The presence of postoperative scars is considered the main disadvantage of plastic surgery.
A postoperative scar can have different shapes and lengths. This depends on the breast lift method chosen. So after an anchor breast lift, the scar is much larger than after a vertical or areola lift.
| Typically, a rough scar is a wide scar protruding from the surface of the skin that differs in color from the surrounding skin. In some cases, the scar may be painful to palpation. |
Scars reach their greatest severity by 2-3 months after surgery. During this period, they are most dense, have a scarlet color and protrude above the surface of the skin. If the healing process of scars is not disturbed, then in the future they become less noticeable, lighten, and are compared with the level of the skin, resembling a white thread. It should be remembered that the post-operative scar will still remain noticeable, but since it runs along the bikini line, it can be easily hidden under clothing.
Reasons for the formation of a rough scar:
- Patient's predisposition to excessive formation of connective tissue.
- Rough work of a surgeon with tissues.
- Strong tension on the edges of the surgical wound, which leads to stretching of the scar and its subsequent hypertrophy.
- Excessive use of electrocoagulation in the scar area, i.e. in close proximity to the dermis of the skin.
- Suturing the surgical wound with absorbable suture material close to the surface of the skin.
The surgical wound must be sutured in such a way that all absorbable sutures are deep inside.
T-shaped breast lift (anchor mastopexy) - Photo
Height: 166. Weight: 57. Girth: 74.
What is the right operation to choose (make the right choice) if you have borderline breasts? Breast augmentation with implants or one-stage breast lift with implant installation, or just a lift?
The patient has borderline breasts, i.e. It is possible to install slightly larger implants to compensate for ptosis, and a lift can be performed. Let's try together to predict how to strategically plan the surgical plan, given that the breast is a very unstable organ.
First way
will give a naturally drooping breast of approximately size 3, but after 2-3 years such breasts will droop under the weight of the implant and you may have to first remove the implants, perform a lift after 6-8 months, and install the implants again after a year. This path is very difficult and, in my opinion, wrong. Plus, imagine the psychological state of the patient all this time.
Second way
many will deny it on a subconscious level, and this is understandable, because this is a T-shaped lift, but with a short incision in the submammary fold. Of course, no one wants to have scars, especially on the chest. But after a breast lift, the breasts become more stable, more correctly shaped, and after a year all possibilities open up for the patient: installing proportional implants or performing breast lipofilling. This operation plan gives stable results at every stage and only positive emotions.
Third way
, in my opinion, the most terrible and insidious is a one-step lift (I often hear from patients that they offer it around the areola) with one-step installation of implants. And the most important thing is that all doctors know very well that with a one-stage operation there is a very high percentage of complications, and after 3-5 years all patients after such operations have their breasts remodeled. This is official statistics - a stubborn and sometimes inexplicable thing. But in this situation, everything is understandable - the implant puts pressure on the seams, they heal poorly, the implant moves down and the areolas fly up, and this happens differently on each side. It is possible to suggest redoing such an operation, but it is difficult. First, remove the implant, then perform a lift, and then install the implant, if the desire still remains. More often, a lift with one-step prosthetics is offered by non-specialized or young doctors, don’t be offended by me. I stand up for patients... so that they don’t end up in such a situation. It’s not all that easy afterwards! Do you know how many such patients come to me from other clinics!
And the fourth way
— take a time out and think, study the issue again. This is a good option and sometimes the most correct one if you are not sure and have doubts. After all, the choice is important and the first step and the vector of your further movement will already be predetermined.
What would you choose after such a consultation?
With respect to all my patients, subscribers and colleagues!
More details
Types of scars:
1. Regular scar
Elastic, consisting of normal connective tissue. Normal color compared to surrounding skin. In terms of softness, it is in no way different from the surrounding skin.
Scar tissue gradually acquires strength and resistance to damage. By three months after surgery, the scar gains 50% of its normal strength. By the year after the operation, the scar strength becomes 100%.
2. Hypertrophic scar
One of the complications related to breast lift is the formation of hypertrophic and keloid scars.
With excessive collagen synthesis, a hypertrophic scar is formed, consisting of dense fibrous tissue. Such scars are characterized by a reddish tint, raised above the surface of the skin, sensitivity and pain, and can cause itching.
How to care for scars after mammoplasty
For the first 3 weeks after surgery, it is not recommended to take a bath; during personal hygiene, the sutures should be protected from water, for example, wrapped in plastic wrap.
To prevent complications, you must follow all the doctor’s recommendations , and first of all, do not rub the scar. Experts advise using silicone bandages, bandages and compression garments. Of course, during the rehabilitation period you will have to give up the beautiful, but uncomfortable bra with underwires.
Find out which method of correcting scars and stretch marks is optimal for you!
doctor Svetlana Viktorovna Ogorodnikova.
doctor
To protect the wounds from inevitable friction with clothing, silicone patches are glued to them. In addition to protection, the patch narrows and softens scars, but this effect is only possible with constant use.
When the wound has completely healed - scarring, crust formation and its death - the operated area can already be smeared with a cream with an anti-scar effect , and after a shower the skin can be nourished with moisturizing lotions.
Among other things, in the first 4 months you should avoid physical activity and lifting weights exceeding 3 kg. This limitation is due to the fact that the skin on the scar is not yet strong enough, there is a risk of tearing the epidermal tissue and getting stretch marks.
Types of hypertrophic scars:
— Conventional hypertrophic scar
A hypertrophic scar never extends beyond the wound. The reasons for its formation are the large size of the wound surface and the presence of constant trauma to the scar, for example, friction against jeans. Also, a hypertrophic scar can form as a result of a reaction to the suture material.
One of the features of hypertrophic scars is a benign course. Over the course of several months or years, they gradually become smaller and turn into ordinary normotrophic scars.
— Keloid
A keloid scar extends beyond the wound, spreading to normal tissue. The formation of a keloid scar usually occurs 1-3 months after the formation of epithelium at the site of the damaged skin surface. The scar constantly grows and becomes rough, protruding above the surface of the skin.
A keloid scar does not get better over time, and in rare cases tends to progress.
The formation of keloid scars is associated with individual characteristics of the healing process. Therefore, people who are predisposed to the formation of keloid scars need to choose techniques with the smallest incisions.
Hypertrophic scars can also be a consequence of postoperative complications such as hematomas, suppuration or suture dehiscence.
How to reduce the appearance of scarring?
At the end of the operation, the affected areas are covered with sutures, after which a long process of scarring begins, eventually forming a scar. Scar formation cannot be avoided, but its visibility can be significantly reduced thanks to the professionalism of the plastic surgeon and the patient following all the specialist’s recommendations during the recovery process.
A breast lift without scars, even if barely noticeable, is impossible, and plastic surgery without stitches or a non-surgical lift is practically ineffective and does not provide long-term results. Taking this into account, the goal is not to perform the operation without incisions, but to ensure that the subsequent scars are as less noticeable as possible.
The characteristics of scarring depend on how correctly the surgeon chose the technique. Only an experienced professional who has taken into account the characteristics of the patient’s body and her wishes is able to correctly select the method of mastopexy and carefully apply markings before the operation along which the incisions will be made.
The choice of surgical technique is not determined by the desire to reduce the number and size of scars - it should be based on several points.
- The larger the bust, the greater the stretching of the skin and the more difficult scarring
- Any impact that increases tension on the edges of a sutured wound will slow down scar formation
- Making scars that are too short may result in insufficient aesthetics of postoperative scars. For example, in the case of a periareolar breast lift without implants, instead of the more suitable vertical or anchor one, unnecessary stretching of the scar may occur, resulting in a wide, unsightly stretched scar.
How to eliminate scars after mastopexy if they are too noticeable? In such situations, peeling or surgical correction is used.
WE ALSO ADVISE YOU TO READ: Breast lift with and without implants
Features of scar care
The appearance of postoperative scars largely depends on how well the patient adheres to the surgeon’s instructions regarding the care of the operated areas. The edges of the incisions fuse 2 weeks after the intervention, after which the surgeon removes the sutures. After this, the doctor examines the scars and determines methods to speed up their healing. To make the scars look more neat, thin and unnoticeable, you need to follow all the surgeon’s instructions.
- Constantly wearing compression garments for a month after surgery, which helps reduce pressure and stress on the bust
- For 4-6 months after surgery, special plasters should be used to secure the edges of the incisions and prevent them from stretching. Reducing the load on the edges of wounds helps reduce the width of the scar and makes it as less noticeable as possible. Scarring almost completely stops six months after surgery, so after this period you can no longer use tightening patches
- The use of special ointments that accelerate scarring and make scars invisible
- Minimizing physical activity during the first 3 months after surgery
- Regular visits to the surgeon to examine the operated areas and correct scar care techniques. It is necessary to control the process of scar formation, so it is important to make visits to the doctor according to the schedule established by him
The process of scarring of sutures is also influenced by the characteristics of the body of each individual patient. For some, this process proceeds quickly and efficiently; the scars end up looking like thin, barely noticeable whitish threads. For others, even with careful adherence to the surgeon’s recommendations and the use of prescribed ointments and patches, scarring is not so successful. Some patients have a genetic predisposition to the formation of keloid scars on the chest after mastopexy.
WE ALSO ADVISE YOU TO READ: Alternative methods of breast enlargement
Prevention of scar formation
- During the operation, try to minimize the tension on the postoperative sutures. Of course, the very meaning of a brace contradicts this, but we must remember that the tension should be reasonable.
- Breast lifts larger than size 4 will typically have more tension and therefore rougher scarring.
- Careful handling of soft tissues during surgery. It depends entirely on the surgeon.
- Careful suturing of the postoperative wound. Also, the care of the surgeon, but not always the most careful suturing of a postoperative wound guarantees a high-quality scar.
Methods of performing mammoplasty
Based on the goals set by the patient, the surgeon performs the operation in different ways. A lot depends on the choice: where the incisions will be made, how long it will take for the sutures to heal after mammoplasty, and whether complications should be expected during the operation. So in practice one of the methods of surgical intervention can be used:
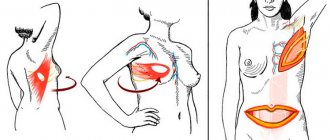
- Transaxillary . The incision is made in the armpit area - the operation is quite complicated, there is a risk of bleeding. Not suitable for correction of asymmetrical breasts and displacement of natural folds.
- Periareolar. At the border between the pigmented areola of the nipple and the surrounding skin. Performed if the purpose of the operation is to tighten the breasts. This way, excess skin is removed, and the stitch heals for 6 months.
- Transabdominal. Insertion of the implant through the periumbilical area. A woman easily tolerates this method and in this case there are no noticeable scars left after mammoplasty.
- Submammary. The fold under the mammary gland is incised. The scar resembles a bra strip.
The doctor decides how to perform mammoplasty. It takes into account the individual characteristics of the patient, her state of health and the desired result.
Whether marks will remain after the procedure depends on how the woman takes care of the stitches after mammoplasty.
Treatment of rough scars
Treatment of rough scars can be either medicinal or surgical.
Surgical treatment involves excision of the scar with plastic surgery using local tissue. There are many methods of scar plastic surgery, which are selected for each specific case.
Drug treatment includes wearing special patches and using ointments that block the excessive formation of connective tissue.
In particularly severe cases, when the scar continues to hypertrophy, glucocorticoid drugs are used in injection form. Such drugs must be used carefully so as not to transform a hypertrophic scar into an atrophic one.