the effects of acne over several procedures. The method involves gently removing the upper keratinized layer; the laser also activates all biochemical processes, including the production of collagen, which provides the necessary elasticity of the skin. The doctor determines the number of required sessions individually for each patient. Their number depends on the condition of the skin and the presence of spots.
- Pulse light therapy - has a bactericidal effect, reduces inflammation, reduces the activity of the sebaceous glands, reduces redness (acts on small capillaries), stimulates the production of collagen fibers (scars become less noticeable). Used to treat if there are red spots from acne and red acne scars. The doctor also determines the number of required sessions individually for each patient.
It is important to remember that when choosing any method of combating post-acne and other consequences of acne, you must first consult a doctor, since only a dermatologist will be able to assess the degree and depth of post-acne, and prescribe not only an effective, but also an adequate method of treatment.
Prevention
Prevention of post-acne involves preventing exacerbations of acne and timely professional treatment of acne, preventing the appearance of deep purulent inflammations. And also in careful handling of inflamed areas and proper skin care. It is necessary to refrain from independently attempting to squeeze or otherwise open pimples. In most cases, it is precisely such attempts that aggravate the situation and lead to the formation of a scar at the site of the pimple, since when trying to squeeze out a pimple, its contents may rush not to the surface of the skin, but, on the contrary, into the depths and create a new focus of inflammation there, which will be much more difficult cure without scar formation.