I did lymphatic drainage massages - to no avail. How to remove bags on the cheekbones that only old people have, but I have had since childhood?
What methods of elimination are there and what are the reasons for the formation of paint bags - we will tell you today in this article.
Photos from open sources
Diseases
Not always, swelling and bruising under the eyes are a sign of an unhealthy lifestyle. Often, the reason is the presence of certain diseases:
- Allergies. Accompanied by lacrimation, sneezing, redness of the eyes, difficulty breathing and coughing;
- Inflammation of the sinuses (sinusitis and sinusitis). They occur with painful sensations localized in the forehead and under the eyes, as well as copious discharge from the nose;
- Kidney diseases. When they occur, fluid retention occurs in the body, which causes not only swelling of the eyes, but also lower back pain and headaches;
- Diseases of the thyroid gland. Due to dysfunction of the thyroid gland, hormonal imbalance occurs - general weakness increases, body weight increases, the menstrual cycle changes, edema occurs;
- Heart failure. It is accompanied by shortness of breath and fatigue. Swelling and bruising under the eyes, almost invisible in the morning, appear in the late afternoon;
- Skin diseases - eczema and dermatitis.
How to remove puffiness under the eyes
There are many techniques for improving the condition of the periorbital zone. But first you need to pay attention to your general health and the presence of accompanying warning signs: difficulty breathing, prolonged pain of any intensity localization, organ dysfunction, problems with blood pressure, and so on. In such cases, immediate consultation with a doctor and examination is required.
If bags and bruises are only a cosmetic defect, you can get rid of them using different techniques.
Prevention measures
It is impossible to completely prevent the formation of hernias under the eyes.
Remember! But you can prevent their rapid development by following these preventive recommendations:
- from time to time wipe your face with ice cubes , for the preparation of which it is better to use not water, but decoctions of medicinal herbs;
- avoid abuse of alcohol, fatty, smoked and spicy foods and, if possible, quit smoking;
- go to bed on time and not disturb the established daily routine;
- Regularly take at least half an hour walks to improve the overall tone of the body.
Remedies for puffiness under the eyes
In the morning, you can quickly remove puffiness from your eyes and get rid of bags after errors in diet or excessive alcohol consumption. To do this, do the following:
- cold compresses: ice cubes, tea bags;
- lymphatic drainage massage in a circle with fingertips and light pats;
- cosmetics containing caffeine substances for eyelids.
Retinol cream will help. This remedy increases the amount of collagen substances in the dermis, which as a result reduces the likelihood of the formation of bags under the eyes. A prescription retinol cream will help.
Remedies at home
First of all, it is necessary to solve the problems of internal organs, nutrition and fluid intake:
- control the drinking regime - for each individual, but it is important that there is no excess or shortage of water;
- review your diet - give up salty, smoked, fatty, fast food, carbonated sweet drinks;
- since an inactive lifestyle and sedentary work can also cause problems, increase physical activity - exercise, walking, running;
- get enough sleep, ventilate the room before going to bed;
- take vitamins;
- use only special cosmetics for the periorbital area.
Cream for the area around the eyes must be applied correctly. In the evening, treat the skin no later than an hour and a half before bedtime. To eliminate puffiness and dark circles, place small dots on the incoming cheekbone and brow bone - from the inner corner to the outer to enhance lymphatic drainage. If a product labeled anti-age is used, it is applied along the lines of least stretch of muscle tissue and skin with light tapping.
Modern patches allow you to restore the freshness and healthy shade of the area around the eyes in 20 minutes. They can be used 3 – 4 times a week or as needed.
(c) Lee Yongwoo
Changes in appearance associated with swelling and deposition of fatty tissue between the lower eyelids and cheekbones are a pressing problem for people of any age, since not only age-related changes, but also somatic pathology and hereditary factors can contribute to this process. Many specialists and patients have the opinion that full correction of this cosmetic defect (malar edema and malar hernias) can only be performed through surgical intervention, simultaneously eliminating fat deposits and excess skin above them [1, 2]. But this method has certain limitations (traumatic, the need for special training, a long recovery period, the risk of scarring, combination with injection and other methods of aesthetic correction) and the result is not always guaranteed. In addition, patients often refuse this option.
All this made it necessary to find an alternative to surgical methods to solve the problem in the least traumatic way.
Injection correction methods can conceal malar hernias by adding volume around them using high-density fillers, although in some cases swelling may occur, exacerbating the defect, or by reducing fat deposits using lipolytics. However, unlike injection methods, which are more effective in the initial stages, hardware technologies also work well for more severe malar edema and hernias.
Anatomy and pathophysiology of malar edema and malar hernias
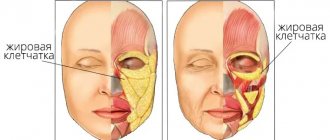
Malar edema , or edema (English: malar edema) is the accumulation of fluid above the zygomatic eminence. It often varies in severity and may increase after a salty meal or in the morning. The consistency is usually soft and plastic. Sometimes a depression appears with a faint bluish-purple tint. Causes may include heart, kidney or liver failure, hypothyroidism, cosmetic injections in the periorbital area, and allergies.
Malar hernia , or suf (English: malar mounds) are deposits of fatty tissue in the area between the lower eyelids and cheekbones, in the prezygomatic space. Malar hernias can be congenital or appear due to genetic predisposition. The first signs of this problem can be noticeable already in childhood, and later, as the volume of the facial muscles increases and the skin tone decreases, they become more pronounced. Unlike malar edema, their occurrence is not directly related to the pathology of internal organs and systems or an unhealthy lifestyle, and the methods of correction must be different.
Severe malar hernia with manifestations of ptosis (English: malar festoons) are cascading folds of weak skin and rounded muscle under the infraorbital margin, caused by age-related changes in the bones of the skull and facial muscles, ptosis of the soft tissues of the face and edema. The anatomical basis for the formation of malar hernias are fatty bags - predominantly infraorbital, medial infraorbital (medial SOOF) and lateral infraorbital (lateral SOOF). The infraorbital fat pad is bounded by the orbicular suspensory ligament (ORL), which begins 1–2 mm below the bony margin of the orbit, passes through the orbicularis oculi muscle, continues to the fascia lining the inner surface of the orbicularis oculi muscle, and reaches the dermis [3]. ORL is involved in the formation of the lacrimal and palpebromalar grooves. Weakness of the ORL caused by aging or hereditary causes contributes to the formation of malar hernias.
Infraorbital fat covers the caudal portion of the orbicularis oculi muscle, which lies just under the skin of the lower eyelid. The lower border of the infraorbital fat packet is the zygomatic ligament, which begins at the junction of the zygomatic arch and the body of the zygomatic bone, runs along the edge of the facial muscles (zygomaticus major, zygomaticus minor and levator labii superioris) [3]. The infraorbital fat packet tends to intensively retain water, which often causes the formation of so-called malar edema [4].
The medial SOOF supports the tissues of the lower eyelid, so the decrease in its volume that occurs with age increases the relaxation of the lower eyelid tissue and the intraorbital fat pad. Hypotrophy of the lateral SOOF facilitates ptosis of the superficial cheek fat pads. Excessive laxity of the skin can play an important role in the appearance of malar hernias, especially severe malar hernias with manifestations of ptosis.
The listed changes create conditions for the formation of malar hernias.
Clinical assessment
Externally, malar hernias are small swellings concentrated under the eyes, in the upper part of the cheekbones. Along their edges there are skin folds. Connective tissue septa give these formations the shape of a semicircle, usually with a clear lower border. Violation of microcirculation in this area causes a dull appearance and a reddish or bluish tint of the skin, a gradual increase in the area of swelling. Inflammation of subcutaneous fat is possible [3]. Characteristic clinical signs are as follows:
- drooping upper eyelid;
- blurred vision;
- profuse lacrimation, which occurs as a result of compression of the tear ducts;
- swelling;
- dark circles in the eye area.
Severe malar hernias give the face a suffering and painful appearance, in addition, the person looks noticeably older than his age.
To differentiate from swelling under the eyes, the doctor can use several techniques:
- with a malar hernia, looking up and down and squinting should not significantly affect the patient’s appearance;
- When you press on the eyeball, a swelling forms [5].
Correction of malar edema and hernias
A group of researchers from the USA led by Newberry K.I. (Newberry CI) analyzed the range of aesthetic cosmetology methods used to correct malar edema and hernias, and described the cosmetic effects that can be achieved using injection and hardware methods ( see table ) [1].
Table. Possibilities of minimally invasive methods for the correction of malar edema and hernias [1]
| Method | Clinical effects |
| Injection methods | |
| Hyaluronidase | Reduce swelling · 1st line of therapy for swelling after injection of hyaluronic filler |
| Phosphatidylcholine/deoxycholate | Reducing the amount of subcutaneous fat by emulsifying it |
| Synthetic biopeptides | Reduce swelling by stimulating microcirculation and lymphatic drainage |
| Tetracycline (intralesional administration) | · Sclerosation of subcutaneous fat Sclerosation of infraorbital fat · Slight thickening of excess skin |
| Fillers | Camouflage and reduce mild subcutaneous swelling Camouflage and elevation of ptotic malar muscles and fat |
| Hardware methods | |
| Laser resurfacing | · Sealing of skin folds · Lightening and evening out skin color |
| High Intensity Focused Ultrasound | · Tightening of excess skin without damaging the epidermis · Lifting at the level of SMAS and supporting ligaments of the skin Fat ablation |
| RF technologies | · Tightening of excess skin without damaging the epidermis Fat ablation |
| Microliposuction | Removal of subcutaneous fat and edema |
To correct malar edema and malar hernias, various hardware methods are used - fractional thermolysis, ultrasound and RF lifting, etc. It is impossible to remove fat with their help, but by strengthening and increasing skin tone, it is possible to smooth out small hernias and prevent their enlargement.
Laser therapy
For more than 15 years, ablative lasers (CO2 and Er:YAG) have been used to correct malar edema and malar hernias [6]. Special protocols have been developed for procedures in the prezygomatic area, involving intensive exposure with several (from 2 to 10) passes. The use of these protocols has shown a certain effectiveness of the method along with a small frequency of adverse events in the form of scarring and ectropion, which, however, must be taken into account, especially in elderly patients with age-related or scarring weakness of the lower eyelids. Their results can be disastrous. Aggressive laser exposure can cause vertical shortening of the anterior lamella. Persistent swelling with chemosis of the conjunctiva may occur, which can lead to irreversible impairment of the position of the lower eyelids. More pronounced positive results have been obtained using ablative fractional lasers (CO2 and Er:YAG). There is a significantly lower risk of scarring, ectropion, and dyspigmentation due to deeper thermal effects, but multiple treatments are required to achieve the desired result [7, 8]. Laser resurfacing can also be used to reduce hyperpigmentation in the area of malar hernias, however it cannot change the location of muscle tissue/fat, eliminate fat deposits, or significantly reduce swelling. Therefore, laser resurfacing is best used for moderately severe malar hernias with little excess skin, as well as for adjuvant therapy during surgical correction. If ectropion is present or develops after correction of malar hernias, the patient should undergo an eyelid strengthening procedure using laser therapy or an alternative surgical intervention. Limitations for laser correction of malar hernias:
- skin types IV–VI Fitzpatrick class (such patients have an increased risk of post-procedural dyspigmentation, especially hyperpigmentation, and laser protocols for the correction of malar hernias are quite aggressive);
- use of oral retinoids within the past year;
- recent history of receiving light therapy for facial skin [9].
High Intensity Focused Ultrasound
Another alternative to the surgical method is the use of focused ultrasound (High Intensity Focused Ultrasound, HIFU), during which acoustic energy causes targeted microthermal damage in the hypodermis and SMAS (superficial muscular aponeurotic system, superficial muscular aponeurotic system). Using probe sensors, in the skin and underlying structures at a given depth (1.5, 3.0, 4.5 mm), it is possible to create heating zones up to 60–70 °C and form thermal coagulation points. Regeneration of post-coagulation point damage leads to intensive tissue restoration and remodeling of collagen fibers, which create a structural “framework” in the tissues. Fibroblasts of the dermis, responding to thermal effects, enhance collagenogenesis. Neocollagenogenesis and neoelastogenesis help improve the structure and quality of the skin, thicken it, tighten it, tighten it and reduce its area. The action of HIFU at the depth of the SMAS provides heating of its structures, their compression and further maintenance of the biomechanical balance of the muscular-ligamentous apparatus of the face. The complex of these processes provides the clinical effect of reducing malar hernias without having a significant epidermal effect [8, 10].
During clinical trials and follow-up, patients generally reported mild and transient side effects, such as: procedure pain (1.6%), bruising (0.4%), post-procedure pain (0.2%), transient nervous irritation (0.2%), swelling (0.2%) and transient erythema (0.1%) [10]. Unlike laser and RF exposure, HIFU affects all structures - skin, supporting ligaments, adipose and muscle tissue, ligamentous apparatus. This method is particularly effective for small malar hernias or as adjuvant therapy; however, for severe malar hernias with manifestations of ptosis and edema, HIFU does not always give the maximum desired effect due to excess tissue volume.
RF therapy is more suitable to achieve the goal in such cases. RF microneedle devices deliver electric current energy to a targeted depth, causing thermal damage to the dermis and fatty tissue but sparing the epidermis. Collagen retraction, remodeling of collagen fibers, increased neocollagenogenesis and neoelastogenesis, potential reduction of adipose tissue and skin tightening allow this method to be used for the correction of moderate to very severe malar hernias, as well as for adjuvant therapy. As with HIFU, side effects are usually minor and temporary (erythema, swelling), and recent studies have shown no significant complications [11]. The procedure can be repeated after 1–2 months if necessary.
Microliposuction
Targeted fat removal from the malar region can be an important tool for reducing malar hernias when there is a significant edematous or fatty component. Excess subcutaneous fat is removed using a small-gauge liposuction cannula (2.3 or 3.0 mm) until the prominence of the malar bone is no longer palpable or visible. Despite all its effectiveness, this technique, according to experts, has its limitations: firstly, puncture marks remain on the skin, and secondly, even minimal inaccuracies in markings and the amount of removed fat can lead to deformation of the cheekbone area and general “aging” faces. It should be noted that this approach does not take into account muscle or ligament weakness, for which liposuction must be combined with a midface lift. If there is excess skin before or after fat removal, adjuvant correction with lasers, RF, HIFU or surgical excision may be performed. Among the adverse events after the procedure, transient swelling was noted in all patients, but there was no infection, bruising, or weakness of the lower eyelids [12].
Post-procedural period
Many patients with malar edema or hernias may experience swelling/lymphedema after procedures. Because prolonged swelling can impair the results of correction, cold compresses and oral steroids for 5 to 7 days are recommended, especially if swelling was the main initial component. In some cases, compression bandages with mastizol can be used to compress the zygomatic area. For severe edema, furosemide 20–40 mg/day is recommended with potassium replacement for approximately 7 days. In more severe cases, massage and injections of hyaluronidase can help, which must be performed until lymphatic drainage improves. Sunscreen and retinoids should be used daily. If there is a history of severe allergies with frequent periorbital edema, second-generation antihistamines can be recommended [12].
Discussion
Analyzing the effectiveness of using hardware cosmetology methods for the correction of malar edema and malar hernias, Newberry K.I. (Newberry CI) et al. noted the following: “A one-size-fits-all approach is likely to leave many patients with unsatisfactory outcomes.” Correction of malar edema and malar hernia is a complex process due to pathophysiological characteristics and clinical manifestations in different patients. When choosing a correction method, it is necessary to take an individual approach, taking into account the severity and “content” (effusion, fat, skin, muscles) of malar edema and hernias, as well as the patient’s preferences. Detailed information to the patient about the possibilities of non-invasive, minimally invasive and surgical correction methods, as well as the doctor’s opinion and recommendations in each specific situation, will also contribute to the maximum possible positive result. Although minimally invasive and non-invasive methods are considered as progressive correction options with minimal recovery time, it should be taken into account that with these options there is often a need for re-correction due to temporary improvement or insufficient correction. These situations may lead to a possible increase in the cost of correction procedures.
Conclusion
Hardware methods can be quite effective and provide long-term stable results in the correction of malar edema and malar hernias, although surgery remains the classic method of reducing the manifestations of this pathology. Thus, the optimal methods of correction have not yet been determined, but a multifaceted and personalized approach using various interventions seems appropriate. Larger studies are needed to examine the effectiveness of different methods and their combinations.
Literature
- Newberry CI, McCrary H, Thomas JR, Cerrati EW Updated Management of Malar Edema, Mounds, and Festoons: A Systematic Review. Aesthet Surg J 2019; 2022: 137.
- Asaadi M. Etiology and treatment of congenital festoons. Aesthetic Plast Surg 2018; 42(4): 1024–1032.
- Mendelson BC, Muzaffar AR, Adams WP Jr. Surgical anatomy of the midcheek and malar mounds. Plast Reconstr Surg 2002; 110(3): 885–911.
- Pessa JE, Rohrich RJ Facial topography. Clinical anatomy of the face. QMP; 2012.
- Kpodzo DS, Nahai F., McCord CD Malar mounds and festoons: review of current management. Aesthet Surg J 2014; 34(2): 235–248.
- Scheiner AJ, Massry GG Laser management of festoons. In: Masters Techniques in Blepharoplasty and Periorbital Rejuvenation. New York: Springer, 2011. pp. 211–221.
- Hunzeker CM, Weiss ET, Geronemus RG Fractionated CO2 laser resurfacing: our experience with more than 2000 treatments. Aesthet Surg J 2009; 29(4): 317–322.
- Lam Kar Wai P. The troublesome triad: festoons, malar mounds, and palpebral bags. J Cosmet Med 2017; 1(1): 1–7.
- Carniol PJ, Woolery-Lloyd H., Zhao AS, Murray K. Laser treatment for ethnic skin. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am 2010; 18(1): 105–110.
- Wulkan AJ, Fabi SG, Green JB Microfocused ultrasound for facial photorejuvenation: a review. Facial Plast Surg 2016; 32(3): 269–275.
- Jeon H., Geronemus RG Successful noninvasive treatment of festoons. Plast Reconstr Surg 2018; 141(6): 977e–978e.
- Liapakis IE, Paschalis EI Liposuction and suspension of the orbicularis oculi for the correction of persistent malar bags: description of technique and report of a case. Aesthetic Plast Surg 2012; 36(3): 546–549.
What will not help in the fight against paint bags:
1. Botox. Promotes even more bag formation. The injected muscle becomes inactive as before, and the outflow of lymph becomes more difficult. Swelling appears above the paint bags - another swelling that will further focus attention on the problem.
2. Fillers with hyaluronic acid, if they are injected superficially. The problem is that any drugs that are injected superficially into this area cause swelling. Because paint grease is very hydrophilic and attracts water.
3. Injections of direct lipolytics (which destroy fat). May lead to atrophy. Indirect - have a lymphatic drainage effect and reduce swelling (but do not destroy fat.
Photos from open sources
Treatment
- In the case when swelling is not a symptom of diseases of various etiologies. But only as a cosmetic problem, it is possible to eliminate swelling of the eyelids by using Pinoxide injections. This is a modern treatment used to relieve swelling and improve circulation.
- For minor swelling, it is enough to drink a diuretic to remove excess fluid from the body (Furasimide).
- In case of a local allergic reaction, it is necessary to identify the allergen and stop contact with it. If necessary, take an antihistamine (Diazolin, Suprastin).
- In the treatment of inflammatory eye diseases, depending on the pathogenesis of the disease. Antiviral (Ciprofloxacin) and antibacterial drugs (Tetracycline ointment) are used locally.
- If you suspect any disease that causes edema, immediately consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and adequate treatment
Symptoms
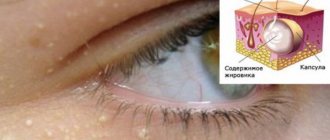
Hernias under the eyes can be recognized by the following signs:
- decreased visual acuity;
- increased lacrimation;
- swollen areas of skin under the eyes do not decrease or increase during the day or when drinking large amounts of water;
- the skin of the eyelids, under which hernias form, takes on a bluish or reddish, plum color;
- the vascular network may more or less appear on the skin of the eyelids.
such hernias also form above the eye - then from the outside it seems that the person’s eye shape is reduced and the swelling affects the periocular area in a circle.
Keep in mind! For the vast majority of people, this problem appears only under the eyes.
Why does swelling occur in dry eye syndrome?
Dry eye syndrome (DES) is a pathological condition that is based on a violation of the stability of the tear film.
It provides nutrition, hydration and protection to the cornea. But when few tears are produced or their composition changes, the tear film quickly begins to evaporate. Because of this, the mucous membrane dries out, a burning sensation, itching, redness, and swelling appears.
Various reasons contribute to the development of dry eye syndrome. This could be taking antidepressants, antihistamines, working at a computer for a long time, or staying in a room with dry air. Dry eye syndrome may progress during sun exposure (summer) because too much air temperature causes tears to evaporate.
You can compensate for moisture deficiency with the help of tear substitutes. These are special drops that contain moisturizing components. But, despite the fact that they have a composition close to tears, they do not contain mucins and lipids, which help the tear film to adhere to the surface of the eyeball and maintain stability.
One of the effective ways to restore the tear film is the use of Delfanto® in capsules. They contain a record amount of antioxidants (at least 35%), which help stimulate the production of your own tears.