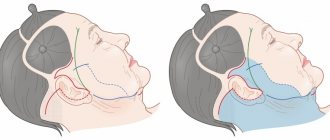
The periorbital zone is the area around the eyes, which includes the upper and lower eyelids and the lacrimal apparatus. She actively participates in facial expressions and is more susceptible to aging than others. Wrinkles appear - facial, age-related, gravitational. They can be both superficial and deep, which occur not only on the skin, but also in the subcutaneous fatty tissues.
The first signs and minor traces can be combated with cosmetics; contour plastic surgery, mesotherapy, and thermolifting can be used. In case of significant changes, surgical periorbital rejuvenation (periorbitoplasty) .
A complex operation aimed at rejuvenating the eye area. Includes:
- Upper and lower blepharoplasty;
- Endoscopic lifting of the upper face;
- Endoscopic midface lift;
- Lipofilling of eyelids;
- Transposition of Bisha's lumps;
- Correction of the levators of the upper eyelids;
- Correction of corrugators;
- Correction of the nasolacrimal trough using your own tissues without the use of implants.
According to indications, it may include a number of other manipulations, while the price remains unchanged.
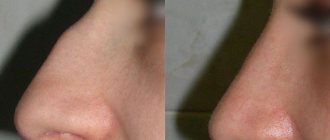
Before/after photos
View all photos
How does biorevitalization work?
In order for the skin to remain young and be able to resist the aging process, it is necessary that it be hydrated, i.e. have the necessary supply of fluid.
In the human body, the ability of tissues to retain water molecules is determined by the content of hyaluronic acid in them. It is capable of attracting and holding water in a volume exceeding its own weight. If skin cells are sufficiently hydrated, they can renew themselves in a timely manner and adequately withstand the adverse effects of the environment. If the amount of hyaluronic acid is not enough, the skin becomes flabby, dull, and fine wrinkles appear on it.
Biorevitalization not only replenishes the deficiency of hyaluronic acid through injection of the drug, but also stimulates its production by the body itself, thereby strengthening the skin’s protective mechanisms by replenishing its own resources.
Reviews
Reviews from social networks and instant messengers
Video reviews
Borzokh Olga Borisovna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, researcher at the Center for Collective Use "Molecular and Cellular Technologies" of Krasnoyarsk State Medical University, Country Expert Teoxane Russia, Voronezh
The periorbital area continues to be the focus of attention of cosmetologists, since, on the one hand, this is one of the most popular requests from patients, and on the other hand, many unresolved questions remain regarding the choice of techniques or drugs. In this article, I propose to somewhat expand the focus of our attention and discuss the correction of not only the infraorbital sulcus, but also other areas around the eyes - the temporal region, the forehead, the middle third, since all these zones can influence the aging process in the periorbital region [1] .
But first of all, you need to understand what the goal of aesthetic correction is when working with age-related changes. The goal of most patients is to correct age-related manifestations, but without traces of intervention, while the most common concerns of patients are unnatural results, contouring of the drug, and swelling in the periorbital area. In my opinion, it is possible to help achieve a better result and natural correction by choosing the right indications and technique for performing the procedure, based on the Teoxane approach.
The Teoxane approach was developed to achieve the most effective and natural-looking aesthetic treatment results while maintaining the safety of injection procedures. When working with the Teoxane approach, we always follow the three Ps (A-T-P) - anatomy (including assessment of the aging process and patient indications), technique and drug selection.
Anatomy
One article or even one book is not enough for the anatomical features of the area around the eyes, so I propose to dwell only on some of the anatomical aspects necessary for work.
Speaking about the area under the eyes, first of all it is necessary to understand the features of the layer-by-layer structure of the zone of the lower edge of the orbit (Fig. 1) [2].
- 1st layer - skin : in the periorbital area it is thin due to a decrease in the number of layers of the epidermis and thinning of the dermis itself;
- 2nd layer - subcutaneous fat : thin, often in Caucasian patients it can be practically absent in the area of the medial corner of the eye;
- 3rd layer - orbicularis oculi muscle : attached to the bony edge of the orbit with the help of the orbicularis oculi ligament (ORL), while its attachment is stronger in the medial corner of the eye, resulting in the formation of the tear groove;
- 4th layer - layer of deep fat pads : presented mainly lateral to the medial canthus of the eye in the form of a deep infraorbital fat pad (SOOF);
- 5th layer - periosteum.
When working in this area, the following are distinguished (Fig. 2) [3]:
- palpebral wrinkles (wrinkles on the skin of the eyelid);
- tear trough - a line of depression running from the medial edge of the eye down to the midpupillary line;
- palpebromalar groove - a lateral continuation of the lacrimal groove;
- midbuccal groove - continuation of the lacrimal groove downwards;
- nasolabial fold - in the middle third.
In the supraorbital region, the five-layer structure is preserved, but, unlike the infraorbital region, the skin is thicker, the subcutaneous fat is full, the deep fat pack is represented by the supraorbital fat pack (ROOF) (Fig. 3) [4].
The temporal region is an area where many questions remain regarding the anatomical structure. Regarding the number of layers of tissue in this area, most experts believe that 10 layers can be distinguished in it.
It is more important in this area to designate safer zones and caution zones (Fig. 4) [5]. Thus, a safer compartment is the superior temporal compartment (UTC), located between the temporal crest (superior temporal septum - STS) and the inferior temporal septum (ITS), in the inferior temporal compartment (LTS) blood vessels and nerves are located.
In the forehead area there are also 5 layers of soft tissues of the face (Fig. 5) [6]: skin, subcutaneous fat, SMAS (represented by the frontal muscle, or aponeurosis), a layer of deep fat packets and periosteum.
A safer level is the layer of deep fatty packets under the SMAS; the main vessels above the safety line (it runs 2 cm above the bony edge of the orbit) are in the superficial fatty layer, below the line - in the deep.
In the area of the midbuccal groove, five layers are also preserved: skin, superficial and deep fat packets, SMAS, periosteum [7–9]. The main level when working with volumizers is the level of deep fat packs (medial deep infraorbital fat pack and deep medial zygomatic fat pack); with pronounced age-related changes, the goal of correction is also the superficial medial fat pack.
In addition to anatomy, the first point of the Teoxane approach involves understanding the aging process in different layers:
- the skin becomes thinner, fibroblasts reduce their synthetic activity, the skin becomes overstretched and its elasticity decreases;
- in subcutaneous fatty tissue and deep fatty tissues, a decrease in fatty tissue and redistribution of fat occurs - a change in the ratio of different fatty tissues;
- muscles, as a rule, undergo atrophy, the ligamentous apparatus stretches and loses its strength;
- the periosteum (or rather, the bone) also undergoes resorption.
As a result of all these processes, we see volume deficits in the upper and middle third of the face, as well as ptosis of the eyebrows, upper eyelid, and the appearance of furrows in the infraorbital region, which appear as a result of loss of support from overlying structures.
Thus, there is a connection between volume deficits and ptosis of certain structures; therefore, replenishment of lost volume will reduce the manifestations of ptosis.
Last but not least, what we look at with the Teoxane approach in point one is patient assessment. In fact, correctly determined indications made on the basis of complaints and examination of the patient are of great importance on the path to ideal aesthetic correction of the periorbital region.
At the same time, it is important that the patient himself points out the areas that he does not like about himself, since each person has his own ideas about beauty, and areas in the patient that are incorrectly identified and corrected by the doctor can give an unsatisfactory result after the procedure. If our patient cannot decide on areas of concern to him, you can give him a mirror and “introduce him to yourself.”
Selection of equipment
The next point in Teoxane's approach is technique. This paragraph assumes the plural because, in our opinion, there is no one correct correction technique - we use our own, using a needle or cannula, but these techniques must “respect” the anatomy in terms of safety and effectiveness. To do this, on the face we highlight areas of increased attention, safety lines, and areas with a lack of volume (Fig. 6).
When working with the upper and middle third of the face, we must remember the location of the angular artery (in the inner corner of the eye), the exit of the infraorbital and supraorbital neurovascular bundles (along the midpupillary line), supratrochlear (1 cm medial to the supraorbital), zygomatic (1 cm below the lateral bony edge of the orbit), the location of the transverse artery (along the lower edge of the zygomatic arch) and the temporal vessels (most often visualized on the patient’s face).
Of the safety lines, we are interested in the midbuccal line and the line in the projection of the zygomatic major muscle - it is safer to work in the superolateral quadrant when these lines intersect. In the temporal region, the safety line runs between the tragus and the lateral edge of the orbit - it delimits the superior temporal compartment. In the forehead area, the safety line is 2 cm above the bony edge of the orbit.
When augmenting the forehead area, we may use a cannula or a needle. The drug is administered at the SMAS; before the procedure, it is important to note areas of volume deficiency, and when working with a cannula, the injection points are determined (between visible vessels) (Fig. 7). When working with a cannula, you can use one (for a more flattened forehead area) or 2 injection points (for a more rounded one); a 25G cannula is safer; a 22G cannula has a smaller diameter and is closer in sharpness to a needle. The drug is distributed fan-wise using a retrograde technique. The SMAS zone requires a distributed, dynamic drug with average G' values; we will talk about the choice of drug in the next paragraph.
To lift the eyebrow, an injection point is used, located under the eyebrow, lateral to the midpupillary line. The drug is located supraniosteally, in the region of the deep supraorbital fat pad (ROOF) (Fig. 8). Typically, when performing this technique, I raise the eyebrow and use a small bolus of drug (0.2 ml) with a high G'.
When working with the temporal region, it is safer to administer the drug deeply (under the temporalis muscle) in the superior temporal compartment. The injection point for the shot gun technique is 1 cm below the temporal crest and 1 cm above the lateral bony rim of the orbit (Fig. 9). The procedure is carried out with a needle, safer 25 mm long (a shorter needle may not be completely on the bone). The injection is made between visible vessels until it touches the bone, then the needle must be tilted so that the needle hole is as close as possible to the bone. The drug will be distributed between the fibers of the temporal muscle, since the muscle is firmly attached to the bone and there is no space under it. Due to the location of the drug, a drug with maximum G' and cohesiveness is required.
When working with infraorbital grooves, injections are carried out strictly in the area of volume deficiency; in the case of working with a cannula, you can select one injection point between the lacrimal and palpebromalar grooves, bypassing the projection of the infraorbital foramen (Fig. 10A, B). When working with a cannula, it is safer to choose larger diameter cannulas (25G, 22G). The drug is administered under the orbicularis oculi muscle. Considering the complex and delicate anatomical structure of the infraorbital region, you should carefully select the drug based on its viscoelastic properties.
When correcting the midbuccal sulcus, the volume of zygomatic fat pads is corrected, but there may be a difference in the technique in patients of the older and middle age groups.
In patients of the middle age group, in young people, with initial manifestations of volume deficiency in the area of the midbuccal sulcus in the pathogenesis of age-related changes, as a rule, only deep fatty packets are involved, therefore, in them, the introduction of a volumizer is carried out only at the level of the medial infraorbital fatty packet or at the level of the deep medial fat pack.
In older patients, volume loss occurs at the level of the superficial medial fat pad, therefore, for a full result, a multilayer technique for correcting the middle third is necessary, as we mentioned in the article [10].
When working with a needle, boluses of the drug are located supraniosteally, lateral and above the safety lines. When working with a cannula, the injection point is located lateral to the midbuccal line and the cannula passes at the level of deep fatty bags. For convenience, you can lift the tissues with your second hand and pass under them in the area of the medial infraorbital fat pad and the medial deep zygomatic fat pad (Fig. 11).
Choice of drug
Sometimes the choice of drug is not given due attention, as a result, the risks of an unnatural correction result, low effectiveness of the correction, contouring and swelling, especially in the periorbital area, increase. It is important to understand that each zone and each tissue layer may require different viscoelastic properties of the drugs. We have already spoken about the rheological properties of drugs quite a large number of times [11, 12]. Let's take a closer look at the choice of drugs based on the anatomical features of each area.
When augmenting the forehead, the space under the SMAS is quite small, there is not a large amount of tissue above it, so the pressure exerted on the injected drug is relatively low, but at the same time the zone is mimically active (movable), so an elastic drug is required, with an average G' index, capable of stretching . Teosyal® RHA2 and Teosyal® RHA3 have these properties (Table 1). Teosyal® RHA is a collection of dynamic fillers that are stretchable and, as a result, maximally adapted to the dynamics of the face. When using them, we obtain maximum efficiency in the area of administration with maximum naturalness of the result. For thinner skin, thin soft tissues and a slight lack of volume, the most suitable drug is Teosyal® RHA2, for greater thickness and the need for volume - Teosyal® RHA3. In my practice, I sometimes use Teosyal® RHA4, but only in cases of large thickness of soft tissues and pronounced loss of volume in the forehead area, when greater volumizing abilities of the drug are needed while maintaining its elastic properties. In this case, the drug should be administered as delicately as possible, avoiding overcorrection.
Table 1. Comparative characteristics of Teosyal® RHA2 and Teosyal® RHA3
| Teosyal® RHA2 _ | Teosyal® RHA3 _ | |
| Compound | Reticulated HA 23 mg/ml | Reticulated HA 23 mg/ml |
| Degree of modification (MoD) | 3,1% | 3,6% |
| Rheological properties | High tensile strength Moderate compression force | Good tensile strength High compression force |
| Indications | Moderate dynamic wrinkles and lip correction | Moderate dynamic wrinkles and lip correction |
When working with the area of the infraorbital grooves, you should choose the drug especially carefully. The anatomical features of the zone dictate the need for a lightly distributed drug (to prevent compression of the lymphatic drainage) (reducing the risk of contouring in an area with a deficiency of fatty tissue) with low residual hygroscopicity. Such a drug is Teosyal® Redensity 2 (Table 2). Teosyal® Redensity 2 was developed specifically for the correction of this delicate area, it has low residual hygroscopicity and is a light, spreadable hyaluronic acid gel. Moreover, it has official indications - correction of infraorbital grooves.
Table 2. Characteristics of the drug Teosyal® Redensity 2
| Teosyal® Redensity 2 | |
| Compound | Reticulated HA 15 mg/ml |
| Degree of modification (MoD) | 5,5% |
| Rheological properties | Good distribution, plasticity, low hygroscopicity |
| Indications | Correction of the lacrimal and palpebromalar grooves |
| Insertion depth | Under the orbicularis oculi muscle |
I have already mentioned the need to use a drug with the highest G' and the highest possible cohesiveness when augmenting the temporal region due to the location of the gel along the muscle fibers of the temporal muscle. Such drugs are Teosyal® RHA4 and Teosyal® Puresense Ultra Deep (Table 3). I generally prefer Teosyal® RHA4 for younger patients and Teosyal® Puresense Ultra Deep for older patients. Both drugs contain 0.3% lidocaine, which is extremely important when working in the area of the temporal fossa.
Table 3. Comparative characteristics of Teosyal® Puresense Ultra Deep and Teosyal® RHA4 volumizers
| Teosyal® Puresense Ultra Deep | Teosyal® RHA4 _ | |
| Compound | Reticulated HA 25 mg/ml | Reticulated HA 23 mg/ml |
| Degree of modification (MoD) | 10,0% | 4,0% |
| Rheological properties | Very high cohesiveness High elasticity | High tensile strength Very high compression force |
| Indications | Insufficient volume in a limited area: cheekbones, chin, etc. | Insufficient volume in the tensile or dynamic area: cheeks, facial contour, etc. |
| Insertion depth | Deep fat pads (nanoperiosteal) | Superficial and deep fat packets |
To carry out eyebrow lifting, I usually use the remainder (0.1–0.2 ml) of the volumizer that was used to correct the middle or upper third of the face.
And finally, when correcting the midbuccal groove, the most rational use of volumizers (see Table 3). When filling deep fat bags in older patients, patients with pronounced thickness of soft tissues, to create maximum projection, I prefer the classic rigid (that is, hard) Teosyal® Puresense Ultra Deep volumizer; it has a very high G', high cohesiveness, and maximum lifting ability. When using the multilayer technique - filling superficial fat bags with a pronounced deficiency in the area of the midbuccal groove, as well as when working with deep fat bags in patients with small thickness of soft tissues of the face, I prefer Teosyal® RHA4. Teosyal® RHA4 is a dynamic volumizer with a high G', high resistance to repetitive stress, but at the same time “respecting” facial expressions and giving the most natural correction.
Conclusion
When working with the area around the eyes, we most often choose complex techniques. The validity of the choice of complex techniques is confirmed by the peculiarities of the aging process in this area. Thus, by filling the deficit in the upper zones (such as the forehead, temporal region, eyebrow area), we restore support for the eyebrow and upper eyelid, and by restoring the middle third, we improve the results of correction of the infraorbital grooves (Fig. 12). In this example, the patient underwent augmentation of the forehead area (Teosyal® RHA4 - 1.0 ml on each side), augmentation of the temporal area (Teosyal® PS Ultra Deep - 0.4 ml each), eyebrow lifting (Teosyal® PS Ultra Deep - 0.2 ml each), correction of the midbuccal groove (Teosyal® PS Ultra Deep - 0.6 ml each) and filling of the lacrimal and palpebromalar grooves (Teosyal® Redensity 2 - 0.5 ml each). As a result, we made the face more harmonious in the ratio of the upper third to the middle and lower third, the patient looked less tired (by reducing the deficit of the middle third and the severity of the infraorbital grooves), the overhang of the eyelid decreased, and the shape of the forehead area and the deficit in the temporal region were corrected.
At the same time, in terms of complex treatment, one should not forget about restoring the quality of the skin. To fully restore the functional activity of fibroblasts, my favorite is Teosyal® Redensity 1, the results of which can be seen after the first procedure.
The article was published in the magazine “Cosmetics and Medicine Special Edition” No. 2/2021
As an advertisement
Literature
- Pessa JE An algorithm of facial aging: verification of Lambros's theory by three-dimensional stereolithography, with reference to the pathogenesis of midfacial aging, scleral show, and the lateral suborbital trough deformity. Plast Reconstr Surg 2000; 106(2): 479–488
- Vrcek I., Ozgur O., Nakra T. Infraorbital Dark Circles: A Review of the Pathogenesis, Evaluation and Treatment. J Cutan Aesthet Surg 2016; 9(2): 65–72.
- Lee JH, Hong G. Definitions of groove and hollowness of the infraorbital region and clinical treatment using soft-tissue filler. Arch Plast Surg 2018; 45(3): 214–221.
- Mustak H., Fiaschetti D., Gupta A., Goldberg R. Eyebrow Contouring with Hyaluronic Acid Gel Filler Injections. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol 2018; 11(2): 38–40.
- Huang R.L., Xie Y., Wang W., et al. Anatomical Study of Temporal Fat Compartments and its Clinical Application for Temporal Fat Grafting. Aesthet Surg J 2017; 37(8): 855–862.
- Peng JH, Peng PH HA Filler Injection and Skin Quality-Literature Minireview and Injection Techniques. Indian J Plast Surg 2020; 53(2): 198–206.
- Rohrich RJ, Pessa JE, Ristow B. The youthful cheek and the deep medial fat compartment. Plast Reconstr Surg 2008; 121(6): 2107–2112.
- Mendelson BC, Muzaffar AR, Adams WP Surgical anatomy of the midcheek and malar mounds. Plast Reconstr Surg 2002: 110(3): 885–896.
- Mendelson BC, Jacobson SR Surgical anatomy of the midcheek. Facial layers, spaces, and the mid cheek segments. Clin Plast Surg 2008; 35(3): 395–404.
- Borzykh O.B. Multi-layer technique for correction of the middle third of the face when working with the periorbital region: addition or necessity? Injection methods in cosmetology 2020; 4:20-27.
- Egorova M.L. A dynamic method of creating volume in the cheekbone area with hyaluronic fillers Teosyal Ultra Deep and Teosyal RHA. An ideal combination for maintaining the natural appearance of the face during its movements. Injection methods in cosmetology 2019; 4:32–38.
- Borzykh O.B. A combination of Teosyal Ultra Deep and Teosyal RHA4 volumizers to create a line of ideal profile. Injection methods in cosmetology 2020; 1:26–31.
Planning surgery to correct the periorbital area
When planning an operation to correct the periorbital zone of the face, several of the most important points in the preoperative examination of the patient can be identified:
- determination of the patient’s visual condition, functions of the lacrimal gland, conjunctiva and lacrimal ducts;
- assessment of the position and shape of the eyebrows, the severity and location of glabella wrinkles, the ratio of the height of the lateral thirds to their medial parts;
- clarification of the degree of protraction of the eyeball in relation to the lower edge of the orbit;
- assessment of the characteristics of the layers of the upper and lower eyelids, as well as the levels of the position of their ciliary edges;
- study of the position and stability of the lateral canthal ligaments;
- determination of the severity of age-related changes in the mid-medial part of the face, the position of the eyelid-buccal and lacrimal grooves in relation to the inferior orbital margin.
Blepharoplasty at the Rostov Plastic Surgery Clinic
An operation is always stressful, so the Medical Park clinic has created the most comfortable environment. We employ highly qualified transplantologists and plastic surgeons, and our offices are equipped with the latest equipment and technology. An individual approach to each patient, the high equipment of the clinic and the golden hands of doctors allow us to achieve excellent aesthetic results against the backdrop of low trauma and the best price for blepharoplasty in Rostov-on-Don. Are you concerned about the shape of your eyes, do you consider it necessary to undergo rhinoplasty, have you decided to undergo a hair transplant, breast enlargement, or for some other reason are you unhappy with your appearance? Start the path to correcting the situation - sign up for a consultation with us.
Contraindications
- The presence of inflammatory foci in the intervention area.
- Autoimmune pathology.
- Presence of cancer.
- The need to take anticoagulants.
- Tendency to form hypertrophied and keloid scars.
- A history of allergic reactions to the components of the proposed drug.
- Pregnancy and lactation period.
The cost of biorevitalization of the periorbital area is 10,000 rubles. To make an appointment, call: +7 (495) 120-08-07 . Our address: 123557 Moscow, Central Administrative District, st. Presnensky Val, 14, building 3, 5 minutes walk from the 1905 Goda metro station
What are periobital wrinkles?
Wrinkles in the periorbital area are age-related or facial changes around the eyes. They can appear even in very young people. The fact is that the skin in this area is very thin and, moreover, has few sebaceous glands, which is why it is most susceptible to various negative influences (such as dry air, incorrectly selected cosmetics, etc.).
In addition, each of us cannot do without regular blinking, and if we also have the habit of squinting, early wrinkles around the eyes are unlikely to be avoided.
Cost of blepharoplasty - principles of pricing
How much eyelid correction can cost can be judged by the chosen method and the tasks that the patient sets for himself. There are two fundamentally different approaches to correcting defects in the periorbital zone.
- Non-surgical (cosmetology). In 2022, cosmetologists have at their disposal a wide range of non-surgical technologies for tightening the eye area, including injection (injection of fillers) and laser (lifting, fractional thermolysis).
- Classic (operation). When cosmetology and facelifting (facelift exercises) are powerless, they resort to drastic methods. Plastic surgery involves removing excess skin and fatty tissue through a direct incision on the eyelids. The transconjunctival method is also used.
The price of blepharoplasty is determined taking into account many factors. The final cost of blepharoplasty is influenced by the complexity and scale of the problem, the method of execution, the reputation of the clinic and the surgeon personally. Some clinics set very high prices, justifying their position with an impeccable reputation. However, even the most talented surgeon is not immune to mistakes and failures, so a too high price tag does not guarantee an excellent result.
Rehabilitation
The rehabilitation period takes up to 2 weeks, only after this time it will be possible to evaluate the result. While the sutures are healing, you must strictly follow the doctor's recommendations. You should not rub or scratch your eyes, wear contact lenses, watch TV, use a computer, or even read. For several days after the operation you will have to sleep with your head elevated and avoid physical activity, and for a month you should not be in the sun without high-quality sunglasses. If blepharoplasty is successful and the patient complies with all instructions, the anti-aging effect will last for an average of 10 years.
Benefits of biorevitalization
- Improves skin structure.
- Stimulates the synthesis of endogenous collagen and elastin.
- Improves the appearance of the skin, making it more elastic and hydrated.
- Eliminates fine wrinkles.
- It has no absolute contraindications.
- Eliminates dark circles under the eyes.
- It has a very small number of side effects, and all of them are temporary.
The result can be assessed immediately, already at the time of the procedure. But it has a cumulative effect and reaches a maximum towards the end of the course of procedures.